实用指南:C++模板进阶
文章目录
1. 非类型模板参数
模板参数分为类型形参与非类型形参。
类型形参即:出现在模板参数列表中,跟在class或者typename之类的参数类型名称。
非类型形参,就是用一个常量作为类(函数)模板的一个参数,在类(函数)模板中可将该参数当成常量来使用。
之前我们都是这样来定义常量:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define N 100
// 静态的栈
template<class T>
class Stack
{
private:
T _a[N];
int _top;
};
int main()
{
Stack<int> st1; // 10
Stack<int> st2; // 100
return 0;
}但是这样写不好让一个栈的大小是10,另一个大小是100。
可以这样解决:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>
// 静态的栈
template<class T, size_t N = 10>
class Stack
{
public:
void func()
{
// N是常量
N++;
}
private:
T _a[N];
int _top;
};
// C++20之前,只允许整形做非类型模板参数
// C++20之后,可以支持double等其他内置类型
template<double X, int* ptr>
class A
{};
//template<double X, string str>
//class A
//{};
int main()
{
Stack<int> st1; // 10
Stack<int, 100> st2; // 100
Stack<int, 1000> st3; // 1000
// 按需实例化
// 不调用不报错,没有使用就没有实例化
//st1.func();
//A<1.1, string("1111")> aa1;
return 0;
}注意:
浮点数、类对象以及字符串是不允许作为非类型模板参数的。
非类型的模板参数必须在编译期就能确认结果。
应用场景:

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <array>
#include <vector>
int main()
{
// 严格越界检查
array<int, 10> aa1;
cout << sizeof(aa1) << endl;
//aa1[10];
//aa1[14] = 1;
// 静态
int aa2[10];
//aa2[11] = 1;
cout << aa2[11] << endl;
aa2[14] = 1;
// array不如用vector,鸡肋的设计
vector<int> v1(10, 1);
//v1[14];
cout << sizeof(v1) << endl;
return 0;
}补充:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <vector>
//void PrintVector(const vector<int>& v)
//{
// vector<int>::const_iterator it = v.begin();
//
// while (it != v.end())
// {
// cout << *it << " ";
// ++it;
// }
//
// cout << endl;
//}
template<class T>
void PrintVector(const vector<T>& v)
{
// 类模板没实例化时,不去里面查细节东西,无法确认是类型还是静态变量
// 加typename明确告诉是类型
//typename vector<T>::const_iterator it = v.begin();
auto it = v.begin();
while (it != v.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 };
vector<double> v2{ 1.1,2.2,3.3,4.4,5.5,6.6,7.7 };
PrintVector(v1);
PrintVector(v2);
int i = 1;
int j = { 1 };
int k{ 1 };
return 0;
}2. 模板的特化
2.1 概念
通常情况下,使用模板可以实现一些与类型无关的代码,但对于一些特殊类型的可能会得到一些错误的结果,需要特殊处理,比如:实现了一个专门用来进行小于比较的函数模板
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator<(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
template<class T>
bool Less(T left, T right)
{
return left < right;
}
int main()
{
Date d1(2022, 7, 7);
Date d2(2022, 7, 8);
cout << Less(d1, d2) << endl; // 可以比较,结果正确
Date* p1 = &d1;
Date* p2 = &d2;
cout << Less(p1, p2) << endl; // 可以比较,结果错误
return 0;
}可以看到,Less绝对多数情况下都可以正常比较,但是在特殊场景下就得到错误的结果。上述示例中,p1指向的d1显然小于p2指向的d2对象,但是Less内部并没有比较p1和p2指向的对象内容,而比较的是p1和p2指针的地址,这就无法达到预期而错误。
此时,就需要对模板进行特化。即:在原模板类的基础上,针对特殊类型所进行特殊化的实现方式。模板特化中分为函数模板特化与类模板特化。
2.2 函数模板特化
函数模板的特化步骤:
必须要先有一个基础的函数模板
关键字template后面接一对空的尖括号<>
函数名后跟一对尖括号,尖括号中指定需要特化的类型
函数形参表: 必须要和模板函数的基础参数类型完全相同,如果不同编译器可能会报一些奇怪的错误。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator<(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
template<class T>
bool Less(T left, T right)
{
return left < right;
}
// 特化
template<>
bool Less<Date*>(Date* left, Date* right)
{
return *left < *right;
}
int main()
{
Date d1(2022, 7, 7);
Date d2(2022, 7, 8);
cout << Less(d1, d2) << endl;
Date* p1 = &d1;
Date* p2 = &d2;
cout << Less(p1, p2) << endl;
return 0;
}class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator<(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
template<class T>
bool Less(const T& left, const T& right)
{
return left < right;
}
// 特化
template<>
bool Less<Date*>(Date* const & left, Date* const & right)
{
return *left < *right;
}
int main()
{
Date d1(2022, 7, 7);
Date d2(2022, 7, 8);
cout << Less(d1, d2) << endl;
Date* p1 = &d1;
Date* p2 = &d2;
cout << Less(p1, p2) << endl;
return 0;
}注意: 一般情况下如果函数模板遇到不能处理或者处理有误的类型,为了实现简单通常都是将该函数直接给出。
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator<(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
template<class T>
bool Less(const T& left, const T& right)
{
return left < right;
}
bool Less(Date* left, Date* right)
{
return *left < *right;
}
int main()
{
Date d1(2022, 7, 7);
Date d2(2022, 7, 8);
cout << Less(d1, d2) << endl;
Date* p1 = &d1;
Date* p2 = &d2;
cout << Less(p1, p2) << endl;
return 0;
}2.3 类模板特化
2.3.1 全特化
全特化即是将模板参数列表中所有的参数都确定化。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 类模板
template<class T1, class T2>
class Data
{
public:
Data() { cout << "Data<T1, T2>-原模板" << endl; }
private:
T1 _d1;
T2 _d2;
};
// 特化:针对某些特殊类型,进行特殊化处理
// 全特化
template<>
class Data<int, char>
{
public:
Data() { cout << "Data<int, char>-全特化" << endl; }
};
int main()
{
Data<int, int> d1;
Data<int, char> d2;
return 0;
}应用:
//PriorityQueue.h
#include <vector>
namespace bit
{
template<class T>
class myless
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
// 特化
template<>
class myless<Date*>
{
public:
bool operator()(Date* const & x, Date* const & y)
{
return *x < *y;
}
};
template<class T>
class mygreater
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};
template<class T, class Container = vector<T>, class Compare = myless<T>>
class priority_queue
{
public:
// 强制编译器生成
priority_queue() = default;
template<class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
_con.push_back(*first);
++first;
}
// 建堆
for (int i = (_con.size() - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
adjust_down(i);
}
}
void adjust_up(int child)
{
Compare comfunc;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
//if (_con[parent] < _con[child])
if (comfunc(_con[parent], _con[child]))
//if (comfunc.operator()(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
adjust_up(_con.size() - 1);
}
void adjust_down(int parent)
{
Compare comfunc;
size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
//if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child] < _con[child + 1])
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && comfunc(_con[child], _con[child + 1]))
{
++child;
}
//if (_con[parent] < _con[child])
if (comfunc(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
adjust_down(0);
}
const T& top()
{
return _con[0];
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}// Test.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator<(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
#include "PriorityQueue.h"
void TestPriorityQueue()
{
// 大堆,需要用户在自定义类型中提供<的重载
bit::priority_queue<Date*> q1;
q1.push(new Date(2018, 10, 29));
q1.push(new Date(2018, 10, 28));
q1.push(new Date(2018, 10, 30));
while (!q1.empty())
{
cout << *q1.top() << " ";
q1.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
TestPriorityQueue();
return 0;
}2.3.2 偏特化
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 类模板
template<class T1, class T2>
class Data
{
public:
Data() { cout << "Data<T1, T2>-原模板" << endl; }
private:
T1 _d1;
T2 _d2;
};
// 特化:针对某些特殊类型,进行特殊化处理
// 全特化
template<>
class Data<int, char>
{
public:
Data() { cout << "Data<int, char>-全特化" << endl; }
};
// 偏特化/半特化
template<class T1>
class Data<T1, int>
{
public:
Data() { cout << "Data<T1, int>-偏特化" << endl; }
private:
T1 _d1;
int _d2;
};
int main()
{
Data<int, int> d1;
Data<int, char> d2;
Data<int, double> d3;
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 类模板
template<class T1, class T2>
class Data
{
public:
Data() { cout << "Data<T1, T2>-原模板" << endl; }
private:
T1 _d1;
T2 _d2;
};
// 特化:针对某些特殊类型,进行特殊化处理
// 全特化
template<>
class Data<int, char>
{
public:
Data() { cout << "Data<int, char>-全特化" << endl; }
};
// 偏特化/半特化
template<class T1>
class Data<T1, int>
{
public:
Data() { cout << "Data<T1, int>-偏特化" << endl; }
private:
T1 _d1;
int _d2;
};
// 限定模板的类型
template <typename T1, typename T2>
class Data<T1*, T2*>
{
public:
Data()
{
cout << typeid(T1).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(T2).name() << endl;
cout << "Data<T1*, T2*>-偏特化" << endl << endl;
T1 x1;
T1* p1;
}
};
int main()
{
Data<int, int> d1;
Data<int, char> d2;
Data<int, double> d3;
Data<int*, double*> d4;
Data<int*, int**> d5;
return 0;
}应用:
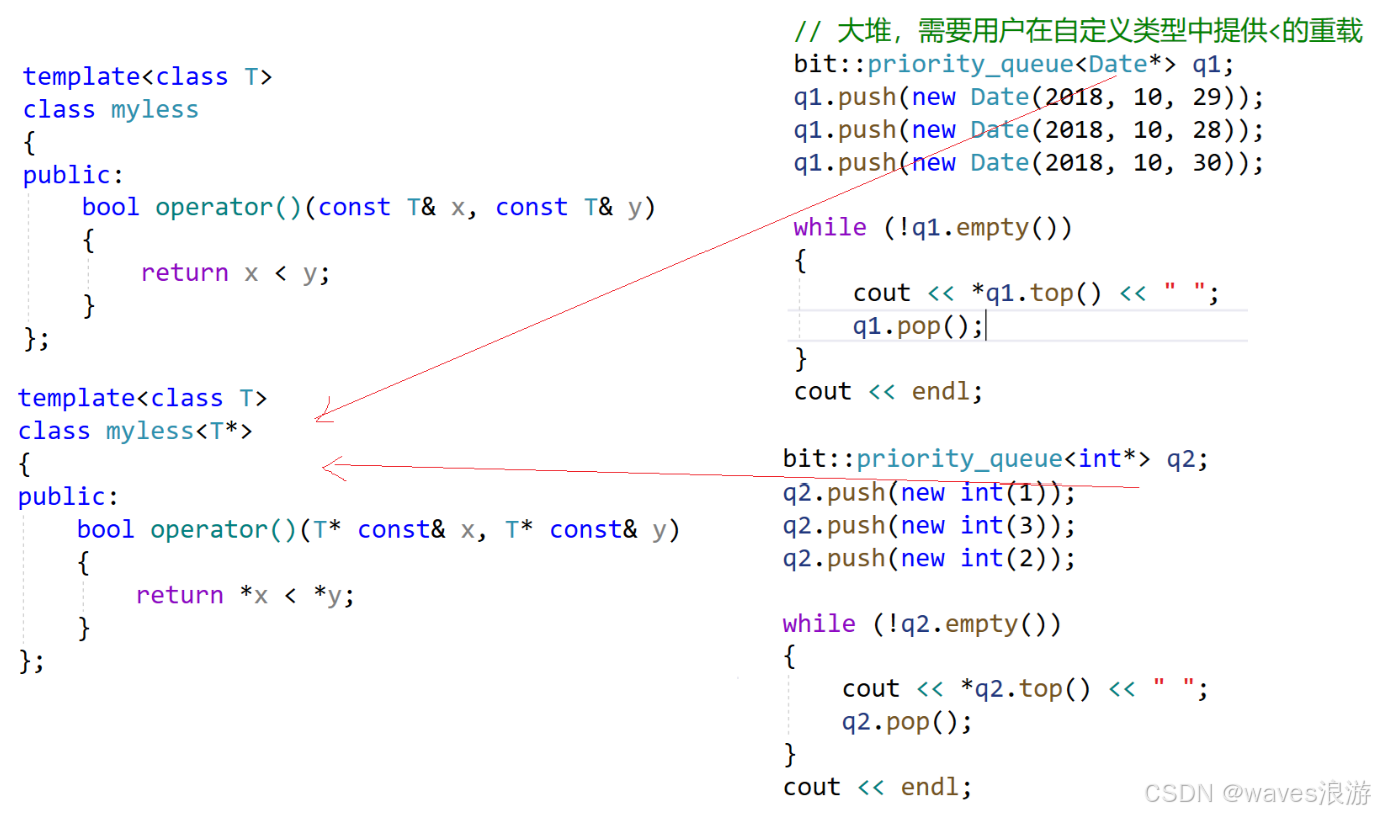
//PriorityQueue.h
#include <vector>
namespace bit
{
template<class T>
class myless
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
// 特化
/*template<>
class myless<Date*>
{
public:
bool operator()(Date* const & x, Date* const & y)
{
return *x < *y;
}
};*/
template<class T>
class myless<T*>
{
public:
bool operator()(T* const& x, T* const& y)
{
return *x < *y;
}
};
template<class T>
class mygreater
{
public:
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};
template<class T, class Container = vector<T>, class Compare = myless<T>>
class priority_queue
{
public:
// 强制编译器生成
priority_queue() = default;
template<class InputIterator>
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
while (first != last)
{
_con.push_back(*first);
++first;
}
// 建堆
for (int i = (_con.size() - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
adjust_down(i);
}
}
void adjust_up(int child)
{
Compare comfunc;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
//if (_con[parent] < _con[child])
if (comfunc(_con[parent], _con[child]))
//if (comfunc.operator()(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
adjust_up(_con.size() - 1);
}
void adjust_down(int parent)
{
Compare comfunc;
size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
//if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child] < _con[child + 1])
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && comfunc(_con[child], _con[child + 1]))
{
++child;
}
//if (_con[parent] < _con[child])
if (comfunc(_con[parent], _con[child]))
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);
_con.pop_back();
adjust_down(0);
}
const T& top()
{
return _con[0];
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}//Test.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
bool operator<(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
#include "PriorityQueue.h"
void TestPriorityQueue()
{
// 大堆,需要用户在自定义类型中提供<的重载
bit::priority_queue<Date*> q1;
q1.push(new Date(2018, 10, 29));
q1.push(new Date(2018, 10, 28));
q1.push(new Date(2018, 10, 30));
while (!q1.empty())
{
cout << *q1.top() << " ";
q1.pop();
}
cout << endl;
bit::priority_queue<int*> q2;
q2.push(new int(1));
q2.push(new int(3));
q2.push(new int(2));
while (!q2.empty())
{
cout << *q2.top() << " ";
q2.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
TestPriorityQueue();
return 0;
}// 类模板
template<class T1, class T2>
class Data
{
public:
Data() { cout << "Data<T1, T2>-原模板" << endl; }
private:
T1 _d1;
T2 _d2;
};
// 特化:针对某些特殊类型,进行特殊化处理
// 全特化
template<>
class Data<int, char>
{
public:
Data() { cout << "Data<int, char>-全特化" << endl; }
};
// 偏特化/半特化
template<class T1>
class Data<T1, int>
{
public:
Data() { cout << "Data<T1, int>-偏特化" << endl; }
private:
T1 _d1;
int _d2;
};
// 限定模板的类型
template <typename T1, typename T2>
class Data<T1*, T2*>
{
public:
Data()
{
cout << typeid(T1).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(T2).name() << endl;
cout << "Data<T1*, T2*>-偏特化" << endl << endl;
T1 x1;
T1* p1;
}
};
template <typename T1, typename T2>
class Data<T1&, T2&>
{
public:
Data()
{
cout << typeid(T1).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(T2).name() << endl;
cout << "Data<T1&, T2&>" << endl << endl;
}
};
template <typename T1, typename T2>
class Data<T1&, T2*>
{
public:
Data()
{
cout << typeid(T1).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(T2).name() << endl;
cout << "Data<T1&, T2*>" << endl << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Data<int, int> d1;
Data<int, char> d2;
Data<int, double> d3;
Data<int*, double*> d4;
Data<int*, int**> d5;
Data<int&, int&> d6;
Data<int&, int*> d7;
return 0;
}3. 模板分离编译
3.1 什么是分离编译
一个程序(项目)由若干个源文件共同实现,而每个源文件单独编译生成目标文件,最后将所有目标文件链接起来形成单一的可执行文件的过程称为分离编译模式。
3.2 模板的分离编译
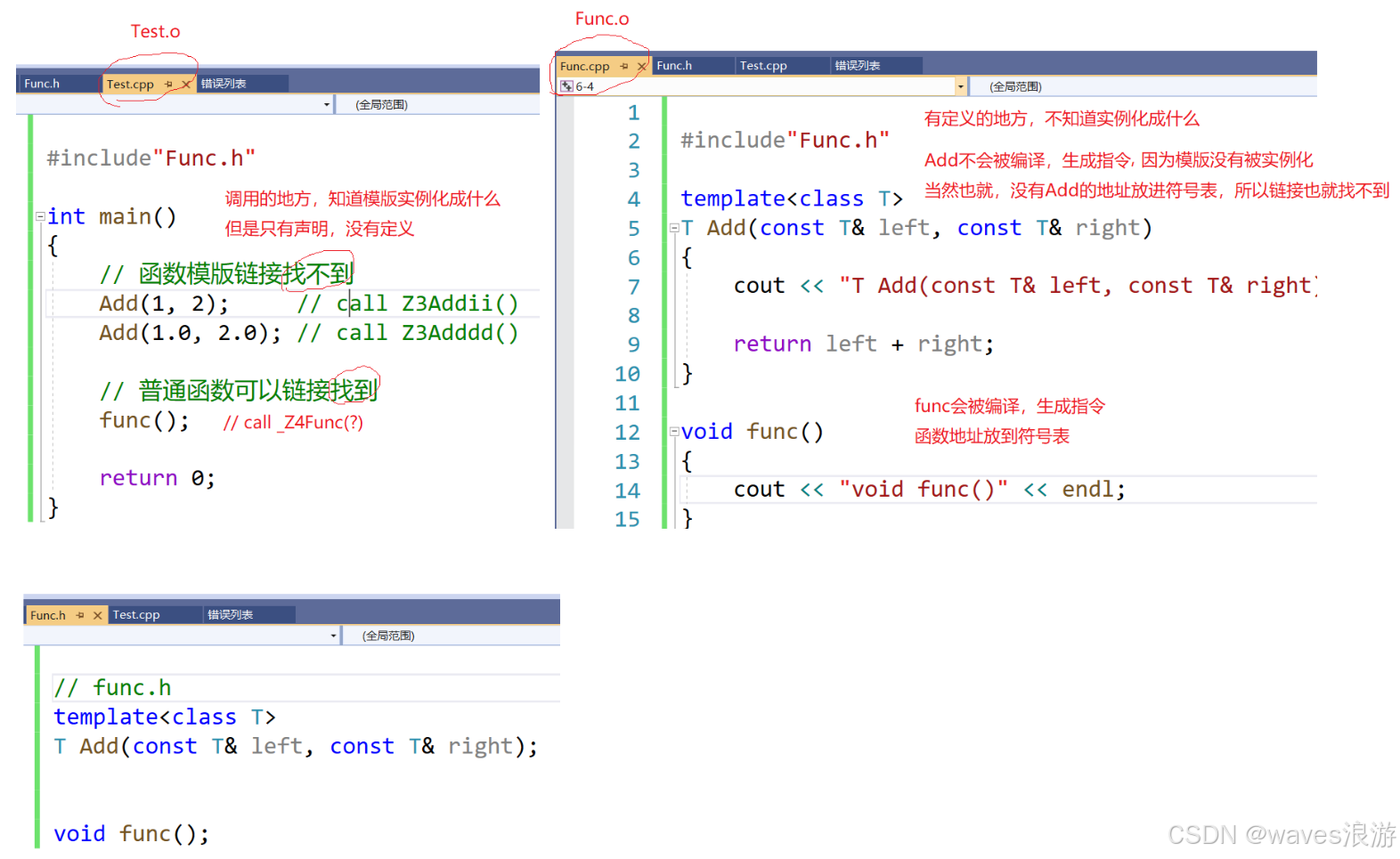
假如有以下场景,模板的声明与定义分离开,在头文件中进行声明,源文件中完成定义:
//Func.h
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
T Add(const T& left, const T& right);
void func();//Func.cpp
#include "Func.h"
template<class T>
T Add(const T& left, const T& right)
{
cout << "T Add(const T& left, const T& right)" << endl;
return left + right;
}
void func()
{
cout << "void func()" << endl;
}//Test.cpp
#include "Func.h"
int main()
{
// 函数模板链接找不到
Add(1, 2); // call Z3Addii()
Add(1.0, 2.0); // call Z3Adddd()
// 普通函数可以链接找到
func();
return 0;
}
3.3 解决方法
- 模板定义的位置显式实例化。这种方法不实用,不推荐使用。
//Func.h
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
T Add(const T& left, const T& right);
void func();//Func.cpp
#include "Func.h"
template<class T>
T Add(const T& left, const T& right)
{
cout << "T Add(const T& left, const T& right)" << endl;
return left + right;
}
// 显示实例化,这种解决方式很被动,需要不断添加显示实例化
template
int Add(const int& left, const int& right);
template
double Add(const double& left, const double& right);
void func()
{
cout << "void func()" << endl;
}//Test.cpp
#include "Func.h"
int main()
{
Add(1, 2); // call Z3Addii()
Add(1.0, 2.0); // call Z3Adddd()
// 链接找不到
Add('x', 'y'); // call Z3Addcc()
func();
return 0;
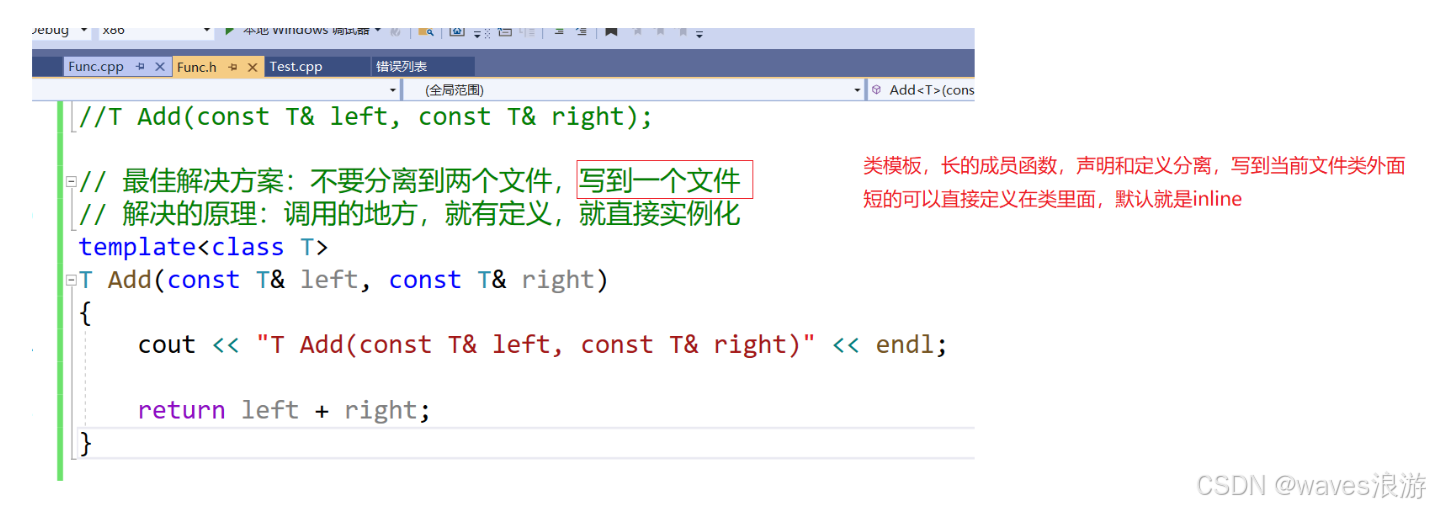
}- 将声明和定义放到一个文件 “xxx.hpp” 里面或者xxx.h其实也是可以的。推荐使用这种。
//Func.h
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//template<class T>
//T Add(const T& left, const T& right);
// 最佳解决方案:不要分离到两个文件,写到一个文件
// 解决的原理:调用的地方,就有定义,就直接实例化
template<class T>
T Add(const T& left, const T& right)
{
cout << "T Add(const T& left, const T& right)" << endl;
return left + right;
}
void func();//Func.cpp
#include "Func.h"
//template<class T>
//T Add(const T& left, const T& right)
//{
// cout << "T Add(const T& left, const T& right)" << endl;
//
// return left + right;
//}
//
//// 显示实例化,这种解决方式很被动,需要不断添加显示实例化
//template
//int Add(const int& left, const int& right);
//
//template
//double Add(const double& left, const double& right);
void func()
{
cout << "void func()" << endl;
}//Test.cpp
#include "Func.h"
int main()
{
Add(1, 2); // call Z3Addii()
Add(1.0, 2.0); // call Z3Adddd()
Add('x', 'y'); // call Z3Addcc()
func();
return 0;
}
4. 模板总结




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号