SpringBoot设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置。另外SpringBoot通过集成大量的框架使得依赖包的版本冲突,以及引用的不稳定性等问题得到了很好的解决。
一、新建springboot
新建一个Spring Initializr项目

选择jdk版本

选择项目所需依赖
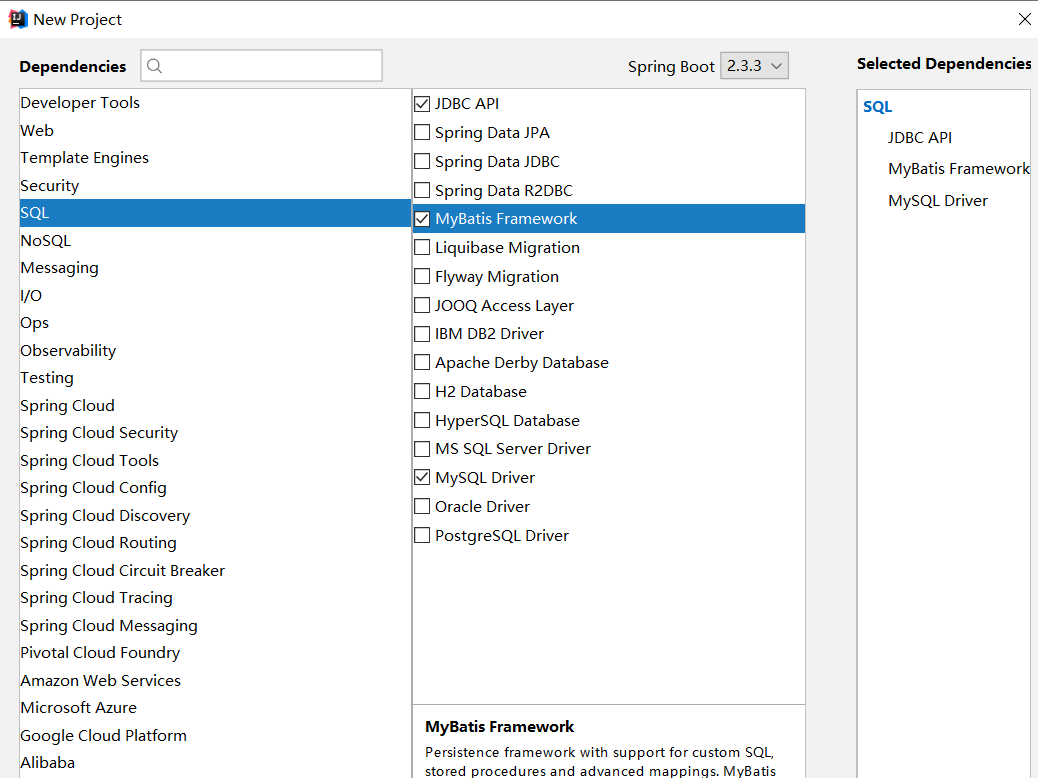
这样就构建好了一个springboot项目,等待maven下载好相应的jar包,查看构建好的pom.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.3.3.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>com.example</groupId> <artifactId>demo</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>demo</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.1.3</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>mysql</groupId> <artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId> <scope>runtime</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId> <artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
修改配置文件,新建一个application.yml文件,删除application.properties文件(备注:其实SpringBoot底层会把application.yml文件解析为application.properties)
server: port: 8080 spring: datasource: username: root password: 123456 url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mysql?useUnicode=true&serverTimezone=UTC driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver mybatis: mapper-locations: classpath:mapping/*Mapper.xml type-aliases-package: com.example.demo.entity #showSql logging: level: com: example: mapper : debug
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
在项目中配置多套环境的配置方法:因为现在一个项目有好多环境,开发环境,测试环境,准生产环境,生产环境,每个环境的参数不同,所以我们就可以把每个环境的参数配置到yml文件中,这样在想用哪个环境的时候只需要在主配置文件中将用的配置文件写上就行如application.yml。
在Spring Boot中多环境配置文件名需要满足application-{profile}.yml的格式,其中{profile}对应你的环境标识,比如:application-dev.yml:开发环境、application-sit.yml:测试环境、application-prod.yml:生产环境,至于哪个具体的配置文件会被加载,需要在application.yml文件中通过spring.profiles.active属性来设置,其值对应{profile}值。
二、实现具体业务
新建数据库表person
CREATE TABLE `Person` (
-> `id` int(32) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
-> `userName` varchar(32) NOT NULL,
-> `passWord` varchar(50) NOT NULL,
-> `realName` varchar(32) DEFAULT NULL,
-> PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
-> ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
查看数据表person是否创建成功,desc person

插入两条数据以备使用
insert into Person(id,userName,passWord,realName) Values(1,'成是非','123456','成坤');
insert into Person(id,userName,passWord,realName) Values(2,'段云','111222','赵云');
插入成功后查看数据表是否存在数据
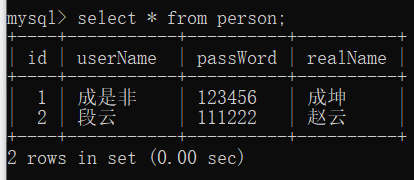
新建bean文件、访问层、实现层、DAO文件以及xml文件
package com.example.demo.entity; public class User { private Integer id; private String userName; private String passWord; private String realName; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getUserName() { return userName; } public void setUserName(String userName) { this.userName = userName; } public String getPassWord() { return passWord; } public void setPassWord(String passWord) { this.passWord = passWord; } public String getRealName() { return realName; } public void setRealName(String realName) { this.realName = realName; } @Override public String toString() { return "User{" + "id=" + id + ", userName='" + userName + '\'' + ", passWord='" + passWord + '\'' + ", realName='" + realName + '\'' + '}'; } }
package com.example.demo.controller; import com.example.demo.service.UserService; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController @RequestMapping("/testBoot") public class UserController { @Autowired private UserService userService; @RequestMapping("getUser/{id}") public String GetUser(@PathVariable int id){ return userService.Sel(id).toString(); } }
package com.example.demo.service; import com.example.demo.entity.User; import com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; @Service public class UserService { @Autowired UserMapper userMapper; public User Sel(int id){ return userMapper.Sel(id); } }
package com.example.demo.mapper; import com.example.demo.entity.User; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; @Repository public interface UserMapper { User Sel(int id); }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper"> <resultMap id="BaseResultMap" type="com.example.demo.entity.User"> <result column="id" jdbcType="INTEGER" property="id" /> <result column="userName" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="userName" /> <result column="passWord" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="passWord" /> <result column="realName" jdbcType="VARCHAR" property="realName" /> </resultMap> <select id="Sel" resultType="com.example.demo.entity.User"> select * from person where id = #{id} </select> </mapper>
完成以上,在启动类里加上注解用于给出需要扫描的mapper文件路径
package com.example.demo; import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; @MapperScan("com.example.demo.mapper") @SpringBootApplication public class DemoApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args); } }
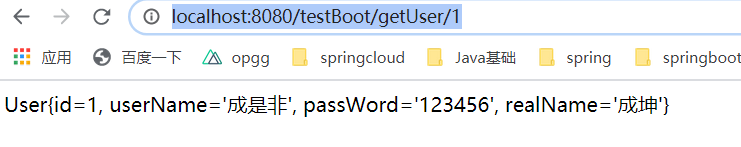
输入地址 http://localhost:8080/testBoot/getUser/1



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号