三种方式
- 显示指定类型
- 参数模板化
- 整体模板化
实例:
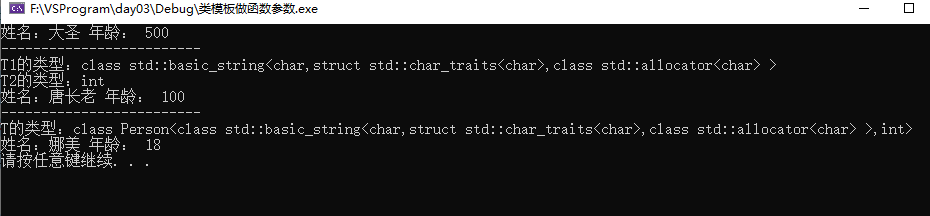
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; //类模板 template<class NameT, class AgeT> //类模板可以有默认类型 class Person { public: Person(NameT name, AgeT age) { this->m_Name = name; this->m_Age = age; } void showPerson() { cout << "姓名:" << this->m_Name << " 年龄: " << this->m_Age << endl; } NameT m_Name; AgeT m_Age; }; //1.指定传入的类型 void doWork(Person<string, int>& p) { p.showPerson(); } void test01() { Person<string, int> p("大圣", 500); doWork(p); } //2.参数模板化 template<class T1, class T2> void doWork2(Person<T1, T2>& p) { //查看传入的参数类型 cout << "T1的类型:" << typeid(T1).name() << endl; cout << "T2的类型:" << typeid(T2).name() << endl; p.showPerson(); } void test02() { Person<string, int> p("唐长老", 100); doWork2(p); } //3.整体模板化 template<class T> void doWork3(T& p) { cout << "T的类型:" << typeid(T).name() << endl; p.showPerson(); } void test03() { Person<string, int> p("娜美", 18); doWork3(p); } int main() { test01(); cout << "-------------------------" << endl; test02(); cout << "-------------------------" << endl; test03(); system("Pause"); return 0; }
结果:


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号