类与对象
函数题
一、定义Person类
请定义Person类,包含两个属性,根据主方法中的调用形式,定义构造方法,输出方法。
类的定义:
class Person{}
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); Person p1; String name = sc.next(); int age = sc.nextInt(); p1= new Person(name,age); p1.show(); sc.close(); } } /* 请在这里填写答案 */
输入样例:
例如:
zhang
18
输出样例:
例如:
name:zhang
age:18
1 class Person{ 2 private int age; 3 private String name; 4 5 public String getName() 6 {return name; 7 8 } 9 public int getAge() 10 { 11 return age; 12 13 } 14 public Person (String name,int age) 15 16 { 17 this.name=name; 18 if(age>=0&&age<=150) 19 this.age=age; 20 else 21 this.age=0; 22 23 24 25 } 26 public void show() 27 { 28 System.out.println("name:"+name); 29 System.out.println("age:"+age); 30 } 31 32 33 }
二、矩形
设计一个表示矩形的类Rectangle,这个类用一个表示坐标点的类Point的对象来表达它的左上角坐标,用一个表示尺寸的类Dimension的对象来表示它的大小。 你的程序要严格按照所给的类和函数的声明来实现。
函数接口定义:
/** * Represents a point in 2D, with x and y, like (x,y). */ class Point { private int x; private int y; /** * Creates a point with coordinate at (x,y) * @param x the x coordinate * @param y the y coordinate */ public Point(int x, int y) { } /* (non-Javadoc) * @see java.lang.Object#toString() * The generated string as: "(x,y) */ @Override public String toString() { } /** * Moves the point with dx and dy. * @param dx the distance to be moved at x-axis * @param dy the distance to be moved at y-axis */ public void move(int dx, int dy) { } /** * Calculate the distance between this and p. * @param p the other point. * @return the distance between this and p. */ public double distance(Point p) { } } /** * A dimension in 2D, with width and height. */ class Dimension { private int width; private int height; /** * Creates a dimension with specified width and height. * @param width the width of the dimension * @param height the height of the dimension */ public Dimension(int width, int height) { } /* (non-Javadoc) * @see java.lang.Object#toString() * The generated string as: "width by height" */ @Override public String toString() { } /** * Resizes the dimension with scales at width and height. * Although the scales are in double, the result should be integers as well. * @param widthScale the scale at width * @param heightScale the scale at height */ public void resize(double widthScale, double heightScale) { } /** * Calculate the area of this dimension. * @return the area of this dimension. */ public int area() { } } /** * Represents a rectangle, with a point at its top-left and a dimension. * */ class Rectangle { private Point topleft; private Dimension size; /** * Creates a rectangle. * @param topleft the coordinate of its top-left * @param size the dimension of its size */ public Rectangle(Point topleft, Dimension size) { } /* (non-Javadoc) * @see java.lang.Object#toString() * The generated string as: "Rectangle at (x,y):width by height" */ public String toString() { } /** * Moves the rectangle some distance. * @param dx the distance to be moved at x-axis * @param dy the distance to be moved at y-axis */ public void move(int dx, int dy) { } /** * Resizes the rectangle at both width and height * @param widthScale the scale at width * @param heightScale the scale at height */ public void resize(double widthScale, double heightScale) { } /** * Calculates the area of this rectangle. * @return the area of this rectangle. */ public double area() { } /** * Calculates the distance between this rectangle and r. * @param r the other rectangle * @return the distance between this rectangle and r. */ public double distance(Rectangle r) { } }
裁判测试程序样例:
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int x = in.nextInt(); int y = in.nextInt(); int width = in.nextInt(); int height = in.nextInt(); Rectangle r = new Rectangle( new Point(x,y), new Dimension(width, height)); Rectangle r2 = new Rectangle( new Point(x,y), new Dimension(width, height)); int dx = in.nextInt(); int dy = in.nextInt(); r.move(dx, dy); double widthScale = in.nextDouble(); double heightScale = in.nextDouble(); r.resize(widthScale, heightScale); System.out.println(r); System.out.printf("%.2f\n", r.area()); System.out.printf("%.2f\n", r.distance(r2)); in.close(); } } /* 请在这里填写答案 */
输入样例:
0 0 100 100 20 20 2 2
输出样例:
Rectangle at (20,20):200 by 200 40000.00 28.28
1 class Point { 2 private int x; 3 private int y; 4 5 /** 6 * Creates a point with coordinate at (x,y) 7 * @param x the x coordinate 8 * @param y the y coordinate 9 */ 10 public Point(int x, int y) { 11 this.x=x; 12 this.y=y; 13 14 } 15 16 /* (non-Javadoc) 17 * @see java.lang.Object#toString() 18 * The generated string as: "(x,y) 19 */ 20 @Override 21 public String toString() { 22 return "("+x+","+y+")"; 23 } 24 25 /** 26 * Moves the point with dx and dy. 27 * @param dx the distance to be moved at x-axis 28 * @param dy the distance to be moved at y-axis 29 */ 30 public void move(int dx, int dy) { 31 this.x=this.x+dx; 32 this.y=this.y+dy; 33 } 34 35 /** 36 * Calculate the distance between this and p. 37 * @param p the other point. 38 * @return the distance between this and p. 39 */ 40 public double distance(Point p) { 41 return Math.sqrt(Math.pow((p.x-this.x),2)+Math.pow((p.y-this.y),2)); 42 } 43 } 44 45 /** 46 * A dimension in 2D, with width and height. 47 */ 48 class Dimension { 49 private double width; 50 private double height; 51 52 /** 53 * Creates a dimension with specified width and height. 54 * @param width the width of the dimension 55 * @param height the height of the dimension 56 */ 57 public Dimension(int width, int height) { 58 this.width=width; 59 this.height=height; 60 } 61 62 /* (non-Javadoc) 63 * @see java.lang.Object#toString() 64 * The generated string as: "width by height" 65 */ 66 @Override 67 public String toString() { 68 return (int)this.width+" by "+(int)this.height; 69 } 70 71 /** 72 * Resizes the dimension with scales at width and height. 73 * Although the scales are in double, the result should be integers as well. 74 * @param widthScale the scale at width 75 * @param heightScale the scale at height 76 */ 77 public void resize(double widthScale, double heightScale) { 78 this.width=this.width*widthScale; 79 this.height=this.height*heightScale; 80 } 81 82 /** 83 * Calculate the area of this dimension. 84 * @return the area of this dimension. 85 */ 86 public double area() { 87 return this.width*this.height; 88 } 89 } 90 91 /** 92 * Represents a rectangle, with a point at its top-left and a dimension. 93 * 94 */ 95 class Rectangle { 96 private Point topleft; 97 private Dimension size; 98 /** 99 * Creates a rectangle. 100 * @param topleft the coordinate of its top-left 101 * @param size the dimension of its size 102 */ 103 public Rectangle(Point topleft, Dimension size) { 104 this.topleft=topleft; 105 this.size=size; 106 } 107 108 /* (non-Javadoc) 109 * @see java.lang.Object#toString() 110 * The generated string as: "Rectangle at (x,y):width by height" 111 */ 112 public String toString() { 113 return "Rectangle at "+topleft+":"+size; 114 } 115 /** 116 * Moves the rectangle some distance. 117 * @param dx the distance to be moved at x-axis 118 * @param dy the distance to be moved at y-axis 119 */ 120 public void move(int dx, int dy) { 121 this.topleft.move(dx,dy); 122 } 123 124 /** 125 * Resizes the rectangle at both width and height 126 * @param widthScale the scale at width 127 * @param heightScale the scale at height 128 */ 129 public void resize(double widthScale,double heightScale) { 130 this.size.resize(widthScale, heightScale); 131 } 132 133 /** 134 * Calculates the area of this rectangle. 135 * @return the area of this rectangle. 136 */ 137 public double area() { 138 return this.size.area(); 139 } 140 141 /** 142 * Calculates the distance between this rectangle and r. 143 * @param r the other rectangle 144 * @return the distance between this rectangle and r. 145 */ 146 public double distance(Rectangle r) { 147 return this.topleft.distance(r.topleft); 148 149 } 150 }
三、设计一个矩形类Rectangle
设计一个名为Rectangle的类表示矩形。这个类包括: 两个名为width和height的double型数据域,它们分别表示矩形的宽和高。width和height的默认值都为1. 一个无参构造方法。 一个为width和height指定值的矩形构造方法。 一个名为getArea()的方法返回这个矩形的面积。 一个名为getPerimeter()的方法返回这个矩形的周长。
类名为:
Rectangle
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner; /* 你的代码将被嵌入到这里 */ public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); double w = input.nextDouble(); double h = input.nextDouble(); Rectangle myRectangle = new Rectangle(w, h); System.out.println(myRectangle.getArea()); System.out.println(myRectangle.getPerimeter()); input.close(); } }
输入样例:
3.14 2.78
输出样例:
8.7292 11.84
1 class Rectangle{ 2 private double width; 3 private double height; 4 public Rectangle(double width,double height) 5 { 6 this.width=width; 7 this.height=height; 8 } 9 public double getArea(){ 10 return width*height; 11 12 } 13 public double getPerimeter() { 14 return width*2+height*2; 15 } 16 17 18 }
四、Book类的设计
阅读测试程序,设计一个Book类。
函数接口定义:
class Book{}
该类有 四个私有属性 分别是 书籍名称、 价格、 作者、 出版年份,以及相应的set 与get方法;该类有一个含有四个参数的构造方法,这四个参数依次是书籍名称、 价格、 作者、 出版年份 。
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.*; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { List <Book>books=new ArrayList<Book>(); Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in); for(int i=0;i<5;i++) { String str=in.nextLine(); String []data=str.split(","); Book book=new Book(data[0],Integer.parseInt(data[1]),data[2],Integer.parseInt(data[3])); books.add(book); } System.out.println(totalprice(books)); } /*计算所有book的总价*/ public static int totalprice(List <Book>books) { int result=0; for(int i=0;i<books.size();i++){result+=books.get(i).getPrice();} return result; } } /* 请在这里填写答案 */
输入样例:
三体,100,无名氏,1998 上下五千年,50,编辑部,2015 海底世界,50,无名氏2,2000 三体1,100,无名氏3,2017 三体3,100,无名氏4,1998
输出样例:
400
1 class Book{ 2 String name; 3 int Price; 4 String writer; 5 int year; 6 7 public Book(String name,int Price,String writer,int year) 8 { 9 this.name=name; 10 this.Price=Price; 11 this.writer=writer; 12 this.year=year; 13 } 14 public int getPrice(){ 15 return this.Price; 16 17 18 } 19 20 21 22 }
五、数组工具类的设计
本题要求设计一个名为MyArrays的类,根据调用的方式实现相应的方法。
函数接口定义:
请同学根据该类的调用方式和结果,自行设计MyArrays类中的方法,满足应用的需要。
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); int n=sc.nextInt(); int array[]= new int[n]; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) { array[i]=sc.nextInt(); } MyArrays.printArray(array);//显示数组的内容 MyArrays.sortArray(array); //对数组元素排序 MyArrays.printArray(array);//显示排序后的结果 int sum=MyArrays.sumOfArray(array);//数组元素求和 System.out.println(sum);//显示数组元素的和 } } /* 请在这里填写MyArrays类的有关代码 */
输入样例:
5 5 4 6 8 3
输出样例:
5,4,6,8,3 3,4,5,6,8 26
1 class MyArrays{ 2 3 static public void printArray(int s[]) { 4 for(int i=0;i<s.length;i++) 5 { 6 if(i==s.length-1) 7 System.out.print(s[i]); 8 else 9 System.out.print(s[i]+","); 10 } 11 System.out.println(); 12 } 13 static public void sortArray(int s[]) { 14 Arrays.sort(s); 15 } 16 static public int sumOfArray(int s[]) { 17 int d=0; 18 for(int i=0;i<s.length;i++) 19 { 20 d+=s[i]; 21 } 22 return d; 23 } 24 25 }
六、TDVector
There is a class TDVector that is incompleted. Please complete the class according to the test code in Main.
函数接口定义:
class TDVector { private double x; private double y; public String toString() { return "("+this.x+","+this.y+")"; } }
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner; class TDVector { private double x; private double y; public String toString() { return "("+this.x+","+this.y+")"; } /** 你所提交的代码将被嵌在这里(替换此行) **/ } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { TDVector a = new TDVector(); // default ctor, x and y are zeros Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); double x,y,z; x = sc.nextDouble(); y = sc.nextDouble(); z = sc.nextDouble(); TDVector b = new TDVector(x, y); // ctor by x and y TDVector c = new TDVector(b); // ctor by another TDVector a.setY(z); System.out.println(a); System.out.println(b); System.out.println(c); c.setX(z); a = b.add(c); System.out.println(a); System.out.println("b.x="+b.getX()+" b.y="+b.getY()); sc.close(); } }
输入样例:
3.14 1.9 2.72
输出样例:
(0.0,2.72) (3.14,1.9) (3.14,1.9) (5.86,3.8) b.x=3.14 b.y=1.9
1 public TDVector(double x,double y) { 2 this.x=x; 3 this.y=y; 4 } 5 public TDVector() { 6 } 7 public TDVector(TDVector c) { 8 this.x=c.x; 9 this.y=c.y; 10 } 11 public void setX(double x) { 12 this.x=x; 13 14 } 15 public void setY(double y) { 16 this.y=y; 17 18 } 19 public TDVector add(TDVector c) { 20 TDVector cd=new TDVector(); 21 cd.x=this.x+c.x; 22 cd.y=this.y+c.y; 23 return cd; 24 } 25 public double getX() { 26 return this.x; 27 28 } 29 public double getY() { 30 return this.y; 31 }
七、Point
There is a class Point that is incompleted. Please complete the class according to the test code in Main.
函数接口定义:
class Point { private double x; private double y; public String toString() { return "("+this.x+","+this.y+")"; } }
裁判测试程序样例:
import java.util.Scanner; class Point { private double x; private double y; public String toString() { return "("+this.x+","+this.y+")"; } /** 你所提交的代码将被嵌在这里(替换此行) **/ } public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Point a = new Point(); // default ctor, x and y are zeros Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); double x,y,z; x = sc.nextDouble(); y = sc.nextDouble(); z = sc.nextDouble(); Point b = new Point(x, y); // ctor by x and y Point c = new Point(b); // ctor by another Point a.setY(z); System.out.println(a); System.out.println(b); System.out.println(c); c.setX(z); a = b.add(c); System.out.println(a); System.out.println("b.x="+b.getX()+" b.y="+b.getY()); sc.close(); } }
输入样例:
3.14 1.9 2.72
输出样例:
(0.0,2.72) (3.14,1.9) (3.14,1.9) (5.86,3.8) b.x=3.14 b.y=1.9
1 public Point (double x,double y) { 2 this.x=x; 3 this.y=y; 4 } 5 public Point() { 6 } 7 public Point(Point c) { 8 this.x=c.x; 9 this.y=c.y; 10 } 11 public void setX(double x) { 12 this.x=x; 13 14 } 15 public void setY(double y) { 16 this.y=y; 17 18 } 19 public Point add(Point c) { 20 Point cd=new Point(); 21 cd.x=this.x+c.x; 22 cd.y=this.y+c.y; 23 return cd; 24 } 25 public double getX() { 26 return this.x; 27 28 } 29 public double getY() { 30 return this.y; 31 }
编程题
一、构造函数与toString
定义一个有关人的Person类,内含属性:String name、int age、boolean gender、int id,所有的变量必须为私有(private)。 注意:属性顺序请严格按照上述顺序依次出现。
###1.编写无参构造函数:
- 打印"This is constructor"。
- 将name,age,gender,id按照
name,age,gender,id格式输出
###2.编写有参构造函数 依次对name,age,gender赋值。
###3.覆盖toString函数: 按照格式:类名 [name=, age=, gender=, id=]输出。建议使用Eclipse自动生成.
###4.对每个属性生成setter/getter方法
###5.main方法中
- 首先从屏幕读取n,代表要创建的对象个数。
- 然后输入n行name age gender , 调用上面2编写的有参构造函数新建对象。
- 然后将刚才创建的所有对象
逆序输出。 - 接下来使用无参构造函数新建一个Person对象,并直接打印该对象。
输入样例:
3 a 11 false b 12 true c 10 false
输出样例:
Person [name=c, age=10, gender=false, id=0] Person [name=b, age=12, gender=true, id=0] Person [name=a, age=11, gender=false, id=0] This is constructor null,0,false,0 Person [name=null, age=0, gender=false, id=0]
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 class Person { 3 private String name; 4 private int age; 5 private boolean gender; 6 private int id; 7 public Person () { 8 9 } 10 public Person(String name,int age,boolean gender) { 11 this.name=name; 12 this.age=age; 13 this.gender=gender; 14 } 15 public void show() { 16 System.out.println("This is constructor"); 17 System.out.println(this.name+","+this.age+","+this.gender+","+this.id); 18 System.out.println("Person [name="+this.name+", age="+this.age+", gender="+this.gender+", id="+this.id+"]"); 19 } 20 21 public String toString() { 22 return "Person [name="+this.name+", age="+this.age+", gender="+this.gender+", id="+this.id+"]"; 23 } 24 public void settername(String name) { 25 this.name=name; 26 27 } 28 29 public void setterage(int age) { 30 this.age=age; 31 32 } 33 34 public void settergender(boolean gender) { 35 this.gender=gender; 36 37 } 38 39 public void setterid(int id) { 40 this.id=id; 41 42 } 43 public String gettername() { 44 return this.name; 45 } 46 public int getterage() { 47 return this.age; 48 } 49 public boolean gettergender() { 50 return this.gender; 51 } 52 public int getterid() { 53 return this.id; 54 } 55 } 56 57 public class Main { 58 59 public static void main (String args[]) { 60 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 61 int n=sc.nextInt(); 62 Person person[]=new Person[n]; 63 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 64 { 65 person[i]=new Person(sc.next(),sc.nextInt(),sc.nextBoolean()); 66 67 68 } 69 for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--) 70 { 71 System.out.println(person[i]); 72 73 } 74 Person s=new Person(); 75 s.show(); 76 sc.close(); 77 } 78 }
二、构造函数与初始化块
##1.定义一个Person类 属性:name(String)、gender(boolean)、age(int)、id(int) ,所有的变量必须为私有(private)。
无参构造函数:Person(), 功能:打印This is constructor 。
有参构造函数:Person(name, gender, age) ,功能:给属性赋值。
建议:使用Eclipse自动生成toString方法
##2.定义类的初始化块 为Person类加入初始化块,在初始化块中对id属性赋值,并且要保证每次的值比上次创建的对象的值+1。然后在下一行打印This is initialization block, id is ... 其中...是id的值。
提示:可为Person类定义一个static属性来记录所创建的对象个数。
##3.编写静态初始化块 打印This is static initialization block
##4.编写main方法
- 首先输入n,代表要创建的对象数量。
- 然后从控制台分别读取n行的
name, gender, age, 并调用有参构造函数Person(name, age, gender)新建对象 。 - 将创建好的n个对象逆序输出(即输出
toString()方法)。 - 使用无参构造函数新建一个Person对象,然后直接打印该对象。
##思考 初始化类与对象有几种方法,构造函数、初始化块、静态初始化块。这三种方法执行的先后顺序是什么?各执行几次。
输入样例:
3 a 11 false b 12 true c 10 false
输出样例:
This is static initialization block This is initialization block, id is 0 This is initialization block, id is 1 This is initialization block, id is 2 Person [name=c, age=10, gender=false, id=2] Person [name=b, age=12, gender=true, id=1] Person [name=a, age=11, gender=false, id=0] This is initialization block, id is 3 This is constructor null,0,false,3 Person [name=null, age=0, gender=false, id=3]
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 class Person { 3 private String name; 4 private int age; 5 private boolean gender; 6 7 static int a=-1; 8 private int id=Person.a+1; 9 10 public Person () { 11 12 } 13 public Person(String name,int age,boolean gender) { 14 this.name=name; 15 this.age=age; 16 this.gender=gender; 17 this.id=Person.a+1; 18 Person.a+=1; 19 20 } 21 public void show() { 22 System.out.println("This is constructor"); 23 System.out.println(this.name+","+this.age+","+this.gender+","+this.id); 24 } 25 26 public String toString() { 27 return "Person [name="+this.name+", age="+this.age+", gender="+this.gender+", id="+this.id+"]"; 28 } 29 public void settername(String name) { 30 this.name=name; 31 32 } 33 34 public void setterage(int age) { 35 this.age=age; 36 37 } 38 39 public void settergender(boolean gender) { 40 this.gender=gender; 41 42 } 43 44 public void setterid(int id) { 45 this.id=id; 46 47 } 48 public String gettername() { 49 return this.name; 50 } 51 public int getterage() { 52 return this.age; 53 } 54 public boolean gettergender() { 55 return this.gender; 56 } 57 public int getterid() { 58 return this.id; 59 } 60 61 } 62 63 public class Main{ 64 65 public static void main (String args[]) { 66 67 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 68 69 int n=sc.nextInt(); 70 71 Person person[]=new Person[n]; 72 73 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 74 { 75 person[i]=new Person(sc.next(),sc.nextInt(),sc.nextBoolean()); 76 } 77 { 78 System.out.println("This is static initialization block"); 79 } 80 for(int i=0;i<n;i++) 81 { 82 System.out.println("This is initialization block, id is "+person[i].getterid()); 83 } 84 for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--) 85 { 86 System.out.println(person[i]); 87 88 } 89 90 Person s=new Person(); 91 System.out.println("This is initialization block, id is "+s.getterid()); 92 s.show(); 93 System.out.println(s); 94 sc.close(); 95 96 97 } 98 }
三、形状
##1. 定义长方形类与圆形类Circle 长方形类-类名:Rectangle,private属性:int width,length
圆形类-类名:Circle,private属性:int radius
编写构造函数:
带参构造函数:Rectangle(width, length),Circle(radius)
编写方法:public int getPerimeter(),求周长。public int getArea(),求面积。toString方法,使用Eclipse自动生成。
注意:
- 计算圆形的面积与周长,使用
Math.PI。 - 求周长和面积时,应先计算出其值(带小数位),然后强制转换为
int再返回。
##2. main方法
- 输入2行长与宽,创建两个Rectangle对象放入相应的数组。
- 输入2行半径,创建两个Circle对象放入相应的数组。
- 输出1:上面2个数组中的所有对象的周长加总。
- 输出2:上面2个数组中的所有对象的面积加总。
- 最后需使用
Arrays.deepToString分别输出上面建立的Rectangle数组与Circle数组
思考:如果初次做该题会发现代码冗余严重。使用继承、多态思想可以大幅简化上述代码。
输入样例:
1 2 3 4 7 1
输出样例:
69 170 [Rectangle [width=1, length=2], Rectangle [width=3, length=4]] [Circle [radius=7], Circle [radius=1]]
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 class Rectangle{ 3 private int width; 4 private int length; 5 public Rectangle(int width,int length) 6 { 7 this.width=width; 8 this.length=length; 9 } 10 public int getPerimeter() { 11 return (width+length)*2; 12 } 13 public String toString() { 14 return "Rectangle [width="+this.width+", length="+this.length+"]"; 15 } 16 public int getArea() { 17 return this.width*this.length; 18 } 19 20 21 } 22 class Cricle{ 23 private int radius; 24 public Cricle(int radius) { 25 this.radius=radius; 26 }public int getPerimeter() { 27 double s=Math.PI*2*radius; 28 return (int )s; 29 } 30 public int getArea() { 31 double s= Math.PI*radius*radius; 32 int i=(int)s; 33 return i; 34 } 35 public String toString () { 36 return "Circle [radius="+this.radius+"]"; 37 } 38 39 } 40 41 42 public class Main { 43 public static void main(String args[]) { 44 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 45 Rectangle s[]=new Rectangle[2]; 46 Cricle r[]=new Cricle[2]; 47 for(int i=0;i<2;i++) 48 { 49 s[i]=new Rectangle(sc.nextInt(),sc.nextInt()); 50 51 } 52 for(int i=0;i<2;i++) 53 { 54 r[i]=new Cricle(sc.nextInt()); 55 } 56 System.out.println( s[0].getPerimeter()+s[1]. getPerimeter()+r[0].getPerimeter()+r[1].getPerimeter()); 57 58 System.out.println(r[0].getArea()+r[1].getArea()+s[0].getArea()+s[1].getArea()); 59 System.out.println("["+s[0]+", "+s[1]+"]"); 60 System.out.println("["+r[0]+", "+r[1]+"]"); 61 sc.close(); 62 } 63 64 65 66 67 }
四、构造方法
请补充以下代码,完成输出要求。
public class Main { public Main(){ System.out.println("构造方法一被调用了"); } public Main(int x){ this(); System.out.println("构造方法二被调用了"); } public Main(boolean b){ this(1); System.out.println("构造方法三被调用了"); } public static void main(String[] args) { } }
输入格式:
无
输出格式:
输出以下三行: 构造方法一被调用了 构造方法二被调用了 构造方法三被调用了
输入样例:
无
输出样例:
构造方法一被调用了
构造方法二被调用了
构造方法三被调用了
1 public class Main { 2 public Main(){ 3 System.out.println("构造方法一被调用了"); 4 } 5 public Main(int x){ 6 this(); 7 System.out.println("构造方法二被调用了"); 8 } 9 public Main(boolean b){ 10 this(1); 11 System.out.println("构造方法三被调用了"); 12 } 13 public static void main(String[] args) { 14 Main s=new Main(true); 15 16 17 } 18 }
五、构造方法
请补充以下代码,完成输出要求。(注意:需要提交完整代码)
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { } } class RR{ public RR(){ System.out.print("8"); } public RR(int x){ this(); System.out.print("."); } public RR(boolean b){ this(1); System.out.print("00"); } }
输入格式:
无
输出格式:
输出以下字符串:8.00
输入样例:
无
输出样例:
8.00
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 RR s=new RR(true); 4 } 5 } 6 class RR{ 7 public RR(){ 8 System.out.print("8"); 9 } 10 public RR(int x){ 11 this(); 12 System.out.print("."); 13 } 14 public RR(boolean b){ 15 this(1); 16 System.out.print("00"); 17 } 18 }
六、定义类
请补充以下代码,完成输出要求。(注意:需要提交完整代码)
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); int a,b,c,d,e; a = in.nextInt(); b = in.nextInt(); c = in.nextInt(); d = in.nextInt(); e = in.nextInt(); RR rr = new RR(); double dd = rr.fun(a,b,c,d,e); System.out.printf("%.2f",dd); } } class RR{ }
输入格式:
在一行中给出5个不超过1000的正整数。
输出格式:
输出5个整数的平均值,保留小数点后两位。
输入样例:
1 2 3 4 5
输出样例:
3.00
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); 5 int a,b,c,d,e; 6 a = in.nextInt(); 7 b = in.nextInt(); 8 c = in.nextInt(); 9 d = in.nextInt(); 10 e = in.nextInt(); 11 RR rr = new RR(); 12 double dd = rr.fun(a,b,c,d,e); 13 System.out.printf("%.2f",dd); 14 } 15 } 16 class RR{ 17 18 public double fun(int a,int b,int c,int d,int e){ 19 return (a+b+c+d+e)*1.0/5; 20 21 } 22 23 24 }
七、定义类2
请补充以下代码,完成输出要求。(注意:需要提交完整代码)
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { double dd = RR.fun(); System.out.printf("%.2f",dd); } } class RR{ }
输入格式:
在一行中给出5个不超过1000的实数。
输出格式:
输出排在中间的那个数,保留小数点后两位。
输入样例:
1 2 5 4 3
输出样例:
5.00
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 5 6 7 int s[]=new int[5]; 8 for(int i=0;i<5;i++) 9 { 10 s[i]=sc.nextInt(); 11 } 12 13 int na=s[2]; 14 double dd = RR.fun(na); 15 System.out.printf("%.2f",dd); 16 } 17 } 18 class RR{ 19 20 static double fun(int a){ 21 return a; 22 } 23 24 25 }
八、计算年龄
定义一个Birthday类,其成员变量有3个整形变量(出生的年月日):year,month,day;提供构造方法对这3个成员变量进行初始化;提供成员变量的get、set方法;成员函数有getAge(),功能是实现计算到2017年12月25日时该Birthday对象的年龄。编写程序测试这个类。
输入格式:
输入出生的年、月、日(注:输入的年月日以换行隔开)
输出格式:
计算得到年龄
输入样例:
在这里给出一组输入。例如:
1995 12 23
输出样例:
在这里给出相应的输出。例如:
age=22
1 import java.util.*; 2 public class Main { 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in); 5 Birthday birth=new Birthday(); 6 birth.setyear(sc.nextInt()); 7 sc.nextLine(); 8 birth.setmonth(sc.nextInt()); 9 sc.nextLine(); 10 birth.setday(sc.nextInt()); 11 System.out.print("age="+birth.getAge()); 12 } 13 } 14 class Birthday{ 15 private int year=0; 16 private int month=0; 17 private int day=0; 18 19 public int getyear(){ 20 return this.year; 21 } 22 public int getmonth(){ 23 return this.month; 24 } 25 public int getday(){ 26 return this.day; 27 } 28 public void setyear(int year) { 29 this.year=year; 30 } 31 public void setmonth(int month) { 32 this.month=month; 33 } 34 public void setday(int day) { 35 this.day=day; 36 } 37 public int getAge() { 38 int years=2017-this.year; 39 int months=12-this.month; 40 int days=25-this.day; 41 if(months<=0&&days<=0) 42 return years+1; 43 else 44 return years; 45 46 } 47 48 }
九、程序改错题
程序改错题。下述代码有错,请参照程序的输出修改程序。
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Person[] p = new Person[3]; p[0].name = "zhangsan"; p[0].age = 18; p[1].name = "lisi"; p[1].age = 20; p[2].name = "wangwu"; p[2].age = 22; for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) { System.out.println(p[i]); } } } class Person { private String name; private int age; public Person(String name, int age) { super(); this.name = name; this.age = age; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
输入格式:
无
输出格式:
无
输入样例:
输出样例:
zhangsan 18 lisi 20 wangwu 22
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Person[] p = new Person[3]; 4 p[0]=new Person("zhangsan",18); 5 p[1]=new Person("lisi",20); 6 p[2]=new Person("wangwu",22); 7 for (int i = 0; i < p.length; i++) { 8 System.out.println(p[i]); 9 } 10 } 11 } 12 13 class Person { 14 private String name; 15 private int age; 16 17 public Person(String name, int age) { 18 super(); 19 this.name = name; 20 this.age = age; 21 } 22 23 public String getName() { 24 return name; 25 } 26 27 public void setName(String name) { 28 this.name = name; 29 } 30 31 public int getAge() { 32 return age; 33 } 34 35 public void setAge(int age) { 36 this.age = age; 37 } 38 public String toString() { 39 return this.name+" "+this.age; 40 } 41 }
十、程序填空题
补全以下程序,使得程序输出结果与下述结果一致。
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Test test = new Test(true); } } class Test { public Test(){ System.out.println("Constructor one invoked!"); } public Test(int x){ //此处添加代码 System.out.println("Constructor two invoked!"); } public Test(boolean b){ //此处添加代码 System.out.println("Constructor three invoked!"); } }
### 输入格式: 无 ### 输出格式: 无 ### 输入样例: ```in ``` ### 输出样例: ```out Constructor one invoked! Constructor two invoked! Constructor three invoked! ```
1 public class Main { 2 public static void main(String[] args) { 3 Test test = new Test(true); 4 } 5 } 6 7 class Test { 8 public Test(){ 9 System.out.println("Constructor one invoked!"); 10 } 11 public Test(int x){ 12 //此处添加代码 13 this(); 14 System.out.println("Constructor two invoked!"); 15 } 16 public Test(boolean b){ 17 //此处添加代码 18 this(1); 19 System.out.println("Constructor three invoked!"); 20 } 21 22 }
十一、定义商品类,封装成员变量,输出对象
定义一个商品类。创建对象并按指定格式输出它。 商品类要求:
(1)成员变量:商品编号(String) 、商品名称(String)、商品单价(double) (2)成员变量封装,定义为私有属性,并为每个成员变量定义getXXXX,setXXXX方法 (3)定义构造方法,要求带三个参数,参数值用于给成员变量赋值。 (4)重写toString()方法,将对象转换为字符串,格式:商品编号,商品名称,商品单价
测试类要求:
按指定的格式 输入商品信息,调用构造方法生成对象,并输出它。 例:输入:WJ002 记事本 5.5 输出:WJ002,记事本,5.5
输入商品的信息,每个属性值之间用1个空格分隔。 输出 格式,商品的每个属性值之间用逗号分隔。
输入样例:
WJ002 记事本 5.5
输出样例:
WJ002,记事本,5.5
1 import java.util.*; 2 class Goods { 3 private String name; 4 private String score; 5 private double Price; 6 public Goods(String score,String name,double Price) { 7 this.name=name; 8 this.score=score; 9 this.Price=Price; 10 } 11 public double getPrice() { 12 return this.Price; 13 } 14 public String toString() { 15 return this.score+","+this.name+","+this.Price; 16 } 17 } 18 19 20 21 22 public class Main{ 23 24 public static void main(String args[]){ 25 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 26 Goods ga =new Goods(sc.next(),sc.next(),sc.nextDouble()); 27 System.out.println(ga); 28 } 29 }
十二、统计商品总价
消费者购买超市5件商品,输入商品名和价格,输出购买的商品信息,并输出应付的总价。
要求:定义Goods类及其成员变量和方法。 (1)定义Goods类:成员变量有 name, price (2)定义Goods类的带两个参数的构造方法。 (3)定义Goods类的toString()方法,getPrice()方法。
输入格式:
输入5行数据,每行一个商品信息,包括商品名和价格,以一个空格分隔。
输出格式:
输出商品信息,格式:商品名,价格
最后输出总价,格式:should pay:总价
裁判程序如下:
class Main{ public static void main(String args[]){ Goods ga[] =new Goods[5]; Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); for(int i =0;i<5;i++){ ga[i]= new Goods(sc.next(),sc.nextDouble()); } double shouldPay = 0; for(Goods g:ga){ shouldPay += g.getPrice(); System.out.println(g.toString()); } System.out.println("should pay:"+shouldPay); } }
输入样例:
book 5.5 pencil 1.2 pen 8.0 ruler 2.5 eraser 1.0
输出样例:
book,5.5 pencil,1.2 pen,8.0 ruler,2.5 eraser,1.0 should pay:18.2
1 import java.util.*; 2 class Goods { 3 private String name; 4 private double Price; 5 public Goods(String name,double Price) { 6 this.name=name; 7 this.Price=Price; 8 } 9 public double getPrice() { 10 return this.Price; 11 } 12 public String toString() { 13 return this.name+","+this.Price; 14 } 15 } 16 17 18 19 20 public class Main{ 21 22 public static void main(String args[]){ 23 Goods ga[] =new Goods[5]; 24 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); 25 26 for(int i =0;i<5;i++){ 27 ga[i]= new Goods(sc.next(),sc.nextDouble()); 28 } 29 30 double shouldPay = 0; 31 for(Goods g:ga){ 32 shouldPay += g.getPrice(); 33 System.out.println(g.toString()); 34 } 35 36 System.out.println("should pay:"+shouldPay); 37 } 38 }
十三、程序改错1:对象与数组
修改如下程序的语法错误和逻辑错误,使程序运行结果如下:
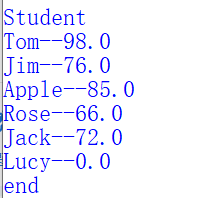
//--------------------Main.java public class Student { private String name; private double score; public String getName(){ return name; } public void setName(String name){ this.name = name; } public double getScore(){ return score; } public void setScore(double score){ this.score =score; } public void toString( ){ return this.name + "--" +this.score ; } } public class Main { public static void main(String args[]) { String []name = {"Tom","Jim","Apple","Rose","Jack" ,"Lucy"}; double [] score = {98,76,85,66,72}; Student [] sGroup = new Student[ name.length ]; for( int i = 0 ; i < sGroup.length ; i++) sGroup[i] = new Student (name[i], score[i]); System.out.println("Student"); for( int i = 0 ; i < sGroup.length ; i++) System.out.println(sGroup[i]); System.out.println("end"); } }
输入格式:
无
输出格式:
Student Tom--98.0 Jim--76.0 Apple--85.0 Rose--66.0 Jack--72.0 Lucy--0.0 end
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 class Student { 3 private String name; 4 private double score; 5 6 public String getName(){ 7 return name; 8 } 9 10 public void setName(String name){ 11 this.name = name; 12 } 13 14 public double getScore(){ 15 return score; 16 } 17 18 public void setScore(double score){ 19 this.score =score; 20 } 21 22 public String toString( ){ 23 return this.name + "--" +this.score ; 24 } 25 public Student(String name,double score) { 26 this.name=name; 27 this.score=score; 28 29 } 30 31 } 32 33 public class Main { 34 public static void main(String args[]) { 35 String []name = new String []{"Tom","Jim","Apple","Rose","Jack","Lucy"}; 36 double [] score = new double []{98,76,85,66,72,0}; 37 38 Student [] sGroup = new Student[ name.length ]; 39 40 for( int i = 0 ; i < sGroup.length ; i++) 41 sGroup[i] = new Student (name[i], score[i]); 42 43 System.out.println("Student"); 44 for( int i = 0 ; i < sGroup.length ; i++) 45 System.out.println(sGroup[i]); 46 47 System.out.println("end"); 48 } 49 }
十四、统计学生年龄异常的人数
定义Student类
(1)成员变量有:姓名,年龄。 (2)对成员变量进行封装。 (3)定义getXXXX,setXXXX方法,其中对年龄的限定条件是:年龄大于0。
定义主类,包含主方法
实现输入5个学生,输出年龄不符合要求 的学生人数和姓名。
如果年龄全部正确,输出“right”,如果全部错误,输出"all wrong"。
输入格式:
5行,每行1个学生信息,包括姓名和年龄
输出格式:
多行,第1行是不符合要求的人数 其余各行是不符合要求的学生的姓名 如果年龄全部正确,输出“right”,如果全部错误,输出"all wrong"。
输入样例:
zhang 18 Li -15 wang 0 zhao 20 wu -20
输出样例:
3
Li
wang
wu
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 class Student { 3 String name; 4 int age; 5 6 public String getName(){ 7 return name; 8 } 9 10 public void setName(String name){ 11 this.name = name; 12 } 13 14 public void setAge(int age){ 15 this.age=age; 16 } 17 public int getAge(){ 18 return this.age; 19 } 20 public Student(String name,int age) { 21 this.name =name; 22 this.age=age; 23 } 24 25 public String toString(){ 26 return this.name; 27 } 28 29 } 30 31 public class Main { 32 public static void main(String args[]) { 33 Scanner sc=new Scanner (System.in); 34 Student [] sGroup = new Student[5]; 35 int s=0; 36 for( int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) 37 { 38 sGroup[i]=new Student(sc.next(),sc.nextInt()); 39 40 } 41 for( int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++) 42 { 43 if(sGroup[i].age<=0) 44 { 45 s+=1; 46 } 47 } 48 if(s==0) 49 { 50 System.out.println("right"); 51 } 52 else if(s==5) 53 { 54 System.out.println("all wrong");} 55 else {System.out.println(s); 56 for( int i = 0 ; i < sGroup.length ; i++) 57 if(sGroup[i].age<=0) 58 System.out.println(sGroup[i]); 59 } 60 61 62 } 63 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号