C语言基础知识-程序流程结构
C语言基础知识-程序流程结构
作者:尹正杰
版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任。
一.概述
C语言支持最基本的三种程序运行结构:顺序结构,选择结构,循环结构。
顺序结构:程序按顺序执行,不发生跳转。
选择结构:依据是否满足条件,有选择的执行相应功能。
循环结构:依据条件是否满足,循环多次执行某段代码。
二.选择结构
1>.if语句
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# cat if_demo.c /* @author :yinzhengjie blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com */ #include <stdio.h> int main(void) { int a = 100; int b = 20; if (a > b) { printf("a > b\n"); } return 0; } [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# gcc -o if_demo if_demo.c [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./if_demo a > b [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]#
2>.if ... else语句

[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# cat if_demo2.c /* @author :yinzhengjie blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com */ #include <stdio.h> int main(void) { int a = 100; int b = 200; if (a > b) { printf("a > b\n"); } else { printf("a < b\n"); } return 0; } [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# gcc -o if_demo2 if_demo2.c [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./if_demo2 a < b [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]#
3>.if ... else if ...else语句

[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# cat if_demo3.c /* @author :yinzhengjie blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com */ #include <stdio.h> int main(void) { int a = 300; int b = 300; if (a > b) { printf("a > b\n"); } else if(a == b) { printf("a == b\n"); } else { printf("a < b\n"); } return 0; } [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# gcc -o if_demo3 if_demo3.c [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./if_demo3 a == b [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]#
4>.三目运算符【其实其内部判断条件和if相似,语法结构简单明了】
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# cat if_demo4.c /* @author :yinzhengjie blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com */ #include <stdio.h> int main(void) { int a = 100; int b = 300; int max; if (a > b) { max = a; } else { max = b; } printf("s1 = %d\n",max); a = 10; b = 20; max = (a > b ? a:b); //上面一大堆代码,我们仅仅用三目运算符一行简写。三目运算符格式为"表达式?选项1[表达式]:选项2",即如果表达式为真,选择选项1的结果,如果为假则选择新选项2。 printf("s2 = %d\n",max); return 0; } [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# gcc -o if_demo4 if_demo4.c [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./if_demo4 s1 = 300 s2 = 20 [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]#
5>.switch语句【注意:if 条件语句执行效率差,switch条件语句执行效率相对较高,但是if可以判断一个区间,而switch则只能用来判断一个值】
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# cat switch_demo.c /* @author :yinzhengjie blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com */ #include <stdio.h> int main(void) { char c; c = getchar(); //注意该方法只会接收第一个字符哟~比如你输入的是100,它只会接收第一个字符“1” switch(c) //参数只能是整型变量 { case '1': printf("OK\n"); break; //switch遇到break就中断了 case '2': printf("not OK\n"); break; default: //如果上面的条件都不满足,那么执行default printf("are u OK?\n"); } return 0; } [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# gcc -o switch_demo switch_demo.c [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./switch_demo 1 OK [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./switch_demo 2 not OK [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./switch_demo 3 are u OK? [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./switch_demo 5 are u OK? [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]#
三.循环结构
1>.while语句
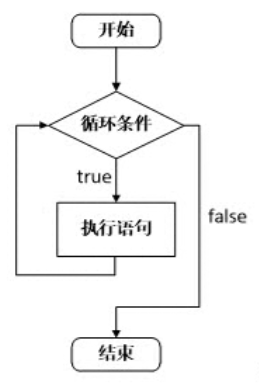
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# cat while_demo.c /* @author :yinzhengjie blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com */ #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main(void) { int a = 1; while(a < 10) { printf("a = %d\n",a); a++; system("sleep 0.5"); } printf("程序执行完毕~\n"); return EXIT_SUCCESS; } [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# gcc -o while_demo while_demo.c [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./while_demo a = 1 a = 2 a = 3 a = 4 a = 5 a = 6 a = 7 a = 8 a = 9 程序执行完毕~ [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]#
2>.do ... while语句

[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# cat narcissus.c /* @author :yinzhengjie blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com */ #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main(void) { int index = 100; do { int one = 0, ten=0, hundred=0; //将一个三位数分解个位,十位,百位 hundred = index / 100; //百位 ten = index / 10 % 10; //十位 one = index % 10; //个位 if (hundred * hundred * hundred + ten * ten * ten + one * one * one == index) //各个位数的立方和等于该数本身,那么它就是一个水仙花 { printf("%d是水仙花数\n",index); } index ++; }while(index < 1000); return EXIT_SUCCESS; } [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# gcc -o narcissus narcissus.c [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./narcissus 153是水仙花数 370是水仙花数 371是水仙花数 407是水仙花数 [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]#
3>.for循环
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# cat for_demo.c /* @author :yinzhengjie blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com */ #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main(void) { int index = 100; int sum = 0; for(index = 0;index<=100;index++) //计算0-100之间所有数字的是总和 { sum += index; } printf("sum = %d\n",sum); return EXIT_SUCCESS; } [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# gcc -o for_demo for_demo.c [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./for_demo sum = 5050 [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]#

[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# cat for_demo2.c /* @author :yinzhengjie blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com */ #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main(void) { for(int i = 100;i<1000;i++) { int one = 0, ten=0, hundred=0; //将一个三位数分解个位,十位,百位 hundred = i / 100; //百位 ten = i / 10 % 10; //十位 one = i % 10; //个位 if (hundred * hundred * hundred + ten * ten * ten + one * one * one == i) //各个位数的立方和等于该数本身,那么它就是一个水仙花 { printf("%d是水仙花数\n",i); } } return EXIT_SUCCESS; } [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# gcc -o for_demo2 for_demo2.c -std=c99 #注意,在Linux系统我们编译for循环代码时需要指定"-std=c99",否则会报错"error: ‘for’ loop initial declarations are only allowed in C99 mode" [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./for_demo2 153是水仙花数 370是水仙花数 371是水仙花数 407是水仙花数 [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]#
4>.嵌套循环(循环之间可以相互嵌套)
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# cat for_99.c /* @author :yinzhengjie blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com */ #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main(void) { int i,j; #我们提前声明了变量i和j,如果我们在这里不声明直接在for循环里面声明也是可以的,只不过在Linux操作系统编译时,我们需要指定std的库为c99,默认使用的是c90库。否则会报错"error: ‘for’ loop initial declarations are only allowed in C99 mode" for(i = 1; i <= 9; i++) { for(j=1; j<=i; j++) { printf("%d x %d = %d\t",i,j,i * j); } printf("\n"); } return EXIT_SUCCESS; } [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# gcc -o for_99 for_99.c [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./for_99 x 1 = 1 x 1 = 2 2 x 2 = 4 x 1 = 3 3 x 2 = 6 3 x 3 = 9 x 1 = 4 4 x 2 = 8 4 x 3 = 12 4 x 4 = 16 x 1 = 5 5 x 2 = 10 5 x 3 = 15 5 x 4 = 20 5 x 5 = 25 x 1 = 6 6 x 2 = 12 6 x 3 = 18 6 x 4 = 24 6 x 5 = 30 6 x 6 = 36 x 1 = 7 7 x 2 = 14 7 x 3 = 21 7 x 4 = 28 7 x 5 = 35 7 x 6 = 42 7 x 7 = 49 x 1 = 8 8 x 2 = 16 8 x 3 = 24 8 x 4 = 32 8 x 5 = 40 8 x 6 = 48 8 x 7 = 56 8 x 8 = 64 x 1 = 9 9 x 2 = 18 9 x 3 = 27 9 x 4 = 36 9 x 5 = 45 9 x 6 = 54 9 x 7 = 63 9 x 8 = 72 9 x 9 = 81 [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]#
5>.循环语句练习一(猜年龄)
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# cat guess_age.c /* @author :yinzhengjie blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com */ #include <stdio.h> #include <time.h> int main(void) { srand((unsigned int)time(NULL)); //加入随机数种子 int num = rand()%100 + 1; int value; for(;;) { printf("猜猜看我年龄多大(请输入一个整数)>>>: "); scanf("%d",&value); if(value > num) { printf("我有那么老吗?\n"); } else if(value < num) { printf("我看起来这么小吗?\n"); } else { printf("太棒了,你猜对啦~\n"); break; } } return 0; } [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# gcc -o guess_age guess_age.c [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./guess_age 猜猜看我年龄多大(请输入一个整数)>>>: 50 我看起来这么小吗? 猜猜看我年龄多大(请输入一个整数)>>>: 80 我有那么老吗? 猜猜看我年龄多大(请输入一个整数)>>>: 70 我有那么老吗? 猜猜看我年龄多大(请输入一个整数)>>>: 60 我看起来这么小吗? 猜猜看我年龄多大(请输入一个整数)>>>: 65 我有那么老吗? 猜猜看我年龄多大(请输入一个整数)>>>: 63 我看起来这么小吗? 猜猜看我年龄多大(请输入一个整数)>>>: 64 太棒了,你猜对啦~ [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]#
6>.循环语句练习二(打印等腰三角形)
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# cat isosceles_triangle.c /* @author :yinzhengjie blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com */ #include <stdio.h> int main(void) { int row; printf("请输入要打印等腰三角形的行数:>>> "); scanf("%d",&row); for (int i = 1;i <= row;i++) { for (int j =1;j <= row - i;j++) { printf(" "); } for (int k = 1;k <= i * 2 -1;k++) { printf("*"); } printf("\n"); } return 0; } [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# gcc -o isosceles_triangle isosceles_triangle.c -std=c99 [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./isosceles_triangle 请输入要打印等腰三角形的行数:>>> 3 * *** ***** [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./isosceles_triangle 请输入要打印等腰三角形的行数:>>> 10 * *** ***** ******* ********* *********** ************* *************** ***************** ******************* [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]#
四.跳转语句break和contiune语句
1>.break语句
在switch条件语句和循环语句中都可以使用break语句:
当它出现在switch条件语句时,作用是终止某个case并跳出switch结构。
当它出现在循环语句中,作用是跳出当前内循环语句,执行后面的代码。
当它出现嵌套循环语句中,跳出最近的内层循环语句,执行后面的代码。

[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# cat do_while.c /* @author :yinzhengjie blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com */ #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main(void) { int a = 0; do { a++; if (a == 100) { break; } }while(a); //需要注意的是,尽管没有上面的if条件判断语句,该循环并非死循环,只是执行的次数较多而已,因为a是一个有符号int类型的数字,而int类型是有上限的 printf("%d\n",a); return EXIT_SUCCESS; } [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# gcc -o do_while do_while.c [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./do_while 100 [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]#
2>.continue语句
在循环语句中,如果希望立即终止本次循环,并执行下一次循环,此时就需要使用continue语句。

[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# cat continue_demo.c /* @author :yinzhengjie blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com */ #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <string.h> int main(void) { int index = 0; while (index < 100) { index++; if(index % 7 == 0 || index % 10 == 7 || index / 10 == 7) //过滤掉带7和7的倍数的数字 { continue; } printf("数字:%d\n",index); } return EXIT_SUCCESS; } [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# gcc -o continue_demo continue_demo.c [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./continue_demo 数字:1 数字:2 数字:3 数字:4 数字:5 数字:6 数字:8 数字:9 数字:10 数字:11 数字:12 数字:13 数字:15 数字:16 数字:18 数字:19 数字:20 数字:22 数字:23 数字:24 数字:25 数字:26 数字:29 数字:30 数字:31 数字:32 数字:33 数字:34 数字:36 数字:38 数字:39 数字:40 数字:41 数字:43 数字:44 数字:45 数字:46 数字:48 数字:50 数字:51 数字:52 数字:53 数字:54 数字:55 数字:58 数字:59 数字:60 数字:61 数字:62 数字:64 数字:65 数字:66 数字:68 数字:69 数字:80 数字:81 数字:82 数字:83 数字:85 数字:86 数字:88 数字:89 数字:90 数字:92 数字:93 数字:94 数字:95 数字:96 数字:99 数字:100 [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]#
3>.goto语句(无条件跳转,尽量少用)
[root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# cat goto_demo.c /* @author :yinzhengjie blog:http://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie EMAIL:y1053419035@qq.com */ #include <stdio.h> int main(void) { goto END; //无条件跳转到END的标识 printf("第一行字母:a\n"); END: //我们定义的END标识,需要注意的是,这里是冒号(":"),而非分号(“;”)哟~ printf("第二行字母:A\n"); return 0; } [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# gcc -o goto_demo goto_demo.c [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# ./goto_demo 第二行字母:A [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]# [root@node101.yinzhengjie.org.cn /yinzhengjie/code/day002]#
本文来自博客园,作者:尹正杰,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/yinzhengjie/p/10987536.html,个人微信: "JasonYin2020"(添加时请备注来源及意图备注,有偿付费)
当你的才华还撑不起你的野心的时候,你就应该静下心来学习。当你的能力还驾驭不了你的目标的时候,你就应该沉下心来历练。问问自己,想要怎样的人生。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号