题目集1~3的总结性Blog
一、前言
前三次题目集整体难度中等,题量也不大。尤其题目集1的大部分题目,几乎第一次提交就通过所有测试点;题目二对我来说有一定的难度,很多测试点不能通过,所以我花费了大量的时间提交测试,虽然最终通过,但多次修改导致代码复杂性高,可读性不高;题目三虽然只有三道题,但我只能写出算法,多次修改到最后也没有通过测试点,找不出问题所在。
二、设计与分析
题目集1
7-8 判断三角形类型
输入三角形三条边,判断该三角形为什么类型的三角形。
输入格式:
在一行中输入三角形的三条边的值(实型数),可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔,其中三条边的取值范围均为[1,200]。
输出格式:
(1)如果输入数据非法,则输出“Wrong Format”;(2)如果输入数据合法,但三条边不能构成三角形,则输出“Not a triangle”;(3)如果输入数据合法且能够成等边三角形,则输出“Equilateral triangle”;(4)如果输入数据合法且能够成等腰直角三角形,则输出“Isosceles right-angled triangle”;(5)如果输入数据合法且能够成等腰三角形,则输出“Isosceles triangle”;(6)如果输入数据合法且能够成直角三角形,则输出“Right-angled triangle”;(7)如果输入数据合法且能够成一般三角形,则输出“General triangle”。
源代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); double a = in.nextDouble(); double b = in.nextDouble(); double c = in.nextDouble(); if(a<1||b<1||c<1||a>200||b>200||c>200) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else if(a+b<=c||a+c<=b||b+c<=a) { System.out.println("Not a triangle"); } else if(a==b&&b==c) { System.out.println("Equilateral triangle"); } else if(((a*a + b*b - c*c)<0.1||(a*a + c*c - b*b)<0.1|| (b*b + c*c - a*a)<0.1)&&(a==b||b==c||c==a)){ System.out.println("Isosceles right-angled triangle"); } else if(a==b||b==c||c==a) { System.out.println("Isosceles triangle"); } else if(a*a + b*b == c*c||a*a + c*c == b*b|| b*b + c*c == a*a) { System.out.println("Right-angled triangle"); } else { System.out.println("General triangle"); } } }
SourceMonitor的生成报表内容如下:
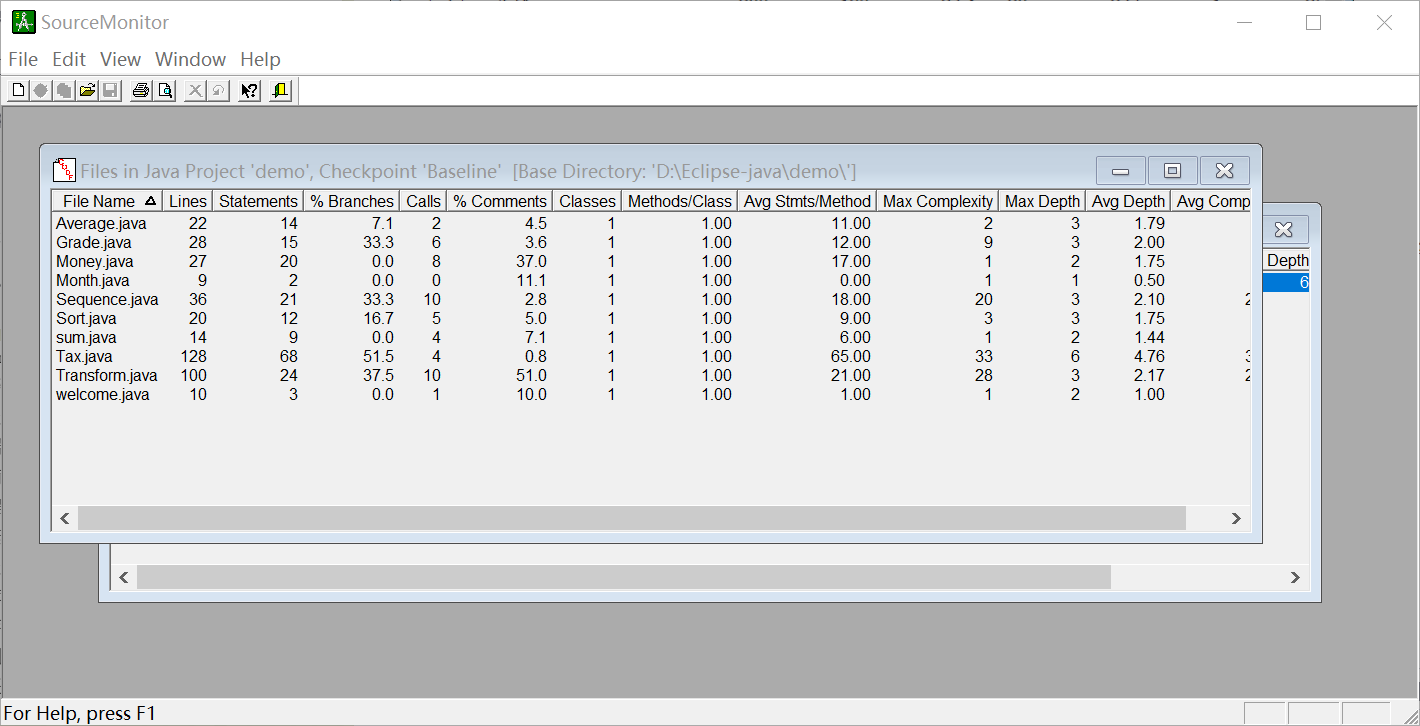
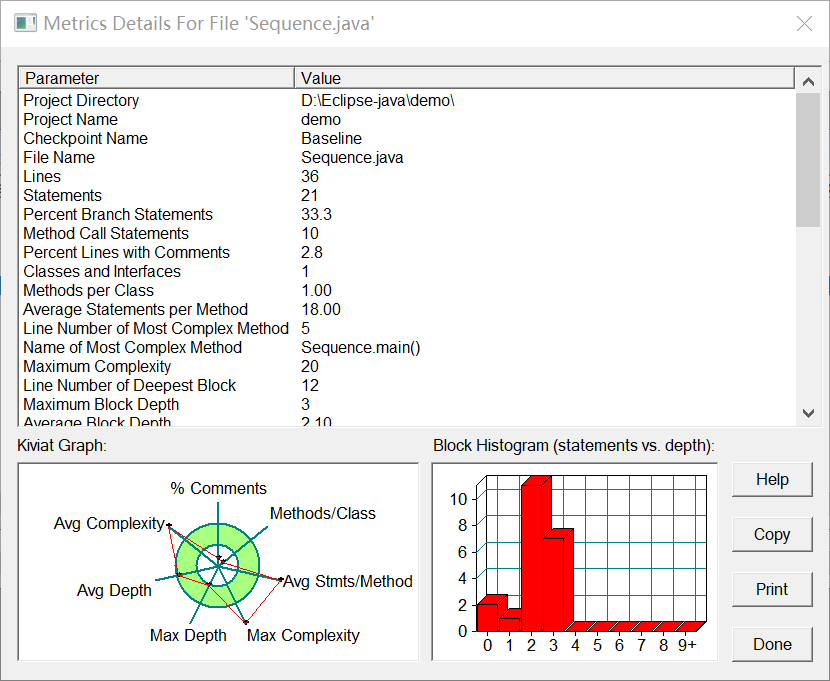
题目集2
7-4 求下一天 (30 分)
输入年月日的值(均为整型数),输出该日期的下一天。 其中:年份的合法取值范围为[1820,2020] ,月份合法取值范围为[1,12] ,日期合法取值范围为[1,31] 。 注意:不允许使用Java中和日期相关的类和方法。
要求:Main类中必须含有如下方法,签名如下:
public static void main(String[] args);//主方法
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) ;//判断year是否为闰年,返回boolean类型
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day);//判断输入日期是否合法,返回布尔值
public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) ; //求输入日期的下一天
输入格式:
在一行内输入年月日的值,均为整型数,可以用一到多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
当输入数据非法及输入日期不存在时,输出“Wrong Format”;
当输入日期合法,输出下一天,格式如下:Next date is:年-月-日
源代码:
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int year = in.nextInt(); int month = in.nextInt(); int day = in.nextInt(); boolean m = new String() != null; boolean n = new String() != null; m = isLeapYear(year); n = checkInputValidity( year, month, day); if((m==true&&(month==2&&day>29))||(m==false&&(month==2&&day>28))|| (month == 4 && day == 31) || (month == 6 && day ==31)|| (month == 9&& day == 31)||(month == 11 && day ==31)) { System.out.println ("Wrong Format"); } else if (n==false) { System.out.println ("Wrong Format"); } else { nextDate( year, month,day); } } public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) { int flag=-1; if(year%4==0||(year%4==0&&year%400==0)) { flag=1; } else if(year%4!=0||(year%4==0&&year%400!=0)) { flag=0; } if(flag==1) { return true; } else { return false; } } public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day) { int flag; if(year <1820 || year > 2020 || month < 1 || month > 12 || day < 1 || day > 31) { return false; } else { return true; } } public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) { boolean m = new String() != null; if(year%4==0||(year%4==0&&year%400==0)) { m = true; } else if(year%4!=0||(year%4==0&&year%400!=0)) { m = false; } if((m==true&&(month==2&&day>29))||(m==false&&(month==2&&day>28))|| (month == 4 && day == 31) || (month == 6 && day ==31)|| (month == 9&& day == 31)||(month == 11 && day ==31)) { System.out.println ("Wrong Format"); } else { String week = new String(); int f,Year = 0 ,Month = 0,Day = 0; if((m==true&&(month==2&&day==29))||(m==false&&(month==2&&day==28))|| ((month == 4||month==6||month==9||month==11) && day == 30)) { Month = month+1; Day = 1; Year = year; } else if (month == 12&&day==31) { Month = 1; Day = 1; Year = year + 1; } else if((month==1||month==3||month==5||month==7||month==8||month==10)&&day==31) { Month = month+1; Day = 1; Year = year; } else { Day = day+1; Year = year; Month = month; } System.out.println("Next date is:"+Year+"-"+Month+"-"+Day); } } }
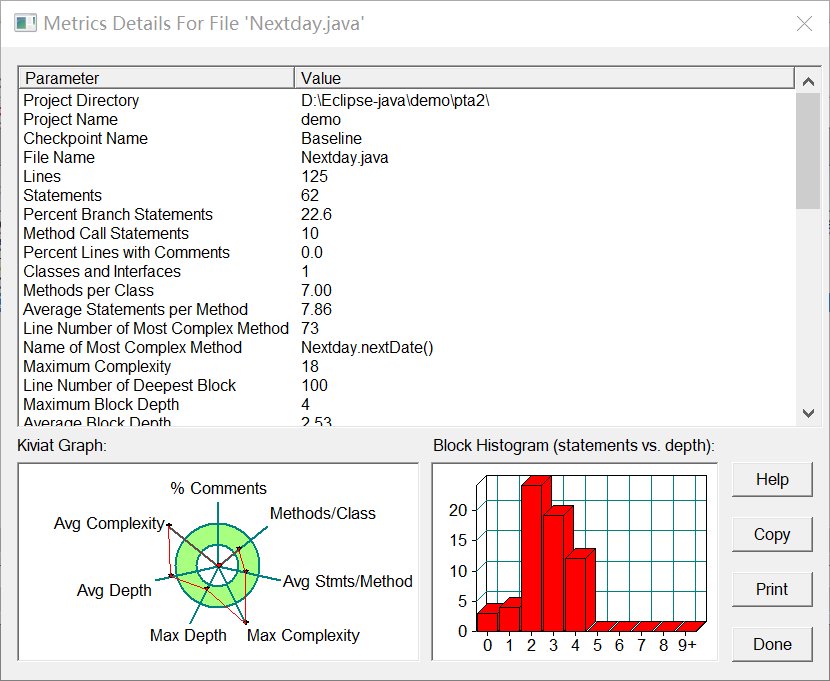
SourceMonitor的生成报表内容如下:
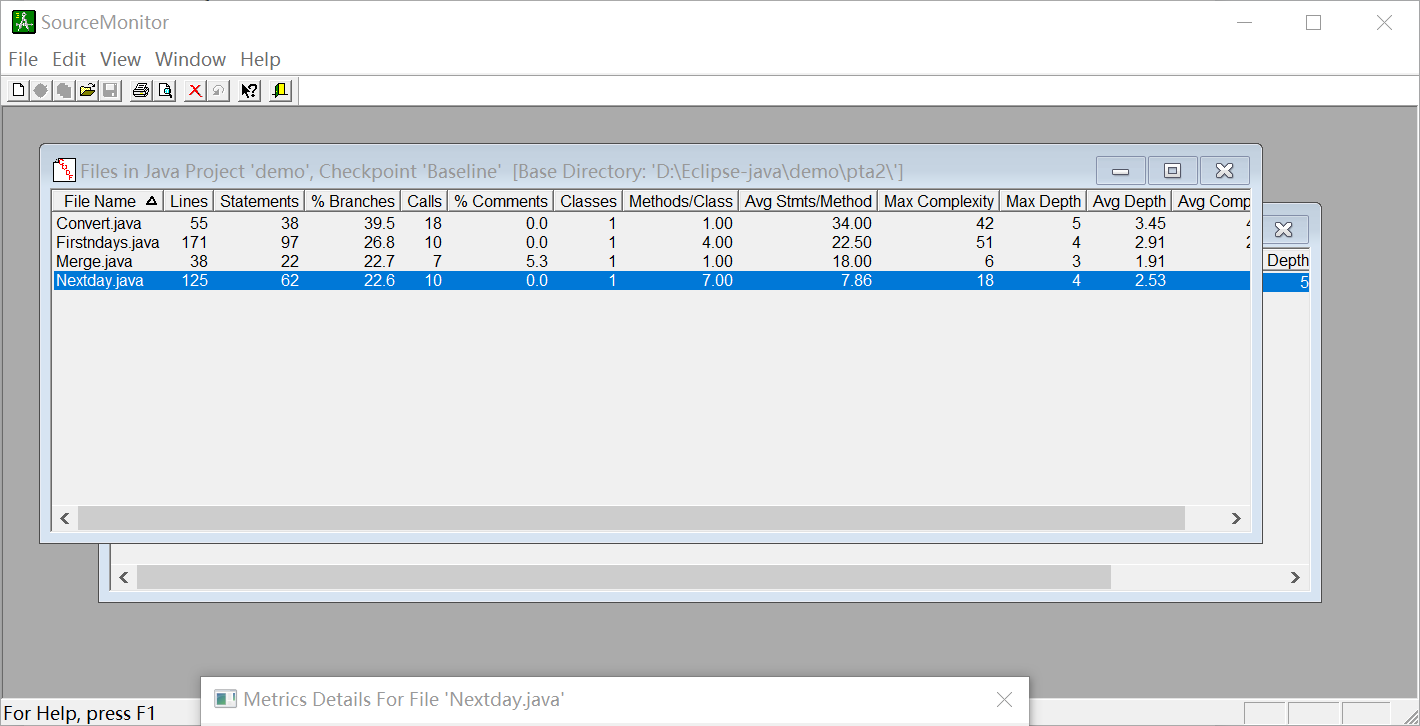
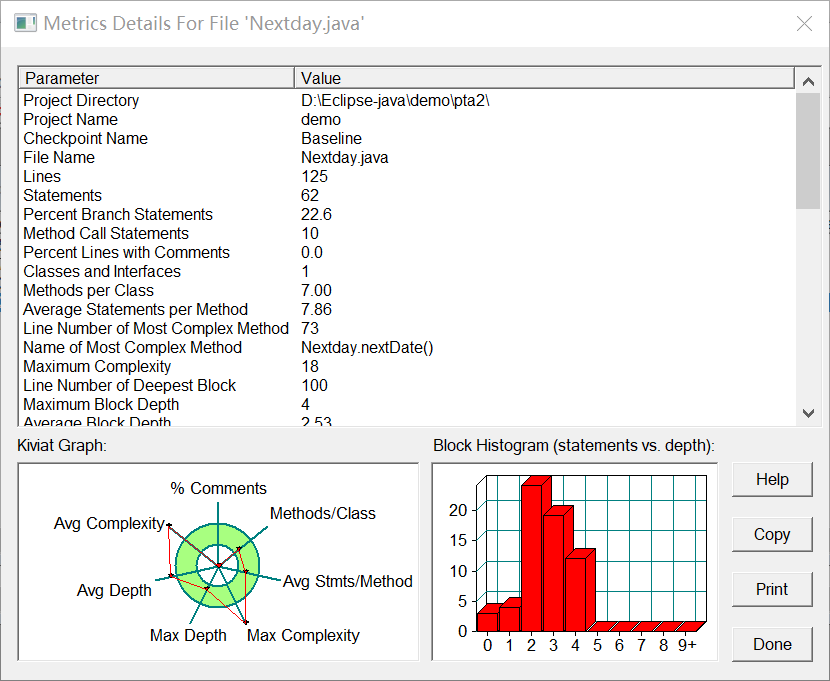
7-5 求前N天 (30 分)
输入年月日的值(均为整型数),同时输入一个取值范围在[-10,10] 之间的整型数n,输出该日期的前n天(当n > 0时)、该日期的后n天(当n<0时)。
其中年份取值范围为 [1820,2020] ,月份取值范围为[1,12] ,日期取值范围为[1,31] 。
注意:不允许使用Java中任何与日期有关的类或方法。
输入格式:
在一行中输入年月日的值以及n的值,可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
当输入的年、月、日以及n的值非法时,输出“Wrong Format”;
当输入数据合法时,输出“n days ago is:年-月-日”
源代码:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int year = in.nextInt(); int month = in.nextInt(); int day = in.nextInt(); int n = in.nextInt(); boolean m = new String() != null; boolean o = new String() != null; m = isLeapYear(year); o = checkInputValidity( year, month, day); if(o==false||n>10||n<-10) { System.out.println ("Wrong Format"); } else if((m==true&&(month==2&&day>29))||(m==false&&(month==2&&day>28))|| (month == 4 && day == 31) || (month == 6 && day ==31)|| (month == 9&& day == 31)||(month == 11 && day ==31)) { System.out.println ("Wrong Format"); } else { DaysAgo (year, month, day, n); } } public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) { int flag=-1; if(year%4==0||(year%4==0&&year%400==0)) { flag=1; } else if(year%4!=0||(year%4==0&&year%400!=0)) { flag=0; } if(flag==1) { return true; } else { return false; } } public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day) { int flag; if(year <1820 || year > 2020 || month < 1 || month > 12 || day < 1 || day > 31){ return false; } else{ return true; } } public static void DaysAgo (int year,int month,int day,int n) { boolean m = new String() != null; int Year = 0 ,Month = 0,Day = 0; if(year%4==0||(year%4==0&&year%400==0)){ m = true; } else if(year%4!=0||(year%4==0&&year%400!=0)){ m = false; } if(n>0) { if(month==1&&day-n<=0) { Day=31-(n-day); Month = 12; Year = year - 1; } else if(day-n<=0&&(month==4||month==6||month==9||month ==11||month==8)) { Day=31-(n-day); Month = month - 1; Year = year ; } else if (day-n<=0&&(month== 12||month==5||month==7||month==10)) { Day=30-(n-day); Month = month - 1; Year = year ; } else if (m==true&&month==3&&day-n<=0) { Day=29-n+day; Month =month - 1; Year = year ; } else if (m==false&&month==3&&day-n<=0) { Day=28-n+day; Month = month -1; Year = year ; } else { Day = day - n; Month = month; Year = year; } } else if(n<0) { if(month==12&&day-n>31) { Day = -(31-day+n); Month = 1; Year = year + 1; } else if ((month ==1 ||month ==3||month==5||month==7||month==8||month==10)&&day-n>31) { Day = -(31-day+n); Month = month + 1; Year = year; } else if ((month==4||month==6||month==9||month ==11)&&day-n>30) { Day = -(30-day+n); Month = month + 1; Year = year; } else if(m==true&&month==2&&day-n>29) { Day = -(29-day+n); Month = month + 1; Year = year; } else if (m==false&&month==2&&day-n>28) { Day = -(28-day+n); Month = month + 1; Year = year; } else { Day = day -n; Month = month ; Year = year; } } else if (n==0) { Day = day; Month = month ; Year = year; } System.out.println(n+" days ago is:"+Year+"-"+Month+"-"+ Day); }
SourceMonitor的生成报表内容如下:
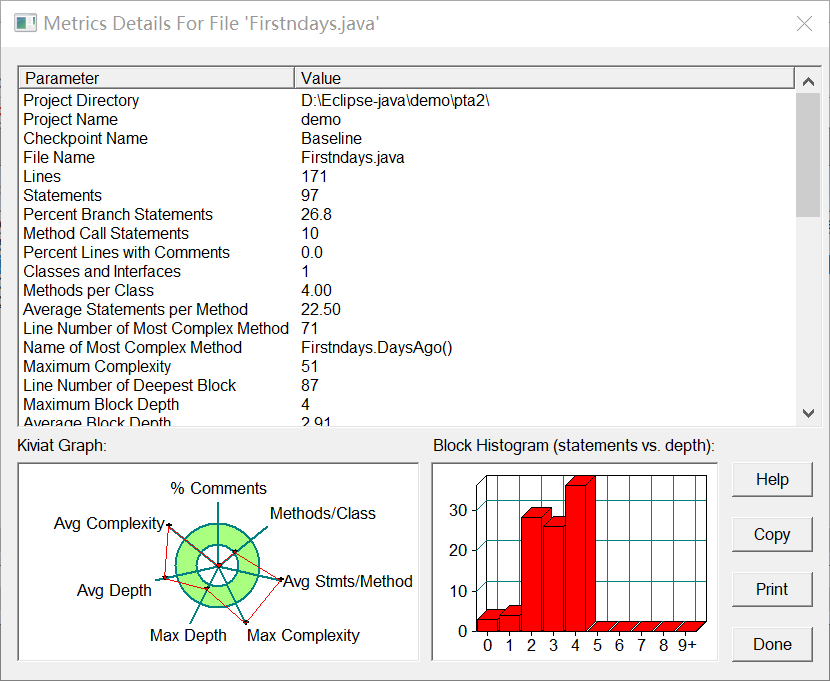
题目集3
7-2 定义日期类 (28 分)
定义一个类Date,包含三个私有属性年(year)、月(month)、日(day),均为整型数,其中:年份的合法取值范围为[1900,2000] ,月份合法取值范围为[1,12] ,日期合法取值范围为[1,31] 。 注意:不允许使用Java中和日期相关的类和方法,否则按0分处理。
源代码:
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int year = in.nextInt(); int month = in.nextInt(); int day = in.nextInt(); boolean m = new String() != null; boolean n = new String() != null; m = isLeapYear(year); n = checkInputValidity( year, month, day); if((m==true&&(month==2&&day>29))||(m==false&&(month==2&&day>28))|| (month == 4 && day == 31) || (month == 6 && day ==31)|| (month == 9&& day == 31)||(month == 11 && day ==31)) { System.out.println ("Date Format is Wrong"); } else if (n==false) { System.out.println ("Date Format is Wrong"); } else { nextDate( year, month,day); } } public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) { int flag=-1; if(year%4==0||(year%4==0&&year%400==0)) { flag=1; } else if(year%4!=0||(year%4==0&&year%400!=0)) { flag=0; } if(flag==1) { return true; } else { return false; } } public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day) { int flag; if(year <1820 || year > 2020 || month < 1 || month > 12 || day < 1 || day > 31) { return false; } else { return true; } } public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) { boolean m = new String() != null; if(year%4==0||(year%4==0&&year%400==0)) { m = true; } else if(year%4!=0||(year%4==0&&year%400!=0)) { m = false; } if((m==true&&(month==2&&day>29))||(m==false&&(month==2&&day>28))|| (month == 4 && day == 31) || (month == 6 && day ==31)|| (month == 9&& day == 31)||(month == 11 && day ==31)) { System.out.println ("Date Format is Wrong"); } else { String week = new String(); int f,Year = 0 ,Month = 0,Day = 0; if((m==true&&(month==2&&day==29))||(m==false&&(month==2&&day==28))|| ((month == 4||month==6||month==9||month==11) && day == 30)) { Month = month+1; Day = 1; Year = year; } else if (month == 12&&day==31) { Month = 1; Day = 1; Year = year + 1; } else if((month==1||month==3||month==5||month==7||month==8||month==10)&&day==31) { Month = month+1; Day = 1; Year = year; } else { Day = day+1; Year = year; Month = month; } System.out.println("Next day is:"+Year+"-"+Month+"-"+Day); } } }
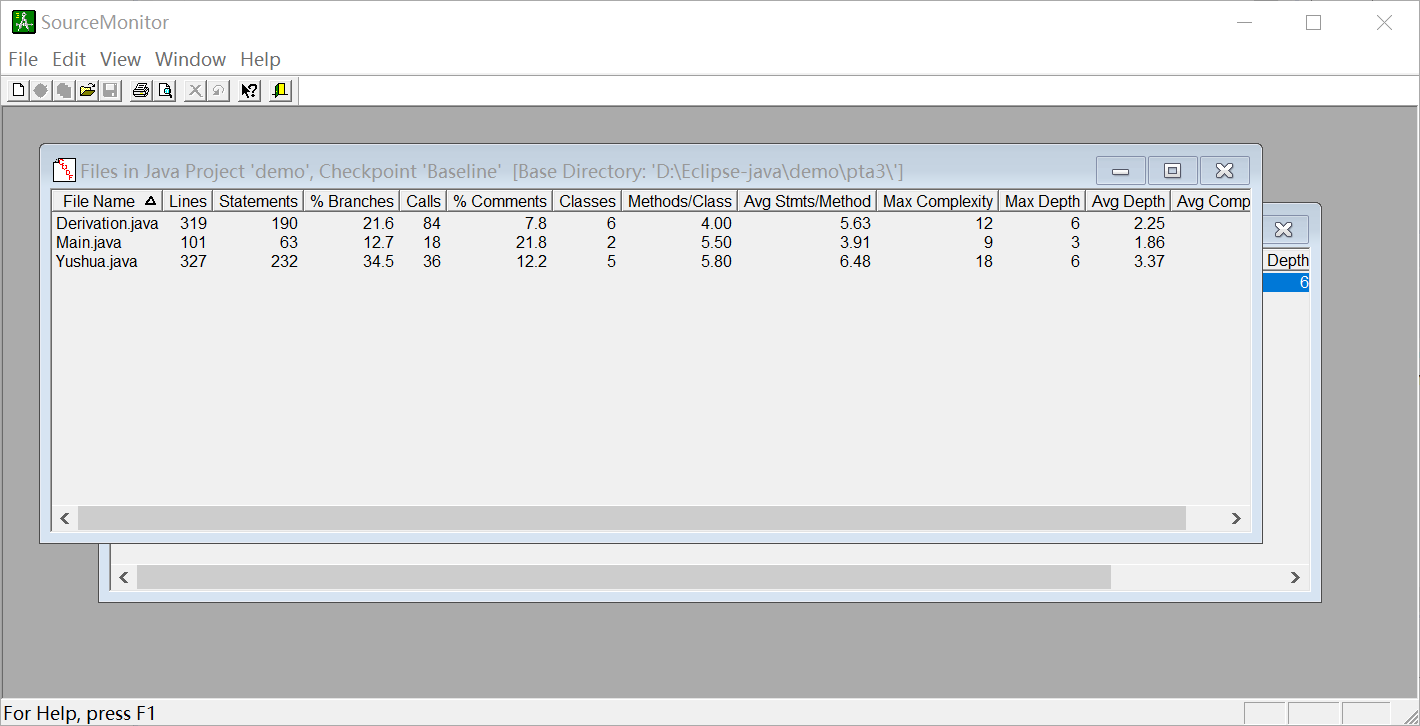
SourceMonitor的生成报表内容如下:
7-3 一元多项式求导(类设计) (50 分)
编写程序性,实现对简单多项式的导函数进行求解。详见作业指导书。
输入格式:
在一行内输入一个待计算导函数的表达式,以回车符结束。
输出格式:
如果输入表达式不符合上述表达式基本规则,则输出“Wrong Format”。
如果输入合法,则在一行内正常输出该表达式的导函数,注意以下几点: 结果不需要排序,也不需要化简;
- 当某一项为“0”时,则该项不需要显示,但如果整个导函数结果为“0”时,则显示为“0”;
- 当输出结果第一项系数符号为“+”时,不输出“+”;
- 当指数符号为“+”时,不输出“+”;
- 当指数值为“0”时,则不需要输出“x^0”,只需要输出其系数即可。
源代码:
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.math.BigInteger; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); String expr = sc.nextLine(); Polynomial polynomial = new Polynomial(expr); if (!polynomial.isPolynomial()) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } else { List<Term> newTerms = new ArrayList<Term>(); try { List<Term> terms = polynomial.getPolynomial(); for (Term term : terms) { newTerms.add(term.getDerivative()); } Expression expression = new Expression(newTerms); System.out.println(expression); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println("Wrong Format"); } } } } class Expression { private List<Term> trems = new ArrayList<Term>(); public Expression() { super(); } public Expression(List<Term> trems) { super(); this.trems = trems; } @Override public String toString() { StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer(); for (Term term : trems) { result.append(term.toString()); } if(result.length() == 0) { return "0"; } else { if(result.charAt(0) == '+') { result.deleteCharAt(0); } return result.toString(); } } } class ConstantTerm extends Term { private BigInteger value; public ConstantTerm() { super(); } public ConstantTerm(BigInteger value) { super(); this.value = value; } // 常数项的导数为0 @Override public Term getDerivative() { return new ConstantTerm(BigInteger.ZERO); } public BigInteger getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(BigInteger value) { this.value = value; } @Override public String toString() { int compareTo = value.compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO); if (compareTo == 0) { return ""; } else if(compareTo > 0) { return "+"+value; } else { return value.toString(); } } } class Polynomial { // 正整数正则 private static Pattern PATTERN1 = Pattern.compile("^[+-]{0,1}[1-9]\\d*$"); // 变量项正则 注意除了数字 任何地方都可以有空格 private static Pattern PATTERN2 = Pattern.compile("^[+-]{0,1}([1-9]\\d*\\s*\\*\\s*){0,1}x\\s*(\\^\\s*[+-]{0,1}[1-9]\\d*){0,1}$"); // 原始多项式 private String data; public Polynomial() { super(); } public Polynomial(String data) { super(); this.data = data; } public boolean isPolynomial() { String value = data; if (value == null) { return false; } // 去除首尾空格 value = value.trim(); // 空字符串 if (value.equals("")) { return false; } // 按照运算加减号分隔原字符串 List<String> arrArea = split(value); if(arrArea == null) { return false; } for (String item : arrArea) { // 验证每一项是否合法 item = item.trim(); if (item.equals("")) { return false; } if(item.indexOf("x") > -1) { // 包含x 需要按变量项判断 Matcher matcher = PATTERN2.matcher(item); if (!matcher.matches()) { return false; } } else { // 不包含x 按常量项判断 只需要判断是否为整数即可 Matcher matcher = PATTERN1.matcher(item); if (!matcher.matches()) { return false; } } } // 所有项校验通过 return true; } public List<Term> getPolynomial() { List<Term> result = new ArrayList<Term>(); String value = data.trim(); List<String> arrArea = split(value); for (String item : arrArea) { // 移除所有空格 item = item.replace(" ", ""); if (item.indexOf("x") > -1) { BigInteger coeff = item.startsWith("-") ? BigInteger.valueOf(-1L) : BigInteger.valueOf(1L); BigInteger index = BigInteger.valueOf(1L); String[] temp = item.split("\\*"); if (temp.length == 1) { temp = temp[0].split("\\^"); if (temp.length == 1) { // x } else { // x^3 index = BigInteger.valueOf(Long.valueOf(temp[1])); } } else { coeff = BigInteger.valueOf(Long.valueOf(temp[0])); temp = temp[1].split("\\^"); if (temp.length == 1) { // 5*x } else { // 5*x^3 index = BigInteger.valueOf(Long.valueOf(temp[1])); } } result.add(new PowerFunctionTerm(coeff,index)); } else { result.add(new ConstantTerm(BigInteger.valueOf(Long.valueOf(item)))); } } return result; } private static List<String> split(String value) { if (value.endsWith("+") || value.endsWith("-")) { return null; } // 先找到只能作为是运算符的+-号 List<String> result = new ArrayList<String>(); char[] charArray = value.toCharArray(); char previous = charArray[0]; List<Integer> indexs = new ArrayList<Integer>(); indexs.add(0); for (int i = 0; i < charArray.length; i++) { if (i == 0) { continue; } char c = charArray[i]; if (c == '+' || c == '-') { if (previous != '^') { indexs.add(i); } else if (previous == '+' || previous == '-') { return null; } } if (c != ' ') { previous = c; } } indexs.add(value.length()); for (int i = 0; i < indexs.size() - 1; i++) { result.add(value.substring(indexs.get(i), indexs.get(i + 1))); } return result; } public static void main(String[] args) { Matcher matcher = PATTERN2.matcher("0*x"); System.out.println(matcher.matches()); } } abstract class Term { // 项求导 - 返回的也是项 public abstract Term getDerivative(); } class PowerFunctionTerm extends Term { // 系数 private BigInteger coeff; // 指数 private BigInteger index; private static final BigInteger ONE = BigInteger.valueOf(1L); public PowerFunctionTerm() { super(); } public PowerFunctionTerm(BigInteger coeff, BigInteger index) { super(); this.coeff = coeff; this.index = index; } @Override public Term getDerivative() { // 指数如果是1 求导后应该变为常数项 if (index.compareTo(ONE) == 0) { return new ConstantTerm(coeff.multiply(index)); } else { // 求导函数 f(x) = ax^b f'(x) = abx^b-1 return new PowerFunctionTerm(coeff.multiply(index), index.subtract(ONE)); } } // 系数和指数都不会为0 @Override public String toString() { int compareTo = coeff.compareTo(BigInteger.ZERO); StringBuffer result = new StringBuffer(); result.append(compareTo > 0 ? "+" : "-"); // 系数绝对值为1的时候不用显示 if (coeff.abs().compareTo(ONE) != 0) { result.append(coeff.abs().toString()); result.append("*"); } result.append("x"); // 指数为1的时候不用显示 if (index.compareTo(ONE) != 0) { result.append("^"); result.append(index.toString()); } return result.toString(); } public BigInteger getCoeff() { return coeff; } public void setCoeff(BigInteger coeff) { this.coeff = coeff; } public BigInteger getIndex() { return index; } public void setIndex(BigInteger index) { this.index = index; } }
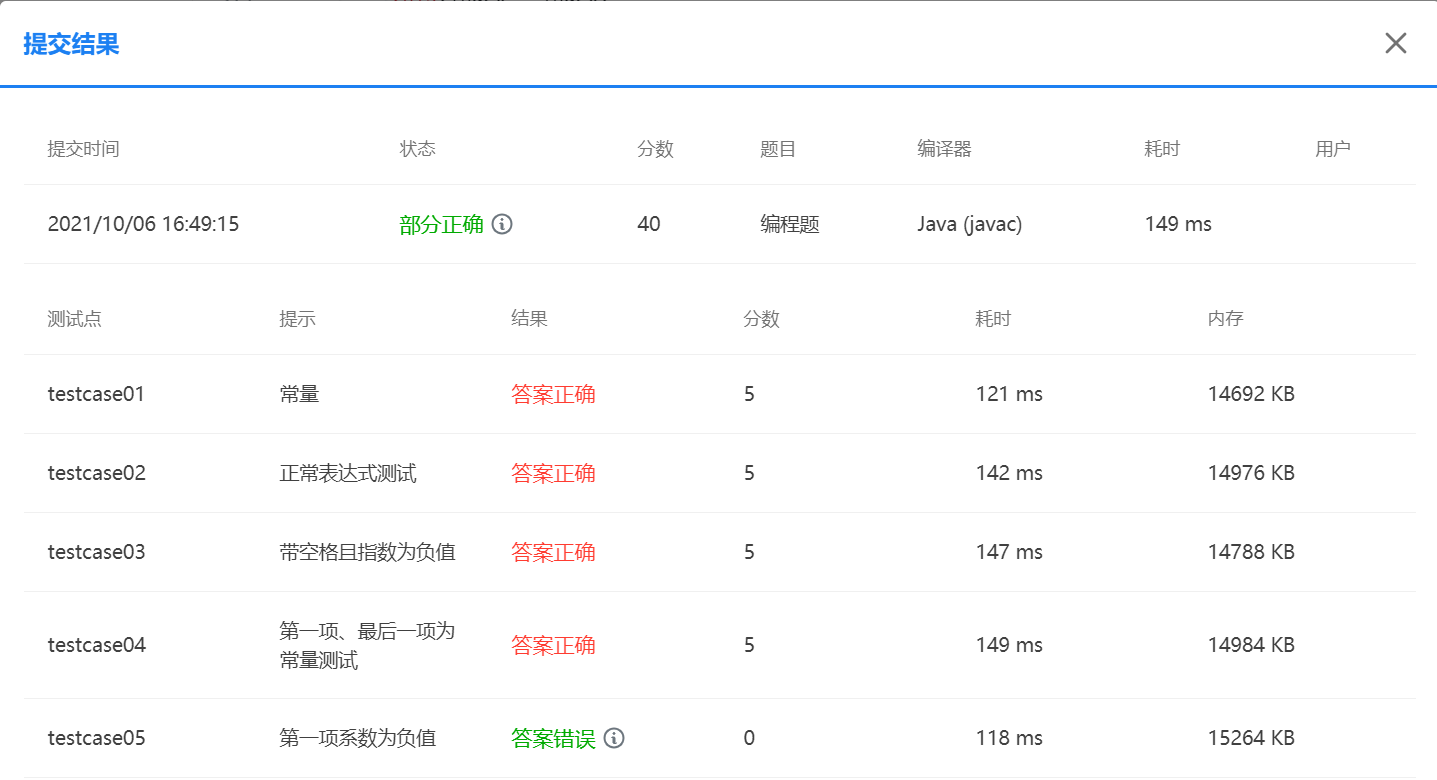
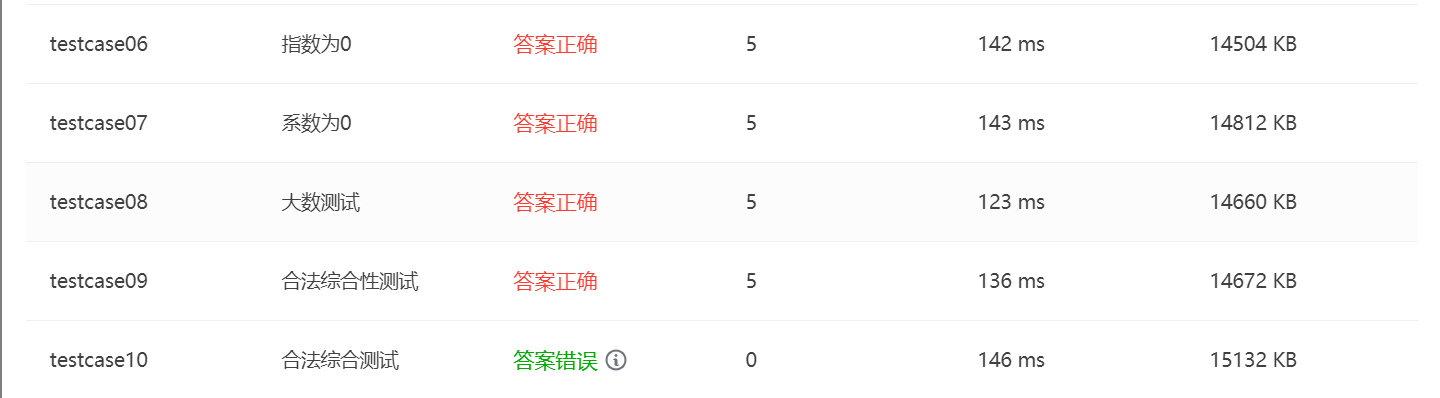
SourceMonitor的生成报表内容如下:
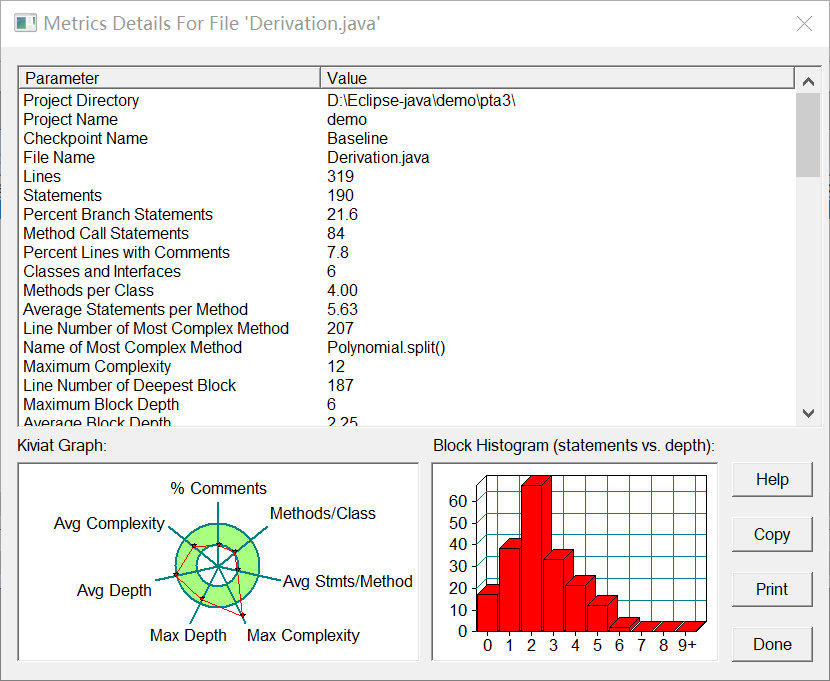
三、采坑心得
1.条件判断表达式比较长的情况下,可以封装成一个方法isXXX(),返回boolean
2.Java中 this 和super 的异同:简单的来说,this调用的是本类中的东西,super调用的是父类中的东西。
如果B类继承了A类,super对应A类,this对应B类。
3.Java变量的命名规则如下:
(1).可以以数字、字母、‘_’、'$'符组成
(2).首字符不能以数字开头
(3).中文可以作为变量名,但不提倡使用
(4).Java大小写敏感,命名变量时要注意
(5).不能使用Java保留字
四、改进建议
写程序时应先确定一个思路再顺着往下写,要是边写边想边改,会造成代码思路不清晰且难以找出错误。
五、总结
目集1的大部分题目,几乎第一次提交就通过所有测试点;题目二对我来说有一定的难度,很多测试点不能通过,所以我花费了大量的时间提交测试,虽然最终通过,但多次修改导致代码复杂性高,可读性不高;题目三虽然只有三道题,但我只能写出算法,多次修改到最后也没有通过测试点,找不出问题所在。所以越长越复杂的题目,越应该确定思路。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号