Python学习第五天基本数据类型及内部方法part1
一、可变类型与不可变类型
可变型:值变了,但ID没变,证明没有新生新的值而是在改变原值,原值是可变类型
y=['a','b','c'] print(id(y)) y[0]='A' print(y) print(id(y)) y的ID没变
不可变型:值变了,ID与变了,证明生成了新的值而不是在改变原值,原值是不可变类型
x=10 print(id(x)) x=11 print(id(x)) #x的ID发生改变
二、数字类型
整型
1、基本使用
(1)用途:记录年龄/等级/各种号码
(2)定义:age=18 age=int(age)
(3)常见操作和内置方法
赋值运算、比较运算、比较运算
2、该类型的总结
(1)只存一个值
(2)不可变
浮点型float
1、基本使用:
(1)用途:记录身高、体重、薪资
(2)定义方式:salary=1.3 salary=float(1.3)
(3)常用操作和内置方法:
赋值、比较、算术
2、该类型总结
(1)存一个值
(2)不可变
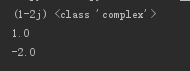
*了解:复数
y=['a','b','c'] print(id(y)) y[0]='A' print(y) print(id(y))
长整型
其他进制=》十进制
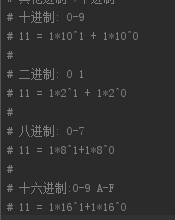
十进制=》其他进制
print(bin(13)) # 十进制=>二进制 print(oct(13)) # 十进制=>八进制 print(hex(13)) # 十进制=>十六进制

三、字符串类型
1、基本使用
(1)用途:记录描述性质的特征,比如名字、地址、性别
(2)定义;在单引号、双引号、三引号内包含的一串字符
msg=''aaa'bbb'''
可以将任意类型转换成字符串
str(1) str(1.3) x=str([1,2,3]) print(x,type(x)
(3)常用操作内置的方法
#1、按索引取值(正向取+反向取):只能取
msg='hello world' print(msg[0]) print(msg[5]) print(msg[len(msg)-1]) print(msg[-1])
#2、切片(顾头不顾尾):想要从一个大字符串中切除一个小字符串
msg='hello world' print(msg[0:5]) print(msg) print(msg[0:5:2]) #0 2 4
*了解
msg='hello world' print(msg[-1:-5:1]) print(msg[-1:-5:-1]) #d l r o print(msg[0:5:1])
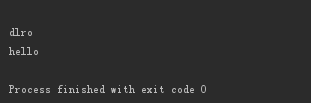
print(msg[-1::-1])#掌握
#3、长度len
字符串里元素的个数
#4、成员运算in和not in
msg='yangyuanhu 老师是一个非常虎的老师' print('yangyuanhu' in msg) print('虎' not in msg) print(not '虎' in msg)
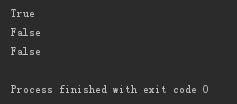
#5、移除字符串左右两边的字符strip:默认是去空格
pwd=' 1 23 ' res=pwd.strip(' ') print(res) #1 23 pwd=input('>>: ').strip() #pwd='123' if pwd == '123': print('密码输入正确') pwd='******12*3****' print(pwd.strip('*')) #12*3 pwd='****/&^**123**^*/*&' print(pwd.strip('*/&^')) #123 print(pwd.strip('*/&')) #^**123**^ #^**123**^
#6、切分split针对有规律字符串按照某个字符切成列表
info='yyhdsb|18|female' li=info.split('|',1) print(li)
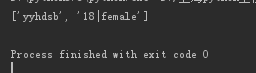
#7、循环
msg='hello' for item in msg: print(item)
2、该类型总结
(1)存一个值
(2)有序
(3)不可变
s1='hello' print(id(s1)) s1='world' print(id(s1))
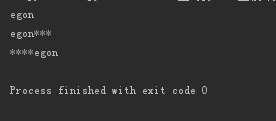
print('****egon***'.strip('*')) print('****egon***'.lstrip('*')) print('****egon***'.rstrip('*'))
2、lower、upper
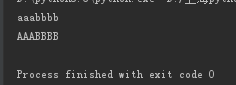
print('AAAbbbb'.lower()) print('AAAbbbb'.upper())
3、startswith,endswith
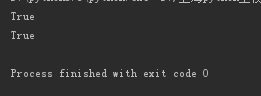
print('alex is sb'.startswith('alex')) print('alex is sb'.endswith('sb'))
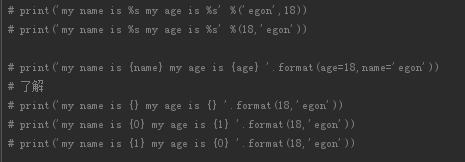
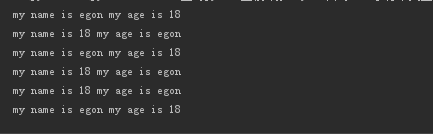
4、format的三种玩法
5、split、rsplit
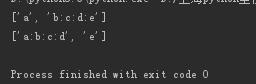
msg='a:b:c:d:e' print(msg.split(':',1)) print(msg.rsplit(':',1))
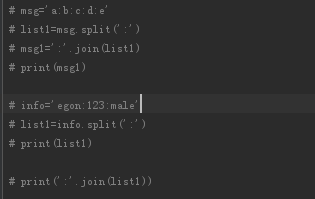
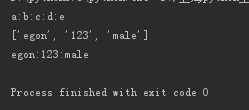
6、join
7、replace
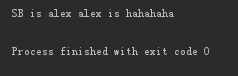
msg='alex is alex alex is hahahaha' print(msg.replace('alex','SB',1))
8、isdigit
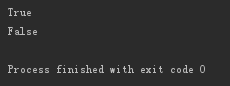
print('123'.isdigit()) # 只能判断纯数字的字符串 print('12.3'.isdigit())
*了解的操作
1、find、rfind、index、rindex、count
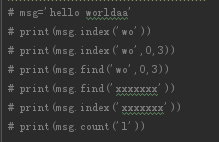
6 报错 -1 -1 报错 3
2、center、ljust、rjust、zfill
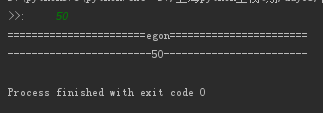
name=input('>>: ').strip() print('egon'.center(50,'=')) print(('%s' %name).center(50,'-'))
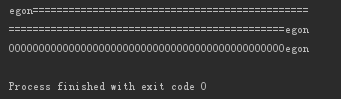
print('egon'.ljust(50,'=')) print('egon'.rjust(50,'=')) print('egon'.zfill(50))
3、expandtabs
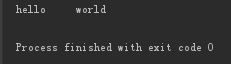
print('hello\tworld'.expandtabs(5))
4、captalize、swapcase、title
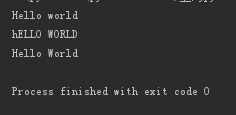
print('hello world'.capitalize()) print('Hello world'.swapcase()) print('Hello world'.title())
5、is数字系列(能否识别里面的数字)
num1=b'4' #bytes num2=u'4' #unicode,python3中无需加u就是unicode num3='四' #中文数字 num4='Ⅳ' #罗马数字
isdigit:bytes,str
isdecimal:str
isnumberic:str,中文,罗马
6、is其他
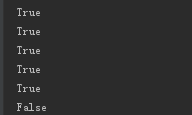
print('aaasdfaA'.isalpha()) # 纯字母组成的字符串 print('aaasdfaA123'.isalnum()) # 字母或数字组成 print('aaasdfaA'.isalnum()) # 字母或数字组成 print('123'.isalnum()) print(' '.isspace()) print(' 12'.isspace())
四、列表
1、基本使用
(1)用途:记录多个值,不如人的多个爱好
(2)定义方式:在【】内用逗号分隔开多个任意类型的值
li=[1,2,3] # li=list([1,2,3])
x=list('hello') ['h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'] x=list({'a':1,'b':2,'c':3}) ['a', 'b', 'c'] print(x)
(3)常用操作和内置的方法(重点)
#1、按索引存取值(正向存取+反向存取):即可存也可以取
li=['a','b','c','d'] print(li[-1]) d li[-1]='D' print(li) ['a', 'b', 'c', 'D'] li[4]='e' ['a','b','c','e']
del li[0] print(li) ['b', 'c', 'e']
#2切片(顾头不顾尾,步长)
li=['a','b','c','d'] print(li[0:3]) ['a', 'b', 'c']
#3、长度
print(len(li)) 4
#4、成员运算in和not in
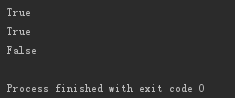
users=['egon','lxx','yxx','cxxx',[1,2,3]] print('lxx' in users) print([1,2,3] in users) print(1 in users)
#5、追加
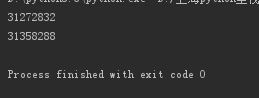
li=['a','b','c','d'] print(id(li)) li.append('e') li.append([1,2,3]) print(li,id(li))
31863624
['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', [1, 2, 3]] 31863624
#6、删除
# li=['a','b','c','d']
# 按照元素值去单纯地删除某个元素
# del li[1]
# res=li.remove('c')
# print(li) ['a','d']
# print(res) None
# 按照元素的索引去删除某个元素并且拿到该元素作为返回值
# res=li.pop(1)
# print(li) ['a', 'c', 'd']
# print(res) b
#7、循环
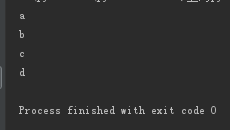
li=['a','b','c','d'] for item in li: print(item)
2、该类型总结
(1)存多个值
(2)有序
(3)可变
print(hash([1,2,3])) 报错:TypeError: unhashable type: 'list'
***需要掌握的操作
li=['a','b','c','d','c','e'] print(li.count('c')) 2 li.extend([1,2,3]) li.append([1,2,3]) print(li) ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'c', 'e', 1, 2, 3, [1, 2, 3]]
print(li.index('z')) 报错 print(li.index('b')) 1 print(li.index('d',0,3)) 报错
li=[3,1,9,11] li.reverse() print(li) [11, 9, 1, 3]
li.sort(reverse=True) print(li) [11, 9, 3, 1]
队列:先进先出 q=[]
入队:
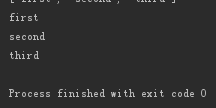
q.append('first') q.append('second') q.append('third') print(q) ['first', 'second', 'third']
出队:
print(q.pop(0)) print(q.pop(0)) print(q.pop(0))
堆栈:先进后出
q=[]
入栈:
q.append('first') q.append('second') q.append('third')
print(q) ['first', 'second', 'third']
出栈
print(q.pop(-1)) print(q.pop(-1)) print(q.pop(-1))



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号