1、level-运行级别
1.1、什么是运行级别
1.2、运行级别类型
System-Init 运行级别 systemd目标名称 作用
0 runlevel0.target, poweroff.target 关机
1 runlevel1.target, rescue.target 单用户模式
2 runlevel2.target, multi-user.target
3 runlevel3.target, multi-user.target 多用户的文本界面
4 runlevel4.target, multi-user.target
5 runlevel5.target, graphical.target 多用户的图形界面
6 runlevel6.target, reboot.target 重启
1.3、调整运行级别
1.3.1、常用的运行级别
1、systemd使用targets 而不是runlevels
2、默认情况下,有两个主要目标:
multi-user.target:类似于运行级别3
graphical.target :类似于运行级别5
1.3.2、查看系统默认运行级别
]# systemctl get-default
multi-user.target
1.3.3、要设置默认目标,请运行
# 例如将默认换为graphical.target
]# systemctl set-default graphical.target
]# systemctl get-default
graphical.target
2、systemd
2.1、基础
2.1.1、systemd的由来
Linux一直以来都是采用init进程作为祖宗进程,但是init有两个缺点:
1、启动时间长。Init进程是串行启动,只有前一个进程启动完,才会启动下一个进程;
2、启动脚本复杂,初始化完成后系统会加载很多脚本,脚本都会处理各自的情况,这会让脚本多而复杂。
Centos5启动速度慢,串行启动过程,无论进程相互之间有无依赖关系。
Centos6启动速度有所改进,有依赖的进程之间依次启动,而其它没有依赖关系的则并行同步启动。
Centos7所有进程无论有无依赖关系则都是并行启动(当然很多时候进程没有真正启动而是只有一个信号或者说是标记而已,在真正利用的时候才会真正启动。)
2.1.2、什么是systemd
systemd即为system daemon守护进程,systemd主要解决上文的问题而诞生。
systemd的目标是,为系统的启动和管理提供—套完整的解决方案。
2.1.3、systemd的优势
1、最新系统都采用systemd管理RedHat7、CentoS7、Ubuntu15;
2、Centos7支持开机并行启动服务,显著提高开机启动效率;
3、Centos7关机只关闭正在运行的服务,而Centos6全部都关闭一次;
4、Centos7服务的启动与停止不在使用脚本进行管理,也就是/etc/init.d下不在有脚本;
5、Centos7使用systemd解决原有模式缺陷,比如:原有service不会关闭程序产生的子进程;
2.1.4、systemd配置文件
/usr/lib/systemd/system/ : 类似centos6系统的启动脚本/etc/init.d/
/etc/systemd/system/ : 类似 centos6系统的/etc/rc.d/rcN.d/
/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/
Systemd 服务配置文件 : https://www.cnblogs.com/hongdada/p/9700900.html
2.2、systemd相关命令
2.2.1、服务启动与停止相关
systemctl命令 作用
systemctl start crond.service 启动服务
systemctl stop crond.service 停止服务
systemctl restart crond.service 重启服务
systemctl reload crond.service 重新加载配置
systemctl status crond.servre 查看服务运行状态
systemctl is-active sshd.service 查看服务是否在运行中
systemctl mask crond.servre 禁止服务运行
systemctl unmask crond.servre 取消禁止服务运行
2.2.2、sysytemctl status查看此守护进程的状态
状态 描述
loaded 服务单元的配置文件已经被处理
active(running) 服务持续运行
active(exited) 服务成功完成一次的配置
active(waiting) 服务已经运行但在等待某个事件
inactive 服务没有在运行
enabled 服务设定为开机运行
disabled 服务设定为开机不运行
static 服务开机不启动,但可以被其他服务调用启动
2.2.3、systemctl设置服务开机启动、不启动、查看各级别下服务启动状态等常用命令
systemctl命令(7系统) 作用
systemctl enable crond.service 开机自动启动
systemctl disable crond.service 开机不自动启动
systemctl list-unit-files 查看各个级别下服务的启动与禁用
systemctl is-enabled crond.service 查看特定服务是否为开机自启动
systemctl daemon-reload 创建新服务文件需要重载变更
2.2.4、systemctl命令来管理服务器重启或关机
#关机相关命令
systemctl poweroff #立即关机,常用
#重启相关命令
systemctl reboot #重启命令,常用
2.2.5、systemctl的journalctl日志
journalctl -n 20 # 查看最后20行
journalctl -f # 动态查看日志
journalctl -p err # 查看日志的级别
journalctl -u crond # 查看某个服务的单元的日志
3、单用户模式
如何使用单用户模式进行变更系统密码?以Centos7系统为例︰(Centos6破解万式请自行百度)
3.1、重启Linux系统主机并出现引导界面时,按下键盘上的e键进入内核编辑界面
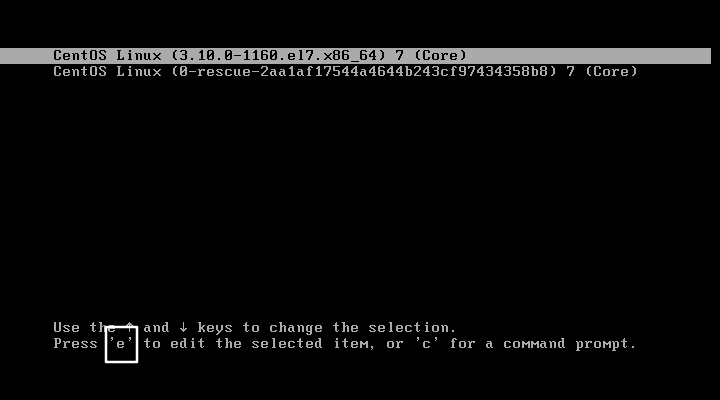
3.2、添加enforcing=0 init=/bin/bash ,然后按下Ctrl +x组合键来运行修改过的内核程序
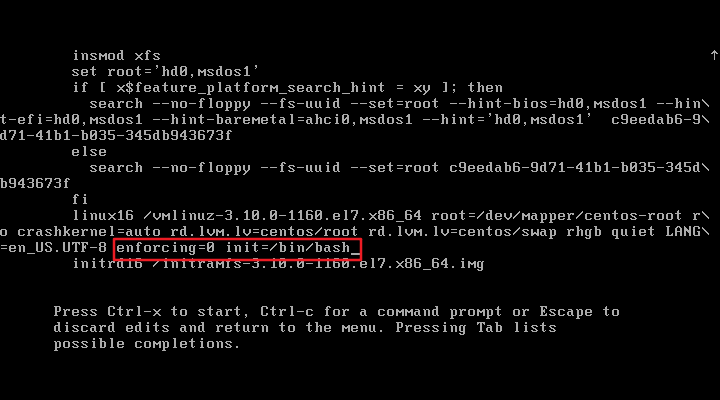
3.3、进入到系统的单用户模式,依次输入以下命令,重启操作系统完毕,然后使用新密码来登录
# /默认是只读,重新挂载可读写
mount -o rw,remount /
# 非交互式,设置root密码
echo "password" | passwd --stdin root
# 执行exec,init重新引导系统
exec /sbin/init
3.4、重新登陆测试是否成功
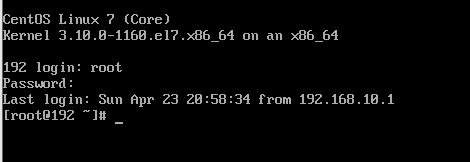





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号