深入解析:How the addition of a feedback loop modifies the transfer functions and performance of the system
本文参照 fundamental of power electronics第九节:
对一个buck电路而言,它的控制框图为:
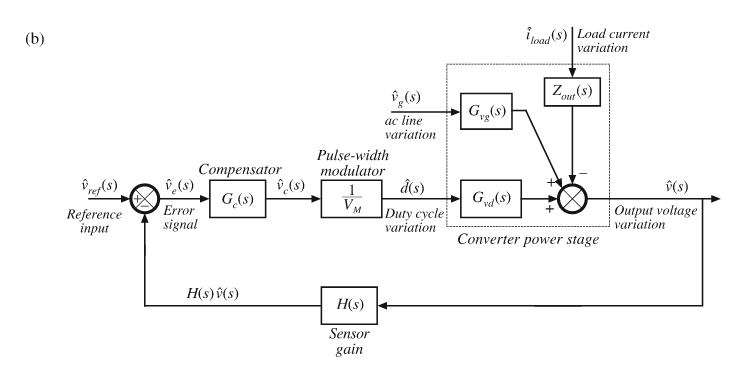
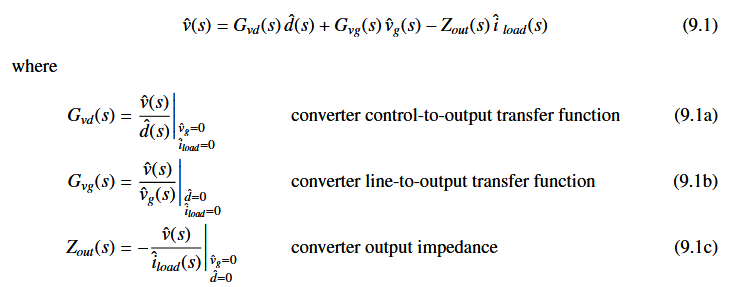
开环输出电压的表达式为:
当加入闭环控制后,输出电压的表达式为:
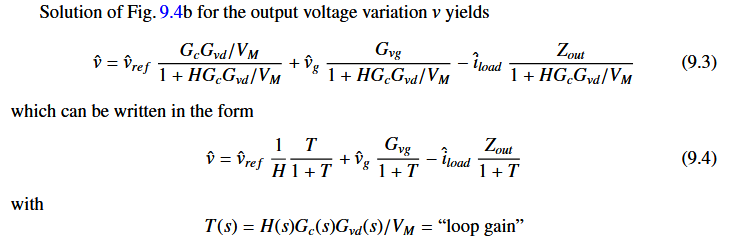
这么做的好处:
1,减少了干扰对输出的影响
以vg的干扰为例:
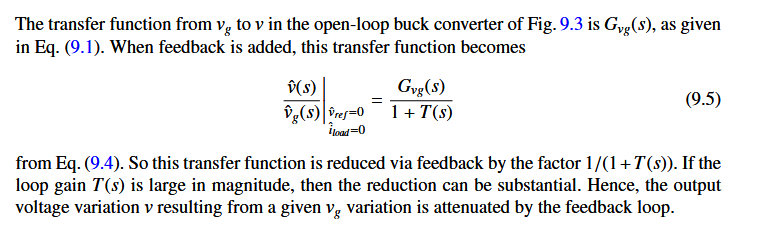
2,反馈会使从参考输入到输出的传递函数对环路前向路径中的增益变化变得不敏感
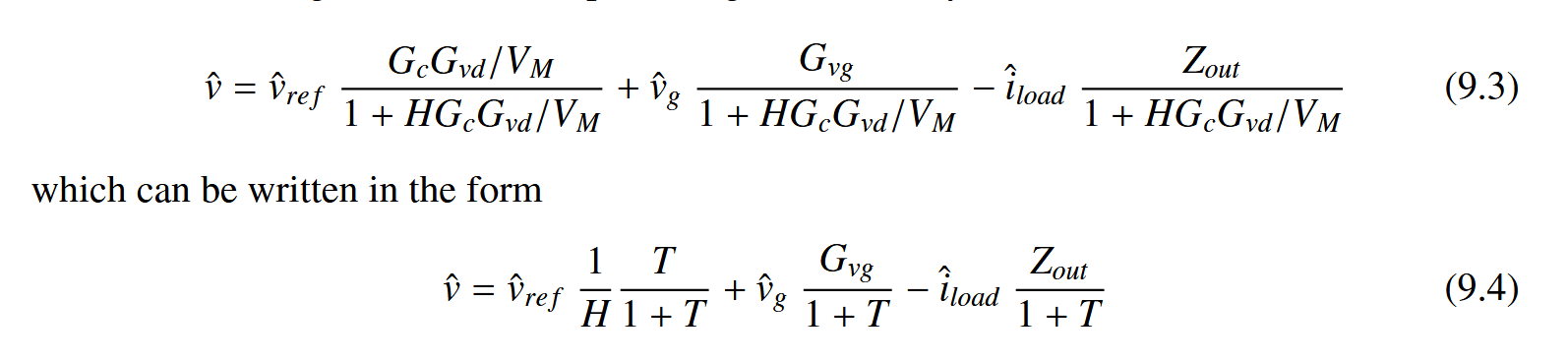
其中T(s)被称为环路增益(“loop gain”),特殊地,对于本例中只有反馈,没有补偿器的buck电路而言:
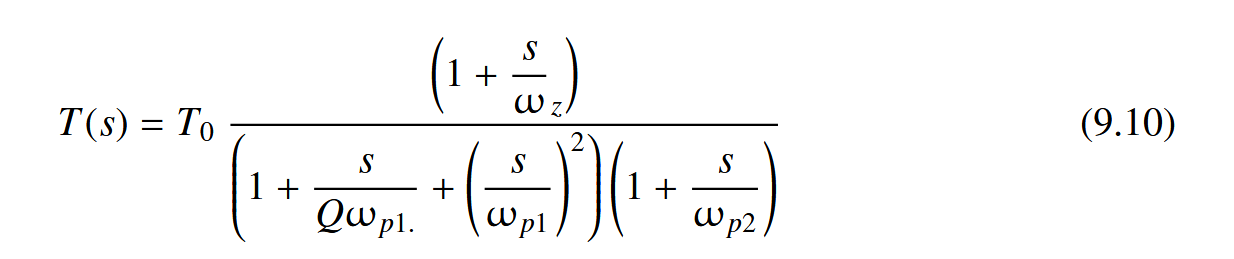
若没加补偿器的环路增益:
闭环增益:
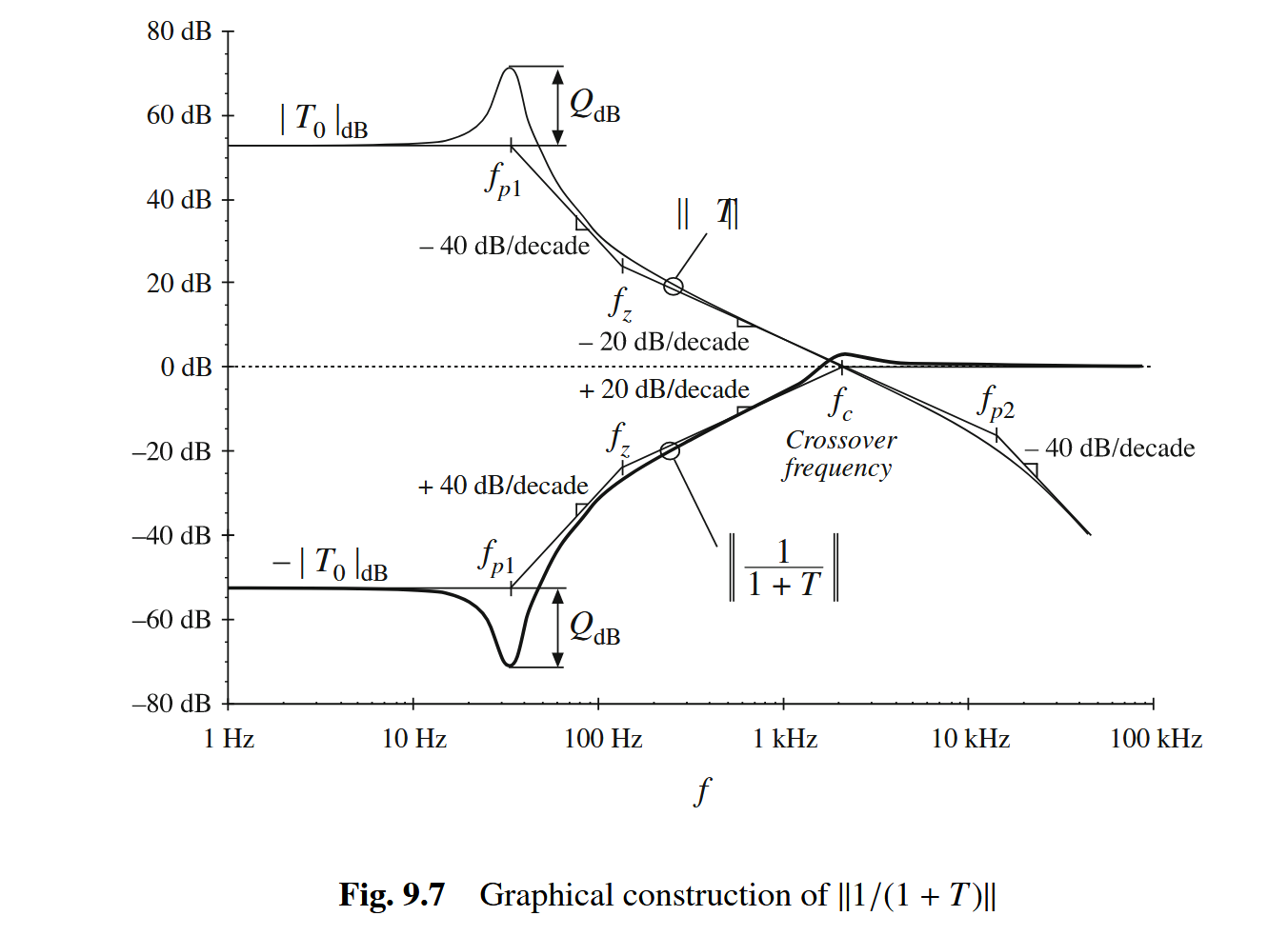
进一步地,对于本buck电路而言:

因此,加入反馈后,负载电流对于输出电压的影响为:
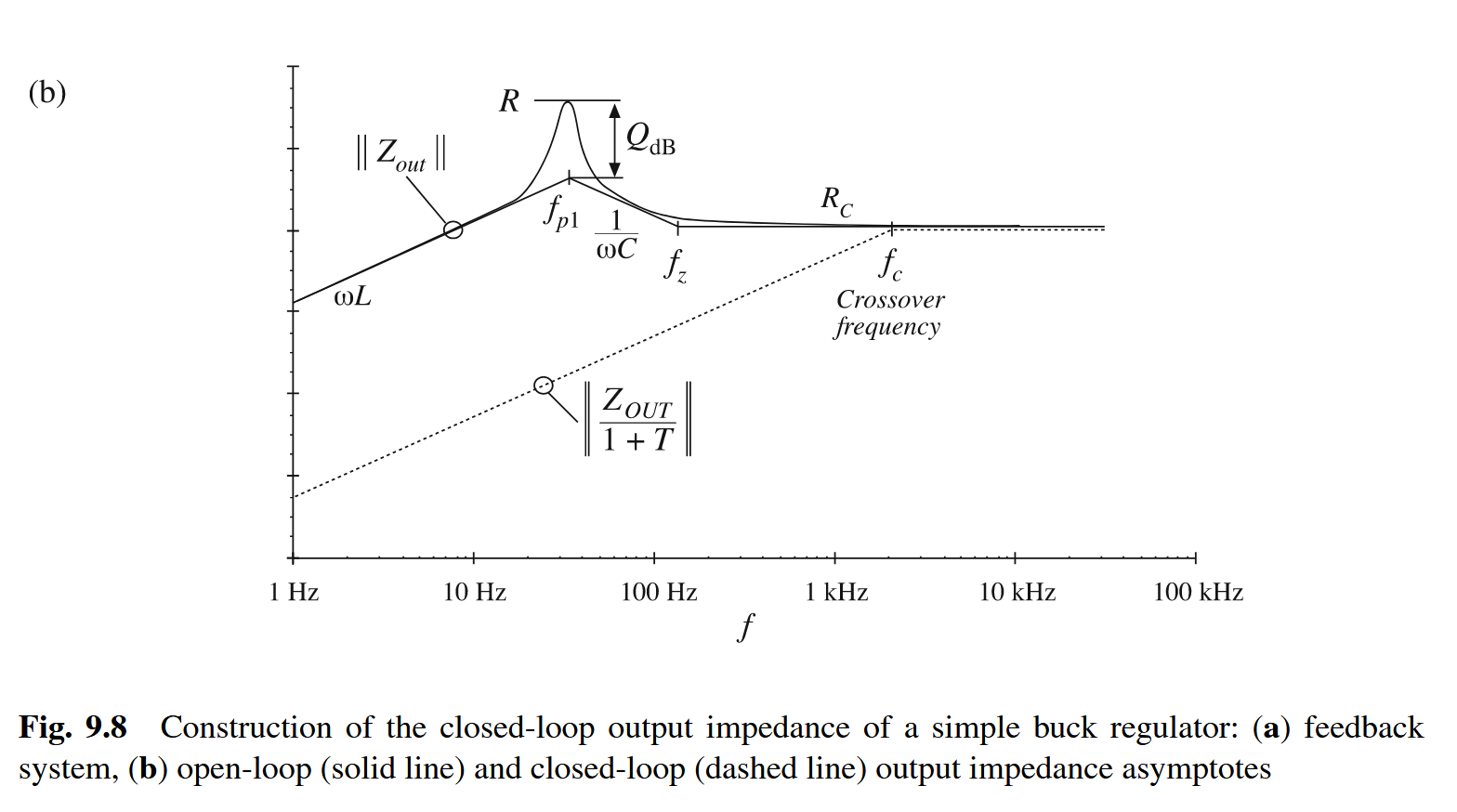
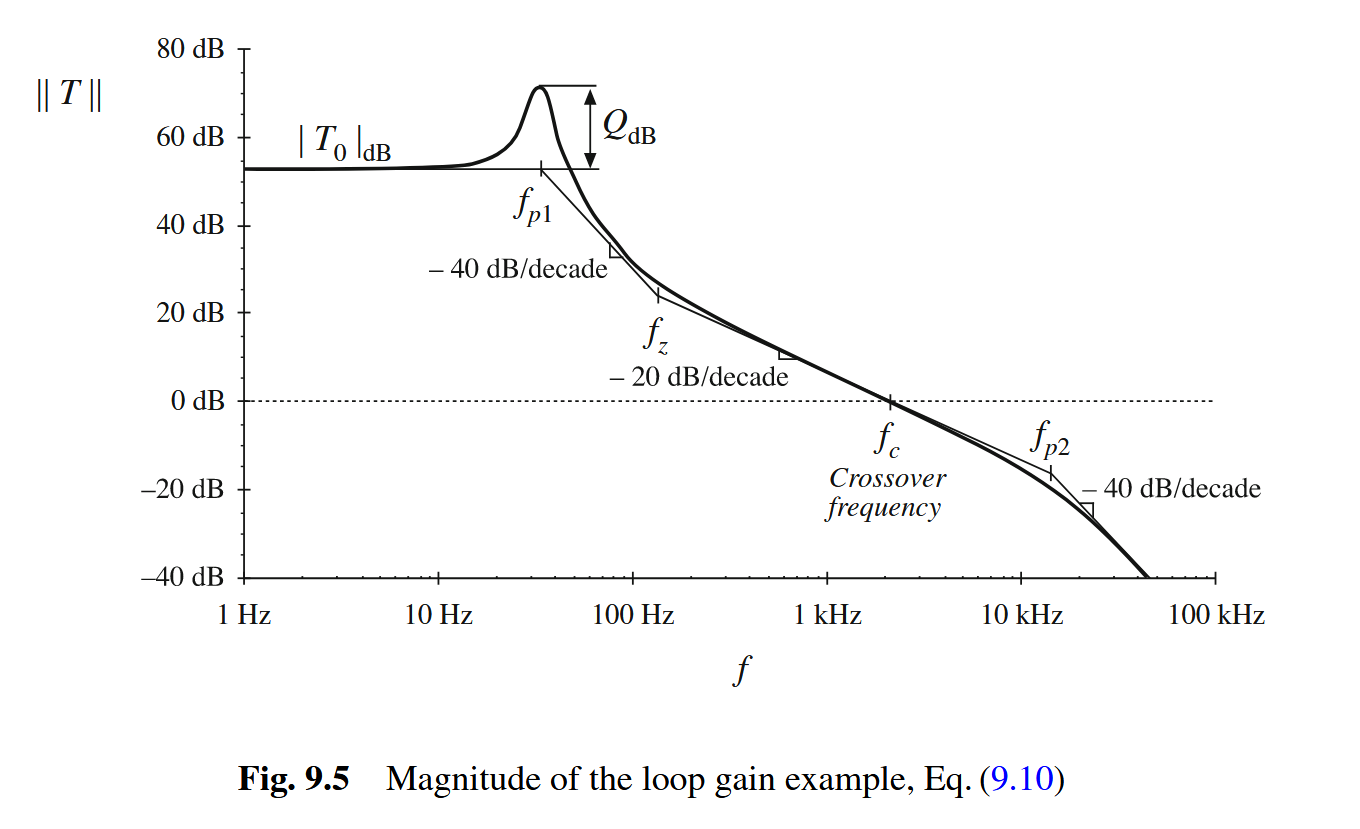
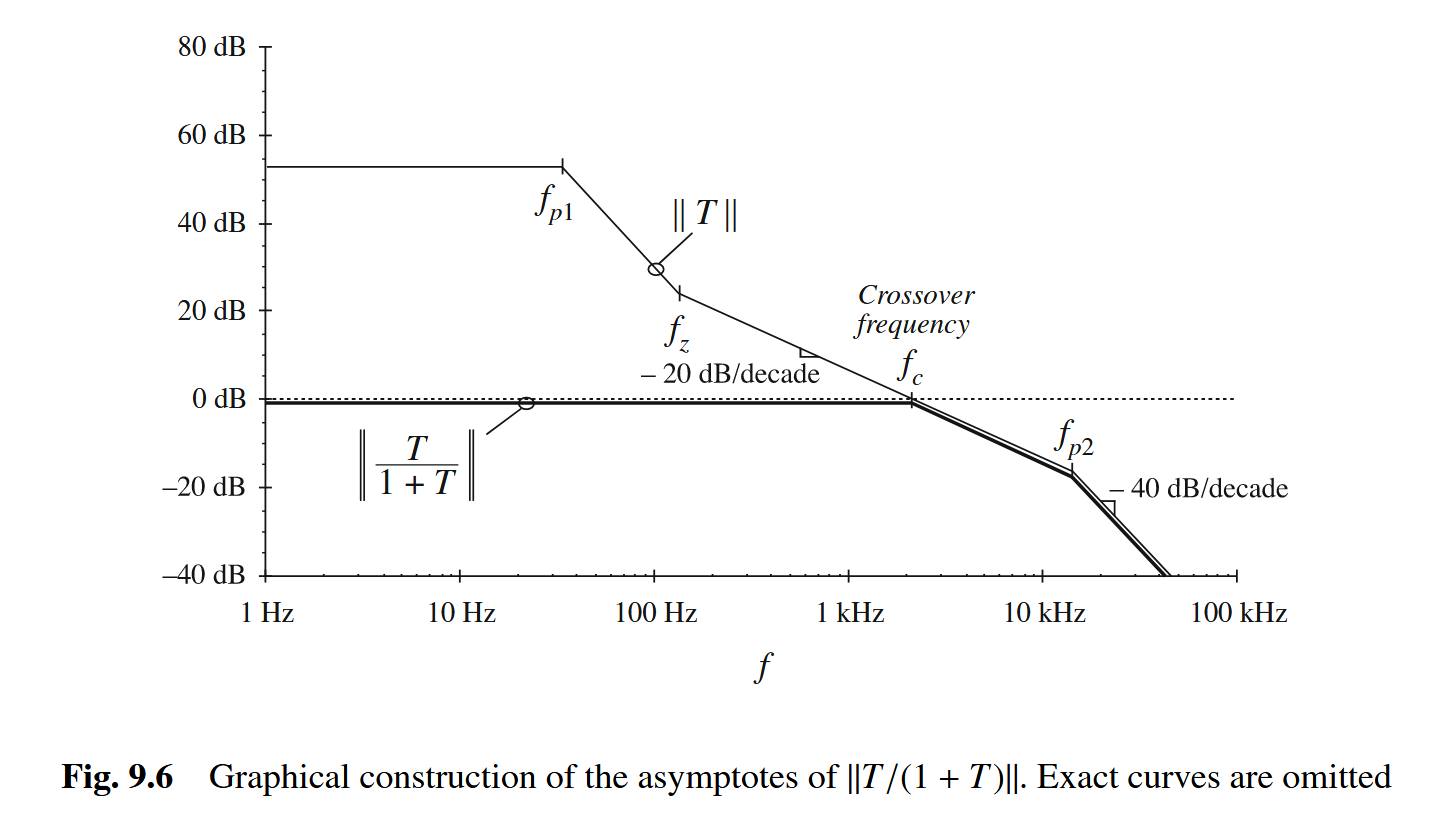
可以看到:在带宽(用穿越频率(“fc, called the “crossover frequency,””)表示)以内,反馈的作用很明显,环路增益越大越好,但在大于带宽频率时,反馈的作用就变得没那么明显,整个框架相当于没加反馈(“So the feedback loop has essentially no effect on the disturbance transfer functions at frequencies above the crossover frequency.”),此外,在带宽内的效果很好,是因为抵消的作用(“These cancellations occur because the power stage circuit introduces the same poles into Gvd(s) and Zout(s).”)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号