题目集4-6的总结性Blog
一、前言
这三次题目较前三次来说难度增大了许多,在做题目的过程中,我遇到了许多问题,
解决过程中学到了很多,也有一些问题到最后也没有解决,还需不断学习。
尤其第四次作业时,第一次运用新学的知识继承、多态等,十分不熟练,导致了成绩也不够理想。
二、设计与分析
①题目集4(7-2)、题目集5(7-4)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较
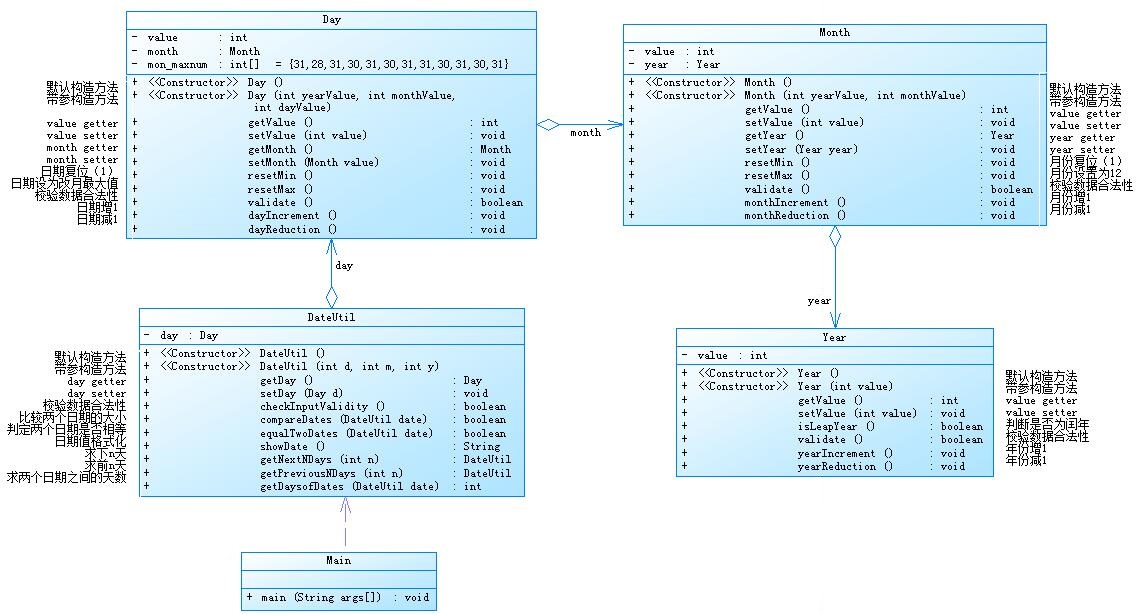
题目集4 7-2日期问题面向对象设计(聚合一)
参考题目7-2的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1900,2050] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
![]()
应用程序共测试三个功能:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
输入格式:
有三种输入方式(以输入的第一个数字划分[1,3]):
- 1 year month day n //测试输入日期的下n天
- 2 year month day n //测试输入日期的前n天
- 3 year1 month1 day1 year2 month2 day2 //测试两个日期之间相差的天数
输出格式:
- 当输入有误时,输出格式如下:
Wrong Format - 当第一个数字为1且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year-month-day - 当第一个数字为2且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year-month-day - 当第一个数字为3且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
天数值
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 2014 2 14 2020 6 14结尾无空行
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
2312结尾无空行
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 1935 2 17 125340结尾无空行
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1591-12-17结尾无空行
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 1999 3 28 6543结尾无空行
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
2017-2-24结尾无空行
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0 2000 5 12 30结尾无空行
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Formatimport java.util.Scanner; class DateUtil { private int y = 0, m = 0, d = 0; Year year = new Year(); Month month = new Month(); Day day = new Day(); // 默认构造方法 public DateUtil() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } // 带参构造方法 public DateUtil(int d, int m, int y) { this.d = d; this.m = m; this.y = y; day.setValue(d); month.setValue(m); year.setValue(y); day.setMonth(month); month.setYear(year); } public int getYear() { return y; } public void setYear(int y) { this.y = y; } public int getMonth() { return m; } public void setMonth(int m) { this.m = m; } public int getDay() { return d; } public void setDay(int d) { this.d = d; } // 校验数据合法性 public boolean checkInputValidity() { if(year.validate() && month.validate() && day.validate()) { return true; } return false; } // 比较两个日期的大小 public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date) { if(this.y > date.y) { return true; } if(this.y == date.y) { if(this.m > date.m) { return true; } if(this.m == date.m) { if(this.d >= date.d) { return true; } } } return false; } // 判定两个日期是否相等 public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date) { return false; } // 日期值格式化 public String showDate() { return year.getValue()+"-"+month.getValue()+"-"+day.getValue(); } // 求下n天 public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n) { for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { day.dayIncrement(); if(!day.validate()) { day.resetMin(); month.monthIncrement(); if(!month.validate()) { month.resetMin(); year.setValue(y+1); } } } return new DateUtil(day.getValue(), month.getValue(), year.getValue()); } // 求前n天 public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n) { int d = day.getValue(); int m = month.getValue(); int y = year.getValue(); for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) { d--; while(d<1) { m--; if(m<1) { m=12; y--; } d += day.getMon_maxnum(month.getValue()-1); if(m==2 && (y % 4 == 0 && y % 100 != 0) || (y % 400 == 0)) { d += 1; } } } return new DateUtil(d, m, y); } // 求两个日期之间的天数 public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date) { int[] mon_month= {0,31,59,90,120,151,181,212,243,273,304,334}; DateUtil date1 = new DateUtil(); DateUtil date2 = new DateUtil(); if(this.compareDates(date)) { date1 = date; date2 = this; } else { date1 = this; date2 = date; } int sum = 0; //记录相差天数 int lynum = 0; //闰年的数量 for(int i = date1.getYear(); i<date2.getYear(); i++) { if((i % 4 == 0 && i % 100 != 0) || (i % 400 == 0)) { lynum++; } } sum = 365*(date2.getYear() - date1.getYear()) + lynum; int sum1 = mon_month[date1.getMonth()-1]+date1.getDay()+(date1.getMonth()>2 && date1.year.isLeapYear()?1:0); int sum2 = mon_month[date2.getMonth()-1]+date2.getDay()+(date2.getMonth()>2 && date2.year.isLeapYear()?1:0); return (sum - sum1 + sum2); } } class Year { private int value = 0; // 默认构造方法 public Year() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } // 带参构造方法 public Year(int value) { this.value = value; } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } // 判断是否为闰年 public boolean isLeapYear() { if ((value % 4 == 0 && value % 100 != 0) || (value % 400 == 0)) { return true; } return false; } // 校验数据合法性 public boolean validate() { if (value >= 1900 && value <= 2050) { return true; } return false; } // 年份增1 public void yearIncrement() { this.value++; } // 年份减1 public void yearReduction() { this.value--; } } class Month { private int value = 0; private Year year; // 默认构造函数 public Month() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } // 带参构造函数 public Month(int yearValue, int monthValue) { } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public Year getYear() { return year; } public void setYear(Year year) { this.year = year; } // 月份设置为1 public void resetMin() { value = 1; } // 月份设置为12 public void resetMax() { value = 12; } // 校验数据合法性 public boolean validate() { if (value >= 1 && value <= 12) { return true; } return false; } // 月份增1 public void monthIncrement() { this.value++; } // 月份减1 public void monthReduction() { this.value--; } } class Day { private int value = 0; private Month month = new Month(); private int[] mon_maxnum = { 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 }; public int getMon_maxnum(int n) { return mon_maxnum[n]; } public void setMon_maxnum(int[] mon_maxnum) { this.mon_maxnum = mon_maxnum; } // 默认构造方法 public Day() { super(); // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } // 带参构造方法 public Day(int yearValue, int monthValue, int dayValue) { } public int getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(int value) { this.value = value; } public Month getMonth() { return month; } public void setMonth(Month value) { this.month = value; } // 日期设置为1 public void resetMin() { value = 1; } // 日期设置为最大 public void resetMax() { value = mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]; } // 校验数据合法性 public boolean validate() { if(value>=1 && value<=mon_maxnum[month.getValue()-1]) { return true; } return false; } // 日期增1 public void dayIncrement() { this.value++; } // 日期减1 public void dayReduction() { this.value--; } } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int year = 0, month = 0, day = 0, choice = 0; Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); choice = in.nextInt(); year = in.nextInt(); month = in.nextInt(); day = in.nextInt(); DateUtil date = new DateUtil(day, month, year); if(!date.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } switch (choice) { case 1:/* 输出日期的后n天 */ System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(in.nextInt()).showDate()); break; case 2:/* 输出日期的前n天 */ System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(in.nextInt()).showDate()); break; case 3:/* 两个日期之间相差的天数 */ int toYear = in.nextInt(); int toMonth = in.nextInt(); int toDay = in.nextInt(); DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(toDay, toMonth, toYear); if(!toDate.checkInputValidity()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); System.exit(0); } System.out.println(date.getDaysofDates(toDate)); break; default: System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } }
结构分析:
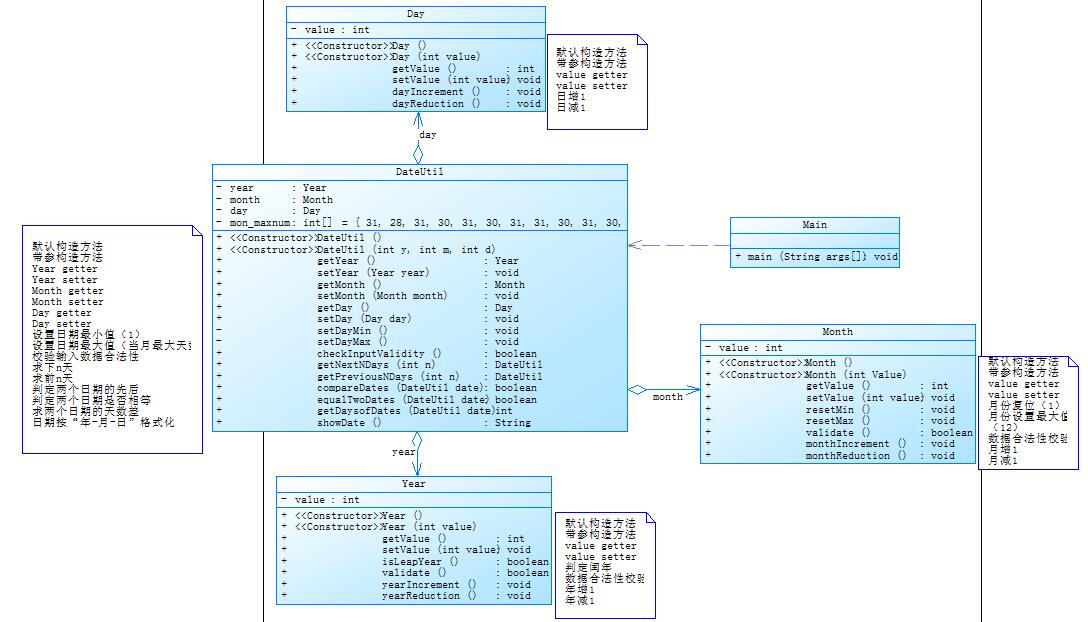
7-5 日期问题面向对象设计(聚合二) (40 分)
参考题目7-3的要求,设计如下几个类:DateUtil、Year、Month、Day,其中年、月、日的取值范围依然为:year∈[1820,2020] ,month∈[1,12] ,day∈[1,31] , 设计类图如下:
应用程序共测试三个功能:
- 求下n天
- 求前n天
- 求两个日期相差的天数
注意:严禁使用Java中提供的任何与日期相关的类与方法,并提交完整源码,包括主类及方法(已提供,不需修改)
输入格式:
有三种输入方式(以输入的第一个数字划分[1,3]):
- 1 year month day n //测试输入日期的下n天
- 2 year month day n //测试输入日期的前n天
- 3 year1 month1 day1 year2 month2 day2 //测试两个日期之间相差的天数
输出格式:
- 当输入有误时,输出格式如下:
Wrong Format - 当第一个数字为1且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year1-month1-day1 next n days is:year2-month2-day2 - 当第一个数字为2且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
year1-month1-day1 previous n days is:year2-month2-day2 - 当第一个数字为3且输入均有效,输出格式如下:
The days between year1-month1-day1 and year2-month2-day2 are:值
输入样例1:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
3 2014 2 14 2020 6 14结尾无空行
输出样例1:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
The days between 2014-2-14 and 2020-6-14 are:2312结尾无空行
输入样例2:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
2 1834 2 17 7821结尾无空行
输出样例2:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1834-2-17 previous 7821 days is:1812-9-19结尾无空行
输入样例3:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1 1999 3 28 6543结尾无空行
输出样例3:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
1999-3-28 next 6543 days is:2017-2-24结尾无空行
输入样例4:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
0 2000 5 12 30结尾无空行
输出样例4:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
Wrong Format



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号