sas宏(2),运行中创建宏与使用宏,多个宏触发器的引用规则、proc sql创建宏, scl中宏处理(暂缺)
1:在程序运行中进行宏定义
CALL routines that enable you to transfer information between an executing DATA step and the macro processor.
You can use the SYMPUT routine to create a macro variable and to assign to that variable any value that is available in the DATA step.

When you use the SYMPUT routine to create a macro variable in a DATA step, the macro variable is not actually created and assigned a value until the DATA step is executed.
options symbolgen pagesize=30; %let crsnum=3; data revenue; set sasuser.all end=final; where course_number=&crsnum; total+1; if paid='Y' then paidup+1; if final then do; if paidup<total then do; call symput('foot','Some Fees Are Unpaid'); /*symput函数能达到运行时给宏赋值的效果*/ /*%let foot=Some Fees Are Unpaid; */ /*使用let不能达到想要的效果,let会被宏处理器先执行,优先于data步*/ end; else do; call symput('foot','All Students Have Paid'); /*%let foot=All Students Have Paid;*/ end; end; run;
symput函数里面的参数为表达式的情况
里面引用的函数不需要使用%这种宏函数的记号
trim去右尾 left去左尾
call symput('numpaid',trim(left(paidup)));
默认去双尾空白,其他效果和symput一样
随后一个参数表示宏储存的位置'L'=local 'G'=global
The SYMPUT routine and the SYMPUTX routine can only create a local macro variable if a local symbol table already exists. If no local symbol table exists when the SYMPUT routine or SYMPUTX routine executes, it will create a global macro variable.
依据变量名建立宏
data _null_; set sasuser.courses; call symput(course_code, trim(course_title));/*每一个observation中的两个变量分别对于宏值与宏变量*/ run; %put _user_;
多个宏触发器的扫描规则
宏处理器将两个&当做一个看待,所以第一次扫描&&&lv2被处理成&(&lv2)->&lv1,第二次扫描就得出res,先将重复的两个变成1个,然后记住扫描的位置,继续扫面后面的。
而&&lv2第一次扫描被处理成&lv2,结果依然为lv1
The Forward Re-Scan Rule
1:When multiple ampersands or percent signs precede a name token, the macroprocessor resolves two ampersands (&&) to one ampersand (&), and re-scans thereference.
2: To re-scan a reference, the macro processor scans and resolves tokens from left to right from the point where multiple ampersands or percent signs are coded, untilno more triggers can be resolved.
/*想要用lv2来得到res*/
data _null_; %let lv1 = res; %let lv2 = lv1; %put &lv2; /*一个红触发器无须解释,结果为lv1*/ %put &&lv2; /*这个看上去有理,但是得出的结果还是lv1*/ %put &&&lv2;/*这个得出的结果为res*/ run;
2:在程序运行中进行宏值得获取
在程序中进行宏值得获取用&是不行的,这个是在编译前就被执行的语句。

data teachers; set sasuser.register; length Teacher $ 20; teacher=symget('teach'||left(course_number)); run;
3:利用proc sql创建宏
This form of the INTO clause does not trim leading or trailing blanks
当时let创建的宏会去掉空白
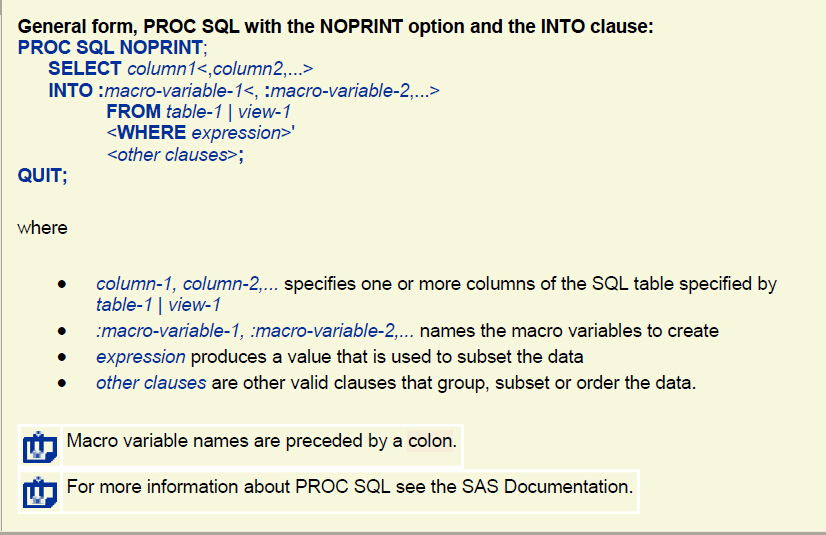
/*在行数未知的情况下创建多个宏变量,*/
proc sql noprint; select count(*) into :numrows from sasuser.schedule where year(begin_date)=2002; %let numrows=&numrows; /*消除首尾空白*/ %put There are &numrows courses in 2002; select course_code, location, begin_date format=mmddyy10. into :crsid1-:crsid&numrows, :place1-:place&numrows, :date1-:date&numrows from sasuser.schedule where year(begin_date)=2002 order by begin_date; %put _user_; quit;
crsid1-crsid3 are assigned values of the data set variable Course_code from each of the first three rows,他们分别对应数据集的前三行的观测的值
如果规定的group数大于实际的数量,那么按照实际多少个来创建宏
create one macro variable that will hold all values of a certain data set variable.

proc sql noprint; select distinct location into :sites separated by ' ' from sasuser.schedule; quit;
Global Symbol Table(符号表中,宏与宏值)
Sites Boston Dallas Seattle
Proc sql中不会进行自动的数据类型转换。对于你想要使用的数据类型要进行手动转换

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号