spring-ai 学习系列(4)-MCP 处理过程分析
上一节,通过1个最基本的MCP Server/Client示例,初步了解了MCP的用法.STDIO模式下,client与server同在1台机器上,client会创建1个子进程来启动server,然后使用json rpc来做为约定的消息格式进行通讯。
如果想知道交互过程中的json原文,可以下载 https://github.com/modelcontextprotocol/java-sdk 源码,找到io.modelcontextprotocol.client.transport.StdioClientTransport 这个类:
在 startInboundProcessing、startOutboundProcessing 这2个方法中,加2行日志,把原文通过日志打印出来
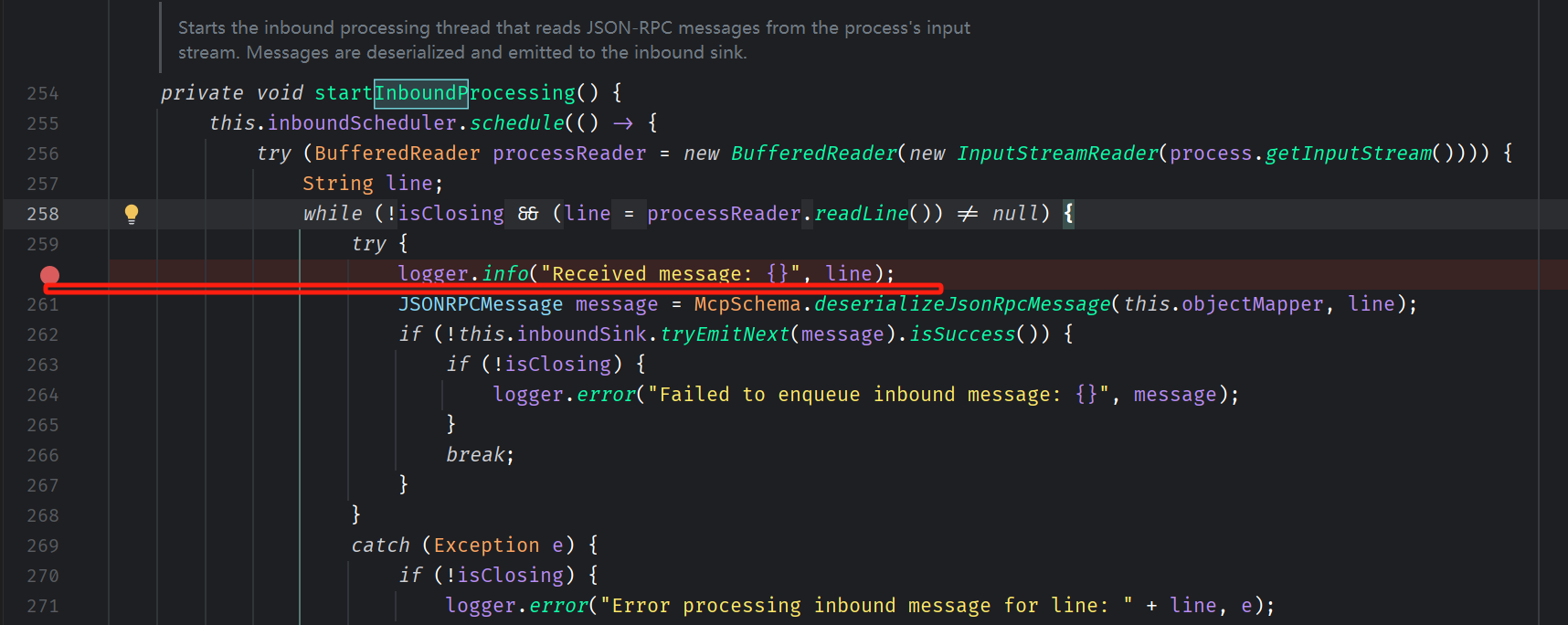
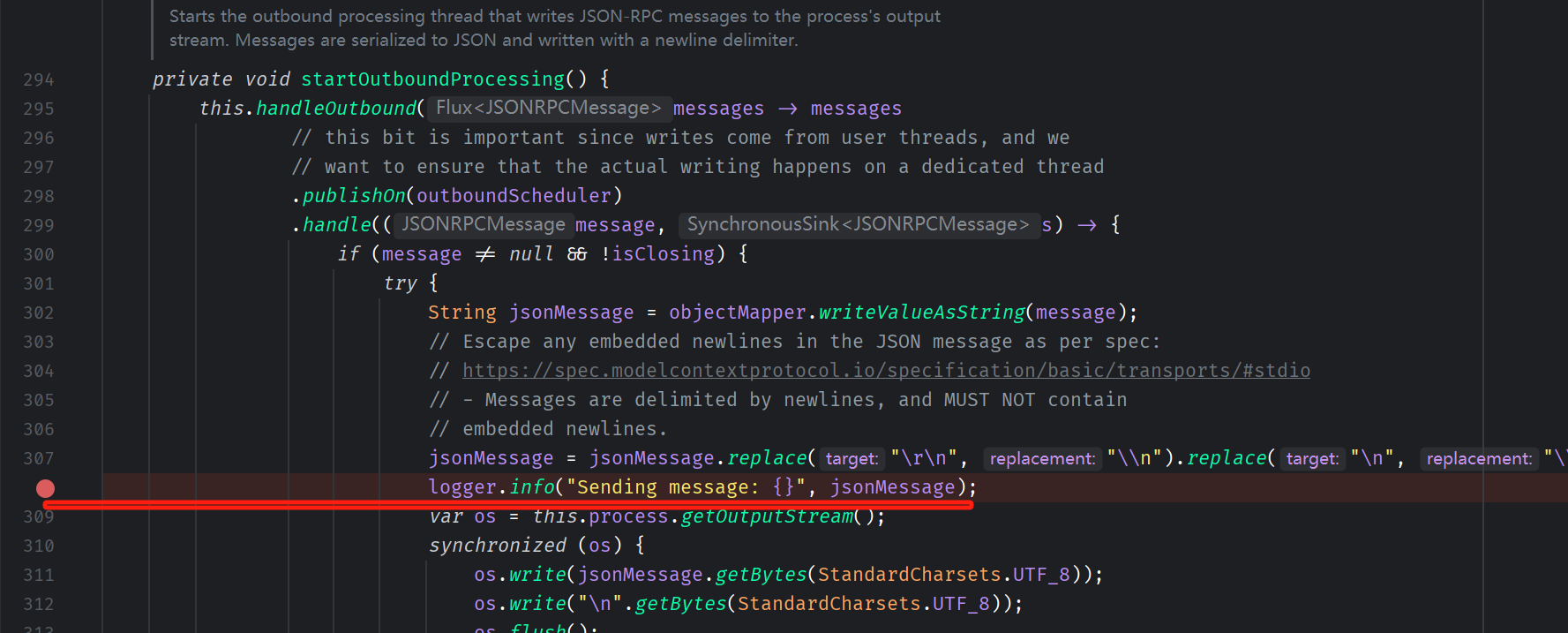
然后mvn install,将本地仓库中的依赖jar包替换。
再调整上一节MCP示例代码中的yaml配置,设置下日志输出级别:
logging:
pattern:
console:
level:
root: INFO
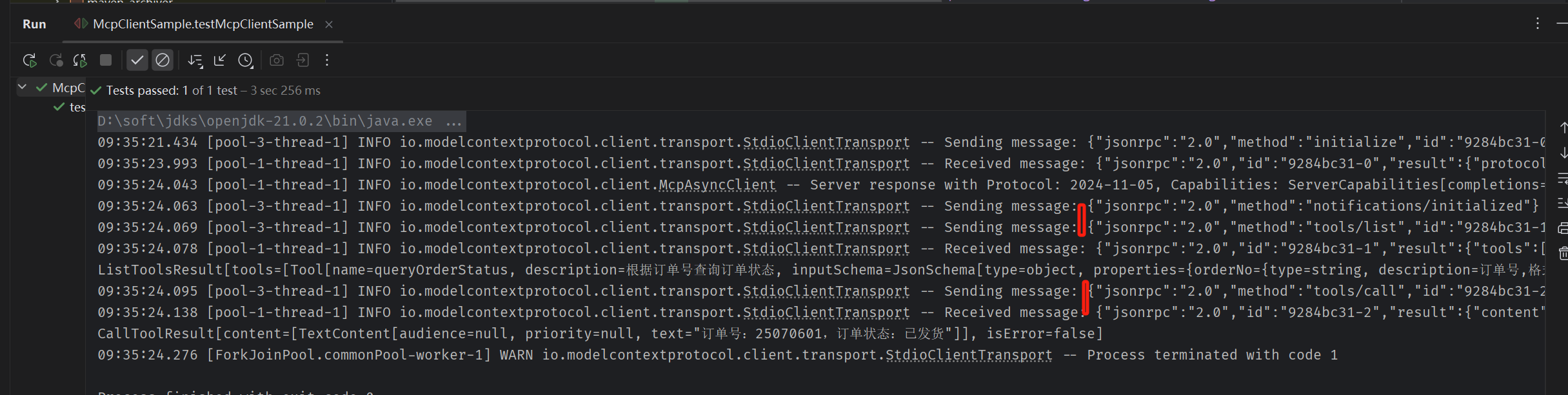
重新运行MCP Client的代码:

1 @Test 2 public void testMcpClientSample() { 3 4 ServerParameters stdioParams = ServerParameters.builder("java") 5 .args("-jar", "D:\\code\\spring-ai-sample\\target\\spring-ai-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar") 6 .build(); 7 8 StdioClientTransport stdioTransport = new StdioClientTransport(stdioParams); 9 10 McpSyncClient mcpClient = McpClient.sync(stdioTransport).build(); 11 12 mcpClient.initialize(); 13 14 McpSchema.ListToolsResult toolsList = mcpClient.listTools(); 15 16 System.out.println(toolsList); 17 18 McpSchema.CallToolResult blogUrl = mcpClient.callTool( 19 new McpSchema.CallToolRequest("queryOrderStatus", 20 Map.of("orderNo", "25070601"))); 21 System.out.println(blogUrl); 22 23 24 mcpClient.closeGracefully(); 25 26 27 }
观察日志,就能看到json原文
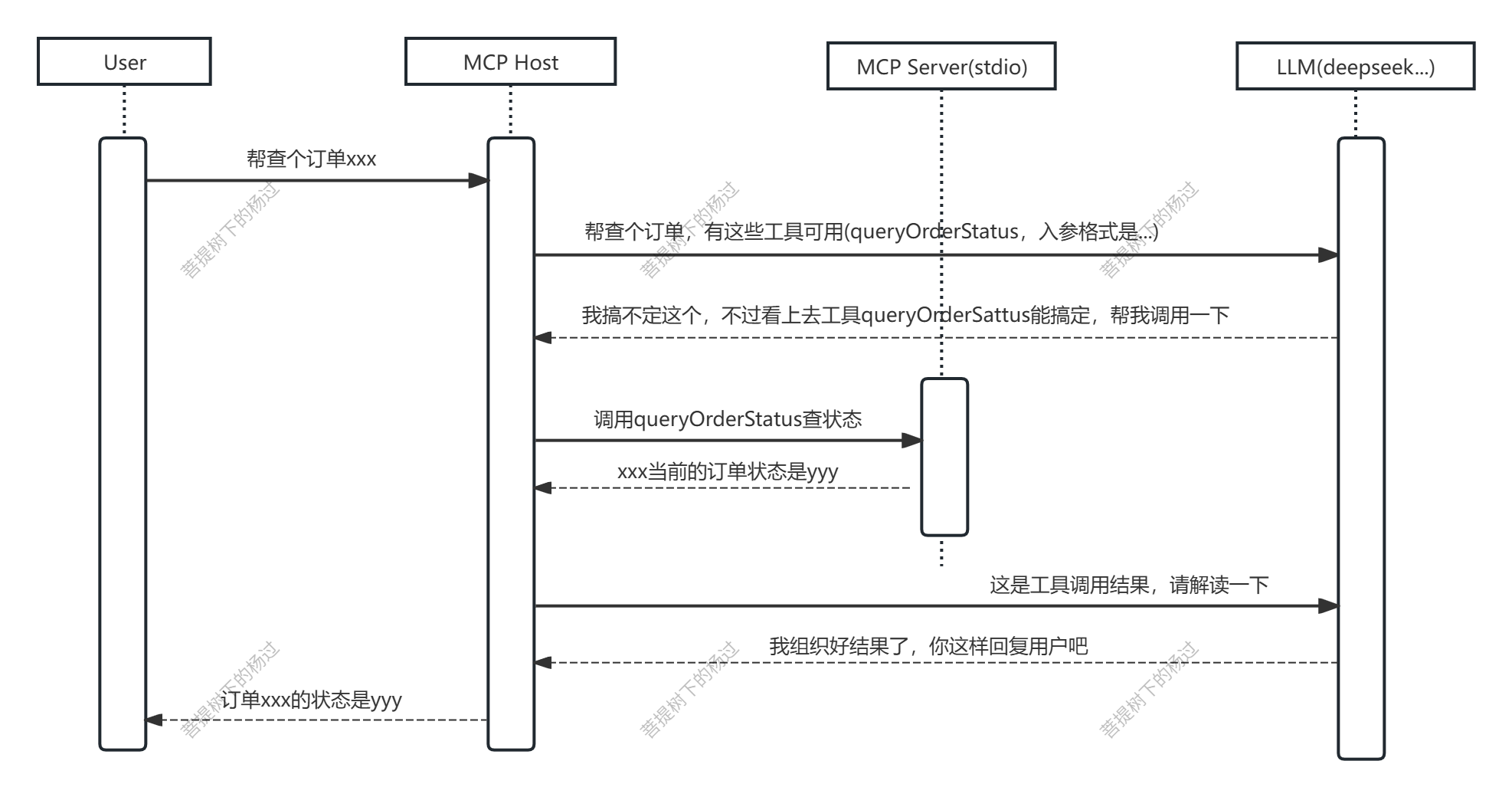
一、MCP Client / Server 调用序列图
按先后顺序梳理一下,得到下面的时序图:

二、MCP Host添加MCP Server过程
当MCP Server写好,在CherryStudio/Cline等MCP Host中添加MCP Server时,大致过程如下(注:仍以stdio模式分析, 不同的MCP Host内部实现细节可能有差异,但是下图不影响新手学习)

三、加持MCP Server后的会话过程
强调2个细节:
1. 大模型本身并没有调用api的能力,它只能简单的接受文本输入,然后输出文本(注:指chat model)
2. 平时我们使用chatgpt之类的app,与大模型聊天,并非直接调用的模型本身,而是通过app来调用的。
所以,要扩展大模型的能力,只能在模型之上抽象一层,让应用层来干这些杂活,调用其它接口,然后再把接口返回结果扔给模型理解。
那么,问题来了:MCP Host向大模型(注:其实是大模型前面的API,比如:OpenAI,或deepseek API或本地ollama API) ,请求查询订单状态时,发出来的prompt到底长啥样?里面关于MCP 工具的描述是如何 写的?
可以用wireshark之类的抓包工具,抓一个看看,考虑到OpenAI, DeepSeek官方API,这些通常都是https加密传输,抓包内容不容易阅读。我们以cherry studio +本地ollama(加载1个小点的模型qwen3:0.6b) 做为试验环境
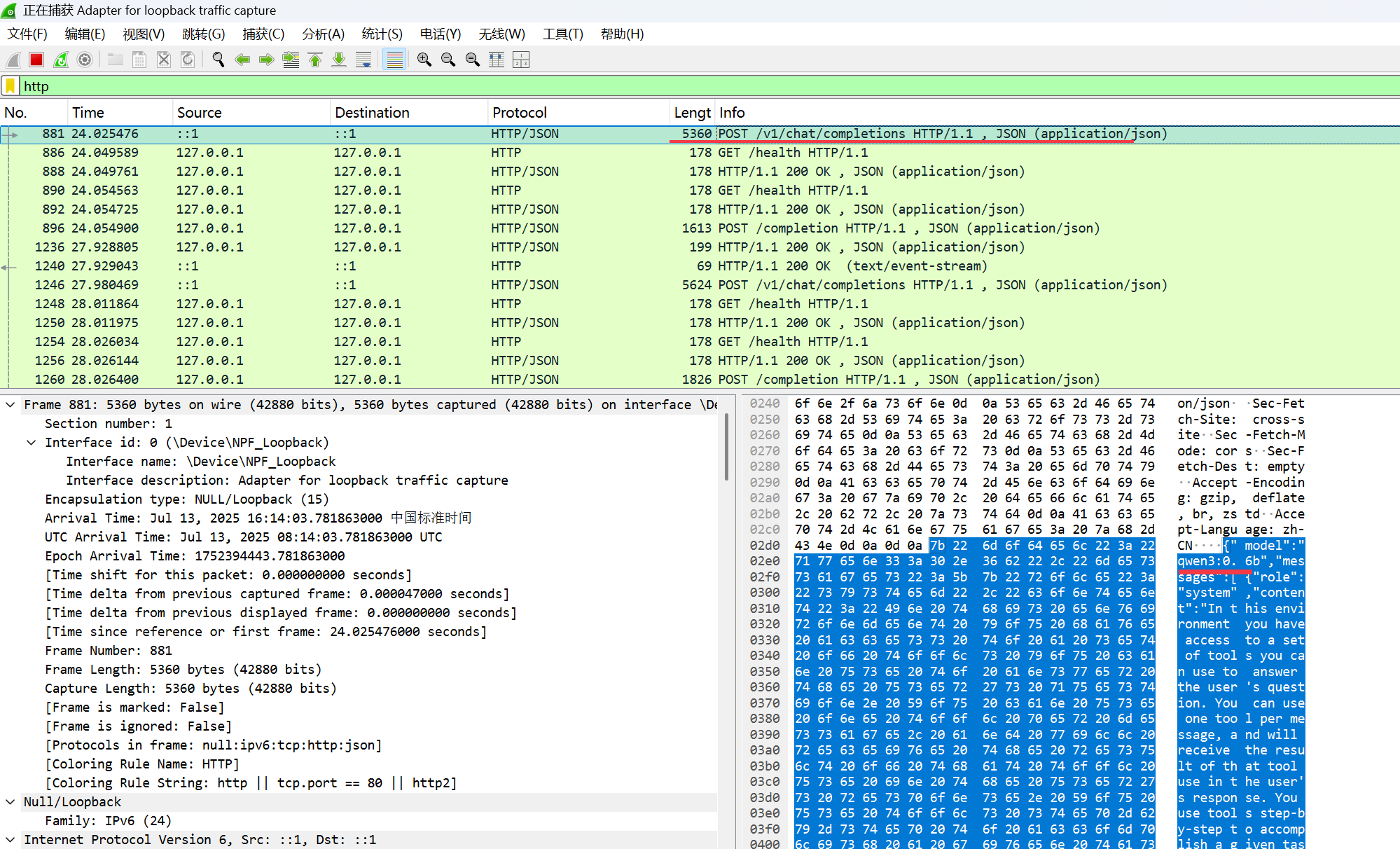
把报文中的内容取出来,整理下,prompt大致长这样:
{
"model": "qwen3:0.6b",
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": "In this environment you have access to a set of tools you can use to answer the user's question. You can use one tool per message, and will receive the result of that tool use in the user's response. You use tools step-by-step to accomplish a given task, with each tool use informed by the result of the previous tool use.\n\n## Tool Use Formatting\n\nTool use is formatted using XML-style tags. The tool name is enclosed in opening and closing tags, and each parameter is similarly enclosed within its own set of tags. Here's the structure:\n\n<tool_use>\n <name>{tool_name}</name>\n <arguments>{json_arguments}</arguments>\n</tool_use>\n\nThe tool name should be the exact name of the tool you are using, and the arguments should be a JSON object containing the parameters required by that tool. For example:\n<tool_use>\n <name>python_interpreter</name>\n <arguments>{\"code\": \"5 + 3 + 1294.678\"}</arguments>\n</tool_use>\n\nThe user will respond with the result of the tool use, which should be formatted as follows:\n\n<tool_use_result>\n <name>{tool_name}</name>\n <result>{result}</result>\n</tool_use_result>\n\nThe result should be a string, which can represent a file or any other output type. You can use this result as input for the next action.\nFor example, if the result of the tool use is an image file, you can use it in the next action like this:\n\n<tool_use>\n <name>image_transformer</name>\n <arguments>{\"image\": \"image_1.jpg\"}</arguments>\n</tool_use>\n\nAlways adhere to this format for the tool use to ensure proper parsing and execution.\n\n## Tool Use Examples\n\nHere are a few examples using notional tools:\n---\nUser: Generate an image of the oldest person in this document.\n\nAssistant: I can use the document_qa tool to find out who the oldest person is in the document.\n<tool_use>\n <name>document_qa</name>\n <arguments>{\"document\": \"document.pdf\", \"question\": \"Who is the oldest person mentioned?\"}</arguments>\n</tool_use>\n\nUser: <tool_use_result>\n <name>document_qa</name>\n <result>John Doe, a 55 year old lumberjack living in Newfoundland.</result>\n</tool_use_result>\n\nAssistant: I can use the image_generator tool to create a portrait of John Doe.\n<tool_use>\n <name>image_generator</name>\n <arguments>{\"prompt\": \"A portrait of John Doe, a 55-year-old man living in Canada.\"}</arguments>\n</tool_use>\n\nUser: <tool_use_result>\n <name>image_generator</name>\n <result>image.png</result>\n</tool_use_result>\n\nAssistant: the image is generated as image.png\n\n---\nUser: \"What is the result of the following operation: 5 + 3 + 1294.678?\"\n\nAssistant: I can use the python_interpreter tool to calculate the result of the operation.\n<tool_use>\n <name>python_interpreter</name>\n <arguments>{\"code\": \"5 + 3 + 1294.678\"}</arguments>\n</tool_use>\n\nUser: <tool_use_result>\n <name>python_interpreter</name>\n <result>1302.678</result>\n</tool_use_result>\n\nAssistant: The result of the operation is 1302.678.\n\n---\nUser: \"Which city has the highest population , Guangzhou or Shanghai?\"\n\nAssistant: I can use the search tool to find the population of Guangzhou.\n<tool_use>\n <name>search</name>\n <arguments>{\"query\": \"Population Guangzhou\"}</arguments>\n</tool_use>\n\nUser: <tool_use_result>\n <name>search</name>\n <result>Guangzhou has a population of 15 million inhabitants as of 2021.</result>\n</tool_use_result>\n\nAssistant: I can use the search tool to find the population of Shanghai.\n<tool_use>\n <name>search</name>\n <arguments>{\"query\": \"Population Shanghai\"}</arguments>\n</tool_use>\n\nUser: <tool_use_result>\n <name>search</name>\n <result>26 million (2019)</result>\n</tool_use_result>\nAssistant: The population of Shanghai is 26 million, while Guangzhou has a population of 15 million. Therefore, Shanghai has the highest population.\n\n\n## Tool Use Available Tools\nAbove example were using notional tools that might not exist for you. You only have access to these tools:\n<tools>\n\n<tool>\n <name>MCP_queryOrderStatus</name>\n <description> </description>\n <arguments>\n {\"type\":\"object\",\"properties\":{\"orderNo\":{\"type\":\"string\",\"description\":\", 8,25070601\"}},\"required\":[\"orderNo\"],\"additionalProperties\":false}\n </arguments>\n</tool>\n\n</tools>\n\n## Tool Use Rules\nHere are the rules you should always follow to solve your task:\n1. Always use the right arguments for the tools. Never use variable names as the action arguments, use the value instead.\n2. Call a tool only when needed: do not call the search agent if you do not need information, try to solve the task yourself.\n3. If no tool call is needed, just answer the question directly.\n4. Never re-do a tool call that you previously did with the exact same parameters.\n5. For tool use, MARK SURE use XML tag format as shown in the examples above. Do not use any other format.\n\n# User Instructions\n\n\nNow Begin! If you solve the task correctly, you will receive a reward of $1,000,000.\n"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": "25070602 /no_think"
}
],
"temperature": 1,
"top_p": 1,
"enable_thinking": false,
"stream": false
}
中间那段content老长了,我把其中的\n换行格式化下,内容如下:
| content原文 | content翻译后 |
"In this environment you have access to a set of tools you can use to answer the user's question. You can use one tool per message, and will receive the result of that tool use in the user's response. You use tools step-by-step to accomplish a given task, with each tool use informed by the result of the previous tool use. ## Tool Use Formatting Tool use is formatted using XML-style tags. |
在这种环境中,您可以使用一系列工具来回答用户的问题。
您每次消息只能使用一个工具,并会在用户的回复中收到该工具使用的结果。
您需要逐步使用工具来完成给定的任务,每次使用工具都要参考前一次工具使用的结果。
## 工具使用格式设置
工具使用格式采用 XML 风格的标签。
工具名称被包含在起始标签和结束标签中,每个参数也以相同的方式被包含在其自身的标签组内。
其结构如下:
<工具使用>
<名称>{工具名称}</名称>
<参数>{json 参数}</参数>
</工具使用>
工具名称应为所使用工具的确切名称,参数应为包含该工具所需参数的 JSON 对象。例如:
<tool_use>
<name>python_interpreter</name>
<arguments>{"code": "5 + 3 + 1294.678"}</arguments>
</tool_use>
用户将用工具使用的结果进行回复,其格式应如下所示:
<工具使用结果>
<名称>{工具名称}</名称>
<结果>{结果}</结果>
</工具使用结果>
结果应为一个字符串,它可以代表一个文件或任何其他输出类型。
您可以将此结果用作下一个操作的输入。
例如,如果工具使用的结果是一个图像文件,您可以在下一个操作中像这样使用它:
<工具使用>
<名称>图像转换器</名称>
<参数>{"图像": "image_1.jpg"}</参数>
</工具使用>
始终遵循此格式使用工具,以确保正确解析和执行。
## 工具使用示例
这里有几个使用概念工具的例子:---
生成这份文件中年龄最大的人的图像。
我可以使用 document_qa 工具来找出文档中提到的最年长的人是谁。
<工具使用>
<名称>document_qa</名称>
<参数>{"document": "document.pdf", "question": "文档中提到的最年长的人是谁?"}
</工具使用>
约翰·多伊,一位 55 岁的伐木工人,居住在纽芬兰。
我可以使用图像生成器工具为约翰·多伊生成一幅肖像。
<工具使用>
<名称>图像生成器</名称>
<参数>{"提示": "一位 55 岁的加拿大男子约翰·多伊的肖像。"}</参数>
</工具使用>
用户: <工具使用结果>
<名称>图像生成器</名称>
<结果>image.png</结果>
</工具使用结果>
图像以 image.png 的形式生成。
---
以下运算的结果是多少:5 + 3 + 1294.678?\"
我可以使用 python_interpreter 工具来计算该运算的结果。
<工具使用>
<名称>python_interpreter</名称>
<参数>{"代码": "5 + 3 + 1294.678"}</参数>
</工具使用>
用户: <工具使用结果>
<名称>python解释器</名称>
<结果>1302.678</结果>
</工具使用结果>
运算结果是 1302.678 。
---
广州和上海,哪个城市人口最多?\"
我可以使用搜索工具来查找广州的人口数量。
<工具使用>
<名称>搜索</名称>
<参数>{"查询": "广州人口"}</参数>
</工具使用>
截至 2021 年,广州的人口为 1500 万。
我可以使用搜索工具来查找上海的人口数量。
<工具使用>
<名称>搜索</名称>
<参数>{"查询": "上海人口"}</参数>
</工具使用>
上海的人口为 2600 万(2019 年),而广州的人口为 1500 万。因此,上海的人口最多。
## 可用工具 工具使用
上述示例中使用的工具可能并不存在于您的可用工具中。您仅能使用以下工具:
<tools>
<工具>
<名称>MCP_queryOrderStatus</名称>
<描述> </描述>
<参数>
{"类型":"对象","属性":{"orderNo":{"类型":"字符串","描述":", 8,25070601"}}, "必需":[ "orderNo" ], "附加属性":false}
</参数>
</工具>
</工具>
## 工具使用规则
以下是您在解决任务时应始终遵循的规则:
1. 始终为工具使用正确的参数。切勿将变量名作为操作参数,而应使用其值。
2. 仅在需要时调用工具:如果不需要信息,就不要调用搜索代理,尽量自己解决问题。
3. 如果不需要调用工具,就直接回答问题。4. 永远不要用完全相同的参数重复调用一个工具。
s5. 对于工具使用,请务必按照上述示例所示使用 XML 标签格式。请勿使用任何其他格式。
# 用户指南
现在开始!如果您正确完成任务,您将获得 100 万美元的奖励。"
|
注意其中有一段:
1 <tool> 2 <name>MCP_queryOrderStatus</name> 3 <description> </description> 4 <arguments> 5 {\"type\":\"object\",\"properties\":{\"orderNo\":{\"type\":\"string\",\"description\":\", 8,25070601\"}},\"required\":[\"orderNo\"],\"additionalProperties\":false} 6 </arguments> 7 </tool>
这就是我们写的MCP Server工具queryOrderStatus的描述。
把这个巨大的prompt扔给ollama后,会得到大模型类似以下的回答:

{
"model": "qwen3:0.6b",
"created_at": "2025-07-13T08:28:26.9799885Z",
"message": {
"role": "assistant",
"content": "<think>\n\n</think>\n\n<tool_use>\n <name>MCP_queryOrderStatus</name>\n <arguments>\n {\"orderNo\": \"25070602\"}\n </arguments>\n</tool_use>\n\nThe order number 25070602 has the status of processing."
},
"done_reason": "stop",
"done": true,
"total_duration": 4771552700,
"load_duration": 30473200,
"prompt_eval_count": 1264,
"prompt_eval_duration": 77797900,
"eval_count": 65,
"eval_duration": 4656713800
}
把其中的content格式化一下:
<think>
</think>
<tool_use>
<name>MCP_queryOrderStatus</name>
<arguments>
{\"orderNo\": \"25070602\"}
</arguments>
</tool_use>
The order number 25070602 has the status of processing.
说明大模型表明了意图:知道自己已有的知识搞不定这个,希望MCP Host来调用工具MCP_queryOrderStatus,感兴趣的同学可以按这个思路,继续看后续的抓包报文,就不一一分析了。理论上,参考cherry studio的这个思路,我们自己也可以重造轮子,写1个自己的MCP Host,本质上就是prompt工程。
参考:
https://modelcontextprotocol.io/specification/2025-06-18/basic/lifecycle
https://docs.spring.io/spring-ai/reference/api/mcp/mcp-overview.html
出处:http://yjmyzz.cnblogs.com
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号