ITK-图像配准优化:自定义收敛判断实现迭代过程优化提速 - 教程
作者:翟天保Steven
版权声明:著作权归作者所有,商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处
前言
在医学图像配准任务中,迭代次数是影响效率的核心因素 —— 传统固定迭代次数的方案,常因迭代 “过度”(后期参数波动极小仍继续计算)导致时间浪费。
本文基于 ITK,通过自定义观察者(Observer)实现动态收敛判断,在保证配准精度的前提下,让迭代提前终止,显著提升配准效率。
环境准备
参见:Windows下用CMake编译ITK及调整测试_itk配置-CSDN博客
为什么应该优化迭代过程?
ITK 默认的图像配准流程(如 GradientDescentOptimizer)通常依赖固定迭代次数或学习率衰减到阈值停止,但这两种方式都存在明显缺陷:
| 停止方式 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| 固定迭代次数 | 逻辑简单,结果可复现 | 迭代不足(精度不够)或过度(时间浪费) |
| 学习率衰减到阈值 | 避免参数震荡 | 学习率设置依赖经验,仍可能存在无效迭代 |
| 动态收敛判断 | 按需停止,兼顾精度与效率 | 需自定义收敛规则,对开发者有一定要求 |
以 2D 脑部 MRI 配准为例:若固定迭代 100 次,可能在第 30 次时参数波动已小于 0.1(满足临床精度),但应用仍会继续执行 70 次无效计算 —— 这正是我们要处理的核心疑问。
核心思路:基于 “参数波动标准差” 的收敛判断
配准迭代的本质是优化目标函数(如互信息),让浮动图像(Moving Image)逐步对齐固定图像(Fixed Image)。当迭代接近收敛时,变换参数(如平移量)的波动会越来越小。
基于此,我们设计以下收敛规则:
- 维护一个 “滑动窗口”(如最近 10 次迭代),记录每次迭代的变换参数(X/Y 轴平移量);
- 计算窗口内参数的标准差(反映波动程度);
- 若标准差小于预设阈值(如 0.2),说明参数已稳定,触发提前终止。
代码模块解析
本文对基于互信息度量的二维平移配准算法进行优化,下面介绍下算法整体流程及优化内容。
1. 配准框架搭建
代码先定义了配准所需的核心组件类型,并完成实例化与关联,构建起完整的配准流水线:
- 变换模型:
TranslationTransform定义了 2D 空间的平移变换,仅有 2 个参数(X、Y 方向的平移量),适用于图像无旋转、缩放的简单对齐场景。 - 相似性度量:
MutualInformationImageToImageMetric通过计算两幅图像灰度分布的统计相关性来评价匹配程度,互信息值越大,说明图像匹配越好。 - 优化器:
GradientDescentOptimizer通过沿梯度方向迭代更新参数,寻找使互信息最大的变换参数。 - 插值器:
LinearInterpolateImageFunction在重采样时通过周围像素的加权平均计算目标位置像素值,比最近邻插值更平滑。
2. 图像读取与预处理
通过itk::ImageFileReader读取固定图像和浮动图像,其中固定图像是作为参考的标准图像,浮动图像是需要变换的图像。代码支持 MHD 格式图像(医学影像常用格式,包含元数据信息)和 PNG 格式输出,通过注册 IO 工厂确保格式支持。
为提升互信息度量的稳定性,代码添加了两项关键预处理:
- 归一化:使用
NormalizeImageFilter将图像灰度归一化到零均值、单位方差,消除灰度尺度差异的影响。 - 高斯模糊:通过
DiscreteGaussianImageFilter对图像进行平滑处理,减少噪声和高频细节对配准的干扰,方差设为 2.0。
3. 优化过程调整
优化器参数直接影响配准收敛速度和精度,本文对梯度下降优化器的关键参数进行了配置:
- 学习率:设为 40,控制每次迭代的步长大小,过大可能导致震荡,过小则收敛缓慢。
- 迭代次数:设为 100 次,避免无限制迭代。
- 最大化开关:开启(
MaximizeOn()),因为互信息值越大表示匹配越好。
此外,代码中还创建了一个迭代观察者 (CommandIterationUpdate),用于在每次迭代时输出当前的迭代次数、度量值和变换参数,便于监控配准过程。而本文提出的优化(基于 “参数波动标准差” 的收敛判断)将在该迭代观察者中实现。
4. 配准参数初始化与样本配置
为使优化器高效搜索最优解,需合理设置初始参数和空间样本:
- 初始变换参数:设为 X=5.0、Y=5.0(单位:mm),为优化器提供一个接近最优解的起点。
- 空间样本数量:取固定图像总像素的 1%(
numberOfPixels * 0.01),减少计算量同时保证度量估计的准确性。
5. 配准结果处理
配准完成后,代码获取最终的变换参数,并使用itk::ResampleImageFilter将浮动图像重采样到固定图像的空间坐标系中。然后通过类型转换和强度重映射,将结果保存为 PNG 图像。
6. 配准效果可视化
为直观对比配准效果,代码生成了配准前后的棋盘格图像:
- 配准前棋盘格:使用恒等变换(无对齐)生成,可见明显错位。
- 配准后棋盘格:使用最终变换生成,棋盘格线条连续,表明图像已对齐。
使用说明
- 需安装ITK库及相关依赖。
- 将ITK官方项目中Examples\Data中的图像文件(文件名字与例程中名字一致),复制到你项目的路径下,并更改代码。
- 编译时需链接 ITK的库文件。
完整代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
// 自定义观察者
class CommandIterationUpdate : public itk::Command
{
public:
using Self = CommandIterationUpdate;
using Superclass = itk::Command;
using Pointer = itk::SmartPointer;
itkNewMacro(Self);
protected:
CommandIterationUpdate() = default;
public:
using OptimizerType = itk::GradientDescentOptimizer;
using OptimizerPointer = const OptimizerType*;
// 设置收敛阈值和检查窗口大小
void SetConvergenceThreshold(double threshold)
{
m_ConvergenceThreshold = threshold;
}
void SetWindowSize(unsigned int windowSize)
{
m_WindowSize = windowSize;
}
void Execute(itk::Object* caller, const itk::EventObject& event) override
{
Execute((const itk::Object*)caller, event);
}
void Execute(const itk::Object* object, const itk::EventObject& event) override
{
auto optimizer = static_cast(object);
if (!itk::IterationEvent().CheckEvent(&event))
{
return;
}
// 获取当前迭代信息
unsigned int currentIteration = optimizer->GetCurrentIteration();
double metricValue = optimizer->GetValue();
auto position = optimizer->GetCurrentPosition();
// 输出当前迭代信息
std::cout = m_WindowSize)
{
// 计算三个序列的标准差
double metricStdDev = CalculateStandardDeviation(m_MetricValues);
double posXStdDev = CalculateStandardDeviation(m_PosXValues);
double posYStdDev = CalculateStandardDeviation(m_PosYValues);
// 输出当前标准差
std::cout (optimizer);
nonConstOptimizer->SetNumberOfIterations(currentIteration);
std::cout m_WindowSize)
{
m_MetricValues.erase(m_MetricValues.begin());
m_PosXValues.erase(m_PosXValues.begin());
m_PosYValues.erase(m_PosYValues.begin());
}
}
}
private:
// 计算向量的标准差
double CalculateStandardDeviation(const std::vector& values)
{
if (values.empty()) return 0.0;
// 计算均值
double sum = std::accumulate(values.begin(), values.end(), 0.0);
double mean = sum / values.size();
// 计算方差
double variance = 0.0;
for (double value : values) {
variance += std::pow(value - mean, 2);
}
variance /= values.size();
// 返回标准差
return std::sqrt(variance);
}
std::vector m_MetricValues;
std::vector m_PosXValues;
std::vector m_PosYValues;
double m_ConvergenceThreshold = 1e-4; // 默认收敛阈值
unsigned int m_WindowSize = 15; // 默认检查窗口大小
};
int main()
{
// 指定输入输出文件名(改为MHD格式)
const char* fixedImageFile = "ExampleData\\BrainProtonDensitySliceBorder20.mhd";
const char* movingImageFile = "ExampleData\\BrainProtonDensitySliceShifted13x17y.mhd";
const char* outputImageFile = "Output\\ImageRegistration2Output.png";
const char* checkerboardBeforeFile = "Output\\ImageRegistration2CheckerboardBefore.png";
const char* checkerboardAfterFile = "Output\\ImageRegistration2CheckerboardAfter.png";
// 创建工厂
itk::MetaImageIOFactory::RegisterOneFactory();
itk::PNGImageIOFactory::RegisterOneFactory();
// 定义图像类型和维度(MHD会自动读取元数据)
constexpr unsigned int Dimension = 2;
using PixelType = unsigned short;
using FixedImageType = itk::Image;
using MovingImageType = itk::Image;
// 定义内部图像类型
using InternalPixelType = float;
using InternalImageType = itk::Image;
// 定义配准组件
using TransformType = itk::TranslationTransform;
using OptimizerType = itk::GradientDescentOptimizer;
using InterpolatorType = itk::LinearInterpolateImageFunction;
using RegistrationType = itk::ImageRegistrationMethod;
using MetricType = itk::MutualInformationImageToImageMetric;
// 实例化并设置
auto transform = TransformType::New();
auto optimizer = OptimizerType::New();
auto interpolator = InterpolatorType::New();
auto registration = RegistrationType::New();
auto metric = MetricType::New();
registration->SetMetric(metric);
registration->SetOptimizer(optimizer);
registration->SetTransform(transform);
registration->SetInterpolator(interpolator);
// 度量需要选择多个参数
metric->SetFixedImageStandardDeviation(0.4);
metric->SetMovingImageStandardDeviation(0.4);
// 定义MHD图像读取器(自动支持MHD格式)
using FixedImageReaderType = itk::ImageFileReader;
using MovingImageReaderType = itk::ImageFileReader;
auto fixedImageReader = FixedImageReaderType::New();
auto movingImageReader = MovingImageReaderType::New();
fixedImageReader->SetFileName(fixedImageFile);
movingImageReader->SetFileName(movingImageFile);
// MHD格式会自动读取元数据,无需手动设置尺寸/类型
try
{
fixedImageReader->UpdateOutputInformation();
std::cout GetOutput()->GetLargestPossibleRegion().GetSize() GetOutput()->GetSpacing() GetOutput()->GetOrigin() ;
using MovingNormalizeFilterType = itk::NormalizeImageFilter;
auto fixedNormalizer = FixedNormalizeFilterType::New();
auto movingNormalizer = MovingNormalizeFilterType::New();
// 配置模糊滤波器
using GaussianFilterType = itk::DiscreteGaussianImageFilter;
auto fixedSmoother = GaussianFilterType::New();
auto movingSmoother = GaussianFilterType::New();
fixedSmoother->SetVariance(2.0);
movingSmoother->SetVariance(2.0);
// 配置输入输出关系
fixedNormalizer->SetInput(fixedImageReader->GetOutput());
movingNormalizer->SetInput(movingImageReader->GetOutput());
fixedSmoother->SetInput(fixedNormalizer->GetOutput());
movingSmoother->SetInput(movingNormalizer->GetOutput());
registration->SetFixedImage(fixedSmoother->GetOutput());
registration->SetMovingImage(movingSmoother->GetOutput());
// 固定图像区域(从MHD元数据获取)
fixedNormalizer->Update();
FixedImageType::RegionType fixedImageRegion = fixedNormalizer->GetOutput()->GetBufferedRegion();
registration->SetFixedImageRegion(fixedImageRegion);
// 初始变换参数
using ParametersType = RegistrationType::ParametersType;
ParametersType initialParameters(transform->GetNumberOfParameters());
initialParameters[0] = 5.0; // 沿X轴的初始偏移(单位:mm)
initialParameters[1] = 5.0; // 沿Y轴的初始偏移(单位:mm)
registration->SetInitialTransformParameters(initialParameters);
// 空间样本数量(从MHD元数据计算)
const unsigned int numberOfPixels = fixedImageRegion.GetNumberOfPixels();
const auto numberOfSamples = static_cast(numberOfPixels * 0.01);
metric->SetNumberOfSpatialSamples(numberOfSamples);
// 用于回归测试时获得一致结果
metric->ReinitializeSeed(121212);
// 互信息值越大表示匹配越好
optimizer->SetLearningRate(40);
optimizer->SetNumberOfIterations(100);
optimizer->MaximizeOn();
// 创建并配置观察者
auto observer = CommandIterationUpdate::New();
observer->SetConvergenceThreshold(0.2); // 设置波动阈值
observer->SetWindowSize(10); // 设置检查窗口大小(迭代次数)
optimizer->AddObserver(itk::IterationEvent(), observer);
// 配准
try
{
registration->Update();
std::cout GetOptimizer()->GetStopConditionDescription()
GetLastTransformParameters();
double TranslationAlongX = finalParameters[0];
double TranslationAlongY = finalParameters[1];
unsigned int numberOfIterations = optimizer->GetCurrentIteration();
double bestValue = optimizer->GetValue();
// 输出结果
std::cout ;
auto finalTransform = TransformType::New();
finalTransform->SetParameters(finalParameters);
finalTransform->SetFixedParameters(transform->GetFixedParameters());
auto resample = ResampleFilterType::New();
resample->SetTransform(finalTransform);
resample->SetInput(movingImageReader->GetOutput());
FixedImageType::Pointer fixedImage = fixedImageReader->GetOutput();
resample->SetSize(fixedImage->GetLargestPossibleRegion().GetSize());
resample->SetOutputOrigin(fixedImage->GetOrigin());
resample->SetOutputSpacing(fixedImage->GetSpacing());
resample->SetOutputDirection(fixedImage->GetDirection());
resample->SetDefaultPixelValue(100);
// 转换图像类型并保存配准结果(仍输出为PNG)
using OutputPixelType = unsigned char;
using OutputImageType = itk::Image;
using CastFilterType = itk::CastImageFilter;
using WriterType = itk::ImageFileWriter;
auto writer = WriterType::New();
auto caster = CastFilterType::New();
writer->SetFileName(outputImageFile);
caster->SetInput(resample->GetOutput());
writer->SetInput(caster->GetOutput());
writer->Update();
// 生成配准前后的棋盘格图像
using CheckerBoardFilterType = itk::CheckerBoardImageFilter;
auto checker = CheckerBoardFilterType::New();
checker->SetInput1(fixedImage);
checker->SetInput2(resample->GetOutput());
caster->SetInput(checker->GetOutput());
writer->SetInput(caster->GetOutput());
// 配准前
auto identityTransform = TransformType::New();
identityTransform->SetIdentity();
resample->SetTransform(identityTransform);
writer->SetFileName(checkerboardBeforeFile);
writer->Update();
// 配准后
resample->SetTransform(finalTransform);
writer->SetFileName(checkerboardAfterFile);
writer->Update();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}测试效果
官方给定的浮动图像在 X 轴方向偏移了 13 像素,Y 轴方向偏移了 17 像素,理想情况下配准结果应该接近这两个值。在实际运行中,优化器会找到使互信息最大的变换参数,输出类似如下的结果,这也是未优化迭代过程的结果,进行了100次迭代。
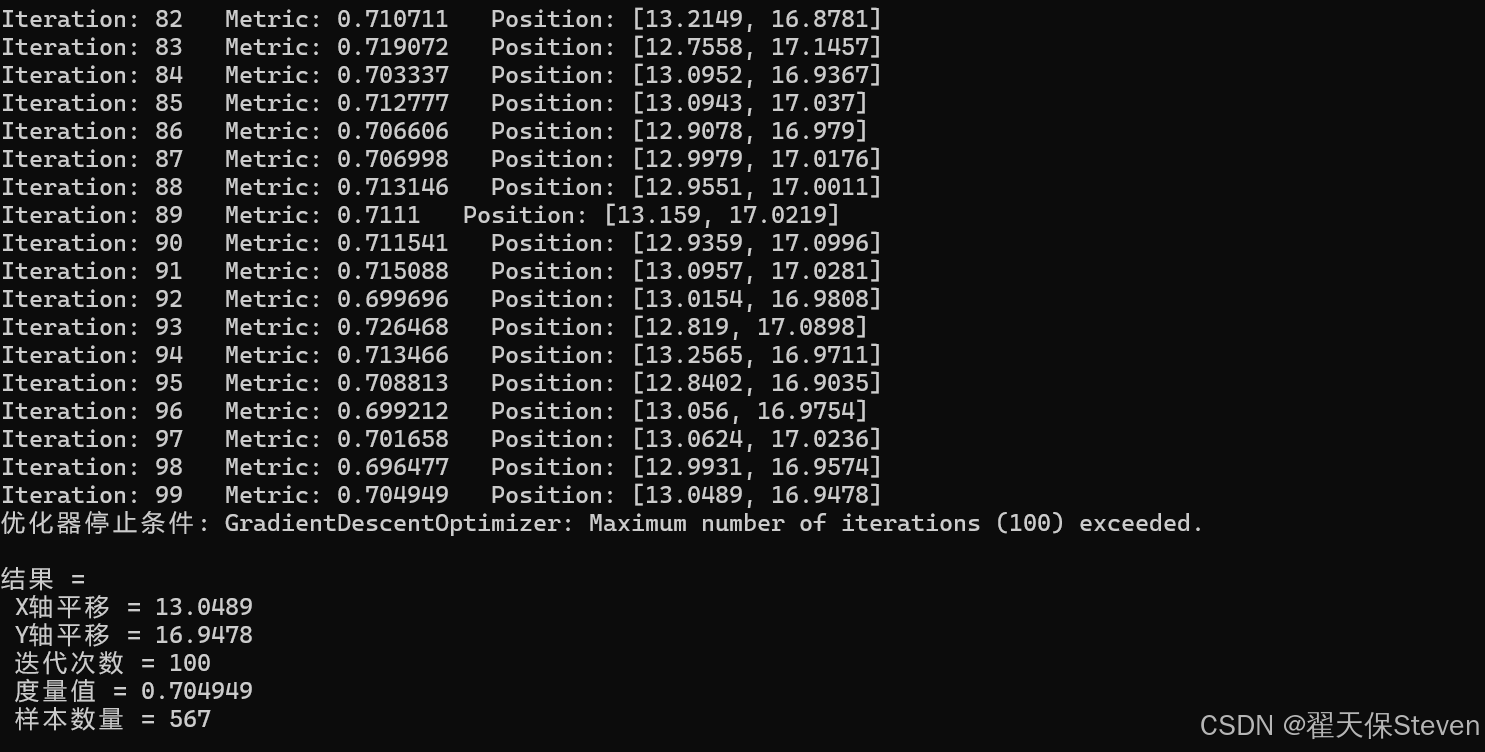
从结果能够看出,配准得到的平移量很接近真实偏移量,说明配准算法成功地找到了最优变换参数。度量值 (互信息) 在迭代过程中逐渐增大,最终收敛到一个较合适的值,表明固定图像和浮动图像在配准后具有很高的相似度。
在使用本文提出的优化方法后,迭代次数从100降至32,结果也是接近13&17,在保证精度的同时极大提高了配准效率。
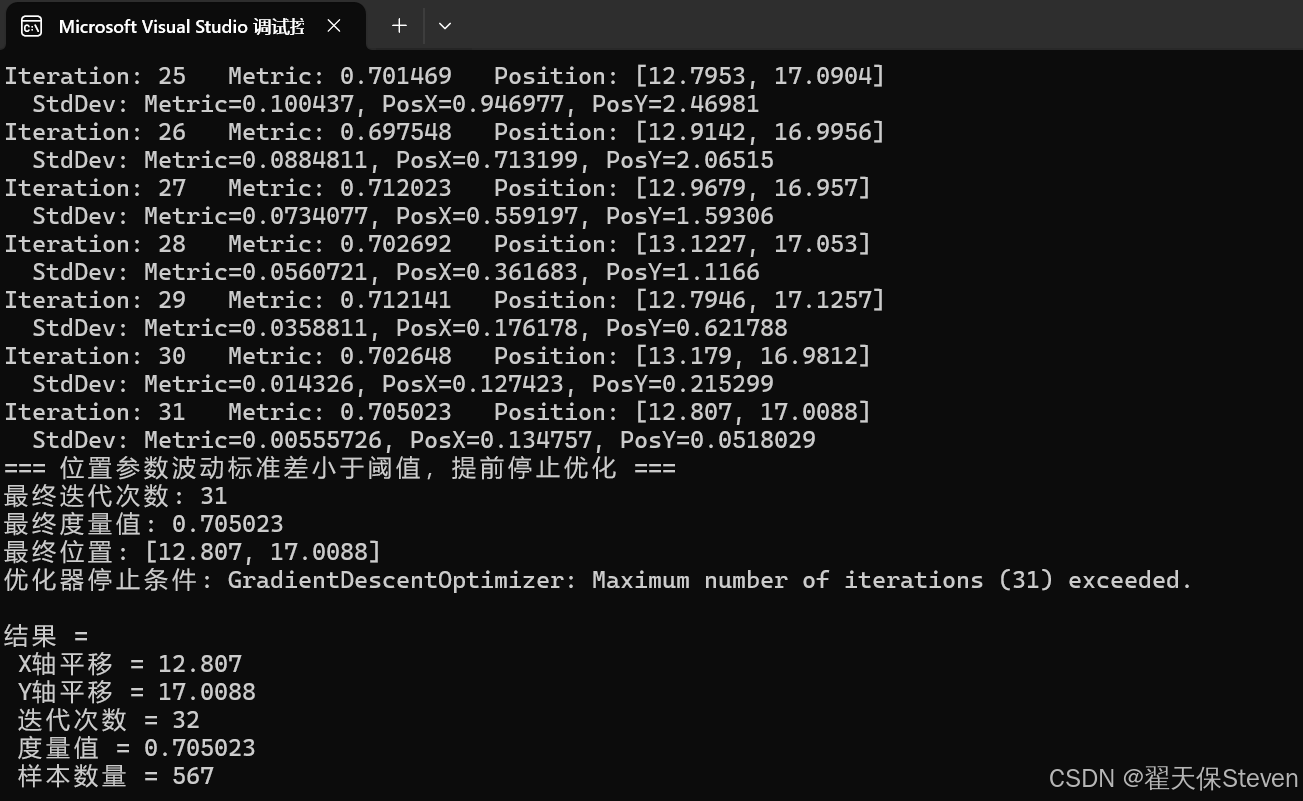
过程图像如下:

固定图像

浮动图像
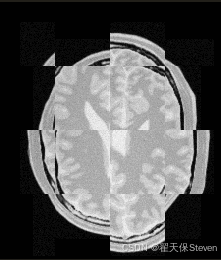
配准前棋盘格图
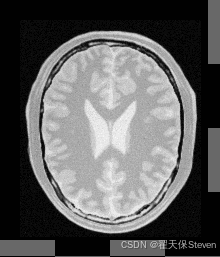
配准后棋盘格图
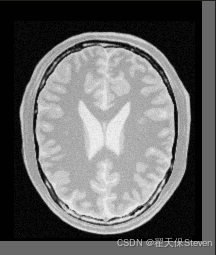
配准后图像
倘若文章帮助到你了,可以点个赞让我知道,我会很快乐~加油!




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号