Jetpack Compose
声明式UI
特点:
- 关注于UI的描述,当需要渲染的数据发生变化时,框架会自动完成UI更新
- 基于Kotlin DSL,开发效率高
与传统XML布局相比:
- 传统XML布局是静态的,无法根据状态变化而变化,我们需要通过findViewById等方式获取到View,然后通过代码驱动更新
- Compose使用声明式UI,我们只需要根据状态描述UI,当状态变化时,Compose会自动更新UI
@Composable
使用@Composable修饰的函数,可以理解为UI组件,用于代替传统的xml布局文件
@Composable修饰的函数,可以嵌套使用来实现复杂的UI结构
Compose中自带的组件都是用@Composable修饰的函数,如Text
@Composable
fun Text(..){
...
}
我们自己写的组件,也需要用@Composable修饰
Activity的变化
使用View体系时,默认使用AppCompatActivity,在Activity中使用setContentView()来设置布局文件
在Compose中,默认使用的是ComposeActivity,使用setContent()来设置Composable组件
class TestActivity : ComponentActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContent {
Text("Hello World")
}
}
}
组合优于继承
传统的View体系中,Button是继承自TextView,这意味着它继承了 TextView 的所有功能,但其中一些功能可能对 Button 并不适用
并且如果TextView 的设计发生变化,可能会影响到 Button 的行为,这造成了设计上的耦合
在Compose中,按钮被设计为具有点击事件的组件(查看源码,onClick和content没有默认值,需要实现)
@Composable
fun Button(
onClick: () -> Unit,
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
enabled: Boolean = true,
shape: Shape = ButtonDefaults.shape,
colors: ButtonColors = ButtonDefaults.buttonColors(),
elevation: ButtonElevation? = ButtonDefaults.buttonElevation(),
border: BorderStroke? = null,
contentPadding: PaddingValues = ButtonDefaults.ContentPadding,
interactionSource: MutableInteractionSource = remember { MutableInteractionSource() },
content: @Composable RowScope.() -> Unit
) {
...
}
如果想要显示文本,不是通过使用text之类的属性,而是通过content参数来显示文本
Button(onClick = { /*TODO*/ }) {
Text(text = "Click")
}

另外,Text默认是不可以复制文字的,想要复制文字,需要使用SelectionContainer包装
SelectionContainer(modifier = Modifier.padding(20.dp)) {
Text("Hello")
}

这些设计使得组件的职责更加单一,也不会出现可以复制文字的按钮,这也是为什么组合优于继承
Compose和View互操作
Compose中使用View
需要添加依赖
implementation("androidx.compose.ui:ui-viewbinding:1.7.8")
定义xml布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Click"/>
</LinearLayout>
定义Compose组件,使用AndroidViewBinding实现添加View
@Composable
fun UseXmlLayout() {
AndroidViewBinding(TestLayoutBinding::inflate) {
btn.setOnClickListener {
Log.d("yimin", "Clicked")
}
}
}

View中使用Compose
定义xml布局,使用ComposeView作为桥梁
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/main"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity2">
<androidx.compose.ui.platform.ComposeView
android:id="@+id/compose_view"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
在Activity中获取ComposeView,通过setContent使用Compose组件
class MainActivity2 : AppCompatActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2)
// ...
findViewById<ComposeView>(R.id.compose_view).setContent {
androidx.compose.material3.Text("Hello World")
}
}
}
总结
- Compose 中使用 View, 借助 AndroidViewBinding
- View 中使用 Compose,借助 ComposeView
主题
创建Compose项目,会自动生成一个文件夹:ui.theme,里面有三个文件:Color.kt,Type.kt和Theme.kt,其中Color.kt定义了颜色,Type.kt定义了字体,Theme.kt定义了主题
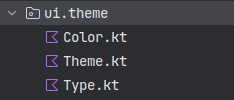
自动生成的主题如下
@Composable
fun MyComposeTheme(
darkTheme: Boolean = isSystemInDarkTheme(),
// Dynamic color is available on Android 12+
dynamicColor: Boolean = true,
content: @Composable () -> Unit
) {
val colorScheme = when {
dynamicColor && Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= Build.VERSION_CODES.S -> {
val context = LocalContext.current
if (darkTheme) dynamicDarkColorScheme(context) else dynamicLightColorScheme(context)
}
darkTheme -> DarkColorScheme
else -> LightColorScheme
}
MaterialTheme(
colorScheme = colorScheme,
typography = Typography,
content = content
)
}
- 安卓12及以上添加了动态配色功能,会使用dynamicColorScheme
- 当系统处于暗色模式时,会使用DarkColorScheme
- 当系统处于亮色模式时,会使用LightColorScheme
其中DarkColorScheme和LightColorScheme我们可以自定义,如果重写了颜色则会使用自定义的颜色,否则会使用系统默认的颜色
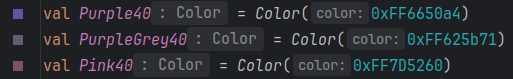
private val LightColorScheme = lightColorScheme(
// 自定义
primary = Purple40,
secondary = PurpleGrey40,
tertiary = Pink40,
primaryContainer = Purple40
/* Other default colors to override
background = Color(0xFFFFFBFE),
surface = Color(0xFFFFFBFE),
onPrimary = Color.White,
onSecondary = Color.White,
onTertiary = Color.White,
onBackground = Color(0xFF1C1B1F),
onSurface = Color(0xFF1C1B1F),
*/
)
所有的颜色都有一个对应的onXXX,比如primary和onPrimary
- primary为主要颜色,比如按钮的背景色
- onPrimary为在primary颜色上显示的内容的颜色,比如按钮上的文本颜色
主题同样是一个组件,一般在setContent的顶层调用
class TestActivity : ComponentActivity() {
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
enableEdgeToEdge()
setContent {
MyComposeTheme { // 应用自定义的主题
Scaffold { // Scaffold和Column在这里的作用是为了配合enableEdgeToEdge(),让内容避开状态栏和导航栏
Column(modifier = Modifier.padding(it)) {
Button(onClick = {}) {
Text("Hello")
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
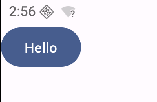
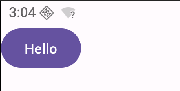
此时并没有使用自定义的颜色,因为当前系统支持动态配色
如果把动态配色代码删除,就能看到效果了
Scaffold
以上测试主题时,使用了Scaffold(脚手架),这个组件可以很方便地创建一个具有顶部导航栏、底部导航栏、悬浮按钮等样式的页面
MyComposeTheme {
Scaffold(
modifier = Modifier.fillMaxSize(),
topBar = {
TopAppBar(
title = { Text("Jetpack Compose App") },
modifier = Modifier.shadow(10.dp), // 阴影
colors = TopAppBarDefaults.topAppBarColors(
// containerColor = Purple80
),// 背景色
actions = {
IconButton(onClick = { /* TODO: handle action */ }) {
Icon(Icons.Default.Settings, contentDescription = "Settings")
}
}
)
},
bottomBar = {
// BottomAppBar {
// Text("Bottom Bar Content")
// }
// 底部导航栏
NavigationBar {
// Tab
NavigationBarItem(
selected = true,
onClick = { },
icon = { Icon(Icons.Default.Home, contentDescription = null) },
label = { Text("Home") }
)
// Tab
NavigationBarItem(
selected = false,
onClick = { },
icon = { Icon(Icons.Default.Settings, contentDescription = null) },
label = { Text("Settings") }
)
}
},
floatingActionButton = { // 右下角的悬浮按钮
FloatingActionButton(onClick = { /*do something*/ }) {
Icon(
Icons.Filled.Favorite,
contentDescription = "Localized description"
)
}
}
) { innerPadding ->
Column(
modifier = Modifier.padding(innerPadding),
) {
Button(onClick = {}) {
Text("Hello")
}
}
}
}

布局
Clonum
相当于纵向的LinearLayout
@Composable
fun ColumnLayout() {
Column {
Text("Hello World")
Text("Hello World")
}
}

Row
相当于横向的LinearLayout
@Composable
fun RowLayout(){
Row {
Text("Hello World")
Text("Hello World")
}
}

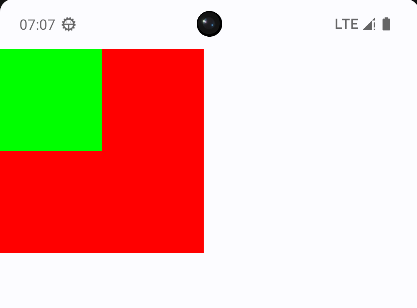
Box
相当于FragmentLayout,组件会叠加在一起
modifier用来修改组件的的尺寸、外观或添加交互(如点击事件),比如这里用来修改了Box的宽度,背景颜色
@Composable
fun BoxLayout() {
Box {
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.width(200.dp)
.aspectRatio(1f) // 保持宽高比为1:1
.background(color = Color.Red)
) {
}
Box(modifier = Modifier
.width(100.dp)
.aspectRatio(1f)
.background(Color.Green)) {
}
}
}
案例
其中用到的组件
- Image
- painterResource:加载资源图片
- contentDescription:用于无障碍
- Spacer:空白组件,用于填充空间
@Composable
fun MessageCard(msg: Message){
Row(
modifier = Modifier.padding(all = 8.dp) // 添加 padding
) {
Image(
painterResource(id = R.drawable.ic_launcher_foreground),
contentDescription = "profile picture", // 无障碍
modifier = Modifier
.size(50.dp) // 图片大小
.clip(RoundedCornerShape(20)) // 剪裁圆角
.border(1.5.dp, MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primary, shape = CircleShape) // 添加边框
)
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.padding(horizontal = 8.dp)) // 用于填充空间
Column {
Text(
text = msg.author,
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primary
)
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.padding(vertical = 2.dp))
Text(
text = msg.body
)
}
}
}
data class Message(val author: String, val body: String)

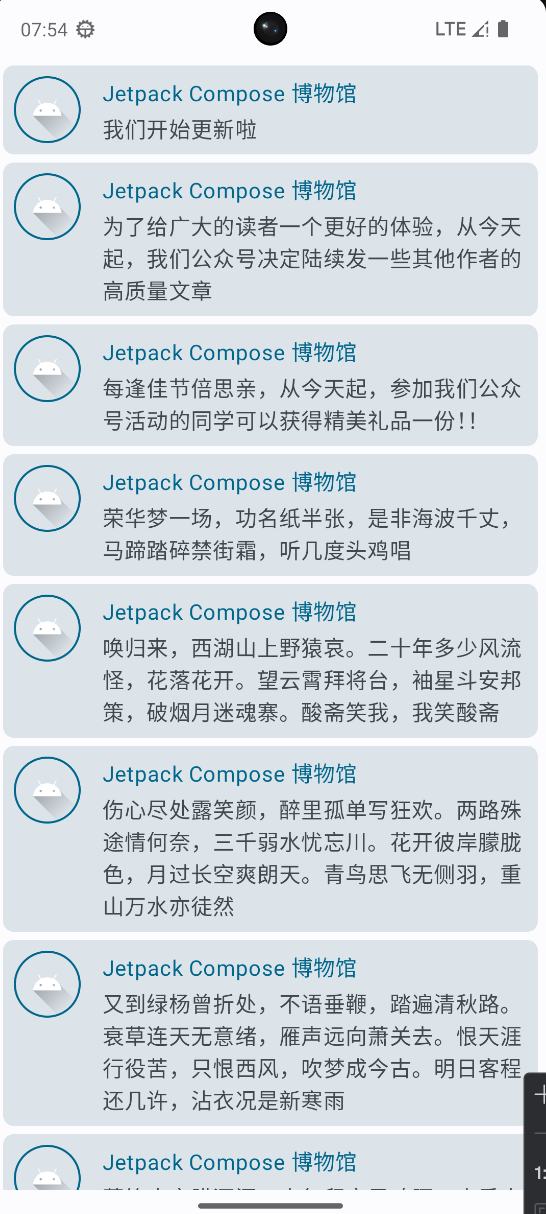
列表 LazyColumn
列表分为可滚动列表和不可滚动列表,不可滚动列表使用Column,可滚动列表使用LazyColumn
LazyColumn只会加载屏幕上可见的项目,而不是一次性加载所有项。使用 items 函数来显示列表中的每一项。
@Composable
fun MessageCardList(messages: List<Message>) {
LazyColumn {
items(messages.size) {
MessageCard(msg = messages[it])
}
}
}
object MsgData {
private const val author = "Jetpack Compose 博物馆"
val messages = listOf(
Message(author, "我们开始更新啦"),
Message(
author,
"为了给广大的读者一个更好的体验,从今天起,我们公众号决定陆续发一些其他作者的高质量文章"
),
Message(author, "每逢佳节倍思亲,从今天起,参加我们公众号活动的同学可以获得精美礼品一份!!"),
Message(author, "荣华梦一场,功名纸半张,是非海波千丈,马蹄踏碎禁街霜,听几度头鸡唱"),
Message(
author,
"唤归来,西湖山上野猿哀。二十年多少风流怪,花落花开。望云霄拜将台,袖星斗安邦策,破烟月迷魂寨。酸斋笑我,我笑酸斋"
),
Message(
author,
"伤心尽处露笑颜,醉里孤单写狂欢。两路殊途情何奈,三千弱水忧忘川。花开彼岸朦胧色,月过长空爽朗天。青鸟思飞无侧羽,重山万水亦徒然"
),
Message(
author,
"又到绿杨曾折处,不语垂鞭,踏遍清秋路。衰草连天无意绪,雁声远向萧关去。恨天涯行役苦,只恨西风,吹梦成今古。明日客程还几许,沾衣况是新寒雨"
),
Message(
author,
"莫笑农家腊酒浑,丰年留客足鸡豚。山重水复疑无路,柳暗花明又一村。箫鼓追随春社近,衣冠简朴古风存。从今若许闲乘月,拄杖无时夜叩门"
)
).run {
val mList = this.toMutableList()
mList.addAll(this)
mList
}
}

Card
可以使用Card组件进一步封装,实现卡片效果
@Composable
fun MessageCardWrapper(msg: Message) {
Card(
shape = RoundedCornerShape(8.dp), // 圆角
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth() // 宽度填满
.padding(horizontal = 6.dp, vertical = 3.dp), // 内边距
elevation =CardDefaults.cardElevation(
// defaultElevation = 5.dp,
) // 设置阴影
) {
MessageCard(msg)
}
}
@Composable
fun MessageCardList(messages: List<Message>) {
LazyColumn {
items(messages.size) {
MessageCardWrapper(msg = messages[it])
}
}
}
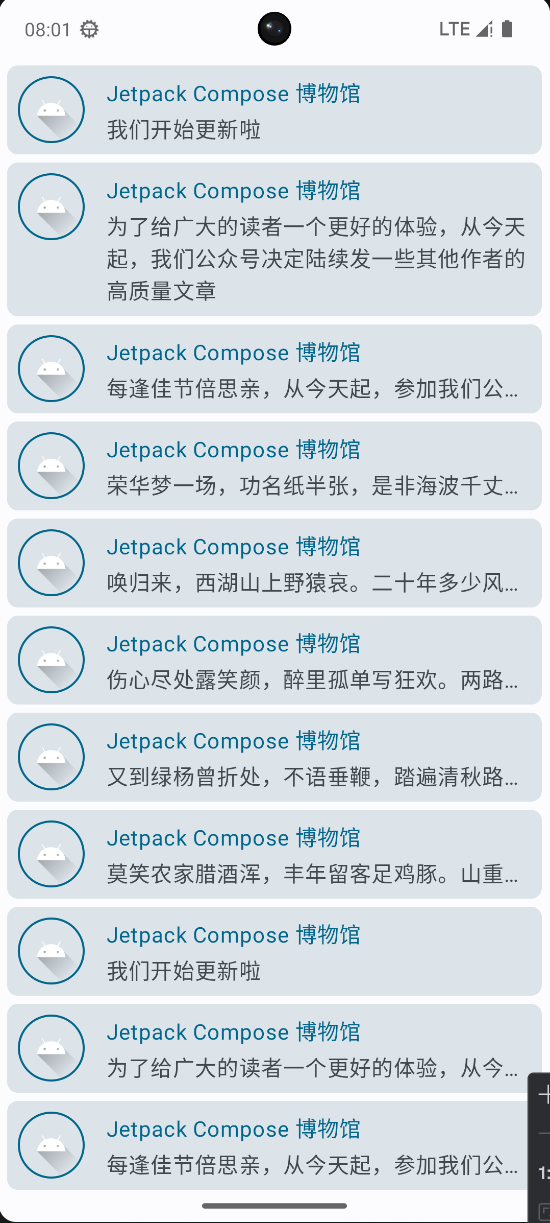
要实现卡片内容默认只显示一行,当点击时展开,并且带有动画效果
- 每个card都需要持有一个状态,判断是否展开
- 给最外层的Row添加点击事件,点击时改变状态
- 使用maxLines属性控制文本显示的行数
- 使用overflow属性控制文本溢出时的显示方式
- 使用animateContentSize实现展开动画
@Composable
fun MessageCard(msg: Message) {
var isExpanded by remember { mutableStateOf(false) } // 创建一个能够检测卡片是否被展开的变量
Row(
modifier = Modifier
.padding(all = 8.dp) // 在我们的 Card 周围添加 padding
.clickable { isExpanded = !isExpanded }
) {
Image(
painterResource(id = R.drawable.ic_launcher_foreground),
contentDescription = "profile picture", // 无障碍
modifier = Modifier
.size(50.dp)
.clip(RoundedCornerShape(20)) // 剪裁圆角
.border(1.5.dp, MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primary, shape = CircleShape) // 添加边框
)
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.padding(horizontal = 8.dp)) // 用于填充空间
Column {
Text(
text = msg.author,
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primary
)
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.padding(vertical = 2.dp))
Text(
text = msg.body,
maxLines = if (isExpanded) Int.MAX_VALUE else 1, // 最大行
overflow = TextOverflow.Ellipsis,
modifier = Modifier.animateContentSize() // 动画
)
}
}
}
这里用到了remember函数,它能够记住一个可组合项(组件)的状态,即使可组合项被重新组合(渲染),它也会保持状态不变。通常配合mutableStateOf函数一起使用,构造状态变量。
重组
重组指的是当Compose可组合项的状态发生变化时,Compose会重新计算并重新渲染该可组合项,这个过程称为重组。
@Composable
fun CounterExample() {
// 定义一个可变状态,初始值为0
var count by remember { mutableIntStateOf(0) }
Column {
// 显示当前计数值
Text("Clicked $count times")
// 当点击时增加计数器的值
Text(
text = "点击这里",
modifier = Modifier.clickable {
count++
}
)
}
}
在这个例子中,定义了一个可变状态count,初始值为0。当点击文本时,count的值会增加1,这会触发CounterExample的重组。
因为第一个Text组件依赖了count,所以会重新渲染,显示新的count值。
状态
状态也就是数据,Compose组件根据状态显示UI,状态变化更新UI。
在View体系中,要实现一个计数器,很容易写出以下代码
val textView = findViewById<TextView>(R.id.tv)
val btnInc = findViewById<Button>(R.id.btn_inc)
val btnDec = findViewById<Button>(R.id.btn_dec)
btnInc.setOnClickListener {
textView.text = (textView.text.toString().toInt() + 1).toString()
}
btnDec.setOnClickListener {
textView.text = (textView.text.toString().toInt() - 1).toString()
}
但是存在一个问题,逻辑和UI高度耦合
于是后面出现了ViewModel,用ViewModel优化上面的代码
class CountViewModel: ViewModel() {
// 修改私有可变的Flow
private var _count: MutableStateFlow<Int> = MutableStateFlow(0)
// 暴露不可变的Flow
val count: StateFlow<Int> get() = _count
fun increase() {
_count.value++
}
fun decrease() {
_count.value--
}
}
class MainActivity2 : AppCompatActivity() {
private val countViewModel by viewModels<CountViewModel>()
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
enableEdgeToEdge()
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2)
// ...
btnInc.setOnClickListener {
countViewModel.increase()
}
btnDec.setOnClickListener {
countViewModel.decrease()
}
lifecycleScope.launch {
repeatOnLifecycle(Lifecycle.State.STARTED) {
countViewModel.count.collect {
textView.text = it.toString()
}
}
}
}
}
此时逻辑被放到了ViewMode中,相应地,数据也被放到了ViewModel中,这本质上是一种状态提升,用来解耦。
按照这个思路,实现Compose版本的计数器,可以得到以下实现:
@Composable
fun Counter() {
Column(horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally) {
var count = 0
Log.d(TAG, "into Counter => ${count}")
Text(text = "$count")
Button(onClick = {
count++
Log.d(TAG, "count++ => ${count}")
}) {
Text(text = "increase")
}
Button(onClick = {
count--
Log.d(TAG, "count-- => ${count}")
}) {
Text(text = "decease")
}
}
}
但是点击并没有效果,查看日志,点击事件是生效的,但是没有触发重组(只有一次into Counter日志)
所以原因很显然就是普通变量的变化不能被Compose感知,需要将其包装为状态变量
15:30:53.524 D into Counter => 0
15:30:58.033 D count++ => 1
15:30:59.402 D count++ => 2
15:31:00.713 D count++ => 3
15:31:02.060 D count++ => 4
15:32:52.307 D count-- => 3
类似于StateFlow 或者 LiveData 将变量包装成一个可观察类型的对象,Compose提供了mutableStateOf将一个普通变量包装为状态变量
这样当这个变量发生变化时,使用了这个变量的组件都会自动更新。
fun Counter() {
Column(horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally) {
val count = mutableStateOf(0)
Log.d(TAG, "into Counter => ${count}")
Text(text = "${count.value}")
Button(onClick = {
count.value++
Log.d(TAG, "count++ => ${count.value}")
}) {
Text(text = "increase")
}
Button(onClick = {
count.value--
Log.d(TAG, "count-- => ${count.value}")
}) {
Text(text = "decease")
}
}
}
这时点击按钮,界面依然不会更新
但是看日志确实是发生重组了,每次点按钮都会有into Counter日志,只是count的值每次都重置了
12:56:52.312 D into Counter => 0
12:56:54.825 D count++ => 1
12:56:54.829 D into Counter => 0
12:56:56.269 D count++ => 1
12:56:56.273 D into Counter => 0
12:56:57.742 D count-- => -1
12:56:57.746 D into Counter => 0
所以还要解决如何让count的值不重置的问题,这需要用到另一个方法:remember
remember的作用是对状态变量进行缓存,在后续发生重组时,不会重新初始化
val count = remember { mutableStateOf(0) }
到此就实现了点击按钮改变数字的效果
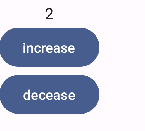
以上写法,可以进一步使用kotlin的委托写法简化
最终版本如下
@Composable
fun Counter() {
Column(horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally) {
var count by remember { mutableStateOf(0) }
Text(text = "${count}")
Button(onClick = {
count++
}) {
Text(text = "increase")
}
Button(onClick = {
count--
}) {
Text(text = "decease")
}
}
}
总结一下,Compose中的状态变量,使用remember和mutableStateOf定义
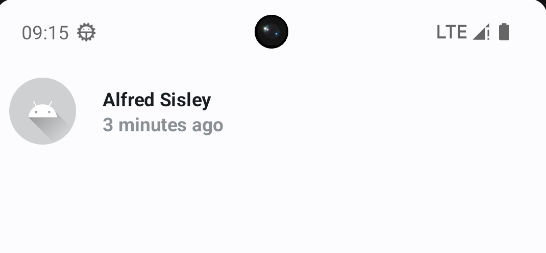
案例
- 想要将一个Image显示为圆形,一种方式是使用Surface组件包装,并设置其shape属性为CircleShape,另外也能控制大小,颜色等
- 将Column中的组件居中显示,可以使用Modifier.align(Alignment.CenterVertically)属性
- 使用CompositionLocalProvider可以修改作用域内的组件样式,实现隐式传参的效果
@Composable
fun PhotoCard() {
Row(
modifier = Modifier
.clickable {} // 点击水波纹效果
.padding(10.dp)
) {
Surface( // 包装Image,使其为圆形
modifier = Modifier.size(50.dp),
shape = CircleShape,
// 修改透明度,默认onSurface为黑色,这里设置为0.2f,显示效果为灰色
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.onSurface.copy(alpha = 0.2f)
) {
Image(
painter = painterResource(id = com.example.mycompose.R.drawable.ic_launcher_foreground),
contentDescription = null
)
}
Spacer(modifier = Modifier.padding(horizontal = 10.dp))
Column(
// 内容垂直居中显示
modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.CenterVertically),
) {
// 隐式传参
// 将范围内的文本样式修改为粗体
CompositionLocalProvider(LocalTextStyle provides MaterialTheme.typography.bodyMedium.copy(fontWeight = FontWeight.Bold)) {
Text(text = "Alfred Sisley")
// 隐式传参
// 将范围内的文本颜色修改为onSurfaceVariant,透明度为0.6
CompositionLocalProvider(LocalContentColor provides MaterialTheme.colorScheme.onSurfaceVariant.copy(alpha = 0.6f)) {
Text(
text = "3 minutes ago",
// style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodySmall
)
}
}
}
}
}
CompositionLocalProvider的实现原理,和修改全局变量类似
提供一个全局变量作为默认值
当需要修改默认值时,通过provider函数传入新的值修改全局变量,并使用try-finally在函数结束后恢复原来的值,这就实现了只在函数作用域内修改默认值,而不会影响其他地方
var color = "Red"
fun provider(value: String, content:()-> Unit) {
val oldColor = color
color = value
try {
content()
} finally {
color = oldColor
}
}
fun Text(){
println("Color is $color")
}
fun main(){
Text()
provider("Blue") {
Text()
Text()
}
Text()
}
Color is Red
Color is Blue
Color is Blue
Color is Red
基础组件
Slider
滑竿组件,可以用作进度条,音量、亮度调整等场景
@Composable
fun SliderDemo() {
var process by remember {
mutableFloatStateOf(0f)
}
Column(
modifier = Modifier.padding(vertical = 10.dp, horizontal = 20.dp)
) {
Slider(
value = process,
onValueChange = { process = it },
steps = 2 // 分段,段数为steps+1
)
Text(text = (process * 100).roundToInt().toString() + "%")
}
}

AlertDialog
一个 Material Design 风格的对话框
和传统对话框最大的区别是,需要通过状态控制显示和隐藏,而不是show,dismiss方法
@Composable
fun AlertDialogDemo(openDialog: MutableState<Boolean>){
val ctx = LocalContext.current
if (openDialog.value) { // 需要靠状态控制显示
AlertDialog(
onDismissRequest = { // 点击Dialog以外的区域
Toast.makeText(ctx, "场外不可操作", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
},
title = { // 标题
Text(
text = "开启位置服务",
fontWeight = FontWeight.W700,
style = MaterialTheme.typography.titleMedium
)
},
text = { // 正文
Text(
text = "这将意味着,我们会给您提供精准的位置服务,并且您将接受关于您订阅的位置信息",
fontSize = 16.sp
)
},
confirmButton = { // 确定
TextButton(
onClick = {
Toast.makeText(ctx, "Confirm", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
openDialog.value = false
},
) {
Text(
"确认",
fontWeight = FontWeight.W700,
style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodyMedium
)
}
},
dismissButton = { //取消
TextButton(
onClick = {
Toast.makeText(ctx, "Dismiss", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
openDialog.value = false
}
) {
Text(
"取消",
fontWeight = FontWeight.W700,
style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodyMedium
)
}
}
)
}
}

ProgressIndicator
进度条组件,分为圆形和线性两种
不设置值时,默认为无限循环
@Composable
fun ProcessDemo(){
Column {
CircularProgressIndicator() // 圆形进度条
LinearProgressIndicator() // 线性进度条
}
}

通过process属性可以控制进度条进度
这里的Button用于增加进度
@Composable
fun ProcessDemo() {
var process by remember { mutableFloatStateOf(0f) }
// 相比直接使用process,会有动画效果
val animatedProcess by animateFloatAsState(
targetValue = process,
)
Column {
CircularProgressIndicator() // 圆形进度条
LinearProgressIndicator(progress = animatedProcess) // 线性进度条
Button(onClick = {
if (process < 1f) { // 进度小于1f,则加0.1f
process += 0.1f
}
}) {
Text("Add")
}
}
}

Modifier
作用域
Compose基于kotlin的DSL,通常组件的最后一个参数为content,用于放置子组件
如Column
@Composable
inline fun Column(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
verticalArrangement: Arrangement.Vertical = Arrangement.Top,
horizontalAlignment: Alignment.Horizontal = Alignment.Start,
content: @Composable ColumnScope.() -> Unit
) {...}
并且,content会指定作用域,这里即ColumnScope,这就表示content中可以调用任何ColumnScope中的方法
@LayoutScopeMarker
@Immutable
@JvmDefaultWithCompatibility
interface ColumnScope {
@Stable
fun Modifier.weight(
weight: Float,
fill: Boolean = true
): Modifier
@Stable
fun Modifier.align(alignment: Alignment.Horizontal): Modifier
@Stable
fun Modifier.alignBy(alignmentLine: VerticalAlignmentLine): Modifier
@Stable
fun Modifier.alignBy(alignmentLineBlock: (Measured) -> Int): Modifier
}
Box也有类似的作用域:BoxScope
@Composable
inline fun Box(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
contentAlignment: Alignment = Alignment.TopStart,
propagateMinConstraints: Boolean = false,
content: @Composable BoxScope.() -> Unit
) {...}
@LayoutScopeMarker
@Immutable
interface BoxScope {
@Stable
fun Modifier.align(alignment: Alignment): Modifier
@Stable
fun Modifier.matchParentSize(): Modifier
}
可以看到BoxScope和ColumnScope中都有Modifier.align方法(参数不一样)
当在Column中嵌套使用Box时,如果需要用到Modifier.align,是不是意味着以上的两个作用域的Modifier.align都可以使用呢?
@Composable
fun ScopeDemo() {
Column(horizontalAlignment = Alignment.CenterHorizontally) {
Text("Hello1")
Text("Hello2")
Box(modifier = Modifier
.size(100.dp)
.background(Color.Cyan)) {
Text("Hello3", modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.TopStart)) // 这是BoxScope中的Modifier.align
Text("Hello4", modifier = Modifier.align(Alignment.BottomEnd))
}
}
}
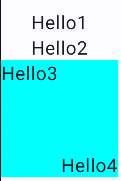
虽然IDE会同时提示两个方法,但是最终只能使用BoxScope中的Modifier.align,使用ColumnScope中的Modifier.align,IDE会报错编译不通过
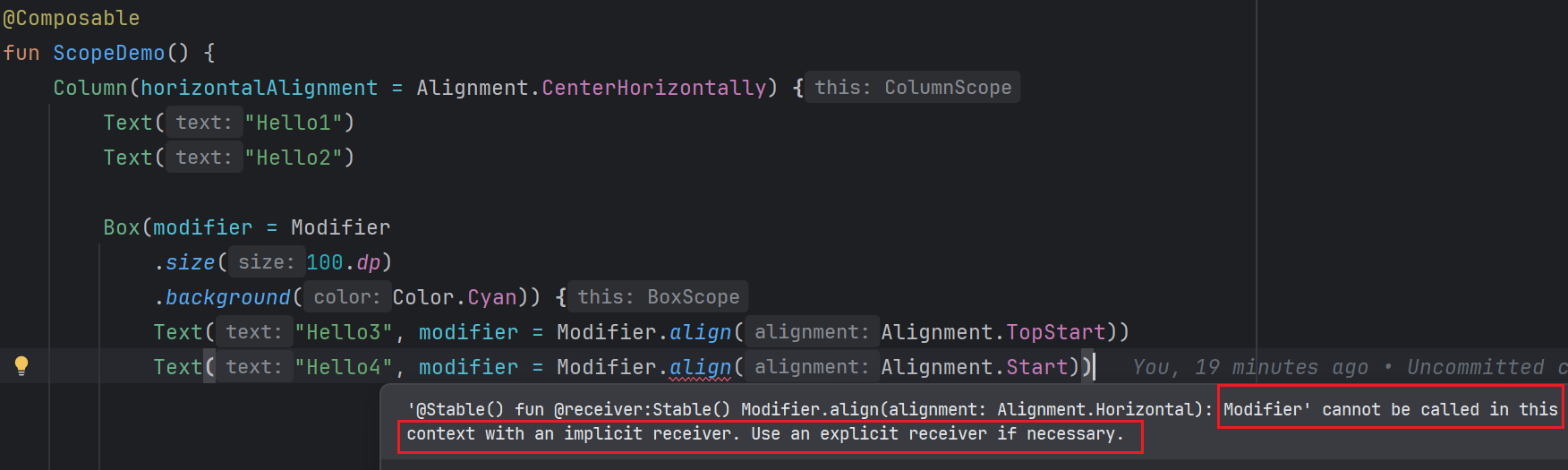
原因是ColumnScope和BoxScope都继使用@LayoutScopeMarker修饰,@LayoutScopeMarker使用了@DslMarker注解,这个注解的作用就是为了在DSL中防止跨级访问
也就是说,在Box的作用域中,只能使用BoxScope中的Modifier.align,而不能跨级访问上一级ColumnScope中的Modifier.align,这就避免了跨级访问带来的混乱,保证类型安全。
关于@DslMarker的用法,可以通过以下例子理解
@MyAnnotation
class AScope {
fun visitA(){}
}
@MyAnnotation
class Bscope {
fun visitB(){}
}
fun funA(scope: AScope.()-> Unit) {
scope(AScope())
}
fun funB(scope: Bscope.()-> Unit) {
scope(Bscope())
}
// 自定义注解,使用 @DslMarker 标记
// 之后用此注解标注的类,在作用域中不能使用其他作用域的方法
@DslMarker
@LayoutScopeMarker
annotation class MyAnnotation
fun main(){
funA {
visitA()
funB {
// visitA() 报错,不能使用上一级作用域的方法
visitB()
}
}
}
Compose组件渲染
- 组合:执行@Composable函数,生成LayoutNode
- 布局:LayoutNode执行measure、layout,确定位置和大小
- 绘制:LayoutNode执行draw,绘制内容
组合
在setContent的时候,执行代码块中所有的Composable函数体,生成LayoutNode视图树
如果Composable依赖的状态发生了变化,会触发当前Composable重新进行组合阶段,并且子Composable也会重新调用
但是子Composable不一定会重组,因为Compose有智能重组机制,只有参数变化时,才会重组,否则会复用之前的LayoutNode
所以通过重组,可以自动维护LayoutNode视图树,保持UI最新
布局
LayoutNode通过父LayoutNode的约束(constraints)进行自我测量(类似MeasureSpec),确定自身大小
可以定制组件的布局阶段实现自己的需求,比如要实现Text的Baseline到父布局顶部的距离,使用padding是无法实现的,这时可以尝试自定义布局阶段来实现
TODO Baseline图片示例
自定义布局通过Modifier.layout实现。使用layout时,传入两个回调参数,分别为measurable和constraints
- measurable:表示被测量的LayoutNode
- constraints:表示父LayoutNode的约束
定义一个Modifier的扩展函数BaselineToTop,表示Baseline到父布局顶部的距离
fun Modifier.firstBaselineToTop(firstBaselineToTop: Dp) =
Modifier.layout { measurable, constraints ->
// 测量后,可摆放,可以获取到宽高
val placeable = measurable.measure(constraints)
// 获取第一个基线
val firstBaseline = placeable.get(FirstBaseline)
// 计算在想要的firstBaselineToTop前提下,组件的y坐标
val placeableY = firstBaselineToTop.roundToPx() - firstBaseline
// 必须调用MeasureScope中的layout,否则Modifier.layout会报错
// 重新定义组件的宽高
layout(width = placeable.width, height = placeableY + placeable.height){
// 重新定义组件的x,y坐标
placeable.placeRelative(0, placeableY)
}
}
使用时可以和padding对比
Row {
Box (modifier = Modifier.background(Color.Yellow)){
Text(
text = "Hello,World",
modifier = Modifier
.firstBaselineToTop(30.dp) // Baseline到父布局顶部的距离
.background(Color.Red)
)
}
Box (modifier = Modifier.background(Color.Yellow)){
Text(
text = "Hello,World",
modifier = Modifier
.padding(top = 30.dp) // 自己顶部到父布局顶部的距离
.background(Color.Red)
)
}
}

如果要自定义布局,比如自己实现一个Column组件,需要使用Layout实现
Layout本身也是一个@Composable函数,所以可以在自定义的@Composable函数中使用
和定义Modifier扩展函数时使用的layout很类似,layout是针对普通组件使用的,而Layout是针对布局使用的,回调参数中是一个子LayoutNode的集合
@Composable
fun MyColumn(
modifier: Modifier = Modifier,
content: @Composable () -> Unit
) {
// 针对布局使用,回调参数中是一个子LayoutNode的集合
Layout(modifier = modifier, content = content) {measurableList, constraints ->
// 遍历测量子LayoutNode
val placeableList = measurableList.map {
it.measure(constraints)
}
var y = 0
// 布局的宽高取父LayoutNode约束的最大值即可
// 这里主要关注的是子LayoutNode如何摆放
layout(constraints.maxWidth,constraints.maxHeight) {
// 排放位置
placeableList.forEach {
it.placeRelative(x = 0, y = y)
// 下一个子LayoutNode的y坐标,一定是要加上当前子LayoutNode的高度,才能实现Column效果
y += it.height
}
}
}
}
在使用时可以像Column那样摆放组件,同时也能修改Modifier
Column(
modifier = Modifier.padding(innerPadding),
) {
MyColumn(modifier = Modifier.padding(10.dp)) {
Text("Hello World")
Text("Hello World")
Text("Hello World")
}
}

Compose中的每个LayoutNode是不允许被多次测量的,但有些场景确实需要,比如以下这个场景:
@Composable
fun TwoText() {
Row(
verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically,
) {
Text("Hello")
Divider(
color = Color.Black,
modifier = Modifier
.width(1.dp)
.fillMaxHeight()
)
Text(
"World",
style = LocalTextStyle.current.copy(fontSize = 30.sp)
)
}
}
Row中放了两个文本和一个分割线,如果直接指定分割线的高度为fillMaxHeight(),会占用整个屏幕高度,因为测量和布局Divider时,并不知道这个高度应该为多少,就直接用了最大值

而现在希望的是分割线高度匹配两个文本的高度(取两者中的较大值),所以需要提前测量两个文本的高度,确定Row的高度,之后在使用fillMaxHeight()时,就是想要的效果了
为了实现这个需求,要用到固有特性测量Intrinsic,它可以预先测量所有子组件,确定自身的大小,并在正式测量阶段也会产生影响
对于内置的组件,大多已经实现了固有特性测量,比如上面使用的Row,只需要使用IntrinsicSize.Min或者IntrinsicSize.Max即可
现在修改代码,给Row添加固有特性测量,确定Row的高度
@Composable
fun TwoText() {
Row(
verticalAlignment = Alignment.CenterVertically,
modifier = Modifier.height(IntrinsicSize.Min) // 添加固有特性测量
) {
Text("Hello")
Divider(
color = Color.Black,
modifier = Modifier
.width(1.dp)
.fillMaxHeight()
)
Text(
"World",
style = LocalTextStyle.current.copy(fontSize = 30.sp)
)
}
}
结果符合预期
绘制
TODO
动画
可见性动画AnimatedVisibility
通过visible属性控制content可见性,当content出现和消失时,会有过度动画效果
@Composable
fun AnimatedDemo() {
var visible by remember {
mutableStateOf(true)
}
Column {
AnimatedVisibility(
visible = visible,
// 多种动画效果可以组合使用
// 滑动进入,展开,缩放,淡入
enter = slideInVertically() + expandVertically() + scaleIn()+ fadeIn(initialAlpha = 0.3f),
exit = slideOutVertically() + shrinkVertically() + scaleOut() + fadeOut(),
) {
Text("Hello World")
}
Button(onClick = { visible = !visible }) {
Text("Change visible")
}
}
}

监听动画状态
AnimatedVisibility还有个重载的方法,可以通过MutableTransitionState监听动画状态,当当前状态和目标状态不同时,会触发动画执行
可以利用这个特性实现自动动画,如开屏动画之类
@Composable
fun AnimatedDemo() {
var visibleState = remember {
MutableTransitionState(false).apply {
targetState = true
}
}
Column {
AnimatedVisibility(
visibleState = visibleState,
// 多种动画效果可以组合使用
// 滑动进入,展开,缩放,淡入
enter = slideInVertically() + expandVertically() + scaleIn() + fadeIn(initialAlpha = 0.3f),
exit = slideOutVertically() + shrinkVertically() + scaleOut() + fadeOut(),
) {
Text("Hello World")
}
}
}

自定义Enter/Exit动画
自定义动画使用transition,会和AnimatedVisibility动画同时进行
以下添加了一个背景色变化动画,当content出现时,背景色变为红色,消失时,背景色从红色变为绿色
@OptIn(ExperimentalAnimationApi::class)
@Composable
fun AnimatedDemo() {
var visible by remember {
mutableStateOf(true)
}
Column {
AnimatedVisibility(
visible = visible,
) {
// 自定义动画
// 需要在AnimatedVisibilityScope内使用
val bg by transition.animateColor {
if (it == EnterExitState.Visible) Color.Red else Color.Green
}
Box(modifier = Modifier.background(bg)) {
Text("Hello World")
}
}
Button(onClick = { visible = !visible }) {
Text("Change visible")
}
}
}

AnimatedContent
AnimatedContent可以监听content的变化,当content变化时,会触发动画效果
需要注意的是,content中必须使用targetState,否则会报错
@OptIn(ExperimentalAnimationApi::class)
@Composable
fun AnimatedDemo() {
var counter by remember {
mutableStateOf(0)
}
Column {
AnimatedContent(
targetState = counter,
) {
Text("Hello World ${it}") // 一定要使用targetState
}
Button(onClick = {counter++ }) {
Text("Add")
}
}
}
默认的动画效果是淡入淡出,可以通过transitionSpec属性自定义动画效果
比如实现从下到上切换
@OptIn(ExperimentalAnimationApi::class)
@Composable
fun AnimatedDemo() {
var counter by remember {
mutableStateOf(0)
}
Column {
AnimatedContent(
targetState = counter,
transitionSpec = {
// 使用togetherWith组合Enter动画和Exit动画
// 进场指定初始位置,出场指定结束位置
// 这里实现的是从下到上切换的效果
slideInVertically { height -> height } + fadeIn() togetherWith
slideOutVertically { height -> -height } + fadeOut()
}
) {
Text("Hello World ${it}")
}
Button(onClick = { counter++ }) {
Text("Add")
}
}
}
类似的,也能实现从右到左切换
@OptIn(ExperimentalAnimationApi::class)
@Composable
fun AnimatedDemo() {
var counter by remember {
mutableStateOf(0)
}
Column {
AnimatedContent(
targetState = counter,
transitionSpec = {
// 这里实现的是从右到左切换的效果
slideInHorizontally { width -> width } + fadeIn() togetherWith
slideOutHorizontally { width -> -width } + fadeOut()
}
) {
Text("Hello World ${it}")
}
Button(onClick = { counter++ }) {
Text("Add")
}
}
}
使用SizeTranstion定义大小动画
当content的大小发生变化时,使用AnimatedContent也会有一个动画效果
@Composable
fun SizeTransitionDemo() {
var isExpanded by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
Surface(
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primary,
onClick = { isExpanded = !isExpanded },
shape = RoundedCornerShape(16.dp),
) {
AnimatedContent(
targetState = isExpanded,
) {
if (it) {
Text(
text = "这是一个详细的展开内容区域,当组件尺寸变化时会触发 SizeTransform 动画。\n" +
"这是一个详细的展开内容区域,当组件尺寸变化时会触发 SizeTransform 动画。\n" +
"这是一个详细的展开内容区域,当组件尺寸变化时会触发 SizeTransform 动画。\n" +
"这是一个详细的展开内容区域,当组件尺寸变化时会触发 SizeTransform 动画。\n" +
"这是一个详细的展开内容区域,当组件尺寸变化时会触发 SizeTransform 动画。\n",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodyMedium,
modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp)
)
} else {
Text(
text = "点击展开/收缩",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.headlineSmall,
modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp)
)
}
}
}
}
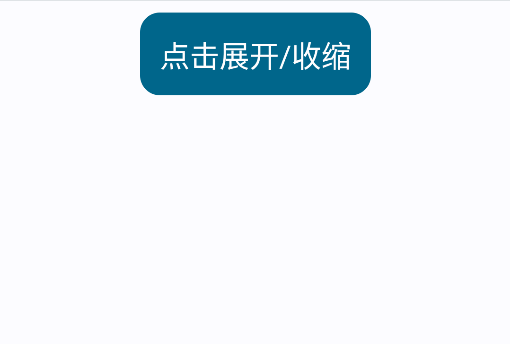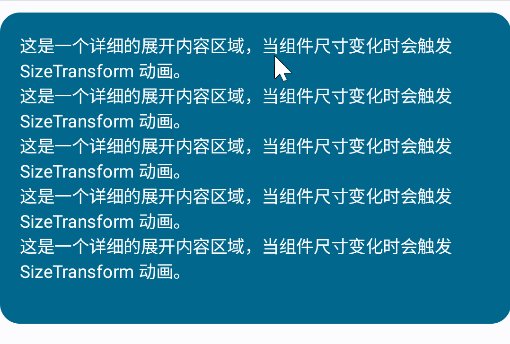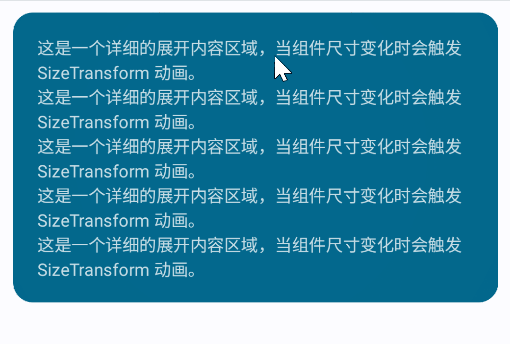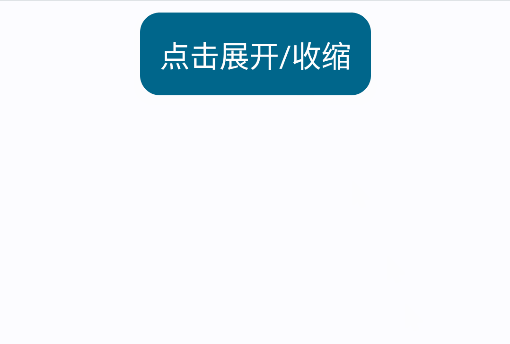
但有时候我们希望自定义大小变化动画,这时可以使用SizeTransition
@Composable
fun SizeTransitionDemo() {
var isExpanded by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
Surface(
color = MaterialTheme.colorScheme.primary,
onClick = { isExpanded = !isExpanded },
shape = RoundedCornerShape(16.dp),
) {
AnimatedContent(
targetState = isExpanded,
transitionSpec = {
fadeIn() togetherWith fadeOut() using
SizeTransform { initSize, targetSize ->
if (targetState) { // 展开时
// 关键帧,指定在某一个时间点的尺寸
// 持续时间为300ms
// 在150ms之前,高度保持不变,宽度逐渐变大
// 等宽度达到目标值时,高度再逐渐变大
keyframes {
IntSize(
targetSize.width,
initSize.height
) at 150
durationMillis = 300
}
} else {
// 同理
keyframes {
IntSize(
initSize.width,
targetSize.height
) at 150
durationMillis = 300
}
}
}
}
) {
if (it) {
Text(
text = "这是一个详细的展开内容区域,当组件尺寸变化时会触发 SizeTransform 动画。\n" +
"这是一个详细的展开内容区域,当组件尺寸变化时会触发 SizeTransform 动画。\n" +
"这是一个详细的展开内容区域,当组件尺寸变化时会触发 SizeTransform 动画。\n" +
"这是一个详细的展开内容区域,当组件尺寸变化时会触发 SizeTransform 动画。\n" +
"这是一个详细的展开内容区域,当组件尺寸变化时会触发 SizeTransform 动画。\n",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.bodyMedium,
modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp)
)
} else {
Text(
text = "点击展开/收缩",
style = MaterialTheme.typography.headlineSmall,
modifier = Modifier.padding(16.dp)
)
}
}
}
}
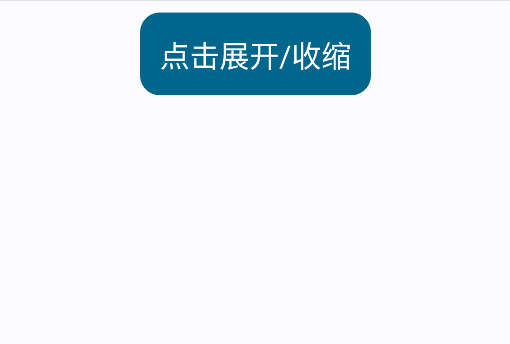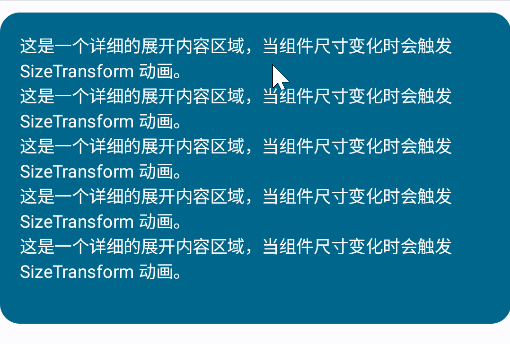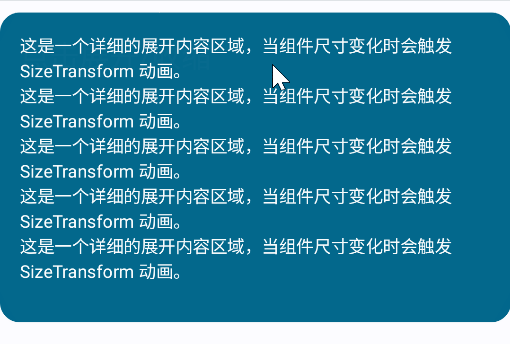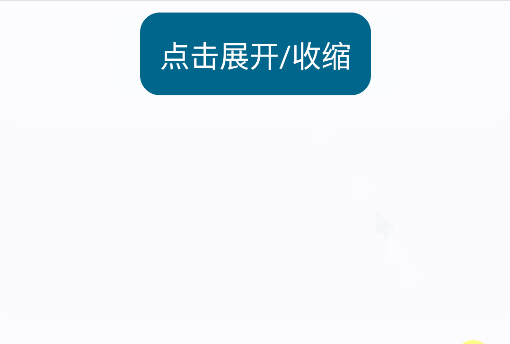
内容大小动画Modifier.animateContentSize
animateContentSize 是一个 Modifier方法,用于在组件内容尺寸变化时自动触发动画,开箱即用。在本文的MessageCardList中已经使用过它。
animateAsState
animateAsState 可以自动完成从当前值到目标值的过度计算,以animateColorAsState为例,targetValue表示目标值,animationSpec定义动画效果
@Composable
fun ColorAnimationDemo() {
var isGreenTheme by remember { mutableStateOf(true) }
val backgroundColor by animateColorAsState(
targetValue = if (isGreenTheme) {
Color.Green
} else {
Color.Red
},
animationSpec = tween(
durationMillis = 1000, // 动画时长 1 秒
easing = FastOutSlowInEasing // 快速开始缓慢结束的效果
),
label = "background_color_animation"
)
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.background(backgroundColor)
) {
Button(
onClick = { isGreenTheme = !isGreenTheme },
modifier = Modifier
.align(Alignment.Center)
.padding(16.dp)
) {
Text(
text = if (isGreenTheme) "切换红色主题" else "切换绿色主题",
color = Color.White
)
}
}
}
多值动画Transition
animate*AsState 只能同时处理一个值,如果需要同时处理多个值,可以使用 updateTransition 函数,它接受一个踏入targetState,返回一个 Transition 对象,当targetState发生变化时,将执行其所有的子动画
Transition可以通过animateXXX添加子动画
例如,实现一个可以点击展开和收缩的卡片,在展开/收缩的时候,卡片的高度,颜色和卡片文字的左边距都会随之变化,并且带有过度动画效果
@Composable
fun ExpandableCard() {
var expanded by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
// 过渡动画控制器
val transition = updateTransition(targetState = expanded, label = "expandTransition")
// 高度变化动画
val cardHeight by transition.animateDp(
transitionSpec = {
if (targetState) {
spring(stiffness = Spring.StiffnessLow) // 弹性动画
} else {
tween(durationMillis = 1000) // 持续时间为1000ms
}
}, label = "heightAnimation"
) { isExpanded ->
if (isExpanded) 200.dp else 80.dp
}
// 颜色变化动画
val cardColor by transition.animateColor(
transitionSpec = { tween(800) },
label = "colorAnimation"
) { isExpanded ->
if (isExpanded) Color(0xFFB39DDB) else Color(0xFFFFAB91)
}
// 文字间距变化动画
val textPadding by transition.animateDp(
transitionSpec = {
if (targetState) {
spring(stiffness = Spring.StiffnessLow) // 弹性动画
} else {
tween(durationMillis = 1000) // 持续时间为1000ms
}
},
label = "paddingAnimation"
) { isExpanded ->
if (isExpanded) 100.dp else 10.dp
}
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(16.dp)
) {
Card(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.height(cardHeight) // 使用带有动画的高度
.clickable { expanded = !expanded },
colors = CardDefaults.cardColors(containerColor = cardColor), // 使用带有动画的颜色
shape = RoundedCornerShape(16.dp)
) {
Text(
text = if (expanded) "点击收起" else "点击展开",
modifier = Modifier.padding(start = textPadding), // 使用带有动画的文字间距
style = MaterialTheme.typography.headlineSmall
)
}
}
}

重复动画
通过rememberInfiniteTransition获取重复动画控制器,然后通过animateXXX添加子动画
重复动画会无限循环,通常需要指定两个值:initialValue和targetValue,分别表示初始值和目标值,当动画从初始值执行到目标值时,再根据设置的循环模式(RepeatMode)决定是回到初始值重复还是反过来执行
可以通过animationSpec参数设置动画效果
@Composable
fun InfiniteLoadingAnimation() {
// 创建无限动画控制器
val infiniteTransition = rememberInfiniteTransition(label = "infiniteLoader")
// 无限动画会有两个值(initialValue,targetValue),在这两个值之间循环
// 定义旋转动画(0°-360°无限循环)
val rotation by infiniteTransition.animateFloat(
initialValue = 0f,
targetValue = 360f,
animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable( // 无限循环的动画效果
animation = tween(1500, easing = LinearEasing), // 1500ms内,线性(匀速)转动
repeatMode = RepeatMode.Restart // 重复模式,Restart:从初始值开始
),
label = "rotationAnimation"
)
// 定义透明度动画(脉冲效果)
val alpha by infiniteTransition.animateFloat(
initialValue = 0.3f,
targetValue = 1f,
animationSpec = infiniteRepeatable(
// 关键帧,定义一个时间点内的动画效果
animation = keyframes {
durationMillis = 1000 // 一次动画时间为1s
0f at 0 // 0s为0f
1f at 1000 // 1s为1f
// 即0-1s内由0f变为1f,后续设置重复模式为Reverse,表示1-2s内由1f变为0f
// 这就实现了一个均匀消失和出现的动画效果
},
repeatMode = RepeatMode.Reverse // 重复模式,Reverse:反过来
),
label = "alphaAnimation"
)
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.background(Color.Black.copy(alpha = 0.7f)),
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center
) {
// 旋转的外圈
CircularProgressIndicator(
modifier = Modifier
.size(64.dp)
.rotate(rotation) // 带有动画的旋转
.alpha(alpha), // 带有动画的透明度
color = Color.Green,
strokeWidth = 4.dp // 宽度
)
// 中心脉冲圆点
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(16.dp)
.alpha(alpha) // 带有动画的透明度
.background(
color = Color.Green,
shape = CircleShape
)
)
}
}

手势
点击
简单的点击手势,通过Modifier.clickable实现
可以通过pointerInput实现监听更复杂的点击手势,例如长按、双击等
@Composable
fun PointerInputExample() {
// 记录点击次数
var tapCount by remember { mutableIntStateOf(0) }
// 记录点击事件
var str by remember { mutableStateOf("") }
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.size(100.dp)
.background(Color.LightGray)
.clickable{}
.pointerInput(Unit) { // 使用 Unit 表示不依赖任何 key,只初始化一次
detectTapGestures(
onPress = {
// 按下还没抬起
str = "按下"
},
onDoubleTap = {
// 双击事件
tapCount += 2
str = "双击"
},
onTap = {
// 单击事件
tapCount += 1
str = "单击"
},
onLongPress = {
// 长按事件
str = "长按"
}
)
},
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center,
) {
Text(
text = "Taps: $tapCount\n$str",
color = Color.Red
)
}
}

滑动
滑动用于显示列表场景,普通的Cloumn可以显示一个列表,但是默认情况下,列表无法滑动,需要通过Modifier.verticalScroll实现
@Composable
fun ScrollExample() {
// 滚动状态
val scrollState = rememberScrollState()
// 协程作用域
val scope = rememberCoroutineScope()
Column(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxSize()
.padding(16.dp)
) {
// 控制滚动的按钮
Row(
modifier = Modifier
.fillMaxWidth()
.padding(bottom = 16.dp),
horizontalArrangement = Arrangement.SpaceBetween // 两端对齐
) {
Button(onClick = {
// 滚动到顶部
scope.launch {
scrollState.animateScrollTo(0)
}
}) {
Text("Scroll to Top")
}
Button(onClick = {
// 滚动到底部
scope.launch {
scrollState.animateScrollTo(scrollState.maxValue)
}
}) {
Text("Scroll to Bottom")
}
}
// 可滚动内容区域
Column(
modifier = Modifier
// 普通的Column可以通过添加滚动状态来实现滚动能力
.verticalScroll(scrollState) // 绑定滚动状态
.border(1.dp, Color.Gray)
.padding(8.dp)
) {
// 生成 50 个文本项作为滚动内容
repeat(50) { index ->
Text(
text = "Item $index",
modifier = Modifier
.padding(8.dp)
.fillMaxWidth(),
fontSize = 18.sp
)
Divider(color = Color.LightGray, thickness = 1.dp)
}
}
}
}
拖动
拖动通过Modifier.draggable实现,本质上是通过获取拖动的偏移量,然后改变组件自身的偏移量
注意使用Modifier.draggable有局限性,只能在水平或垂直方向上拖动,不能随意拖动
@Composable
fun DraggableExample() {
// 记录水平和垂直偏移量
var horizontalOffset by remember { mutableFloatStateOf(0f) }
var verticalOffset by remember { mutableFloatStateOf(0f) }
var isDragging by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
// 可拖动方块
Box(
modifier = Modifier
// 拖动的本质就是改变偏移量
.offset {
IntOffset(horizontalOffset.roundToInt(), verticalOffset.roundToInt())
}
.size(100.dp)
.background(Color.Red)
.draggable( // x轴拖动
orientation = Orientation.Horizontal,
state = rememberDraggableState { delta ->
horizontalOffset += delta
}
)
.draggable( // y轴拖动
orientation = Orientation.Vertical,
state = rememberDraggableState { delta ->
verticalOffset += delta
}
),
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center,
) {
// 显示坐标信息
Text(
text = "X: ${horizontalOffset.roundToInt()}px\nY: ${verticalOffset.roundToInt()}px",
color = Color.White
)
}
}

如果需要实现任意方向的拖动,需要使用Modifier.pointerInput,配合detectDragGestures实现
@Composable
fun DraggableExample() {
// 记录水平和垂直偏移量
var horizontalOffset by remember { mutableFloatStateOf(0f) }
var verticalOffset by remember { mutableFloatStateOf(0f) }
// 记录是否正在拖动,给个颜色变化
var isDragging by remember { mutableStateOf(false) }
// 可拖动方块
Box(
modifier = Modifier
// 拖动的本质就是改变偏移量
.offset {
IntOffset(horizontalOffset.roundToInt(), verticalOffset.roundToInt())
}
.size(100.dp)
.background(if (isDragging) Color.Red else Color.Green)
.background(Color.Red)
// .draggable(
// orientation = Orientation.Horizontal,
// state = rememberDraggableState { delta ->
// horizontalOffset += delta
// }
// )
// .draggable(
// orientation = Orientation.Vertical,
// state = rememberDraggableState { delta ->
// verticalOffset += delta
// }
// ),
.pointerInput(Unit) {
detectDragGestures( // 监听拖动事件
onDragStart = { isDragging = true },
onDragEnd = { isDragging = false },
onDragCancel = {},
onDrag = { change, offset ->
horizontalOffset += offset.x
verticalOffset += offset.y
change.consume() // 表示消费了事件
}
)
},
contentAlignment = Alignment.Center,
) {
// 显示坐标信息
Text(
text = "X: ${horizontalOffset.roundToInt()}px\nY: ${verticalOffset.roundToInt()}px",
color = Color.White
)
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号