寒假集训专题三:基础数据结构
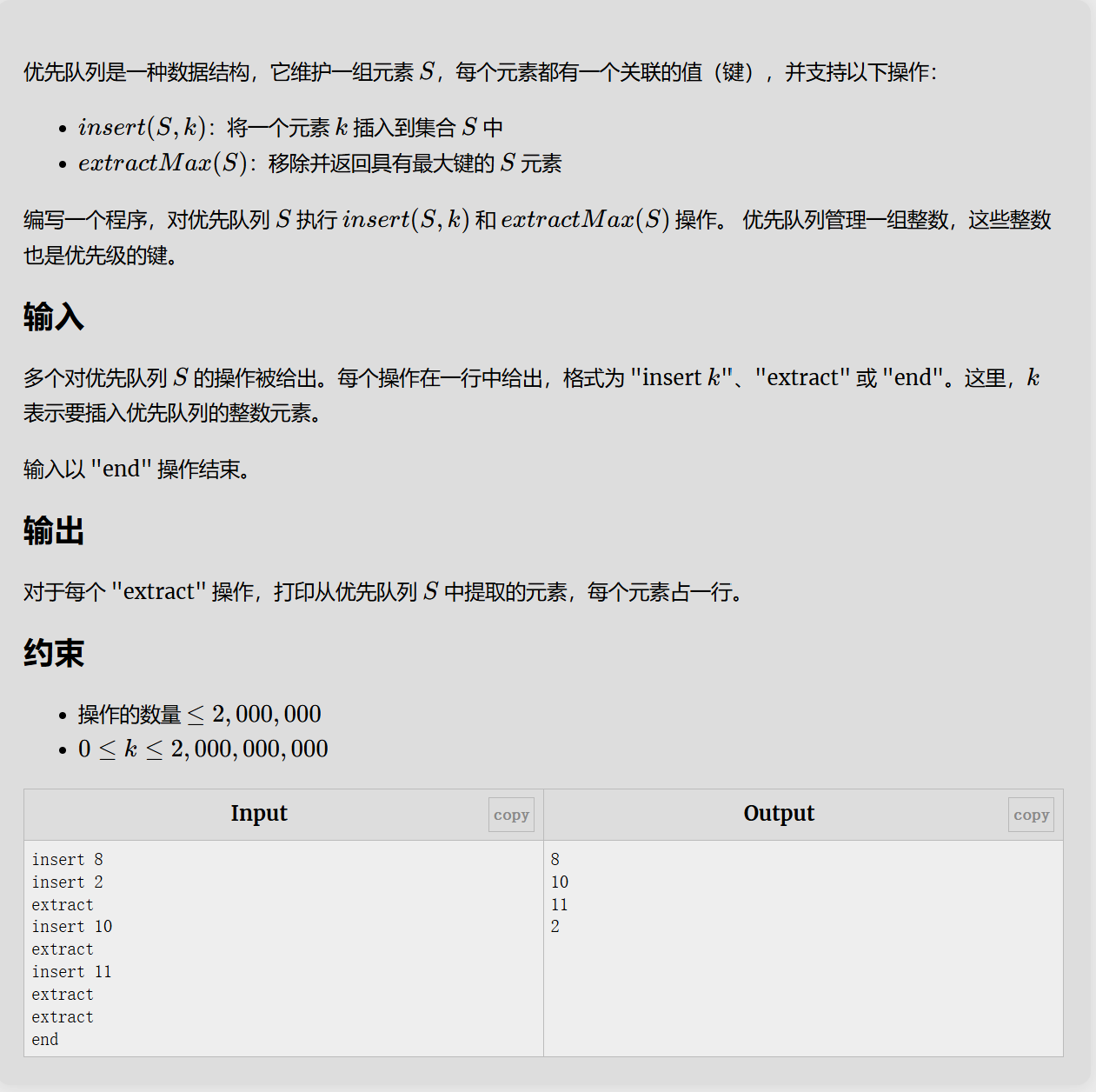
ESAY1:Priority Queue
解题思路:
这道题是很基础的对于优先队列数据结构的应用,目的可能是熟悉优先队列的使用,题目提到的insert()函数就是库函数对优先队列定义的push()函数,插入完成后会对队列优先级进行一个维护,本质上优先队列是一种堆数据结构,默认是大顶堆。可以更改它的优先级,在后面题目中可以使用.
那么在对于输入指令的执行中,我们就可以直接地调用我们要使用的优先队列对应的函数
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string op = "";
priority_queue<long long> pq;
while( op != "end" )
{
cin >> op;
if( op == "insert" )
{
long long k;
cin >> k;
pq.push(k);
}
else if( op == "extract" )
{
cout << pq.top() << endl;
pq.pop();
}
else
{
continue;
}
}
return 0;
}
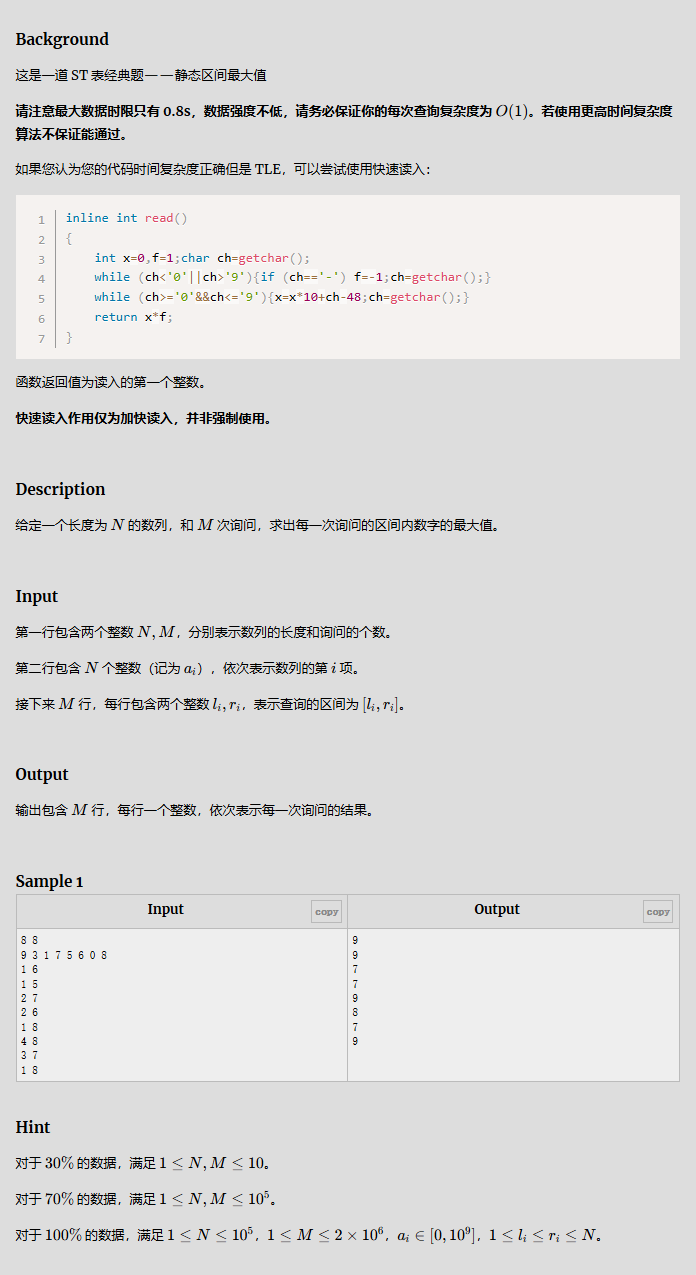
ESAY2:ST 表 && RMQ 问题
解题思路:
st表通常用来解决区间最值问题
st[i][j] 表示从位置 i 开始,长度为2的j次方的区间的最大值。
通过递推公式:
st[i][j]=max(st[i][j−1],st[i+2的j−1次方][j−1])
对于任意区间 [l,r],可以将其拆分为两个长度为2的k次方的区间,其中 k=⌊log2(r−l+1)⌋。
查询结果为:max(st[l][k],st[r−2的k次方+1][k])
此题快速读入是为了不卡时间限制,但是同时也可以通过cin关闭流同步Std::ios::sync_with_stdio (false)
将cin和stdin解绑,同时把std::endl换成"\n",这样就不会刷新缓冲区,加快代码运行速度
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
inline int read() {
int x = 0, f = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') {
if (ch == '-') f = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = x * 10 + ch - '0';
ch = getchar();
}
return x * f;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int N = read(), M = read();
int h[N + 1], li[N + 1] = {0}, smax[N + 1][20];
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
h[i] = read();
}
// 倍增关系,预处理数组
for (int i = 2; i <= N; i++) {
li[i] = li[i >> 1] + 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; i++) {
smax[i][0] = h[i];
}
for (int j = 1; (1 << j) <= N; j++) {
for (int i = 1; i <= N - (1 << j) + 1; i++) {
smax[i][j] = max(smax[i][j - 1], smax[i + (1 << (j - 1))][j - 1]);
}
}
while (M--) {
int a = read(), b = read();
int w = li[b - a + 1]; // 步长
int A = max(smax[a][w], smax[b - (1 << w) + 1][w]);
cout << A << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
MEDIUM1:合并果子

解题思路:
这道题在ds上对优先队列的实验学习中有类似的题,并且根据贪心算法的思想,我们要做到让总时间最小,那么我们尽可能让每一次使用的时间最小,那么每一次都拿出最小的两个数据合并再次推入队列中,不就能做到了吗。最后设置循环终止条件为队列中仅存最后一个元素,此时合并已经完成。
我们要注意优先队列默认为大顶堆,我们可以通过priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>>
来设置优先队列为小顶堆,当然自己设计优先队列就按需求来。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
//利用小顶堆来存储数据
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> pq;
int sum = 0;
cin >> n;
for( int i = 0; i < n; i++ )
{
int x;
cin >> x;
pq.push(x);
}
//当堆中仅有一个数据时,合并完成
while( pq.size() != 1 )
{
//取出最小数
int a = pq.top();
pq.pop();
//取出第二小的数
int b = pq.top();
pq.pop();
//合并两数,加入结果并将结果推进堆内
sum += a+b;
pq.push(a+b);
}
cout << sum << "\n";
}
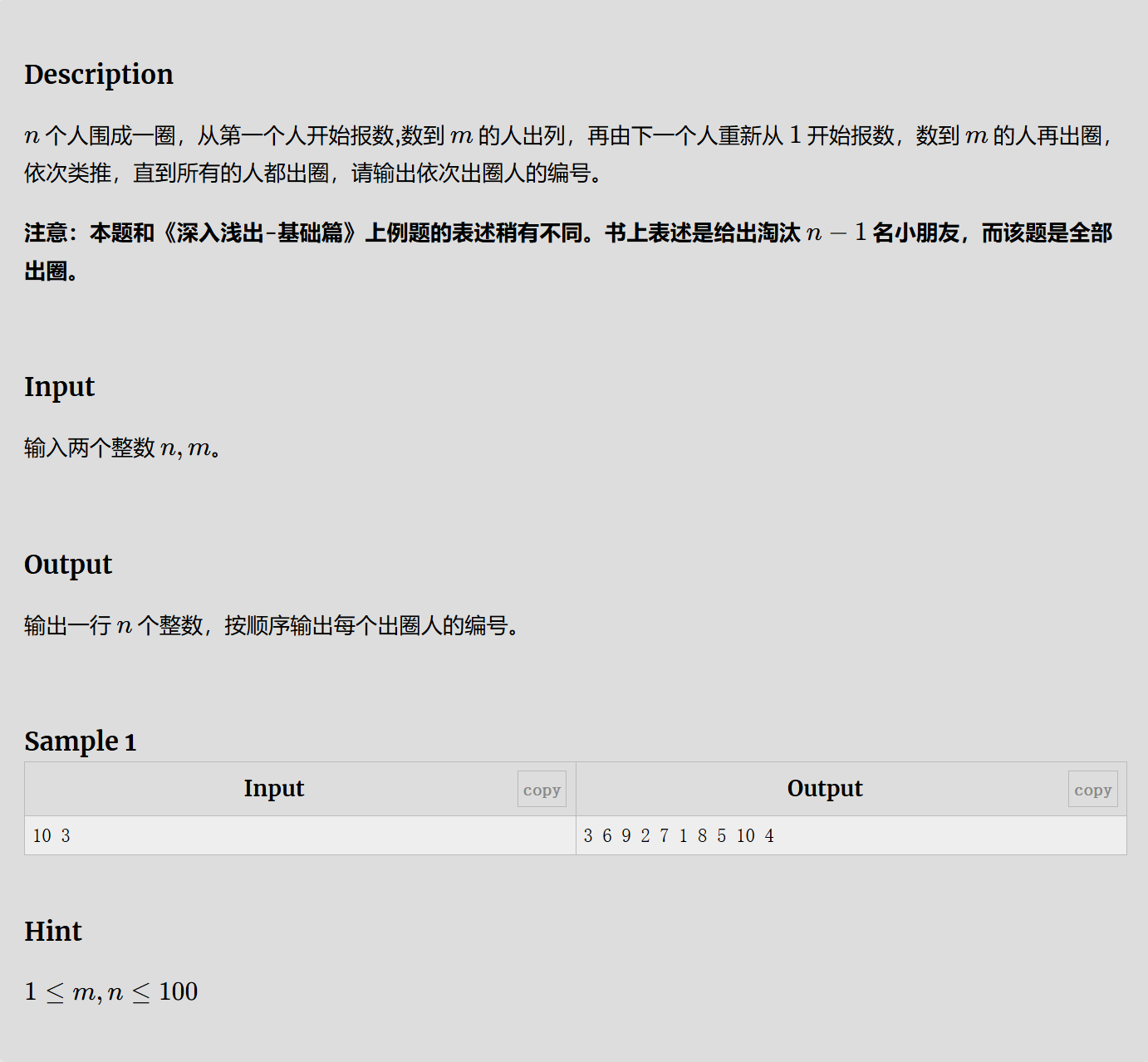
MEDIUM2:约瑟夫问题
解题思路:
一开始想到的是循环数组和循环链表这一类的数据结构,数组的下标处理较为麻烦,并且很可能出现越界这类情况,链表的代码比较麻烦(我个人认为),最后选择了队列作为载体完成这一题。
我们可以进行队列元素的顺序遍历,把不符合编号要求的推到队列尾部,形成一个圆环,将符合要求的推出,输出编号。检测循环终止条件就设计为题设强调的队列为空。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int count = 0;
queue<int> q;
int m,n;
cin >> n >> m;
for( int i = 1; i <= n; i++ )
{
q.push(i);
}
while( !q.empty() )
{
count++;
if( count != m )
{
int temp = q.front();
q.pop();
q.push(temp);
}
else
{
int ans = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << ans << ((!q.empty()) ? " " : "\n");
count = 0;
}
}
return 0;
}
学习总结:
之前从来没有学过st表相关内容,只能说能学的还很多,st表可以很高效的解决区间最值问题,不用遍历滑动窗口就能找到最值。
其他倒是都还用过。
我自己的st表模板:
int N,M;
cin >> N >> M;
int h[N], li[N]={0}, smax[N][N], smin[N][N];
for( int i = 1; i <= N; i++ )
{
cin >> h[i];
}
//倍增关系
for( int i = 2; i <= N; i++ )
{
li[i] = li[i>>1] + 1;
}
for( int i = 1; i <= N; i++ )
{
smax[i][0] = h[i];
smin[i][0] = h[i];
}
for( int j = 1; ( 1<<j ) <= N; j++ ) //1<<j是st表容量,倍增型的
{
for( int i = 1; i <= N - (1<<j) + 1 ; i++ )
{
//1<<(j-1)是步长
smax[i][j] = max( smax[i][j-1],smax[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1] );
smin[i][j] = min( smin[i][j-1],smin[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1] );
}
}
while( M-- )
{
// int a,b;
// cin >> a >> b;
// int w = li[b-a+1];//步长
// int A = max( smax[a][w], smax[b-(1<<w)+1][w] );
// int B = min( smin[a][w], smin[b-(1<<w)+1][w] );
// cout << A << " " << B << endl;
int a,b;
cin >> a >> b;
int w = li[b-a+1];//步长
int A = max( smax[a][w], smax[b-(1<<w)+1][w] );
cout << A << endl;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号