Point and Spot Shadows Perspective Shadows - 教程
实现点光源与聚光灯的烘焙与实时阴影混合
配置第二张阴影图集
采用透视投影进行阴影渲染与采样
使用自定义立方体贴图
本教程是创建自定义可编程渲染管线系列的第十部分,新增了对点光源与聚光灯实时阴影的支持。
本教程基于Unity 2019.4.1f1创建,并升级至2022.3.5f1版本。

100% realtime shadows 100% 实时阴影
1. Spot Light Shadows 聚光灯阴影
我们将从支持聚光灯的实时阴影开始。采用与定向光源相同的技术方案,但会进行一些调整。我们将尽可能简化支持方式,使用统一划分的阴影图集,并按照Unity提供的顺序填充需要投射阴影的光源
1.1 Shadow Mixing 阴影混合
第一步是实现烘焙阴影与实时阴影的混合。在Shadows中调整GetOtherShadowAttenuation函数,使其行为类似于GetDirectionalShadowAttenuation,区别在于它使用其他阴影数据并依赖一个新的GetOtherShadow函数。由于其他光源尚未支持实时阴影,新函数初始返回值为1
float GetOtherShadow (
OtherShadowData other, ShadowData global, Surface surfaceWS
) {
return 1.0;
}
float GetOtherShadowAttenuation (
OtherShadowData other, ShadowData global, Surface surfaceWS
) {
#if !defined(_RECEIVE_SHADOWS)
return 1.0;
#endif
float shadow;
if (other.strength * global.strength <= 0.0) {
shadow = GetBakedShadow(
global.shadowMask, other.shadowMaskChannel, abs(other.strength)
);
}
else {
shadow = GetOtherShadow(other, global, surfaceWS);
shadow = MixBakedAndRealtimeShadows(
global, shadow, other.shadowMaskChannel, other.strength
);
}
return shadow;
}全局阴影强度用于判断是否跳过实时阴影采样,这可能是因为超出阴影距离或位于最大级联球体之外。但级联仅适用于定向光源阴影,对其他光源并不适用——因为这些光源位置固定,其阴影贴图不会随视角移动。尽管如此,采用相同方式淡化所有阴影仍是最佳实践,否则可能出现屏幕某些区域没有定向光源阴影却存在其他类型阴影的情况。因此我们将统一使用全局阴影强度进行处理。
需要特别处理的一种边界情况是:当存在其他光源阴影但不存在定向光源阴影时。此时由于没有任何级联数据,级联不应影响全局阴影强度。但我们仍需获取阴影距离淡化值。因此,我们将把设置级联数量和距离淡化的代码从Shadows.RenderDirectionShadows移至Shadows.Render方法,并在适当时机将级联数量设为零
public void Render () {
…
buffer.SetGlobalInt(
cascadeCountId,
shadowedDirLightCount > 0 ? settings.directional.cascadeCount : 0
);
float f = 1f - settings.directional.cascadeFade;
buffer.SetGlobalVector(
shadowDistanceFadeId, new Vector4(
1f / settings.maxDistance, 1f / settings.distanceFade,
1f / (1f - f * f)
)
);
buffer.EndSample(bufferName);
ExecuteBuffer();
}
void RenderDirectionalShadows () {
…
//buffer.SetGlobalInt(cascadeCountId, settings.directional.cascadeCount);
buffer.SetGlobalVectorArray(
cascadeCullingSpheresId, cascadeCullingSpheres
);
buffer.SetGlobalVectorArray(cascadeDataId, cascadeData);
buffer.SetGlobalMatrixArray(dirShadowMatricesId, dirShadowMatrices);
//float f = 1f - settings.directional.cascadeFade;
//buffer.SetGlobalVector(
// shadowDistanceFadeId, new Vector4(
// 1f / settings.maxDistance, 1f / settings.distanceFade,
// 1f / (1f - f * f)
// )
//);
…
}接下来需要确保在GetShadowData的级联循环之后,全局阴影强度不会被错误设置为零
if (i == _CascadeCount && _CascadeCount > 0) {
data.strength = 0.0;
}1.2 Other Realtime Shadows 其他实时阴影
定向光源拥有独立的阴影图集。我们将为所有其他投射阴影的光源单独分配一个图集,并进行独立计数。设定最多支持16个带实时阴影的其他光源
const int maxShadowedDirLightCount = 4, maxShadowedOtherLightCount = 16;
const int maxCascades = 4;
…
int shadowedDirLightCount, shadowedOtherLightCount;
…
public void Setup (…) {
…
shadowedDirLightCount = shadowedOtherLightCount = 0;
useShadowMask = false;
}这意味着有些启用了阴影的光源可能无法存入图集。哪些光源无法获得阴影取决于它们在可见光列表中的位置。对于无法存入的光源,我们不会为其保留阴影空间,但如果它们拥有烘焙阴影,则仍可保留该功能。为实现这一点,首先重构ReserveOtherShadows方法:当光源不包含阴影时立即返回;否则检查阴影遮罩通道(默认使用-1),然后始终返回阴影强度和通道信息
public Vector4 ReserveOtherShadows (Light light, int visibleLightIndex) {
if (light.shadows == LightShadows.None || light.shadowStrength <= 0f) {
return new Vector4(0f, 0f, 0f, -1f);
}
float maskChannel = -1f;
//if (light.shadows != LightShadows.None && light.shadowStrength > 0f) {
LightBakingOutput lightBaking = light.bakingOutput;
if (
lightBaking.lightmapBakeType == LightmapBakeType.Mixed &&
lightBaking.mixedLightingMode == MixedLightingMode.Shadowmask
) {
useShadowMask = true;
maskChannel = lightBaking.occlusionMaskChannel;
}
return new Vector4(
light.shadowStrength, 0f, 0f,
maskChannel
);
//}
//}
//return new Vector4(0f, 0f, 0f, -1f);
}随后在返回前检查:若增加光源数量将超出最大值,或该光源无需渲染阴影,则返回负的阴影强度及遮罩通道,以便在适当时使用烘焙阴影。否则继续递增光源计数并设置图块索引
if (
shadowedOtherLightCount >= maxShadowedOtherLightCount ||
!cullingResults.GetShadowCasterBounds(visibleLightIndex, out Bounds b)
) {
return new Vector4(-light.shadowStrength, 0f, 0f, maskChannel);
}
return new Vector4(
light.shadowStrength, shadowedOtherLightCount++, 0f,
maskChannel
);1.3 Two Atlases 双图集架构
由于定向阴影和其他类型阴影是分开处理的,我们可以对它们进行不同的配置。在ShadowSettings中添加新的配置结构和字段用于其他阴影,仅包含图集尺寸和过滤器设置(因为级联不适用于这些阴影
[System.Serializable]
public struct Other {
public MapSize atlasSize;
public FilterMode filter;
}
public Other other = new Other {
atlasSize = MapSize._1024,
filter = FilterMode.PCF2x2
};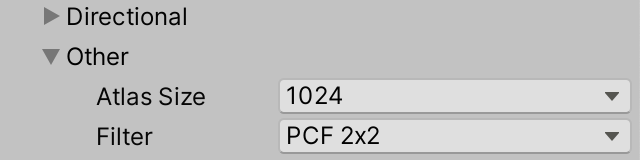
Settings for other shadows 其他阴影的设置
在我们的Lit着色器的CustomLit通道中添加多重编译指令,以支持其他阴影的过滤功能
#pragma multi_compile _ _OTHER_PCF3 _OTHER_PCF5 _OTHER_PCF7并在Shadows中添加对应的关键字数组
static string[] otherFilterKeywords = {
"_OTHER_PCF3",
"_OTHER_PCF5",
"_OTHER_PCF7",
};我们还需要追踪其他阴影图集和矩阵的着色器属性标识符,同时维护一个存储矩阵的数组
static int
dirShadowAtlasId = Shader.PropertyToID("_DirectionalShadowAtlas"),
dirShadowMatricesId = Shader.PropertyToID("_DirectionalShadowMatrices"),
otherShadowAtlasId = Shader.PropertyToID("_OtherShadowAtlas"),
otherShadowMatricesId = Shader.PropertyToID("_OtherShadowMatrices"),
…;
…
static Matrix4x4[]
dirShadowMatrices = new Matrix4x4[maxShadowedDirLightCount * maxCascades],
otherShadowMatrices = new Matrix4x4[maxShadowedOtherLightCount];我们已使用向量的XY分量将定向光源图集尺寸发送至GPU。现在还需要发送其他图集的尺寸,可将其置于同一向量的ZW分量中。将该向量提升为字段,并将设置全局向量的代码从RenderDirectionalShadows移至Render方法。这样RenderDirectionalShadows只需赋值给该字段的XY分量即可
Vector4 atlasSizes;
…
public void Render () {
…
buffer.SetGlobalVector(shadowAtlasSizeId, atlasSizes);
buffer.EndSample(bufferName);
ExecuteBuffer();
}
void RenderDirectionalShadows () {
int atlasSize = (int)settings.directional.atlasSize;
atlasSizes.x = atlasSize;
atlasSizes.y = 1f / atlasSize;
…
//buffer.SetGlobalVector(
// shadowAtlasSizeId, new Vector4(atlasSize, 1f / atlasSize)
//);
buffer.EndSample(bufferName);
ExecuteBuffer();
}随后,复制RenderDirectionalShadows方法并将其重命名为RenderOtherShadows。修改该方法使其使用正确的配置、图集和矩阵,并设置正确的尺寸分量。同时移除其中的级联和剔除球体代码。保留循环结构,但移除对RenderDirectionalShadows的调用
void RenderOtherShadows () {
int atlasSize = (int)settings.other.atlasSize;
atlasSizes.z = atlasSize;
atlasSizes.w = 1f / atlasSize;
buffer.GetTemporaryRT(
otherShadowAtlasId, atlasSize, atlasSize,
32, FilterMode.Bilinear, RenderTextureFormat.Shadowmap
);
buffer.SetRenderTarget(
otherShadowAtlasId,
RenderBufferLoadAction.DontCare, RenderBufferStoreAction.Store
);
buffer.ClearRenderTarget(true, false, Color.clear);
buffer.BeginSample(bufferName);
ExecuteBuffer();
int tiles = shadowedOtherLightCount;
int split = tiles <= 1 ? 1 : tiles <= 4 ? 2 : 4;
int tileSize = atlasSize / split;
for (int i = 0; i < shadowedOtherLightCount; i++) {
//RenderDirectionalShadows(i, split, tileSize);
}
//buffer.SetGlobalVectorArray(
// cascadeCullingSpheresId, cascadeCullingSpheres
//);
//buffer.SetGlobalVectorArray(cascadeDataId, cascadeData);
buffer.SetGlobalMatrixArray(otherShadowMatricesId, otherShadowMatrices);
SetKeywords(
otherFilterKeywords, (int)settings.other.filter - 1
);
//SetKeywords(
// cascadeBlendKeywords, (int)settings.directional.cascadeBlend - 1
//);
buffer.EndSample(bufferName);
ExecuteBuffer();
}现在我们可以在RenderShadows中根据需要同时渲染定向光源和其他光源的阴影。如果不存在其他光源阴影,我们需要为其提供虚拟纹理——就像处理定向光源阴影时一样。直接使用定向阴影图集作为虚拟纹理即可
public void Render () {
if (shadowedDirLightCount > 0) {
RenderDirectionalShadows();
}
else {
buffer.GetTemporaryRT(
dirShadowAtlasId, 1, 1,
32, FilterMode.Bilinear, RenderTextureFormat.Shadowmap
);
}
if (shadowedOtherLightCount > 0) {
RenderOtherShadows();
}
else {
buffer.SetGlobalTexture(otherShadowAtlasId, dirShadowAtlasId);
}
…
}在Cleanup方法中释放其他阴影图集时,仅在实际获取到图集的情况下执行释放操作
public void Cleanup () {
buffer.ReleaseTemporaryRT(dirShadowAtlasId);
if (shadowedOtherLightCount > 0) {
buffer.ReleaseTemporaryRT(otherShadowAtlasId);
}
ExecuteBuffer();
}1.4 Rendering Spot Shadows 渲染聚光灯阴影
为了渲染聚光灯的阴影,我们需要获取其可见光源索引、斜率比例偏差和法线偏差。因此需要创建一个ShadowedOtherLight结构体来存储这些字段,并添加对应的数组字段,类似于我们处理定向光源阴影数据的方式
struct ShadowedOtherLight {
public int visibleLightIndex;
public float slopeScaleBias;
public float normalBias;
}
ShadowedOtherLight[] shadowedOtherLights =
new ShadowedOtherLight[maxShadowedOtherLightCount];在返回之前,在ReserveOtherShadows末尾复制相关数据
public Vector4 ReserveOtherShadows (Light light, int visibleLightIndex) {
…
shadowedOtherLights[shadowedOtherLightCount] = new ShadowedOtherLight {
visibleLightIndex = visibleLightIndex,
slopeScaleBias = light.shadowBias,
normalBias = light.shadowNormalBias
};
return new Vector4(
light.shadowStrength, shadowedOtherLightCount++, 0f,
maskChannel
);
}然而此时我们应该意识到,由于照明系统会为其他光源传递自身索引,这并不能保证向ReserveOtherShadows传递正确光源索引。当存在带阴影的定向光源时,索引将会出错。我们通过在光照设置方法中添加正确的可见光源索引参数,并在预留阴影时使用该索引来解决此问题。为保持一致性,让我们对定向光源也采用相同处理方式
void SetupDirectionalLight (
int index, int visibleIndex, ref VisibleLight visibleLight
) {
…
dirLightShadowData[index] =
shadows.ReserveDirectionalShadows(visibleLight.light, visibleIndex);
}
void SetupPointLight (
int index, int visibleIndex, ref VisibleLight visibleLight
) {
…
otherLightShadowData[index] =
shadows.ReserveOtherShadows(light, visibleIndex);
}
void SetupSpotLight (
int index, int visibleIndex, ref VisibleLight visibleLight
) {
…
otherLightShadowData[index] =
shadows.ReserveOtherShadows(light, visibleIndex);
}调整SetupLights函数,使其将可见光源索引传递给各设置方法
switch (visibleLight.lightType) {
case LightType.Directional:
if (dirLightCount < maxDirLightCount) {
SetupDirectionalLight(
dirLightCount++, i, ref visibleLight
);
}
break;
case LightType.Point:
if (otherLightCount < maxOtherLightCount) {
newIndex = otherLightCount;
SetupPointLight(otherLightCount++, i, ref visibleLight);
}
break;
case LightType.Spot:
if (otherLightCount < maxOtherLightCount) {
newIndex = otherLightCount;
SetupSpotLight(otherLightCount++, i, ref visibleLight);
}
break;
}回到Shadows部分,创建一个RenderSpotShadows方法,其功能与带参数的RenderDirectionalShadows方法类似,但无需遍历多个图块、没有级联阴影、也没有剔除系数。此时我们可以使用CullingResults.ComputeSpotShadowMatricesAndCullingPrimitives方法,其工作原理与ComputeDirectionalShadowMatricesAndCullingPrimitives类似,但参数仅包含可见光源索引、矩阵和分割数据。在Unity 2022中,我们还需使用BatchCullingProjectionType.Perspective来替代正交投影
void RenderSpotShadows (int index, int split, int tileSize) {
ShadowedOtherLight light = shadowedOtherLights[index];
var shadowSettings = new ShadowDrawingSettings(
cullingResults, light.visibleLightIndex,
BatchCullingProjectionType.Perspective
);
cullingResults.ComputeSpotShadowMatricesAndCullingPrimitives(
light.visibleLightIndex, out Matrix4x4 viewMatrix,
out Matrix4x4 projectionMatrix, out ShadowSplitData splitData
);
shadowSettings.splitData = splitData;
otherShadowMatrices[index] = ConvertToAtlasMatrix(
projectionMatrix * viewMatrix,
SetTileViewport(index, split, tileSize), split
);
buffer.SetViewProjectionMatrices(viewMatrix, projectionMatrix);
buffer.SetGlobalDepthBias(0f, light.slopeScaleBias);
ExecuteBuffer();
context.DrawShadows(ref shadowSettings);
buffer.SetGlobalDepthBias(0f, 0f);
}在RenderOtherShadows的循环内部调用此方法
for (int i = 0; i < shadowedOtherLightCount; i++) {
RenderSpotShadows(i, split, tileSize);
}
Shadow atlas for three spot lights.三盏聚光灯的阴影图集
1.5 No Pancaking 取消薄饼式渲染
聚光灯现在可以渲染阴影了,使用的依然是定向阴影所用的ShadowCaster通道。这种方法本身没有问题,但阴影薄饼压缩仅适用于正交投影的阴影——也就是假设无限远光源的定向光。而对于具有实际位置的聚光灯,阴影投射物很可能部分位于光源后方。由于此时使用的是透视投影,将顶点钳制到近平面会严重扭曲这类阴影。因此,在不适用的场合我们应当关闭薄饼压缩。
我们可以通过全局着色器属性_ShadowPancaking向着色器传递是否启用薄饼压缩。请在Shadows类中记录该属性的标识符。
static int
…
shadowDistanceFadeId = Shader.PropertyToID("_ShadowDistanceFade"),
shadowPancakingId = Shader.PropertyToID("_ShadowPancaking");在RenderDirectionalShadows渲染阴影之前,将其设置为1
buffer.ClearRenderTarget(true, false, Color.clear);
buffer.SetGlobalFloat(shadowPancakingId, 1f);
buffer.BeginSample(bufferName);并在RenderOtherShadows中将其设为零
buffer.ClearRenderTarget(true, false, Color.clear);
buffer.SetGlobalFloat(shadowPancakingId, 0f);
buffer.BeginSample(bufferName);接下来将其作为布尔值添加到Lit着色器的ShadowCaster通道中,仅在适当时机进行钳位处理
bool _ShadowPancaking;
Varyings ShadowCasterPassVertex (Attributes input) {
…
if (_ShadowPancaking) {
#if UNITY_REVERSED_Z
output.positionCS.z = min(
output.positionCS.z, output.positionCS.w * UNITY_NEAR_CLIP_VALUE
);
#else
output.positionCS.z = max(
output.positionCS.z, output.positionCS.w * UNITY_NEAR_CLIP_VALUE
);
#endif
}
output.baseUV = TransformBaseUV(input.baseUV);
return output;
}1.6 Sampling Spot Shadows 采样聚光灯阴影
为采样其他光源阴影,我们需要调整Shadows文件。首先定义其他阴影的滤波器和最大投射阴影的其他光源数量宏。随后添加其他阴影图集和其他阴影矩阵数组
#if defined(_OTHER_PCF3)
#define OTHER_FILTER_SAMPLES 4
#define OTHER_FILTER_SETUP SampleShadow_ComputeSamples_Tent_3x3
#elif defined(_OTHER_PCF5)
#define OTHER_FILTER_SAMPLES 9
#define OTHER_FILTER_SETUP SampleShadow_ComputeSamples_Tent_5x5
#elif defined(_OTHER_PCF7)
#define OTHER_FILTER_SAMPLES 16
#define OTHER_FILTER_SETUP SampleShadow_ComputeSamples_Tent_7x7
#endif
#define MAX_SHADOWED_DIRECTIONAL_LIGHT_COUNT 4
#define MAX_SHADOWED_OTHER_LIGHT_COUNT 16
#define MAX_CASCADE_COUNT 4
TEXTURE2D_SHADOW(_DirectionalShadowAtlas);
TEXTURE2D_SHADOW(_OtherShadowAtlas);
#define SHADOW_SAMPLER sampler_linear_clamp_compare
SAMPLER_CMP(SHADOW_SAMPLER);
CBUFFER_START(_CustomShadows)
…
float4x4 _DirectionalShadowMatrices
[MAX_SHADOWED_DIRECTIONAL_LIGHT_COUNT * MAX_CASCADE_COUNT];
float4x4 _OtherShadowMatrices[MAX_SHADOWED_OTHER_LIGHT_COUNT];
…
CBUFFER_END复制SampleDirectionalShadowAtlas和FilterDirectionalShadow函数,进行重命名和调整使其适用于其他光源的阴影。请注意,在此版本中我们需要使用图集尺寸向量的另一组分量。
float SampleOtherShadowAtlas (float3 positionSTS) {
return SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D_SHADOW(
_OtherShadowAtlas, SHADOW_SAMPLER, positionSTS
);
}
float FilterOtherShadow (float3 positionSTS) {
#if defined(OTHER_FILTER_SETUP)
real weights[OTHER_FILTER_SAMPLES];
real2 positions[OTHER_FILTER_SAMPLES];
float4 size = _ShadowAtlasSize.wwzz;
OTHER_FILTER_SETUP(size, positionSTS.xy, weights, positions);
float shadow = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < OTHER_FILTER_SAMPLES; i++) {
shadow += weights[i] * SampleOtherShadowAtlas(
float3(positions[i].xy, positionSTS.z)
);
}
return shadow;
#else
return SampleOtherShadowAtlas(positionSTS);
#endif
}OtherShadowData结构体现在还需要包含图块索引
struct OtherShadowData {
float strength;
int tileIndex;
int shadowMaskChannel;
};该索引由Light中的GetOtherShadowData函数设置
OtherShadowData GetOtherShadowData (int lightIndex) {
OtherShadowData data;
data.strength = _OtherLightShadowData[lightIndex].x;
data.tileIndex = _OtherLightShadowData[lightIndex].y;
data.shadowMaskChannel = _OtherLightShadowData[lightIndex].w;
return data;
}现在我们可以在GetOtherShadow函数中对阴影贴图进行采样,而不再始终返回1。其工作原理与GetCascadedShadow类似,区别在于无需与第二级联混合且采用透视投影,因此需要将变换后位置的XYZ分量除以其W分量。另外,我们尚未实现法线偏置功能,暂时先将其乘以零值处理。
float GetOtherShadow (
OtherShadowData other, ShadowData global, Surface surfaceWS
) {
float3 normalBias = surfaceWS.interpolatedNormal * 0.0;
float4 positionSTS = mul(
_OtherShadowMatrices[other.tileIndex],
float4(surfaceWS.position + normalBias, 1.0)
);
return FilterOtherShadow(positionSTS.xyz / positionSTS.w);
}
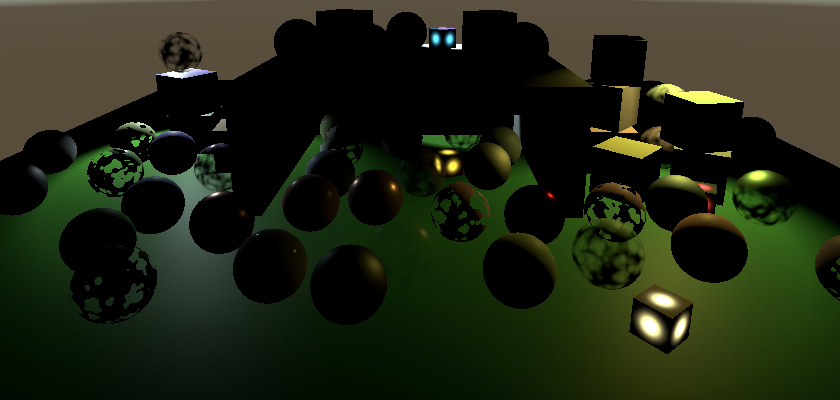
Direct spot lighting only, with and without realtime shadows.
仅使用直接聚光照明,含实时阴影与不含实时阴影的对比效果
1.7 Normal Bias 法线偏置
聚光灯与定向光一样会遇到阴影痤疮问题。但由于透视投影的缘故,纹素尺寸并不恒定,因此痤疮分布也不均匀——离光源越远,痤疮现象越明显。
Texel size increases with distance from light
纹素尺寸随光源距离增加而增大
纹素尺寸随着与光平面距离的增加而线性增大。光平面是将空间划分为光源前后区域的分界平面。因此,我们可以计算出在单位距离处的纹素尺寸及相应法线偏移量,并将其传入着色器,在着色器中按实际距离进行比例缩放。
在世界坐标系中,当与光平面距离为1时,阴影贴图单元的尺寸等于聚光灯半角弧度值的正切值的两倍
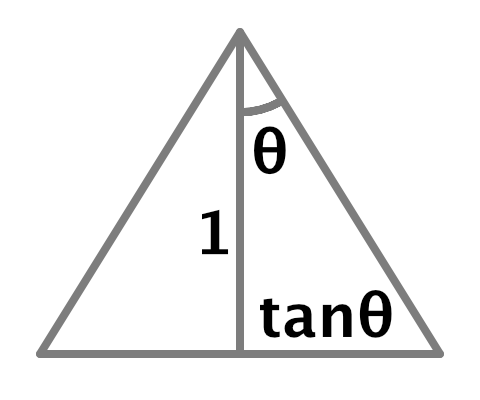
World-space tile size derivation
世界空间图块尺寸推导
这与透视投影相匹配,因此在单位距离处的世界空间纹素尺寸等于2除以投影缩放系数(可使用投影矩阵左上角的值)。我们可以据此计算法线偏置,计算方式与定向光源相同,不过由于不存在多级联阴影,我们可以直接将光源的法线偏置因子纳入计算。请在Shadows.RenderSpotShadows中设置阴影矩阵之前执行此计算
float texelSize = 2f / (tileSize * projectionMatrix.m00);
float filterSize = texelSize * ((float)settings.other.filter + 1f);
float bias = light.normalBias * filterSize * 1.4142136f;
otherShadowMatrices[index] = ConvertToAtlasMatrix(
projectionMatrix * viewMatrix,
SetTileViewport(index, split, tileSize), tileScale
);现在我们需要将偏置数据发送到着色器。后续每个图块还需要传递更多数据,因此让我们添加一个_OtherShadowTiles向量数组着色器属性。在Shadows类中为其添加标识符和数组,并在RenderOtherShadows中随同矩阵一起设置该属性
static int
…
otherShadowMatricesId = Shader.PropertyToID("_OtherShadowMatrices"),
otherShadowTilesId = Shader.PropertyToID("_OtherShadowTiles"),
…;
static Vector4[]
cascadeCullingSpheres = new Vector4[maxCascades],
cascadeData = new Vector4[maxCascades],
otherShadowTiles = new Vector4[maxShadowedOtherLightCount];
…
void RenderOtherShadows () {
…
buffer.SetGlobalMatrixArray(otherShadowMatricesId, otherShadowMatrices);
buffer.SetGlobalVectorArray(otherShadowTilesId, otherShadowTiles);
…
}创建一个新的SetOtherTileData方法,包含索引和偏置参数。将该偏置值存入向量的最后一个分量,然后存储到图块数据数组中
void SetOtherTileData (int index, float bias) {
Vector4 data = Vector4.zero;
data.w = bias;
otherShadowTiles[index] = data;
}在计算出偏置值后,于RenderSpotShadows方法中调用此函数
float bias = light.normalBias * filterSize * 1.4142136f;
SetOtherTileData(index, bias);随后将其他阴影图块数组添加到阴影缓冲区,并在Shadows中使用它来缩放法线偏置。
CBUFFER_START(_CustomShadows)
…
float4x4 _OtherShadowMatrices[MAX_SHADOWED_OTHER_LIGHT_COUNT];
float4 _OtherShadowTiles[MAX_SHADOWED_OTHER_LIGHT_COUNT];
float4 _ShadowAtlasSize;
float4 _ShadowDistanceFade;
CBUFFER_END
…
float GetOtherShadow (
OtherShadowData other, ShadowData global, Surface surfaceWS
) {
float4 tileData = _OtherShadowTiles[other.tileIndex];
float3 normalBias = surfaceWS.interpolatedNormal * tileData.w;
…
}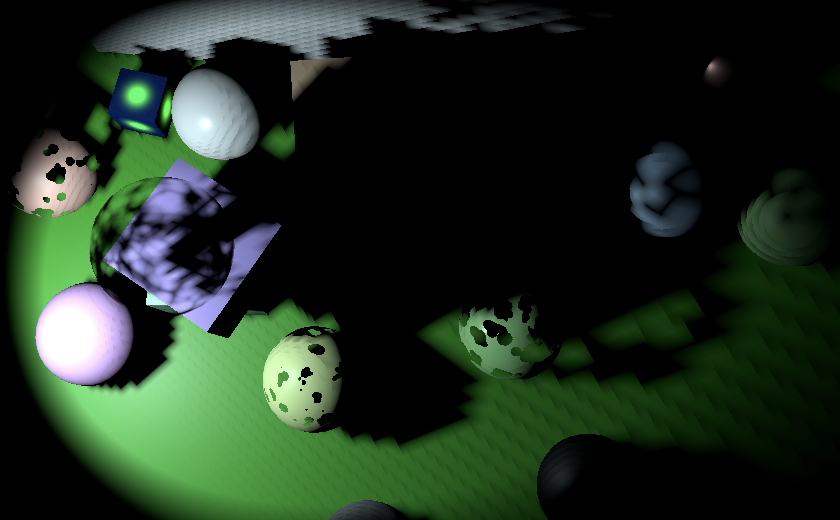
Constant normal bias, set to 1. 将法线偏置常量设置为1
此时我们获得的法线偏置仅在固定距离下准确。若要使其随光平面距离动态缩放,需要获取世界空间下的光源位置和聚光方向,请将它们添加到OtherShadowData中。
struct OtherShadowData {
float strength;
int tileIndex;
int shadowMaskChannel;
float3 lightPositionWS;
float3 spotDirectionWS;
};让Light文件将这些值复制到OtherShadowData中。由于这些值来源于光源本身而非阴影数据,请在GetOtherShadowData中将其初始化为零,并在GetOtherLight中进行赋值操作
OtherShadowData GetOtherShadowData (int lightIndex) {
…
data.lightPositionWS = 0.0;
data.spotDirectionWS = 0.0;
return data;
}
Light GetOtherLight (int index, Surface surfaceWS, ShadowData shadowData) {
Light light;
light.color = _OtherLightColors[index].rgb;
float3 position = _OtherLightPositions[index].xyz;
float3 ray = position - surfaceWS.position;
…
float3 spotDirection = _OtherLightDirections[index].xyz;
float spotAttenuation = Square(
saturate(dot(spotDirection, light.direction) *
spotAngles.x + spotAngles.y)
);
OtherShadowData otherShadowData = GetOtherShadowData(index);
otherShadowData.lightPositionWS = position;
otherShadowData.spotDirectionWS = spotDirection;
…
}在GetOtherShadow函数中,通过计算表面到光源的向量与聚光方向的点积来获取到光平面的距离,并据此缩放法线偏置。
float4 tileData = _OtherShadowTiles[other.tileIndex];
float3 surfaceToLight = other.lightPositionWS - surfaceWS.position;
float distanceToLightPlane = dot(surfaceToLight, other.spotDirectionWS);
float3 normalBias =
surfaceWS.interpolatedNormal * (distanceToLightPlane * tileData.w);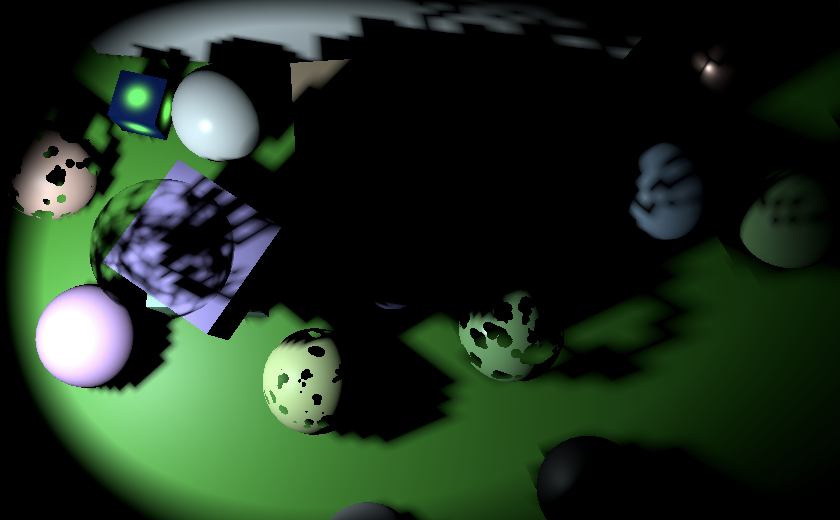
Correct normal bias everywhere 实现各位置的法线偏置校正
1.8 Clamped Sampling 钳位采样
我们为定向阴影配置级联球体的目的,是确保采样范围始终不会超出对应的阴影贴图区块。但这种方法无法直接应用于其他类型的阴影。以聚光灯为例,其贴图区块被严格限定在光锥范围内——当锥形边缘逐渐贴近区块边界时,法线偏移和滤镜尺寸的叠加效应将导致采样区域突破区块边界
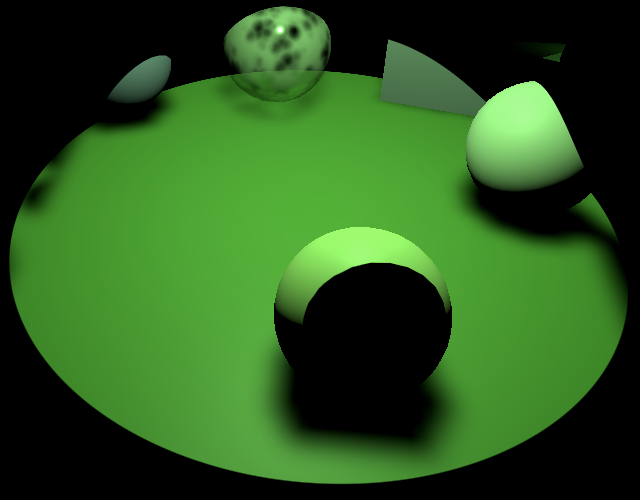
Shadows from wrong tiles intrude near edges 邻近边缘处出现错误图块的阴影渗入
解决此问题最简单的方法是手动将采样范围钳制在图块边界内,就像每个图块都是独立纹理一样。这样虽然仍会使边缘区域的阴影产生拉伸,但能避免无效阴影的引入。
调整SetOtherTileData方法,使其基于新参数提供的偏移量和缩放比例,计算并存储图块边界。图块的最小纹理坐标即缩放后的偏移量,我们将将其存储在数据向量的XY分量中。由于图块是正方形,只需将图块缩放比例存储在Z分量中,W分量仍保留给偏置值。同时,我们还需在两个维度上将边界缩小半个纹素,以确保采样不会溢出边缘
void SetOtherTileData (int index, Vector2 offset, float scale, float bias) {
float border = atlasSizes.w * 0.5f;
Vector4 data;
data.x = offset.x * scale + border;
data.y = offset.y * scale + border;
data.z = scale - border - border;
data.w = bias;
otherShadowTiles[index] = data;
}在RenderSpotShadows方法中,将通过SetTileViewport获取的偏移量以及分割值的倒数作为SetOtherTileData的新参数传入
Vector2 offset = SetTileViewport(index, split, tileSize);
SetOtherTileData(index, offset, 1f / split, bias);
otherShadowMatrices[index] = ConvertToAtlasMatrix(
projectionMatrix * viewMatrix, offset, split
);ConverToAtlasMatrix方法同样使用了分割值的倒数,因此我们可以预先计算该值并同时传递给这两个方法
float tileScale = 1f / split;
SetOtherTileData(index, offset, tileScale, bias);
otherShadowMatrices[index] = ConvertToAtlasMatrix(
projectionMatrix * viewMatrix, offset, tileScale
);这样ConvertToAtlasMatrix方法就无需自行执行除法运算
Matrix4x4 ConvertToAtlasMatrix (Matrix4x4 m, Vector2 offset, float scale) {
…
//float scale = 1f / split;
…
}这需要RenderDirectionalShadows方法代替执行除法运算,而该方法只需对所有级联统一执行一次计算即可。
void RenderDirectionalShadows (int index, int split, int tileSize) {
…
float tileScale = 1f / split;
for (int i = 0; i < cascadeCount; i++) {
…
dirShadowMatrices[tileIndex] = ConvertToAtlasMatrix(
projectionMatrix * viewMatrix,
SetTileViewport(tileIndex, split, tileSize), tileScale
);
…
}
}为应用边界限制,请在SampleOtherShadowAtlas方法中添加一个float3类型参数,并使用该参数在阴影图块空间中对位置进行钳制。FilterOtherShadows方法也需要相同的参数以便传递。而GetOtherShadow方法则需从图块数据中获取该参数
float SampleOtherShadowAtlas (float3 positionSTS, float3 bounds) {
positionSTS.xy = clamp(positionSTS.xy, bounds.xy, bounds.xy + bounds.z);
return SAMPLE_TEXTURE2D_SHADOW(
_OtherShadowAtlas, SHADOW_SAMPLER, positionSTS
);
}
float FilterOtherShadow (float3 positionSTS, float3 bounds) {
#if defined(OTHER_FILTER_SETUP)
…
for (int i = 0; i < OTHER_FILTER_SAMPLES; i++) {
shadow += weights[i] * SampleOtherShadowAtlas(
float3(positions[i].xy, positionSTS.z), bounds
);
}
return shadow;
#else
return SampleOtherShadowAtlas(positionSTS, bounds);
#endif
}
float GetOtherShadow (
OtherShadowData other, ShadowData global, Surface surfaceWS
) {
…
return FilterOtherShadow(positionSTS.xyz / positionSTS.w, tileData.xyz);
}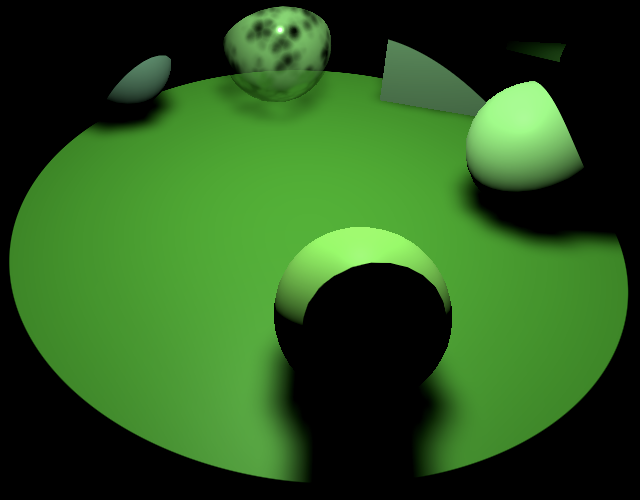
No more shadows from wrong tiles 不再出现错误图块的阴影
2. Point Light Shadows 点光源阴影
点光源的阴影实现方式与聚光灯类似。不同之处在于点光源不受锥形范围限制,因此我们需要将它们的阴影渲染到立方体贴图上。这是通过分别渲染立方体六个面的阴影来实现的。因此,为了实现实时阴影,我们将一个点光源视为六个独立光源。这会导致它在阴影图集中占用六个图块。也就是说,我们最多能同时支持两个点光源的实时阴影,因为它们会占用十六个可用图块中的十二个。如果剩余图块少于六个,点光源将无法获得实时阴影
2.1 Six Tiles for One Light 单个光源占用六个图块
首先,在渲染阴影时我们需要识别当前处理的是点光源,为此请在ShadowedOtherLight中添加一个布尔值作为标识。
struct ShadowedOtherLight {
…
public bool isPoint;
}在ReserveOtherShadows中检查是否为点光源。如果是,新增光源数量需在当前基础上加6;否则仅加1。若该数值超出最大值,则该光源最多只能拥有烘焙阴影。若图集空间充足,还需在返回的阴影数据第三分量中存储是否为点光源的标识,以便在着色器中快速识别点光源
public Vector4 ReserveOtherShadows (Light light, int visibleLightIndex) {
…
bool isPoint = light.type == LightType.Point;
int newLightCount = shadowedOtherLightCount + (isPoint ? 6 : 1);
if (
newLightCount > maxShadowedOtherLightCount ||
!cullingResults.GetShadowCasterBounds(visibleLightIndex, out Bounds b)
) {
return new Vector4(-light.shadowStrength, 0f, 0f, maskChannel);
}
shadowedOtherLights[shadowedOtherLightCount] = new ShadowedOtherLight {
visibleLightIndex = visibleLightIndex,
slopeScaleBias = light.shadowBias,
normalBias = light.shadowNormalBias,
isPoint = isPoint
};
Vector4 data = new Vector4(
light.shadowStrength, shadowedOtherLightCount,
isPoint ? 1f : 0f, maskChannel
);
shadowedOtherLightCount = newLightCount;
return data;
}2.2 Rendering Point Shadows 渲染点光源阴影
调整RenderOtherShadows方法,在其循环中根据光源类型调用新增的RenderPointShadows方法或现有的RenderSpotShadows方法。同时,由于点光源按六个图块计算,需要根据各光源类型对应的图块数量递增迭代器,而非简单自增。
for (int i = 0; i < shadowedOtherLightCount;) { //i++) {
if (shadowedOtherLights[i].isPoint) {
RenderPointShadows(i, split, tileSize);
i += 6;
}
else {
RenderSpotShadows(i, split, tileSize);
i += 1;
}
}新的RenderPointShadows方法是RenderSpotShadows的复制版本,主要有两点区别:首先,它需要渲染六次而非一次,循环处理其六个图块;其次,必须使用ComputePointShadowMatricesAndCullingPrimitives来替代ComputeSpotShadowMatricesAndCullingPrimitives。该方法在光源索引后需要两个额外参数:立方体面索引和偏置值。我们为每个面渲染一次,目前暂时将偏置值设为零。
void RenderPointShadows (int index, int split, int tileSize) {
ShadowedOtherLight light = shadowedOtherLights[index];
var shadowSettings = new ShadowDrawingSettings(
cullingResults, light.visibleLightIndex,
BatchCullingProjectionType.Perspective
);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
cullingResults.ComputePointShadowMatricesAndCullingPrimitives(
light.visibleLightIndex, (CubemapFace)i, 0f,
out Matrix4x4 viewMatrix, out Matrix4x4 projectionMatrix,
out ShadowSplitData splitData
);
shadowSettings.splitData = splitData;
int tileIndex = index + i;
float texelSize = 2f / (tileSize * projectionMatrix.m00);
float filterSize = texelSize * ((float)settings.other.filter + 1f);
float bias = light.normalBias * filterSize * 1.4142136f;
Vector2 offset = SetTileViewport(tileIndex, split, tileSize);
float tileScale = 1f / split;
SetOtherTileData(tileIndex, offset, tileScale, bias);
otherShadowMatrices[tileIndex] = ConvertToAtlasMatrix(
projectionMatrix * viewMatrix, offset, tileScale
);
buffer.SetViewProjectionMatrices(viewMatrix, projectionMatrix);
buffer.SetGlobalDepthBias(0f, light.slopeScaleBias);
ExecuteBuffer();
context.DrawShadows(ref shadowSettings);
buffer.SetGlobalDepthBias(0f, 0f);
}
}
Shadow atlas for two point lights 包含两个点光源的阴影图集
立方体贴图面的视野角度始终为90°,因此在单位距离处的世界空间图块尺寸恒定为2。这意味着我们可以将偏置计算移至循环外部,图块缩放比例的计算同样可以外提。
float texelSize = 2f / tileSize;
float filterSize = texelSize * ((float)settings.other.filter + 1f);
float bias = light.normalBias * filterSize * 1.4142136f;
float tileScale = 1f / split;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
…
//float texelSize = 2f / (tileSize * projectionMatrix.m00);
//float filterSize = texelSize * ((float)settings.other.filter + 1f);
//float bias = light.normalBias * filterSize * 1.4142136f;
Vector2 offset = SetTileViewport(tileIndex, split, tileSize);
//float tileScale = 1f / split;
…
}2.3 Sampling Point Shadows 采样点光源阴影
核心思路是将点光源阴影存储在立方体贴图中供着色器采样。但由于我们将立方体贴图的面作为图块存储在图集中,因此无法使用标准的立方体贴图采样方式,需要自行确定应采样的对应面。为此,我们需要在OtherShadowData中添加点光源标识和表面到光源的方向向量这两个参数
struct OtherShadowData {
float strength;
int tileIndex;
bool isPoint;
int shadowMaskChannel;
float3 lightPositionWS;
float3 lightDirectionWS;
float3 spotDirectionWS;
};在Light中设置这两个值。当其他光源的阴影数据第三分量等于1时,即可判定为点光源
OtherShadowData GetOtherShadowData (int lightIndex) {
…
data.isPoint = _OtherLightShadowData[lightIndex].z == 1.0;
data.lightPositionWS = 0.0;
data.lightDirectionWS = 0.0;
data.spotDirectionWS = 0.0;
return data;
}
Light GetOtherLight (int index, Surface surfaceWS, ShadowData shadowData) {
…
otherShadowData.lightPositionWS = position;
otherShadowData.lightDirectionWS = light.direction;
otherShadowData.spotDirectionWS = spotDirection;
…
}接下来,针对点光源的情况,我们需要在GetOtherShadow中调整图块索引和光平面参数。首先将它们转换为变量形式(初始配置为聚光灯参数)。将图块索引设为浮点类型,因为后续要为其添加同样定义为浮点型的偏移量
float GetOtherShadow (
OtherShadowData other, ShadowData global, Surface surfaceWS
) {
float tileIndex = other.tileIndex;
float3 lightPlane = other.spotDirectionWS;
float4 tileData = _OtherShadowTiles[tileIndex];
float3 surfaceToLight = other.lightPositionWS - surfaceWS.position;
float distanceToLightPlane = dot(surfaceToLight, lightPlane);
float3 normalBias =
surfaceWS.interpolatedNormal * (distanceToLightPlane * tileData.w);
float4 positionSTS = mul(
_OtherShadowMatrices[tileIndex],
float4(surfaceWS.position + normalBias, 1.0)
);
return FilterOtherShadow(positionSTS.xyz / positionSTS.w, tileData.xyz);
}若处理点光源,则必须改用对应的轴对齐平面。通过向CubeMapFaceID函数传入取反后的光源方向,可获取面偏移量。该函数可能是内置函数或定义在Core RP库中,返回值为浮点型。立方体贴图面的顺序为+X、-X、+Y、-Y、+Z、-Z,这与我们渲染时的顺序一致。将偏移量叠加到图块索引上即可。
float GetOtherShadow (
OtherShadowData other, ShadowData global, Surface surfaceWS
) {
float tileIndex = other.tileIndex;
float3 lightPlane = other.spotDirectionWS;
if (other.isPoint) {
float faceOffset = CubeMapFaceID(-other.lightDirectionWS);
tileIndex += faceOffset;
}
…
}接下来,我们需要使用与立方体表面方向匹配的光平面。创建一个静态常量数组存储这些平面,并使用表面偏移量作为索引。注意平面法线必须指向与表面相反的方向,就像聚光灯方向指向光源那样
static const float3 pointShadowPlanes[6] = {
float3(-1.0, 0.0, 0.0),
float3(1.0, 0.0, 0.0),
float3(0.0, -1.0, 0.0),
float3(0.0, 1.0, 0.0),
float3(0.0, 0.0, -1.0),
float3(0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
};
float GetOtherShadow (
OtherShadowData other, ShadowData global, Surface surfaceWS
) {
float tileIndex = other.tileIndex;
float3 plane = other.spotDirectionWS;
if (other.isPoint) {
float faceOffset = CubeMapFaceID(-other.lightDirectionWS);
tileIndex += faceOffset;
lightPlane = pointShadowPlanes[faceOffset];
}
…
}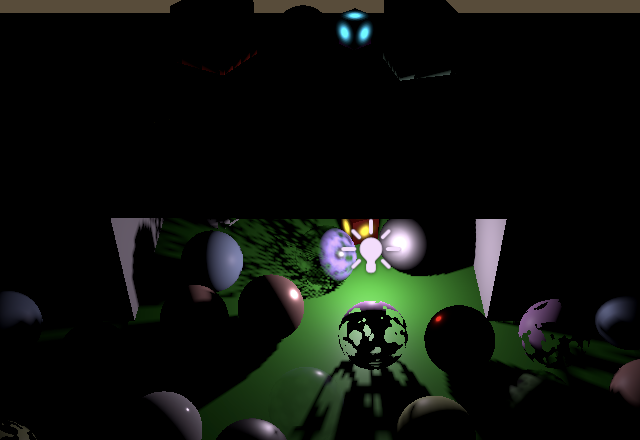

Direct point light only, with and without realtime shadows; no biases
仅使用直接点光源,含实时阴影与不含实时阴影的对比效果;未应用任何偏置技术
2.4 Drawing the Correct Faces 绘制正确的表面
我们现在可以看到点光源的实时阴影了。即使偏置值为零,它们似乎也没有出现阴影痤疮问题。但遗憾的是,现在光线会穿透物体泄漏到其背面的邻近表面上。增加阴影偏置会使该问题加剧,同时还会在靠近其他表面的物体阴影上产生空洞。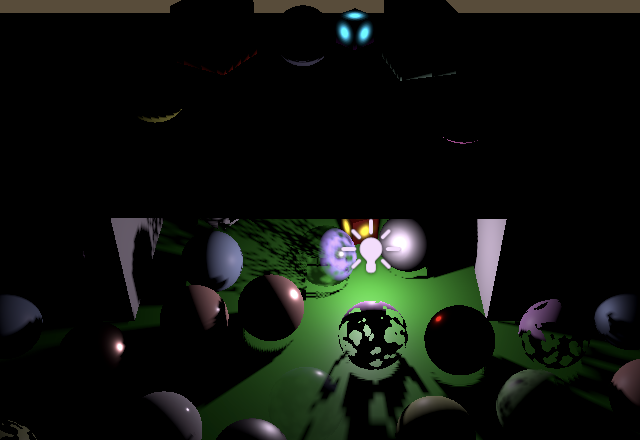
Maximum normal bias 3 最大法线偏置值为3
出现这种情况是因为Unity渲染点光源阴影的方式。它会将阴影上下翻转绘制,从而反转了三角形的缠绕顺序。通常情况下会绘制正面(从光源视角看),但现在渲染的却是背面。这种做法虽然避免了大部分阴影痤疮,却导致了光线泄漏。我们无法阻止这种翻转,但可以通过对ComputePointShadowMatricesAndCullingPrimitives返回的视图矩阵中的某一行取反来抵消该效果。让我们将其第二行取反。这样会在图集中进行二次上下翻转,使所有内容恢复常态。由于该行第一个分量始终为零,我们只需对另外三个分量取反即可。
cullingResults.ComputePointShadowMatricesAndCullingPrimitives(
light.visibleLightIndex, (CubemapFace)i, fovBias*0,
out Matrix4x4 viewMatrix, out Matrix4x4 projectionMatrix,
out ShadowSplitData splitData
);
viewMatrix.m11 = -viewMatrix.m11;
viewMatrix.m12 = -viewMatrix.m12;
viewMatrix.m13 = -viewMatrix.m13;

Front-face shadow rendering, normal bias 0 and 1
正面阴影渲染,法线偏置值0与1的对比效果
这种改变对渲染阴影的影响在对比阴影贴图时最为明显


Front and back versions of the shadow map
阴影贴图的正反面版本对比
请注意,将MeshRenderer的投射阴影模式设置为"双面"的物体不会受影响,因为它们的两个面都不会被剔除。例如,我已让所有使用裁剪或透明材质的球体投射双面阴影,使它们看起来更立体

Clip and transparent spheres with two-sided shadows
采用双面阴影的裁剪球体与透明球体
2.5 Field of View Bias 视野偏置
立方体贴图的各个面之间始终存在不连续性,因为纹理平面的方向会突然改变90°。常规的立方体贴图采样能在一定程度上隐藏这个问题,因为它可以在不同面之间进行插值,但我们现在每个片段只从单个图块采样。这导致了与聚光阴影图块边缘相同的问题,但由于没有聚光衰减的遮掩,这些缺陷就完全暴露出来了
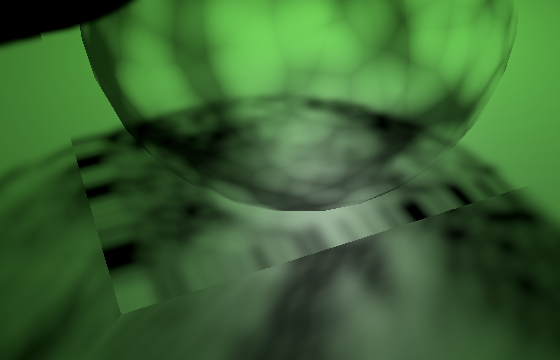
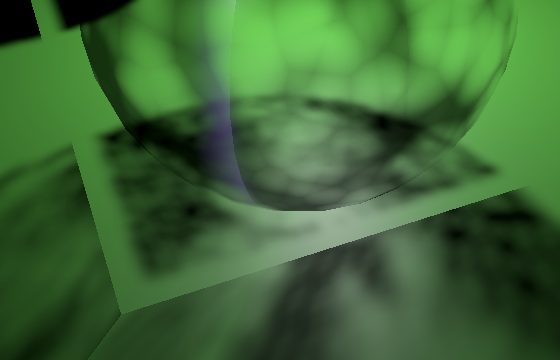
Discontinuities between faces, with and without tile clamping
面与面之间存在不连续性(启用与禁用图块钳位对比)
我们可以通过在渲染阴影时适当增大视野角度(简称FOV)来减轻这些瑕疵,这样就能确保采样不会超出图块边界。这正是ComputePointShadowMatricesAndCullingPrimitives方法中偏置参数的设计用途。具体实现时,我们将光源单位距离处的图块尺寸略微扩大到超过2。具体来说,需要在每个边缘增加法线偏置与滤镜尺寸的叠加值。对应的半角FOV正切值则等于1加上偏置和滤镜尺寸。将该值乘以2后转换为角度制,再减去90°,最终将结果作为FOV偏置值传入RenderPointShadows
Increasing the world-space tile size 增大世界空间图块尺寸
float fovBias =
Mathf.Atan(1f + bias + filterSize) * Mathf.Rad2Deg * 2f - 90f;
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
cullingResults.ComputePointShadowMatricesAndCullingPrimitives(
light.visibleLightIndex, (CubemapFace)i, fovBias,
out Matrix4x4 viewMatrix, out Matrix4x4 projectionMatrix,
out ShadowSplitData splitData
);
…
}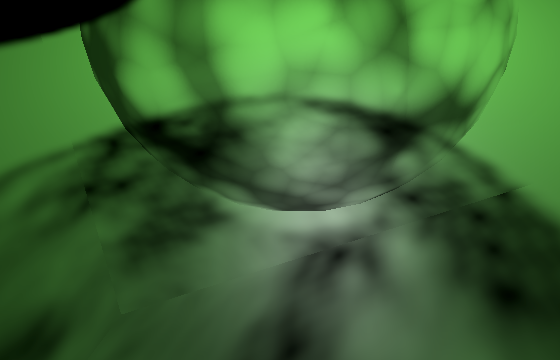
With FOV bias 已应用视野偏置
需要注意的是,这种方法并非完美无缺——因为随着图块尺寸的增大,纹素尺寸也会相应增加。这将导致滤镜尺寸扩大,同时法线偏置也需增强,意味着我们必须再次增大视野角度。不过,在通常情况下这种差异微小到可以忽略不计,除非是在使用大尺寸法线偏置与滤镜组合且图集尺寸较小的情况下
Could we use the same approach for spot lights?
我们能否对聚光灯采用相同方法?
确实可以——只需稍加调整就能让图块钳位变得不再必要。但问题在于ComputeSpotShadowMatricesAndCullingPrimitives函数并未提供FOV偏置参数,这就需要我们创建其自定义变体,而这已超出本教程的范围
The next tutorial is Post Processing.

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号