matlab 三维激光雷达点云的地面与障碍物检测
基于激光雷达的地面与障碍物检测
这个例子告诉我们如何去检测地平面并且找到三维LIDAR数据中与车相近的障碍物。
这个过程能够方便我们对汽车导航的可行驶区域规划。
注:每一帧的雷达属于都被存储为三维的雷达点云。为了能够高效的处理这些数据。快速的指出与搜索能力是需要的。通过kd-tree结构处理数据。周围平面通过RANSAC算法来拟合(RANSAC算法是一个稳健的模型拟合方法)。这个例子也展示了如何使用点云来实现多帧点云的动画过程。
选择要显示的点云区域
首先, 在车辆周围选择一个目标区域, 并配置pcplayer以显示它。
1.加载点云序列。
load('01_city_c2s_fcw_10s_Lidar.mat');
pcloud = d.LidarPointCloud;
2.为了规定车辆周围的环境, 在左右边20米(自由配置,此处选20)左右的车辆, 和50米(自由配置,此处选50)的前面和后面的车辆被纳入检测范围。
%% 设置第一帧点云格式 pc = pcloud(1).ptCloud; %设置目标区域. xBound = 50; yBound = 20; xlimits = [-xBound, xBound]; ylimits = [-yBound, yBound]; zlimits = pc.ZLimits; player = pcplayer(xlimits, ylimits, zlimits); % 将点云数据导入目标区域,不合规的点云将不会被导入 indices = find(pc.Location(:, 2) >= -yBound ... & pc.Location(:, 2) <= yBound ... & pc.Location(:, 1) >= -xBound ... & pc.Location(:, 1) <= xBound); % 选择并图形化精简后的点云 pc = select(pc, indices); view(player, pc)
分离地面平面与障碍物
找到地面平面并移出地面平面。使用RANSAC算法来找到并拟合地平面。正常平面方向应该粗略指向Z轴。所有内收的点都应该在地面平面的20cm内。
maxDistance = 0.2; % 0.2米 referenceVector = [0, 0, 1]; [~, inPlanePointIndices, outliers] = pcfitplane(pc, maxDistance, referenceVector);
为点云中所有的点附着一种颜色标签。使用绿色来表示地平面,红色来表示10米内LIDAR传感器能找到的障碍物。
labelSize = [pc.Count, 1];
colorLabels = zeros(labelSize, 'single');
% 设置颜色谱来描述不同的点云
colors = [0 0 1; ... %蓝色作为未被标签化的点云
0 1 0; ... % 绿色作为地面点云
1 0 0; ... % 红色作为障碍物点云
0 0 0]; % 汽车点云
blueIdx = 0; % 将所有点云初始化为蓝色
greenIdx = 1;
redIdx = 2;
blackIdx = 3;
% 标签化地面点云
colorLabels(inPlanePointIndices) = greenIdx;
% 选择出不是地面点云的点云
pcWithoutGround = select(pc, outliers);
重新获得的点云在10米半径以内的障碍物
sensorLocation = [0,0,0]; % 将LIDAR传感器放在车的中心坐标 radius = 10; nearIndices = findNeighborsInRadius(pcWithoutGround, sensorLocation, radius); nearPointIndices = outliers(nearIndices); % 将障碍物点云标签化 colorLabels(nearPointIndices) = redIdx;
分离本车雷达点云
因为雷达安装在车的本身,所有的点云数据会包括雷达他本身,比如车顶或者车身。这些点云离车最近却不是障碍物。重新获得这些包围着汽车的点云。使用这些点云来形成一个三维边界立方体来代表本车。
radius = 3; nearIndices = findNeighborsInRadius(pcWithoutGround, sensorLocation, radius); vehiclePointIndices = outliers(nearIndices); pcVehicle = select(pcWithoutGround, nearIndices);
形成一个三维立方体并标签化本车点云
delta = 0.1;
selfCube = [pcVehicle.XLimits(1)-delta, pcVehicle.XLimits(2)+delta ...
pcVehicle.YLimits(1)-delta, pcVehicle.YLimits(2)+delta ...
pcVehicle.ZLimits(1)-delta, pcVehicle.ZLimits(2)+delta];
colorLabels(vehiclePointIndices) = blackIdx;
显示所有被标签化的点云进入点云播放器,使用我们之前设定的数字化的标签。
colormap(player.Axes, colors) view(player, pc.Location, colorLabels); title(player.Axes, 'Segmented Point Cloud');
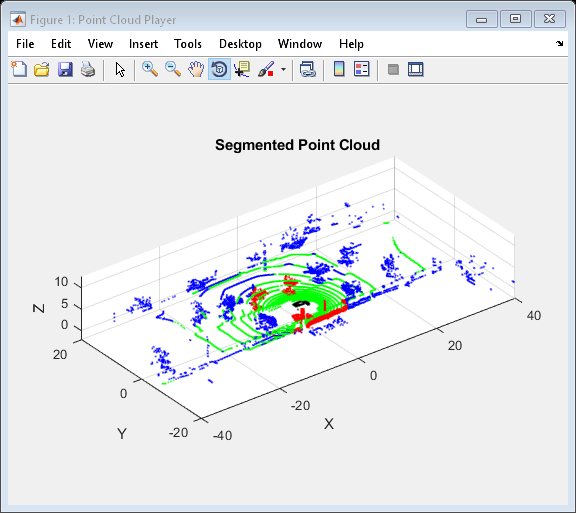
处理点云序列(注:形成点云播放器)
现在我们有了点云播放器,并已经配置好它并且已经处理好标签化点云过程。现在开始处理整个点云序列。
for k = 2:length(pcloud)
pc = pcloud(k).ptCloud;
% 将下一帧的点云数据导入
indices = find(pc.Location(:, 2) >= -yBound ...
& pc.Location(:, 2) <= yBound ...
& pc.Location(:, 1) >= -xBound ...
& pc.Location(:, 1) <= xBound);
pc = select(pc, indices);
colorLabels = zeros(pc.Count, 1, 'single'); % 创造标签阵列
% 拟合地面平面
[~, inPlanePointIndices, outliers] = pcfitplane(pc, maxDistance, referenceVector);
colorLabels(inPlanePointIndices) = greenIdx;
pcWithoutGround = select(pc, outliers);
% 找到与障碍物相关的点
radius = 10;
nearIndices = findNeighborsInRadius(pcWithoutGround, sensorLocation, radius);
nearPointIndices = outliers(nearIndices);
colorLabels(nearPointIndices) = redIdx;
%找到与本车相关的点
nearIndices = findPointsInROI(pcWithoutGround, selfCube);
vehiclePointIndices = outliers(nearIndices);
colorLabels(vehiclePointIndices) = blackIdx;
% 显示结果
view(player, pc.Location, colorLabels);
end
这样你就可以看到连续的点云处理界面。
posted on 2018-09-07 17:13 组合导航定位感知研究 阅读(7076) 评论(7) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号