1.props和方法
一、父组件向子组件传值
父组件通过属性的方式传递参数,子组件通过props来接收父组件传递过来的参数
React中是单向数据流,数据只能从父组件通过属性的方式传给其子组件,如下图: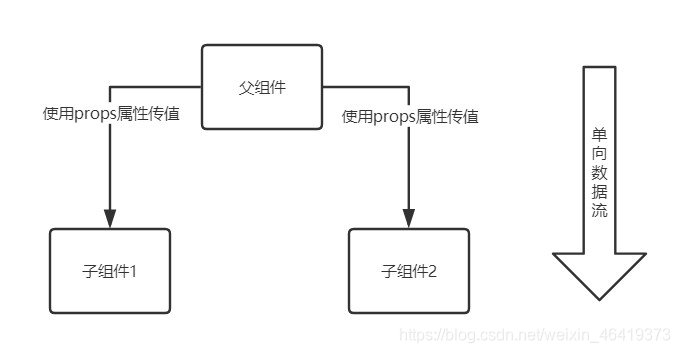
在引用子组件的时候传递,相当于一个属性,例如:在子组件内通过porps.param获取到这个param的值。
父组件向子组件传值,通过props,将父组件的state传递给了子组件。
父组件(直接定义一个属性传值即可):
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import NavigationBar from './NavigationBar'
export class App extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<NavigationBar title="我是父组件向子组件传的值" />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App
子组件(通过this.props.父组件定义的属性 来接收父组件传递过来的参数):
import React from "react";
class NavigationBar extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {
title:''
}
}
render(){
return(
<div>
{this.state.title}
</div>
)
}
componentDidMount(){
this.setState({
title:this.props.title
})
}
}
export default NavigationBar;
效果:
二、子组件向父组件传值
子组件通过调用父组件传递到子组件的方法向父组件传递消息的
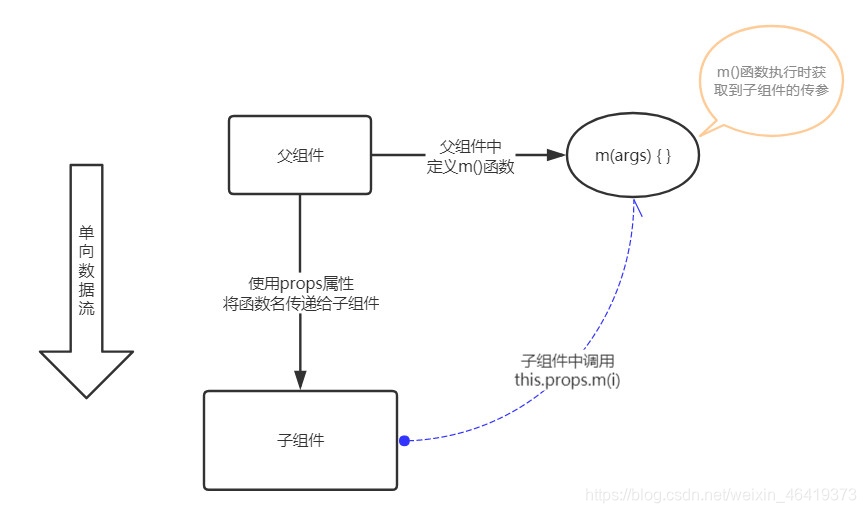
子组件(通过this.props.事件名(参数)的方式向父组件传递参数):
import React from "react";
class NavigationBar extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state = {
title:''
}
}
render(){
return(
<div>
{this.state.title}
<button onClick={()=>{
this.props.titleMessage("我是子组件向父组件传的值")
}}>点击</button>
</div>
)
}
componentDidMount(){
this.setState({
title:this.props.title
})
}
}
export default NavigationBar;
父组件:
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import NavigationBar from './NavigationBar'
export class App extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state={
titleMassage:''
}
}
message=(titleMessage)=>{
console.log(titleMessage);
this.setState({
titleMassage:titleMessage
})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{this.state.titleMassage}
<NavigationBar title="我是父组件向子组件传的值" titleMessage={this.message} />
</div>
)
}
}
export default App
效果:
点击后的效果:
2.Evnentbus
class EventBus {
constructor() {
this.events = this.events || new Object();
}
}
//首先构造函数需要存储event事件,使用键值对存储
//然后我们需要发布事件,参数是事件的type和需要传递的参数
EventBus.prototype.emit = function(type, ...args) {
let e;
e = this.events[type];
// 查看这个type的event有多少个回调函数,如果有多个需要依次调用。
if (Array.isArray(e)) {
for (let i = 0; i < e.length; i++) {
e[i].apply(this, args);
}
} else {
e[0].apply(this, args);
}
};
//然后我们需要写监听函数,参数是事件type和触发时需要执行的回调函数
EventBus.prototype.addListener = function(type, fun) {
const e = this.events[type];
if (!e) { //如果从未注册过监听函数,则将函数放入数组存入对应的键名下
this.events[type]= [fun];
} else { //如果注册过,则直接放入
e.push(fun);
}
};
// 移除监听
EventBus.prototype.removeListener = function (type, fn) {
const handler = this._events.get(type); // 获取对应事件名称的函数清单
// 如果是函数,说明只被监听了一次
if (handler && typeof handler === 'function') {
this._events.delete(type, fn);
} else {
let postion;
// 如果handler是数组,说明被监听多次要找到对应的函数
for (let i = 0; i < handler.length; i++) {
if (handler[i] === fn) {
postion = i;
} else {
postion = -1;
}
}
// 如果找到匹配的函数,从数组中清除
if (postion !== -1) {
// 找到数组对应的位置,直接清除此回调
handler.splice(postion, 1);
// 如果清除后只有一个函数,那么取消数组,以函数形式保存
if (handler.length === 1) {
this._events.set(type, handler[0]);
}
} else {
return this;
}
}
};
const eventBus = new EventBus(); export default eventBus;
然后,我们在login组件中加入
EventBus.emit('login',values.userName)
在需要监听的组件加入
EventBus.addListener('login',(name)=>{
this.setState({user:name})
})
也可以利用node自己的EventEmitter。 解决步骤 1、直接引入并新建实例,不用额外npm install events --save
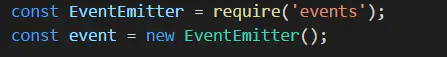
直接引入并新建实例 2、把第一步实例化的event传入子组件
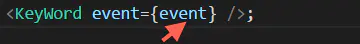
传入子组件 3、发送事件
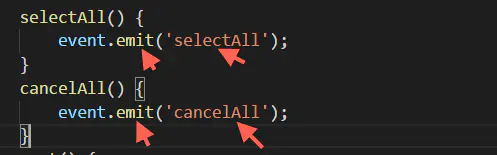
发送事件
注意:event.emit方法中可以传第二个参数用来传值,如下:
event.emit('selectAll', 1);
4、在子组件中监听
下面截图中监听事件中this所指对象已经改变,render方法中的this指组件实例,但this.props.event.on方法的回调函数中的this指EventEmitter实例。
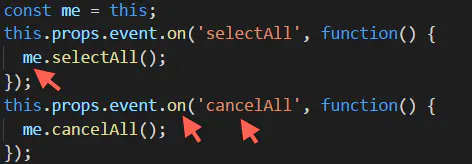
子组件
注意:回调函数的参数用来接收父组件发送过来的值,如下:
this.props.event.on('selectAll', function(value) {
// 参数value即是父组件传过来的值,即value = 1
});
另:第4步截图中监听事件中的回调函数是匿名形式的写法,也可以传入实名参数,如下:
this.props.event.on('selectAll', this.selectAll);
this.props.event.on('cancelAll', this.cancelAll);
需要注意的是,监听事件可以传入匿名函数也可以传入实名函数,但是移除事件的时候,必须传入实名函数,传入匿名函数会有错误
5、移除事件的监听器
componentWillUnmount() {
this.props.event.removeAllListeners('selectAll', this.selectAll);
this.props.event.removeAllListeners('cancelAll', this.cancelAll);
}
这里没有用removeListener,而是用了removeAllListeners,这样更保险,因为在多次切换组件时,我发现removeListener并不能很好的移除事件的监听器。另外触发事件是点击等事件时,监听事件最好用once,而不是on。
3.redux&&react-redux
4.context
旧版本context——适用于React版本为16.x之前
祖先组件
1 import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
2
3 class Child extends Component {
4 static contextTypes = {
5 text: PropTypes.string
6 }
7 render() {
8 return <div>{this.context.text}</div>
9 }
10 }
后代组件
1 import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
2 class Ancestor extends Component {
3 static childContextTypes = {
4 text: PropTypes.string
5 }
6
7 getChildContext() {
8 return {
9 text: 'aaa'
10 }
11 }
12 }
新版本context
创建一个全局context
1 import React from 'react' 2 3 const GlobalContext = React.createContext(); 4 5 export default GlobalContext;
子组件
1 import React, {Component} from 'react'
2 import GlobalContext from './globalContext' // 导入全局context
3
4 export default class Child extends Component {
5 render() {
6 return (
7 <GlobalContext.Consumer>
8 {context => {
9 console.log(context)
10 return (
11 <div>
12 <h4>{context.name}</h4>
13 </div>
14 )
15 }}
16 </GlobalContext.Consumer>
17 )
18 }
19 }
App.js
import Child from './Component/Child'
import GlobalContext from './globalContext'
render() {
return (
<div className="App">
<GlobalContext.Provider
value = {{
name: 'aaa',
}}>
<Child /> // 被传递的子组件,可多个
</GlobalContext.Provider>
)
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号