【动态规划】——打家劫舍问题
今天我们来总结一下动态规划中的打家劫舍问题
1、打家劫舍问题
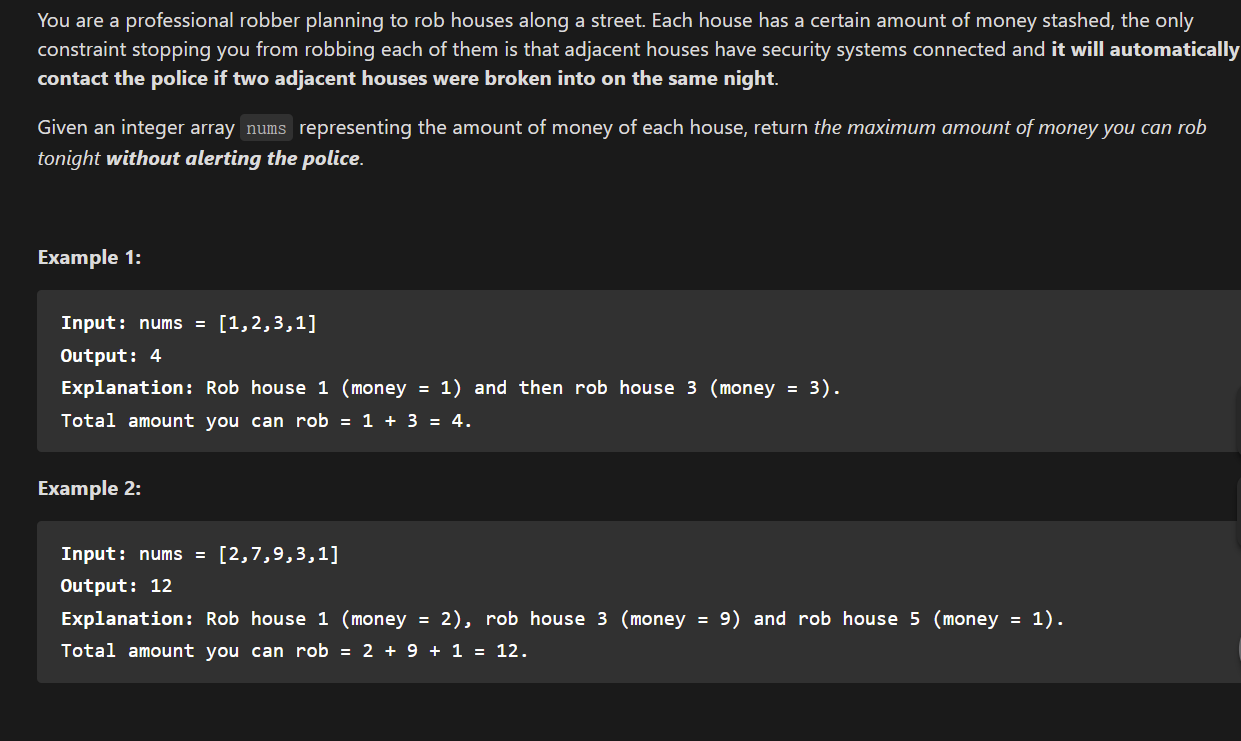
分析:设dp[i]表示打劫到第i座房屋时所抢劫到的总金额。此时有两种情况:我们不能打劫第i家房屋,因为我们已经打劫了第i-1家房屋。此时dp[i]=dp[i-1]。第二种情况,我们没有打劫第i-1家,所以我们可以打劫第i家。此时dp[i]=dp[i-2]+nums[i-1](因为我们没有打劫第i-1家房屋,所以我们已经获得的最大收益是dp[i-2])。则状态转移方程为:
dp[i]=max(dp[i-1],dp[i-2]+nums[i-1])
class Solution {
public:
int rob(vector<int>& nums) {
int n=nums.size();
vector<int> dp(n+1,0);
dp[1]=nums[0];
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
dp[i]=max(dp[i-2]+nums[i-1],dp[i-1]);
}
return dp[n];
}
};2、打家劫舍问题II

Example 1:
Input: nums = [2,3,2]
Output: 3
Explanation: You cannot rob house 1 (money = 2) and then rob house 3 (money = 2), because they are adjacent houses.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [1,2,3,1]
Output: 4
Explanation: Rob house 1 (money = 1) and then rob house 3 (money = 3).
Total amount you can rob = 1 + 3 = 4.
Example 3:
Input: nums = [1,2,3]
Output: 3
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 100
0 <= nums[i] <= 1000
分析:此题与正常打家劫舍问题唯一的区别在于所给数组为环形,即首尾是相接的。首先考虑n>3的情况:由于是环形数组,所以要想获得最大收益首尾元素只能取其一。因此我们只需要用到两个数组来分别dp去掉首元素和去掉尾元素的情况,再取两者中的较大值即可。
n<=3时,我们只需要返回数组中的最大值就行了。因为当数组长度小于3时,我们只能抢劫一家,自然挑价值最大的下手。
class Solution {
public:
int rob(vector<int>& nums) {
int n=nums.size();
if(n==1) return nums[0];
if(n==2) return max(nums[0],nums[1]);
if(n==3) return max(nums[0],max(nums[1],nums[2]));
vector<int> leftDp(n+1,0);
vector<int> rightDp(n+1,0);
leftDp[1]=nums[0];
for(int i=2;i<n;i++){
leftDp[i]=max(leftDp[i-1],leftDp[i-2]+nums[i-1]);
}
leftDp[n]=leftDp[n-1];
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
rightDp[i]=max(rightDp[i-1],rightDp[i-2]+nums[i-1]);
}
return max(leftDp[n],rightDp[n]);
}
};变式题:删除与获得点数(题自力扣)
You are given an integer array nums. You want to maximize the number of points you get by performing the following operation any number of times:
Pick any nums[i] and delete it to earn nums[i] points. Afterwards, you must delete every element equal to nums[i] - 1 and every element equal to nums[i] + 1.
Return the maximum number of points you can earn by applying the above operation some number of times.
Example 1:
Input: nums = [3,4,2]
Output: 6
Explanation: You can perform the following operations:
- Delete 4 to earn 4 points. Consequently, 3 is also deleted. nums = [2].
- Delete 2 to earn 2 points. nums = [].
You earn a total of 6 points.
Example 2:
Input: nums = [2,2,3,3,3,4]
Output: 9
Explanation: You can perform the following operations:
- Delete a 3 to earn 3 points. All 2's and 4's are also deleted. nums = [3,3].
- Delete a 3 again to earn 3 points. nums = [3].
- Delete a 3 once more to earn 3 points. nums = [].
You earn a total of 9 points.
Constraints:
1 <= nums.length <= 2 * 104
1 <= nums[i] <= 104
这道题为打家劫舍I的变式。题中要求是取了nums[i]可以赚取相应的点数,但是值为nums[i]-1和nums[i]+1的点数我们就无法赚取。我们可以得到当选取了nums[i]后,我们需要将nums中所有的nums[i]全部取出,以尽可能多地获取点数。
因此我们需要统计nums中各元素出现的频率,可以使用hash技术,但此处需要有序,所以我们使用C++中的map容器。然后将其中的键值存入一个数组vec中,对该数组进行dp,方法与打家劫舍问题类似,即可获得答案。
class Solution {
public:
int deleteAndEarn(vector<int>& nums) {
int n=nums.size();
map<int,int> freq;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) freq[nums[i]]++;
vector<int> vec;
for(auto it=freq.begin();it!=freq.end();it++) vec.push_back(it->first);
int size=vec.size();
vector<int> dp(size,0);
dp[0]=vec[0]*freq[vec[0]];
int res=dp[0];
for(int i=1;i<size;i++){
if(vec[i]==vec[i-1]+1){
dp[i]=max(dp[i-1],(i-2>=0?dp[i-2]:0)+vec[i]*freq[vec[i]]);//
}
else{
dp[i]=dp[i-1]+vec[i]*freq[vec[i]];
}
res=max(res,dp[i]);
}
return res;
}
};


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号