C# 错误和异常

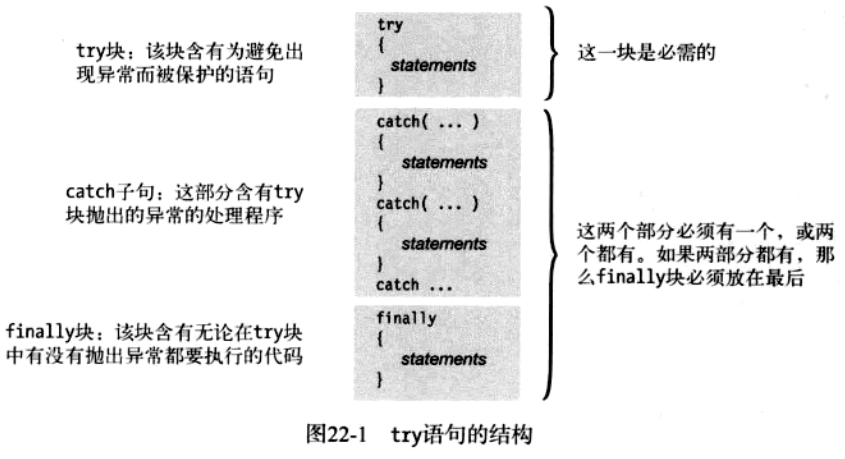
Try,catch和finally语句组成
异常层次结构

部分异常属性:
Message
类型:string
描述:含有解释异常原因的消息(只读)
StackTrace
类型:string
描述:含有描述异常发生在何处的消息
InnerExcption
类型:Exception
描述:如果当前异常是由另一个异常引起的,这个属性包含前一个异常的引用
HelpLink
类型:string
描述:为异常原因信息提供URN或URL
Source
类型:string
描述:如果没有应用程序定义的异常设定,那么这个属性含有异常所在的程序集的名称
Date
类型:IDdictionary
描述:其他异常信息的键值对的集合
Targetsite
引发当前异常的方法
finally块
如果try块内部没有异常发生,那么在try块结尾,控制流跳过任何catch子句并到finally块
如果在try块内内部发生了异常,那么catch子句段中无论哪一个被执行,接下来就是finally块执行
即使try块中有return语句或在catch块抛出一个异常,
finally块也总是在返回到调用代码之前执行。
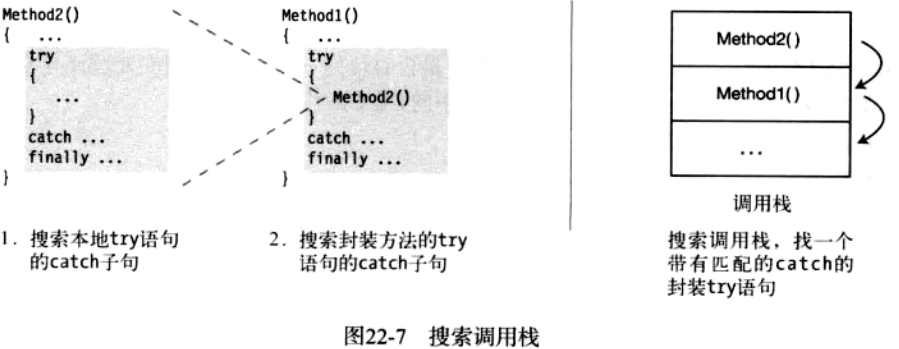
异常的进一步搜索
如果一个没有被try语句保护的代码中产生异常,或者try语句没有匹配到异常处理程序时。系统将会进一步寻找匹配的处理代码。
为此它为按顺序搜索调用栈,以看看是否存在带匹配的处理程序的封装try块。
比如:Method2被从Method1的try块内部调用,现在异常发生在Method2类的try块内部。
如果Method2中能处理异常,程序会继续执行
没有,系统会随着调用栈找到Method1,寻找合适的处理程序
如果Method1有适当的catch子句,那么
回到栈顶,即回到Method2
执行Method2的finally块,并把Method2弹出栈
执行Method1的catch子句和finally块
如果Method1也没有,则继续搜索
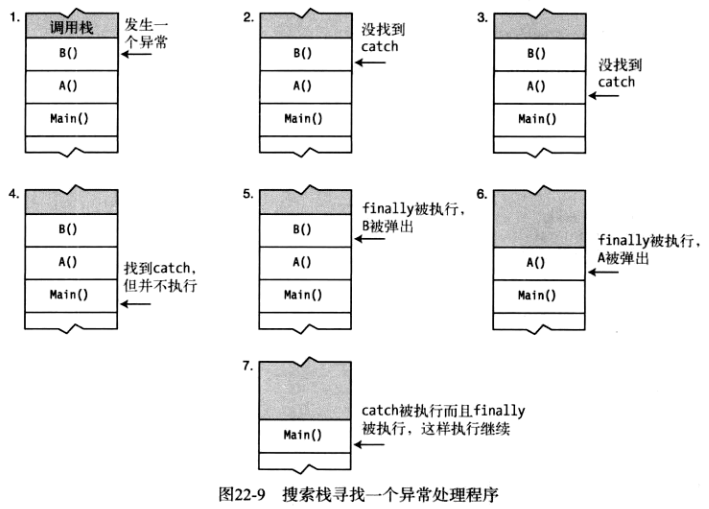
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class Program { class MyClass { void B() { int x = 10, y = 0; try { x /= y; } catch (IndexOutOfRangeException) { Console.WriteLine("catch clause B()"); } finally { Console.WriteLine("finally clause in B()"); } } public void A() { try { B(); } catch(NullReferenceException) { Console.WriteLine("catch clause in A()"); } finally { Console.WriteLine("finally clause in A()"); } } } static void Main(string[] args) { MyClass MCls = new MyClass(); try { MCls.A(); } catch(DivideByZeroException e) { Console.WriteLine("catch clause in Main()"); } finally { Console.WriteLine("finally clause in Main()"); } Console.WriteLine("After try statement in Main."); Console.WriteLine(" -- Keep running."); } } }
找到catch(DivideByZeroException e)后,不会立即执行,而是
1 回到栈顶执行B的finally
2 B弹出,执行A的finally
3 执行自己
4 执行main剩下语句
显式抛出异常
可以使用throw语句使代码显式引发一个异常
throw ExceptionObject
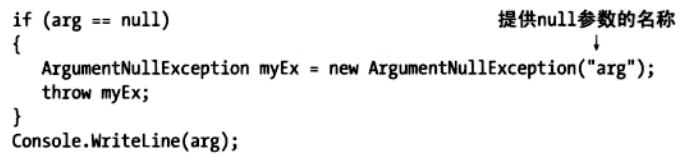
不带异常对象的抛出

throw几种方式的区别
throw;可追溯到原始异常点,获取所有异常(范围粒度较大)
throw ex;会将到现在为止的所有信息清空,认为你catch到的异常已经被处理了,只不过处理过程中又抛出新的异常,从而找不到真正的错误源。
throw new Exception("errstr",ex);经过对异常重新包装,会保留原始异常点信息。
异常参数使用
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ConsoleApplication1 { class MyClass { public static int Parse(string textDigit) { string[] digitTexts = { "zero","one","two","three","four","five","six","seven","eight","nine" }; int result = Array.IndexOf(digitTexts, textDigit.ToLower()); Console.WriteLine(result); if (result < 0) { throw new ArgumentException("the argument did not represent a digit", "textDigit"); } return result; } static void Main(string[] args) { int a=Parse("one"); Console.WriteLine(a); } } }
其中:throw new ArgumentException("the argument did not represent a digit", "textDigit");
-1 未经处理的异常: System.ArgumentException: the argument did not represent a digit 参数名: textDigit
异常类型的区别
ArgumentNullException和NullReferenceExcetion
前者在错误传递了null时引发,null是无效参数特例,如果不为null,无效参数引发的异常是ArgumentException或ArgumentOutOfRangeException
NullReferenceExcetion一般只有在底层“运行时”解引用null值(想调用对象成员,但发现对象的值为null),不要自己引发NullReferenceExcetion,相反还需要检查引用的参数变量是否为空,并在null的前提下引发ArgumentNullException
引发异常时需要注意的地方


异常处理规范
只捕捉能处理的异常
不要隐藏你不能完全处理的异常
尽可能少的使用System.Exception和常规catch块,处理某些异常System.Exception的最佳方式是不对它们进行处理,或者尽快以正常方式关闭应用程序,这些异常包括:
System.OutOfMemoryException和System.StackOverflowException等
避免在调用栈较低的位置报告或记录异常
在catch块中使用throw,而不是throw<异常对象>



自定义异常
自定义异常唯一的要求是必须从System.Exception或者它的某个子类派生
创建自定义异常类应严格遵循几个原则
1. 声明可序列化(用于进行系列化,当然如果你不需要序列化。那么可以不声明为可序列化的)
2. 添加一个默认的构造函数
3. 添加包含message的构造函数
4. 添加一个包含message,及内部异常类型参数的构造函数
5. 添加一个序列化信息相关参数的构造函数.
public class DatabaseException : System.Exception { ///<summary> ///默认构造函数 /// </summary> public DatabaseException() { } public DatabaseException(string message) : base(message) { } public DatabaseException(string message,Exception inner) : base(message, inner) { } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号