2. List详解
简介
本篇主要就List中常用的3个子类进行介绍
ArrayList详解
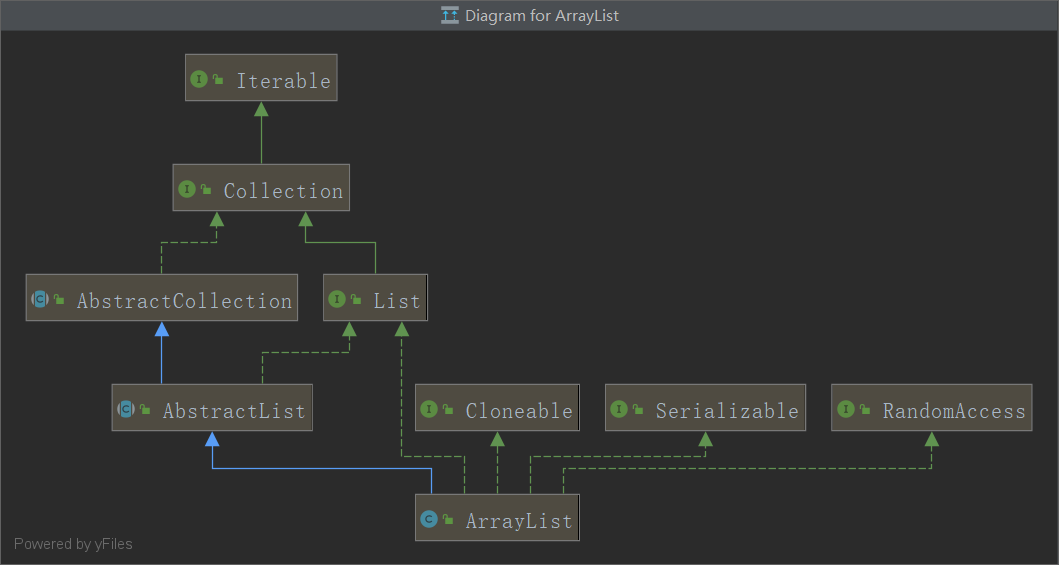
属性介绍
elementData即为底层实现数组,用于存储元素
size为大小
DEFAULT_CAPACITY默认容量为10
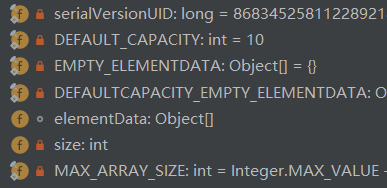
构造函数
比较简单,看看就行了
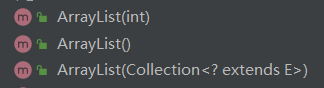
ArrayList(int initialCapacity)
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
ArrayList()
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c)
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
elementData = c.toArray();
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
新增方法
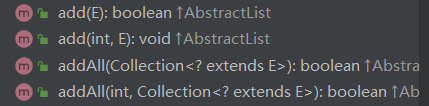
后两个方法注意一是保证扩容之后能插入进去,二是使用System.arraycopy方法进行数据拷贝,讲一下前两个方法
boolean add(E e)
源码如下:
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
关键要看一下ensureCapacityInternal方法
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
//
ensureExplicitCapacity(calculateCapacity(elementData, minCapacity));
}
private static int calculateCapacity(Object[] elementData, int minCapacity) {
// 如果当前是空数组,则返回默认容量10和添加元素后容量的较大值
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
return Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
// 否则返回需要的容量值
return minCapacity;
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
// 结构改变计数+1
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
// 先按扩容50%计算一个新容量
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
// 保证新容量够用
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
// TODO 为何-8?
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
注意扩容到了1.5倍,
void add(int index, E element)
多了个下标的检查,别的没啥
private void rangeCheckForAdd(int index) {
if (index > size || index < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
获取方法
没啥好讲的,就是检查下标,返回元素
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
return elementData(index);
}
private void rangeCheck(int index) {
if (index >= size)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException(outOfBoundsMsg(index));
}
E elementData(int index) {
return (E) elementData[index];
}
删除方法
clear()
原本以为直接把引用指向一个新的空数组,没想到是遍历置空,看注释是帮助gc
public void clear() {
modCount++;
// clear to let GC do its work
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
elementData[i] = null;
size = 0;
}
E remove(int index)
- 下标检查
- 把下标之后的元素用arrayCopy复制到下标开始的位置,即大家一起往前移
- 此时最后一个元素是多余的,置空
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // clear to let GC do its work
return oldValue;
}
boolean remove(Object o)
移除思路和上面一致,关键是要确定下标,遍历找到第一个符合条件的,允许找null
设置方法
E set(int index, E element)
注意会返回老元素
Vector
关于Vector,看了下源码,就是方法上加Sychronized关键字,底层实现还是数组,注意扩容直接扩大一倍。
现在用线程安全,可以用Collections.synchronizedList,里面用的是 final Object mutex,方法中Synchronized(mutex),mutex可以由构造函数传入。
LinkedList
底层为双向链表,实现Deque接口
// TODO 数据结构的实现后续安排一下。
添加方法
boolean add(E e)
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null);
last = newNode;
if (l == null)
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
就是追加,注意Node的pre和next就好,考虑一下边界值
void add(int index, E element)
凡是有index的,必然先检查index
找到那个元素,然后进行解绑绑定操作,关键就是下面的linkBefore
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// assert succ != null;
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}
获取太简单,理解Node就ok
移除
关键理解unlink方法就可以
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
// assert x != null;
final E element = x.item;
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}
总结
list比较简单,瞄一眼源码就明明白白。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号