Linux防火墙
该文章来自与马哥教育linux防火墙的课堂笔记整理。
1.1、Netfilter
Linux防火墙是由Netfilter组件提供的,Netfilter工作在内核空间,集成在linux内核中。 Netfilter 是Linux 2.4.x之后新一代的Linux防火墙机制,是linux内核的一个子系统。Netfilter采用模块 化设计,具有良好的可扩充性,提供扩展各种网络服务的结构化底层框架。Netfilter与IP协议栈是无缝 契合,并允许对数据报进行过滤、地址转换、处理等操作 Netfilter官网文档:https://netfilter.org/documentation/
[root@centos8 ~]#grep -m 10 NETFILTER /boot/config-4.18.0-193.el8.x86_64 CONFIG_NETFILTER=y CONFIG_NETFILTER_ADVANCED=y CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_INGRESS=y CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_FAMILY_BRIDGE=y CONFIG_NETFILTER_FAMILY_ARP=y # CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_ACCT is not set CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_QUEUE=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_LOG=m [root@centos7 ~]#grep -m 10 NETFILTER /boot/config-3.10.0-1127.el7.x86_64 CONFIG_NETFILTER=y # CONFIG_NETFILTER_DEBUG is not set CONFIG_NETFILTER_ADVANCED=y CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_ACCT=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_QUEUE=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_LOG=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_QUEUE_CT=y CONFIG_NETFILTER_SYNPROXY=m [root@centos6 ~]#grep -m 10 NETFILTER /boot/config-2.6.32-754.el6.x86_64 CONFIG_NETFILTER=y # CONFIG_NETFILTER_DEBUG is not set CONFIG_NETFILTER_ADVANCED=y CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER=y CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_QUEUE=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_LOG=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_TPROXY=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_XTABLES=y CONFIG_NETFILTER_XT_TARGET_AUDIT=m [root@ubuntu2004 ~]#grep -m 10 NETFILTER /boot/config-5.4.0-33-generic CONFIG_NETFILTER=y CONFIG_NETFILTER_ADVANCED=y CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_INGRESS=y CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_FAMILY_BRIDGE=y CONFIG_NETFILTER_FAMILY_ARP=y CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_ACCT=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_QUEUE=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_LOG=m [root@ubuntu1804 ~]#grep -m 10 NETFILTER /boot/config-4.15.0-29-generic CONFIG_NETFILTER=y CONFIG_NETFILTER_ADVANCED=y CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_INGRESS=y CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_ACCT=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_QUEUE=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_LOG=m CONFIG_NETFILTER_NETLINK_GLUE_CT=y CONFIG_NETFILTER_SYNPROXY=m
iptables
由软件包iptables提供的命令行工具,工作在用户空间,用来编写规则,写好的规则被送往netfilter,
[root@centos8 ~]#rpm -qi iptables Name : iptables Version : 1.8.2 Release : 9.el8 Architecture: x86_64 Install Date: Wed 25 Sep 2019 09:29:06 PM CST Group : Unspecified Size : 2050086 License : GPLv2 and Artistic 2.0 and ISC Signature : RSA/SHA256, Tue 02 Jul 2019 06:50:00 AM CST, Key ID 05b555b38483c65d Source RPM : iptables-1.8.2-9.el8.src.rpm Build Date : Sat 11 May 2019 10:21:57 PM CST Build Host : x86-01.mbox.centos.org Relocations : (not relocatable) Packager : CentOS Buildsys <bugs@centos.org> Vendor : CentOS URL : http://www.netfilter.org/ Summary : Tools for managing Linux kernel packet filtering capabilities Description : The iptables utility controls the network packet filtering code in the Linux kernel. If you need to set up firewalls and/or IP masquerading, you should either install nftables or this package. Note: This package contains the nftables-based variants of iptables and ip6tables, which are drop-in replacements of the legacy tools. [root@centos8 ~]# iptables --version iptables v1.8.2 (nf_tables) [root@centos8 ~]#ll /usr/sbin/iptables lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 17 May 11 2019 /usr/sbin/iptables -> xtables-nft-multi [root@centos7 ~]#ll /usr/sbin/iptables lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 13 Dec 9 2018 /usr/sbin/iptables -> xtables-multi [root@centos7 ~]# iptables --version iptables v1.4.21 [root@centos6 ~]#iptables --version iptables v1.4.7 [root@centos6 ~]#ll /sbin/iptables lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 33 Dec 12 2018 /sbin/iptables -> /etc/alternatives/iptables.x86_64 [root@centos6 ~]#ll /etc/alternatives/iptables.x86_64 lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 20 Dec 12 2018 /etc/alternatives/iptables.x86_64 -> /sbin/iptables-1.4.7 [root@centos6 ~]#ll /sbin/iptables lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 33 Dec 12 2018 /sbin/iptables -> /etc/alternatives/iptables.x86_64
范例:安装iptables的service包
[root@centos8 ~]#dnf -y install iptables-services [root@centos8 ~]#rpm -ql iptables-services /etc/sysconfig/ip6tables /etc/sysconfig/iptables /usr/lib/systemd/system/ip6tables.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/iptables.service /usr/libexec/initscripts/legacy-actions/ip6tables /usr/libexec/initscripts/legacy-actions/ip6tables/panic /usr/libexec/initscripts/legacy-actions/ip6tables/save /usr/libexec/initscripts/legacy-actions/iptables /usr/libexec/initscripts/legacy-actions/iptables/panic /usr/libexec/initscripts/legacy-actions/iptables/save /usr/libexec/iptables /usr/libexec/iptables/ip6tables.init /usr/libexec/iptables/iptables.init [root@node1 ~]#yum install iptables-services [root@node1 ~]# rpm -ql iptables /etc/sysconfig/ip6tables-config /etc/sysconfig/iptables-config /usr/bin/iptables-xml /usr/lib64/libip4tc.so.0 /usr/lib64/libip4tc.so.0.1.0 /usr/lib64/libip6tc.so.0 /usr/lib64/libip6tc.so.0.1.0 /usr/lib64/libiptc.so.0 /usr/lib64/libiptc.so.0.0.0 /usr/lib64/libxtables.so.10 /usr/lib64/libxtables.so.10.0.0 /usr/lib64/xtables /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_DNAT.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_DNPT.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_HL.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_LOG.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_MASQUERADE.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_NETMAP.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_REDIRECT.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_REJECT.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_SNAT.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_SNPT.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_ah.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_dst.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_eui64.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_frag.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_hbh.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_hl.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_icmp6.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_ipv6header.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_mh.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libip6t_rt.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_CLUSTERIP.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_DNAT.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_ECN.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_LOG.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_MASQUERADE.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_MIRROR.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_NETMAP.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_REDIRECT.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_REJECT.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_SAME.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_SNAT.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_TTL.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_ULOG.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_ah.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_icmp.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_realm.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_ttl.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libipt_unclean.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_AUDIT.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_CHECKSUM.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_CLASSIFY.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_CONNMARK.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_CONNSECMARK.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_CT.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_DSCP.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_HMARK.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_IDLETIMER.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_LED.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_MARK.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_NFLOG.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_NFQUEUE.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_NOTRACK.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_RATEEST.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_SECMARK.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_SET.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_SYNPROXY.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_TCPMSS.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_TCPOPTSTRIP.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_TEE.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_TOS.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_TPROXY.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_TRACE.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_addrtype.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_bpf.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_cgroup.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_cluster.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_comment.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_connbytes.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_connlabel.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_connlimit.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_connmark.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_conntrack.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_cpu.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_dccp.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_devgroup.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_dscp.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_ecn.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_esp.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_hashlimit.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_helper.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_iprange.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_ipvs.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_length.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_limit.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_mac.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_mark.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_multiport.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_nfacct.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_osf.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_owner.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_physdev.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_pkttype.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_policy.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_quota.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_rateest.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_recent.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_rpfilter.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_sctp.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_set.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_socket.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_standard.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_state.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_statistic.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_string.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_tcp.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_tcpmss.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_time.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_tos.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_u32.so /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_udp.so /usr/sbin/ip6tables /usr/sbin/ip6tables-restore /usr/sbin/ip6tables-save /usr/sbin/iptables /usr/sbin/iptables-restore /usr/sbin/iptables-save /usr/sbin/xtables-multi /usr/share/doc/iptables-1.4.21 /usr/share/doc/iptables-1.4.21/COPYING /usr/share/doc/iptables-1.4.21/INCOMPATIBILITIES /usr/share/man/man1/iptables-xml.1.gz /usr/share/man/man8/ip6tables-restore.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/ip6tables-save.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/ip6tables.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/iptables-extensions.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/iptables-restore.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/iptables-save.8.gz /usr/share/man/man8/iptables.8.gz
firewalld
从CentOS 7 版开始引入了新的前端管理工具 软件包: firewalld firewalld-config 管理工具: firewall-cmd 命令行工具 firewall-config 图形工作
此软件是CentOS 8 新特性,Nftables最初在法国巴黎的Netfilter Workshop 2008上发表,然后由长期的 netfilter核心团队成员和项目负责人Patrick McHardy于2009年3月发布。它在2013年末合并到Linux内 核中,自2014年以来已在内核3.13中可用。
它重用了netfilter框架的许多部分,例如连接跟踪和NAT功能。它还保留了命名法和基本iptables设计的 几个部分,例如表,链和规则。就像iptables一样,表充当链的容器,并且链包含单独的规则,这些规 则可以执行操作,例如丢弃数据包,移至下一个规则或跳至新链。
从用户的角度来看,nftables添加了一个名为nft的新工具,该工具替代了iptables,arptables和 ebtables中的所有其他工具。从体系结构的角度来看,它还替换了内核中处理数据包过滤规则集运行时 评估的那些部分。
范例:查看软件包
[root@centos8 ~]#rpm -qi nftables Name : nftables Epoch : 1 Version : 0.9.0 Release : 8.el8 Architecture: x86_64 Install Date: Wed 25 Sep 2019 09:29:06 PM CST Group : Unspecified Size : 758622 License : GPLv2 Signature : RSA/SHA256, Tue 02 Jul 2019 08:19:09 AM CST, Key ID 05b555b38483c65d Source RPM : nftables-0.9.0-8.el8.src.rpm Build Date : Sat 11 May 2019 11:06:46 PM CST Build Host : x86-01.mbox.centos.org Relocations : (not relocatable) Packager : CentOS Buildsys <bugs@centos.org> Vendor : CentOS URL : http://netfilter.org/projects/nftables/ Summary : Netfilter Tables userspace utillites Description : Netfilter Tables userspace utilities.
范例:CentOS 8 支持三种防火墙工具
[root@centos8 ~]#systemctl status iptables.service ● iptables.service - IPv4 firewall with iptables Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/iptables.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: inactive (dead) [root@centos8 ~]#systemctl status firewalld.service ● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: inactive (dead) Docs: man:firewalld(1) [root@centos8 ~]#systemctl status nftables.service ● nftables.service - Netfilter Tables Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/systemd/system/nftables.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled) Active: inactive (dead) Docs: man:nft(8)
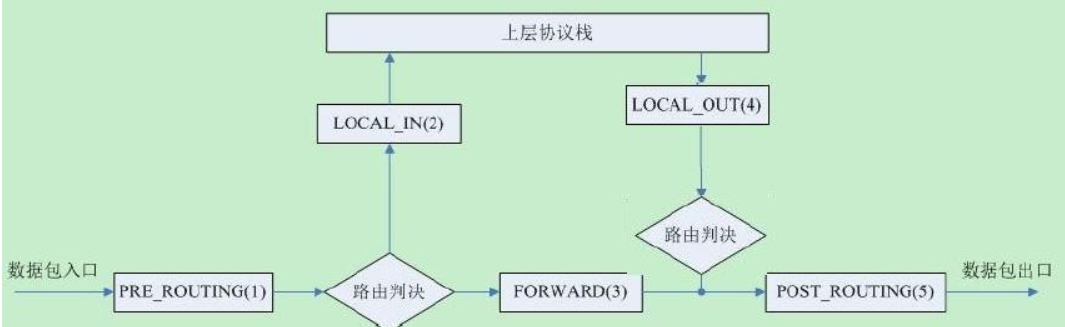
流入本机:PREROUTING --> INPUT-->用户空间进程 流出本机:用户空间进程 -->OUTPUT--> POSTROUTING 转发:PREROUTING --> FORWARD --> POSTROUTING
iptables由五个表table和五个链chain以及一些规则组成 链 chain: 1、内置链:每个内置链对应于一个钩子函数 2、自定义链:用于对内置链进行扩展或补充,可实现更灵活的规则组织管理机制;只有Hook钩子调 用自定义链时,才生效。
filter表:过滤规则表,根据预定义的规则过滤符合条件的数据包,默认表 nat表:network address translation 地址转换规则表 mangle:修改数据标记位规则表 raw:关闭启用的连接跟踪机制,加快封包穿越防火墙速度 security:用于强制访问控制(MAC)网络规则,由Linux安全模块(如SELinux)实现
优先级由高到低的顺序为:
security -->raw-->mangle-->nat-->filter
表和链对应关系

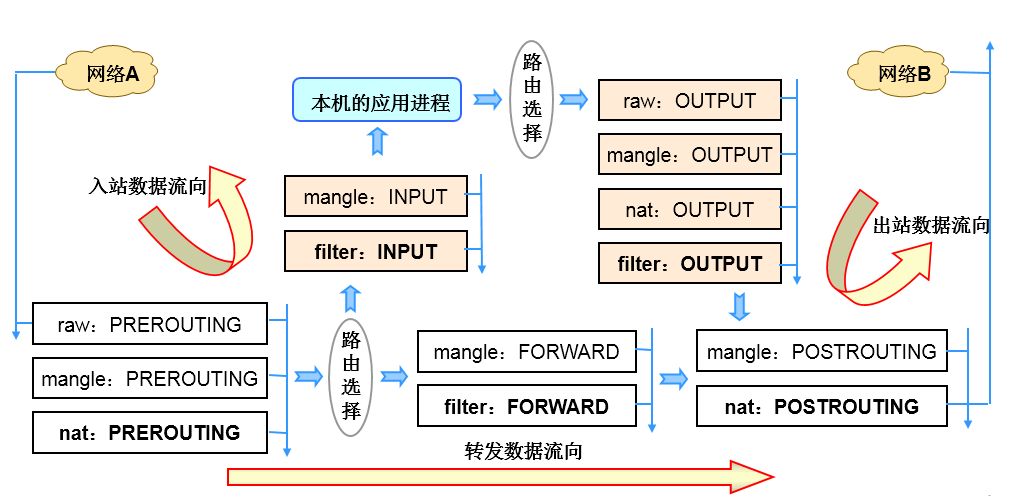
数据包过滤匹配流程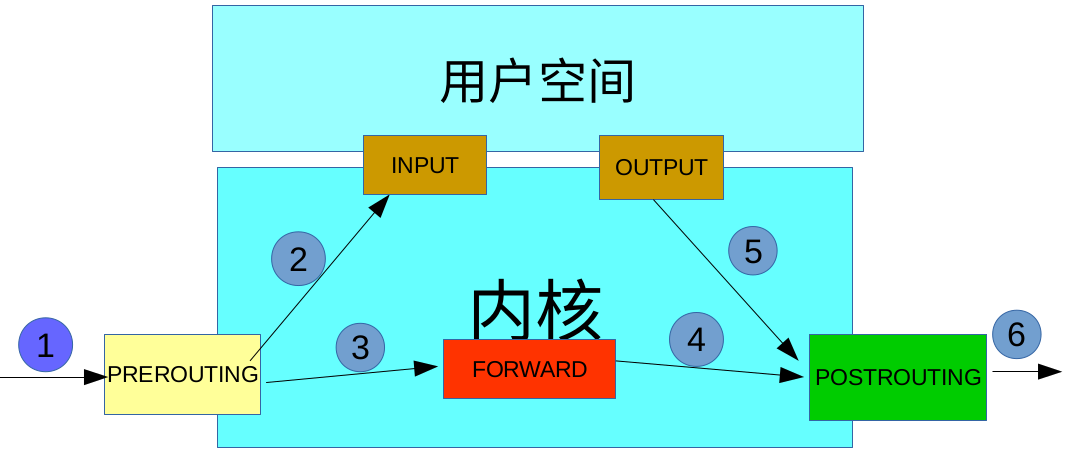
数据包先经过PREOUTING,由该链确定数据包走向: 目的地址是本地,则发送到INPUT,让INPUT决定是否接收下来送到用户空间,流程为①--->②; 若满足PREROUTING的nat表上的转发规则,则发送给FORWARD,然后再经过POSTROUTING发送出去,流程为: ①--->③--->④--->⑥; 主机发送数据包时,流程则是⑤--->⑥; 其中PREROUTING和POSTROUTING指的是数据包的流向,如上图所示POSTROUTING指的是发往公网的数据包,而PREROUTING指的是来自公网的数据包。
内核中数据包的传输过程
当一个数据包进入网卡时,数据包首先进入PREROUTING链,内核根据数据包目的IP判断是否需要转送出去。
如果数据包是进入本机的,数据包就会沿着图向下移动,到达INPUT链。数据包到达INPUT链后,任何进程都会收到它。本机上运行的程序可以发送数据包,这些数据包经过OUTPUT链,然后到达POSTROUTING链输出。
如果数据包是要转发出去的,且内核允许转发,数据包就会向右移动,经过FORWARD链,然后到达POSTROUTING链输出。
范例:
#centos7和centos8的表信息是一样的 #filter表 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -vnL -t filter Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination #nat表 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -vnL -t nat Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination #mangle表 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -vnL -t mangle Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination #raw表 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -vnL -t raw Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination #security表 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -vnL -t security Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination #CentOS 6 nat表不支持INPUT链 [root@centos6 ~]#iptables -vnL -t nat Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
2.1、iptables 规则说明
2.1.1 iptables 规则组成
规则rule:根据规则的匹配条件尝试匹配报文,对匹配成功的报文根据规则定义的处理动作作出处理,规则在链接上的次序即为其检查时的生效次序。
匹配条件:
默认为与条件,同时满足。
基本匹配:IP,端口,TCP的Flags(SYN,ACK等)。
扩展匹配:通过复杂高级功能匹配。 处理动作:称为target,跳转目标。
内建处理动作:ACCEPT,DROP,REJECT,SNAT,DNAT,MASQUERADE,MARK,LOG...
自定义处理动作:自定义chain,利用分类管理复杂情形,规则要添加在链上,才生效;添加在自定义链上不会自动生效
2.1.2 iptables规则添加时考量点
要实现哪种功能:判断添加在哪张表上
报文流经的路径:判断添加在哪个链上
报文的流向:判断源和目的
systemctl stop firewalld.service
systemctl disable firewalld. service
或者
systemctl disable --now firewalld. service
centos6关闭防护墙
service iptables stop
chkconfig iptables off
帮助:man 8 iptables
iptables [-t table] {-A|-C|-D} chain rule-specification
iptables [-t table] -I chain [rulenum] rule-specification
iptables [-t table] -R chain rulenum rule-specification
iptables [-t table] -D chain rulenum
iptables [-t table] -S [chain [rulenum]]
iptables [-t table] {-F|-L|-Z} [chain [rulenum]] [options...]
iptables [-t table] -N chain
iptables [-t table] -X [chain]
iptables [-t table] -P chain target
iptables [-t table] -E old-chain-name new-chain-name
rule-specification = [matches...] [target]
match = -m matchname [per-match-options]
target = -j targetname [per-target-options]
范例:Filter表中INPUT规则
表 链 源/目标 执行的动作 iptables -t filter -A INPUT -s 192.168.1.0/24 -j dorp #在filter表的INPUT链中定义源为192.168.1.0/24网段的全部丢弃。
iptables命令格式详解:
iptables [-t table] SUBCOMMAND chain [-m matchname [per-match-options]] -j targetname [per-target-options]
1、-t table:指定表 raw, mangle, nat, [filter]默认
2、SUBCOMMAND:子命令
2.2.1链管理类:
-N:new, 自定义一条新的规则链 -E:重命名自定义链;引用计数不为0的自定义链不能够被重命名,也不能被删除 -X:delete,删除自定义的空的规则链 -P:Policy,设置默认策略;对filter表中的链而言,其默认策略有:ACCEPT:接受, DROP:丢弃
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#iptables -N web_chain #创建一条自定义链并命名为web_chain [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -N web_chain -t nat #创建自定义链web_chain的nat表 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -X web_chain -t nat #删除自定义链web_chain的nat表 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -E web_chain WEB_CHAIN #把创建的自定义链web_chain重命名为WEB_CHAIN [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -A WEB_CHAIN -s 10.0.0.6 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,443 -j REJECT #给自定义链创建规则 #拒绝10.0.0.6的主机访问tcp的80和443端口 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -R WEB_CHAIN 1 -s 10.0.0.6 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,443,8080 -j REJECT #拒绝10.0.0.6的主机访问tcp的80、8080和443端口 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -vnL WEB_CHAIN Chain WEB_CHAIN (1 references) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 60 REJECT tcp -- * * 10.0.0.6 0.0.0.0/0 multiport dports 80,443,8080 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -A INPUT -j WEB_CHAIN #在input链中调用WEB_CHAIN链的规则 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -X WEB_CHAIN iptables v1.8.2 (nf_tables): CHAIN_USER_DEL failed (Device or resource busy): chain WEB_CHAIN #删除WEB_CHAIN链,删除失败,只能删除空的自定义链 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -F WEB_CHAIN #清空自定义链WEB_CHAIN [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -X WEB_CHAIN iptables v1.8.2 (nf_tables): CHAIN_USER_DEL failed (Device or resource busy): chain WEB_CHAIN [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -D INPUT 1 #取消input链调用的WEB_CHAIN规则 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -X WEB_CHAIN #删除成功 #自定义链删除步骤 #1、取消所有该自定义链的调用 #2、清空改自定义链 #3、删除自定义链
范例: 创建自定义链实现WEB的访问控制
[root@centos8 ~]#iptables -N web_chain #创建自定义链web_chain [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -E web_chain WEB_CHAIN #把自定义链改名为WEB_CHAIN [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -A WEB_CHAIN -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,443,8080 -j ACCEPT #创建自定义链的规程 #规则:允许访问tcp的80,443和8080端口 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -I INPUT 3 -s 10.0.0.0/24 -j WEB_CHAIN #把10.0.0.0/24的访问规则设置为WEB_CHAIN的规则,并插入到input链的第3条规则中 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -A WEB_CHAIN -p icmp -j ACCEPT #在WEB_CHAIN链的最后插入一条允许icmp的规则 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -I WEB_CHAIN 2 -s 10.0.0.6 -j REJECT #在WEB_CHAIN链中的第2条插入来主机10.0.0.6的全部拒绝 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -vnL --line-numbers Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 10 867 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 2 5637 423K ACCEPT all -- * * 10.0.0.1 0.0.0.0/0 3 248 20427 WEB_CHAIN all -- * * 10.0.0.0/240.0.0.0/0 4 4278 248K REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain WEB_CHAIN (1 references) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 36 2619 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 multiport dports 80,443,8080 2 16 1344 RETURN all -- * * 10.0.0.6 0.0.0.0/0 3 184 15456 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 [root@centos6 ~]#curl 10.0.0.8 centos8 website [root@centos6 ~]#curl 10.0.0.8 centos8 website [root@centos6 ~]#ping -c1 10.0.0.8 PING 10.0.0.8 (10.0.0.8) 56(84) bytes of data. From 10.0.0.8 icmp_seq=1 Destination Port Unreachable --- 10.0.0.8 ping statistics --- 1 packets transmitted, 0 received, +1 errors, 100% packet loss, time 1ms [root@centos7 ~]#ping 10.0.0.8 -c1 PING 10.0.0.8 (10.0.0.8) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 10.0.0.8: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.25 ms --- 10.0.0.8 ping statistics --- 1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms [root@centos6 ~]#curl 10.0.0.8 centos8 website [root@centos6 ~]#curl 10.0.0.8 centos8 website [root@centos6 ~]#ping -c1 10.0.0.8 PING 10.0.0.8 (10.0.0.8) 56(84) bytes of data. From 10.0.0.8 icmp_seq=1 Destination Port Unreachable --- 10.0.0.8 ping statistics --- 1 packets transmitted, 0 received, +1 errors, 100% packet loss, time 1ms [root@centos7 ~]#ping 10.0.0.8 -c1 PING 10.0.0.8 (10.0.0.8) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 10.0.0.8: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.25 ms --- 10.0.0.8 ping statistics --- 1 packets transmitted, 1 received, 0% packet loss, time 0ms
范例: 删除自定义链
#无法直接删除自定义链,删除自定议链和创建的顺序相反 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -X WEB_CHAIN iptables v1.8.4 (nf_tables): CHAIN_USER_DEL failed (Device or resource busy): chain WEB_CHAIN [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -D INPUT 3 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -X WEB_CHAIN iptables v1.8.4 (nf_tables): CHAIN_USER_DEL failed (Device or resource busy): chain WEB_CHAIN [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -F WEB_CHAIN [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -L WEB_CHAIN Chain WEB_CHAIN (0 references) target prot opt source destination [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -X WEB_CHAIN [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -vnL --line-numbers Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 10 867 ACCEPT all -- lo * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 2 5824 437K ACCEPT all -- * * 10.0.0.1 0.0.0.0/0 3 4279 248K REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source xdestination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
-L:list, 列出指定鏈上的所有规则,本选项须置后 -n:numberic,以数字格式显示地址和端口号 -v:verbose,详细信息 -vv 更详细 -x:exactly,显示计数器结果的精确值,而非单位转换后的易读值 --line-numbers:显示规则的序号 -S selected,以iptables-save 命令格式显示链上规则
常用组合:
-vnL
-vvnxL --line-numbers
-A:append,追加 -I:insert, 插入,要指明插入至的规则编号,默认为第一条 -D:delete,删除 (1) 指明规则序号 (2) 指明规则本身 -R:replace,替换指定链上的指定规则编号 -F:flush,清空指定的规则链 -Z:zero,置零 iptables的每条规则都有两个计数器 (1) 匹配到的报文的个数 (2) 匹配到的所有报文的大小之和
2.2.4处理动作
简单的动作
ACCEPT
DROP
扩展动作:
REJECT:--reject-with:icmp-port-unreachable默认
RETURN:返回调用链
REDIRECT:端口重定向
LOG:记录日志,dmesg
MARK:做防火墙标记
DNAT:目标地址转换
SNAT:源地址转换
MASQUERADE:地址伪装
自定义链
2.3.1基本匹配条件:
无需加载模块,由iptables/netfilter自行提供
[!] -s, --source address[/mask][,...]:源IP地址或者不连续的IP地址 [!] -d, --destination address[/mask][,...]:目标IP地址或者不连续的IP地址 [!] -p, --protocol protocol:指定协议,可使用数字如0(all) protocol: tcp, udp, icmp, icmpv6, udplite,esp, ah, sctp, mh or“all“ 参看:/etc/protocols [!] -i, --in-interface name:报文流入的接口;只能应用于数据报文流入环节,只应用于INPUT、FORWARD、PREROUTING链 [!] -o, --out-interface name:报文流出的接口;只能应用于数据报文流出的环节,只应用于FORWARD、OUTPUT、POSTROUTING链
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#iptables -A INPUT -s 10.0.0.6,10.0.0.10 -j REJECT #在input链上拒绝主机10.0.0.6和10.0.0.10的访问 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -I INPUT -i lo -j ACCEPT #在input链上允许lo接口流入的报文 [root@centos8 ~]#curl 127.0.0.1 10.0.0.8 [root@centos8 ~]#curl 10.0.0.8 10.0.0.8 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -I INPUT 2 -s 10.0.0.6 ! -p icmp -j ACCEPT #在input链的第2条规则插入来自主机10.0.0.6的非icmp的报文都允许
2.3.2iptables 扩展匹配条件
扩展匹配条件:需要加载扩展模块(/usr/lib64/xtables/*.so),方可生效 扩展模块的查看帮助 :man iptables-extensions
扩展匹配条件:隐式扩展和显式扩展
iptables 在使用-p选项指明了特定的协议时,无需再用-m选项指明扩展模块的扩展机制,不需要手动加 载扩展模块
tcp协议的扩展选项
[!] --source-port, --sport port[:port]:匹配报文源端口,可为端口连续范围 [!] --destination-port,--dport port[:port]:匹配报文目标端口,可为连续范围 [!] --tcp-flags mask comp mask 需检查的标志位列表,用,分隔 , 例如 SYN,ACK,FIN,RST comp 在mask列表中必须为1的标志位列表,无指定则必须为0,用,分隔tcp协议的扩展选项 [!] --syn:用于匹配第一次握手, 相当于:--tcp-flags SYN,ACK,FIN,RST SYN
范例:
--tcp-flags SYN,ACK,FIN,RST SYN 表示要检查的标志位为SYN,ACK,FIN,RST四个,其中SYN必须为1,余下的必须为0,第一次握手 --tcp-flags SYN,ACK,FIN,RST SYN,ACK 第二次握手 #错误包 --tcp-flags ALL ALL --tcp_flags ALL NONE
udp 协议的扩展选项
[!] --source-port, --sport port[:port]:匹配报文的源端口或端口范围
[!] --destination-port,--dport port[:port]:匹配报文的目标端口或端口范围
icmp 协议的扩展选项
[!] --icmp-type {type[/code]|typename}
type/code
0/0 echo-reply icmp应答
8/0 echo-request icmp请求
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#iptables -A INPUT -s 10.0.0.6 -p tcp --dport 21:23 -j REJECT [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -vnL Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 1 60 REJECT tcp -- * * 10.0.0.6 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpts:21:23 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destina
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --syn -j REJECT
#拒绝tcp的第一个报文(拒绝tcp的第一次握手)
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#iptables -A INPUT -s 10.0.0.6 -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -j REJECT #拒绝主机10.0.0.6的icmp的请求报文
2.3.2.2显式扩展及相关模块
[-m matchname [per-match-options]]
multiport扩展
以离散方式定义多端口匹配,最多指定15个端口
#指定多个源端口 [!] --source-ports,--sports port[,port|,port:port]... # 指定多个目标端口 [!] --destination-ports,--dports port[,port|,port:port]... #多个源或目标端 [!] --ports port[,port|,port:port]...
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#iptables -A INPUT -s 172.16.0.0/16 -d 172.16.100.10 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 20:22,80 -j ACCEPT [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -A INPUT -s 10.0.0.6 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 445,139 -j REJECT [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -vnL Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 2 120 REJECT tcp -- * * 10.0.0.6 0.0.0.0/0 multiport dports 445,139 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
iprange扩展
[!] --src-range from[-to] 源IP地址范围
[!] --dst-range from[-to] 目标IP地址范围
范例:
iptables -A INPUT -d 172.16.1.100 -p tcp --dport 80 -m iprange --src-range 172.16.1.5-172.16.1.10 -j DROP #拒绝172.168.1.5-172.168.1.10的主机访问172.16.1.100的80端口
mac 模块可以指明源MAC地址,,适用于:PREROUTING, FORWARD,INPUT chains
[!] --mac-source XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX
范例:
iptables -A INPUT -s 172.16.0.100 -m mac --mac-source 00:50:56:12:34:56 -j ACCEPT #允许mac为00:50:56:12:34:56,源ip为172.16.0.100的主机访问 iptables -A INPUT -s 172.16.0.100 -j REJECT #拒绝172.16.0.100的主机访问
string扩展
--algo {bm|kmp} 字符串匹配检测算法
bm:Boyer-Moore
kmp:Knuth-Pratt-Morris
--from offset 开始偏移
--to offset 结束偏移
[!] --string pattern 要检测的字符串模式
[!] --hex-string pattern要检测字符串模式,16进制格式
范例:
iptables -A OUTPUT -p tcp --dport 80 -m string --algo bm --from 62 --string "baidu" -j REJECT #拒绝目标端口是80并带有"baidu"的报文出去
time扩展
注意:CentOS 8 此模块有问题
--datestart YYYY[-MM[-DD[Thh[:mm[:ss]]]]] 日期 --datestop YYYY[-MM[-DD[Thh[:mm[:ss]]]]] --timestart hh:mm[:ss] 时间 --timestop hh:mm[:ss] [!] --monthdays day[,day...] 每个月的几号 [!] --weekdays day[,day...] 星期几,1 – 7 分别表示星期一到星期日 --kerneltz:内核时区(当地时间),不建议使用,CentOS 7 系统默认为 UTC 注意: centos6 不支持kerneltz ,--localtz指定本地时区(默认)
[root@centos8 ~]#rpm -ql iptables |grep time /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_time.so [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -A INPUT -m time --timestart 12:30 --timestop 13:30 -j ACCEPT iptables v1.8.4 (nf_tables): Couldn't load match `time':No such file or directory centos7下没有问题 [root@centos7 ~]#rpm -ql iptables |grep time /usr/lib64/xtables/libxt_time.so [root@centos7 ~]#iptables -A INPUT -m time --timestart 12:30 --timestop 13:30 -j ACCEPT
范例: 关于 -- kerneltz 选项
[root@centos7 ~]#iptables -A INPUT -s 172.16.0.0/16 -d 172.16.100.10 -p tcp --dport 80 -m time --timestart 14:30 --timestop 18:30 --weekdays Sat,Sun --kerneltz -j DROP
connlimit扩展
根据每客户端IP做并发连接数数量匹配
可防止Dos(Denial of Service,拒绝服务)攻击
--connlimit-upto N #连接的数量小于等于N时匹配
--connlimit-above N #连接的数量大于N时匹配
范例:
iptables -A INPUT -d 172.16.100.10 -p tcp --dport 22 -m connlimit --connlimitabove 2 -j REJECT #对主机172.16.100.10的22端口访问数超过2时,则拒绝(第3次及以后的都被拒绝)
limit扩展
基于收发报文的速率做匹配 , 令牌桶过滤器
--limit-burst number #前多少个包不限制
--limit #[/second|/minute|/hour|/day]
范例:
iptables -I INPUT -d 172.16.100.10 -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -m limit --limit 10/minute --limit-burst 5 -j ACCEPT #对到达主机172.16.100.10的icmp的请求报文限速为每分钟10个包,前5个包不做任何限制 iptables -I INPUT 2 -p icmp -j REJECT
范例:
#对本主机的icmp包限速为每分钟20个,前10个没有限制 [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -m limit --limit-burst 10 --limit 20/minute -j ACCEPT [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -A INPUT -p icmp -j REJECT [root@centos6 ~]#ping 10.0.0.8 PING 192.168.39.8 (192.168.39.8) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.779 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.436 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.774 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=4 ttl=64 time=0.391 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=5 ttl=64 time=0.441 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=6 ttl=64 time=0.356 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=7 ttl=64 time=0.553 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=8 ttl=64 time=0.458 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=9 ttl=64 time=0.459 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=10 ttl=64 time=0.479 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=11 ttl=64 time=0.450 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=12 ttl=64 time=0.471 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=13 ttl=64 time=0.531 ms 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=14 ttl=64 time=0.444 ms From 192.168.39.8 icmp_seq=15 Destination Port Unreachable 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=16 ttl=64 time=0.668 ms From 192.168.39.8 icmp_seq=17 Destination Port Unreachable From 192.168.39.8 icmp_seq=18 Destination Port Unreachable 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=19 ttl=64 time=0.692 ms From 192.168.39.8 icmp_seq=20 Destination Port Unreachable From 192.168.39.8 icmp_seq=21 Destination Port Unreachable 64 bytes from 192.168.39.8: icmp_seq=22 ttl=64 time=0.651 ms
state 扩展模块,可以根据”连接追踪机制“去检查连接的状态,较耗资源
conntrack机制:追踪本机上的请求和响应之间的关系
状态类型:
NEW:新发出请求;连接追踪信息库中不存在此连接的相关信息条目,因此,将其识别为第一次发出的请求
ESTABLISHED:NEW状态之后,连接追踪信息库中为其建立的条目失效之前期间内所进行的通信状态
RELATED:新发起的但与已有连接相关联的连接,如:ftp协议中的数据连接与命令连接之间的关系
INVALID:无效的连接,如flag标记不正确
UNTRACKED:未进行追踪的连接,如:raw表中关闭追踪
已经追踪到的并记录下来的连接信息库
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /proc/net/nf_conntrack ipv4 2 tcp 6 431325 ESTABLISHED src=10.0.0.7 dst=10.0.0.8 sport=49900 dport=80 src=10.0.0.8 dst=10.0.0.7 sport=80 dport=49900 [ASSURED] mark=0 zone=0 use=2 ipv4 2 tcp 6 431325 ESTABLISHED src=10.0.0.7 dst=10.0.0.8 sport=49886 dport=80 src=10.0.0.8 dst=10.0.0.7 sport=80 dport=49886 [ASSURED] mark=0 zone=0 use=2 ipv4 2 tcp 6 431325 ESTABLISHED src=10.0.0.7 dst=10.0.0.8 sport=49892 dport=80 src=10.0.0.8 dst=10.0.0.7 sport=80 dport=49892 [ASSURED] mark=0 zone=0 use=2 ipv4 2 tcp 6 431325 ESTABLISHED src=10.0.0.7 dst=10.0.0.8 sport=49904 dport=80 src=10.0.0.8 dst=10.0.0.7 sport=80 dport=49904 [ASSURED] mark=0 zone=0 use=2 ipv4 2 tcp 6 431325 ESTABLISHED src=10.0.0.7 dst=10.0.0.8 sport=49890 dport=80 src=10.0.0.8 dst=10.0.0.7 sport=80 dport=49890 [ASSURED] mark=0 zone=0 use=2 ipv4 2 tcp 6 431325 ESTABLISHED src=10.0.0.7 dst=10.0.0.8 sport=49888 dport=80 src=10.0.0.8 dst=10.0.0.7 sport=80 dport=49888 [ASSURED] mark=0 zone=0 use=2 ipv4 2 tcp 6 431325 ESTABLISHED src=10.0.0.7 dst=10.0.0.8 sport=49896 dport=80 src=10.0.0.8 dst=10.0.0.7 sport=80 dport=49896 [ASSURED] mark=0 zone=0 use=2 ipv4 2 tcp 6 431325 ESTABLISHED src=10.0.0.7 dst=10.0.0.8 sport=49898 dport=80 src=10.0.0.8 dst=10.0.0.7 sport=80 dport=49898 [ASSURED] mark=0 zone=0 use=2 ipv4 2 tcp 6 431325 ESTABLISHED src=10.0.0.7 dst=10.0.0.8 sport=49894 dport=80 src=10.0.0.8 dst=10.0.0.7 sport=80 dport=49894 [ASSURED] mark=0 zone=0 use=2 ipv4 2 tcp 6 431325 ESTABLISHED src=10.0.0.7 dst=10.0.0.8 sport=49902 dport=80 src=10.0.0.8 dst=10.0.0.7 sport=80 dport=49902 [ASSURED] mark=0 zone=0 use=2
调整连接追踪功能所能够容纳的最大连接数量
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /proc/sys/net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_max 26624 [root@centos8 ~]#cat /proc/sys/net/nf_conntrack_max 26624
查看连接跟踪有多少条目
[root@centos8 ~]#cat /proc/sys/net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_count 10
不同的协议的连接追踪时长
[root@centos8 ~]#ll /proc/sys/net/netfilter/ total 0 -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_acct -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_buckets -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_checksum -r--r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_count -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_dccp_loose -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_dccp_timeout_closereq -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_dccp_timeout_closing -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_dccp_timeout_open -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_dccp_timeout_partopen -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_dccp_timeout_request -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_dccp_timeout_respond -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_dccp_timeout_timewait -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_events -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_expect_max -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_generic_timeout -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_helper -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_icmp_timeout -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_log_invalid -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:13 nf_conntrack_max -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_sctp_timeout_closed -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_sctp_timeout_cookie_echoed -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_sctp_timeout_cookie_wait -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_sctp_timeout_established -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_sctp_timeout_heartbeat_acked -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_sctp_timeout_heartbeat_sent -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_sctp_timeout_shutdown_ack_sent -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_sctp_timeout_shutdown_recd -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_sctp_timeout_shutdown_sent -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_tcp_be_liberal -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_tcp_loose -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_tcp_max_retrans -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close_wait -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_fin_wait -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_last_ack -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_max_retrans -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_syn_recv -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_syn_sent -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_time_wait -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_unacknowledged -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_timestamp -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_udp_timeout -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_conntrack_udp_timeout_stream -dr-xr-xr-x 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_log -rw-r--r-- 1 root root 0 Mar 19 18:14 nf_log_all_netns
说明:
连接跟踪,需要加载模块: modprobe nf_conntrack_ipv4
当服务器连接多于最大连接数时dmesg 可以观察到 :kernel: ip_conntrack: table full, dropping
packet错误,并且导致建立TCP连接很慢。
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#echo 1 > /proc/sys/net/netfilter/nf_conntrack_max [root@centos8 ~]#tail /var/log/messages Jul 8 10:03:53 centos8 kernel: nf_conntrack: nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet [root@centos6 ~]#tail /var/log/messages Jul 8 09:51:16 centos6 kernel: nf_conntrack: table full, dropping packet.
vi /etc/sysctl.conf net.nf_conntrack_max = 393216 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_max = 393216
(2) 降低 nf_conntrack timeout时间
vi /etc/sysctl.conf net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_established = 300 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_time_wait = 120 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_close_wait = 60 net.netfilter.nf_conntrack_tcp_timeout_fin_wait = 120 iptables -t nat -L -n
格式:
[!] --state state
范例: 不允许10.0.0.7 访问本机,但本机可以访问10.0.0.7
[root@centos8 ~]#iptables -S -P INPUT ACCEPT -P FORWARD ACCEPT -P OUTPUT ACCEPT -A INPUT -s 10.0.0.1/32 -j ACCEPT -A INPUT ! -s 10.0.0.7/32 -m state --state NEW -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT -A INPUT -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
范例:
iptables -A INPUT -d 172.16.1.10 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 22,80 -m state --state NEW,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -s 172.16.1.10 -p tcp -m multiport --sports 22,80 -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT [root@centos8 ~]#iptables -A INPUT -m state --state NEW -j REJECT
案例:开放被动模式的ftp服务
CentOS 8 此模块有bug
vim /etc/sysconfig/iptables-config IPTABLES_MODULES=“nf_conntrack_ftp" modprobe nf_conntrack_ftp
iptables -I INPUT -d LocalIP -p tcp -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -d LocalIP -p tcp --dport 21 -m state --state NEW -j ACCEPT
(3) 放行响应报文:
iptables -I OUTPUT -s LocalIP -p tcp -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT
范例:开放被动模式的ftp服务示例
yum install vsftpd systemctl start vsftpd modprobe nf_conntrack_ftp iptables -F iptables -A INPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED,RELATED -j ACCEPT iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 21 -m state --state NEW -j ACCEPT iptables -A OUTPUT -m state --state ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT iptables -P INPUT DROP iptables -P OUTPUT DROP iptables -vnL
自定义链, ACCEPT, DROP, REJECT,RETURN,LOG,SNAT,DNAT,REDIRECT,MASQUERADE LOG:非中断target,本身不拒绝和允许,放在拒绝和允许规则前,并将日志记录在/var/log/messages系 统日志中 --log-level level 级别: debug,info,notice, warning, error, crit, alert,emerg --log-prefix prefix 日志前缀,用于区别不同的日志,最多29个字符
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#iptables -I INPUT -s 10.0.0.0/24 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,21,22,23 -m state --state NEW -j LOG --log-prefix "new connections: " [root@centos8 ~]#tail -f /var/log/messages Mar 19 18:41:07 centos8 kernel: iptables tcp connection: IN=eth0 OUT= MAC=00:0c:29:f8:5d:b7:00:50:56:c0:00:08:08:00 SRC=10.0.0.1 DST=10.0.0.8 LEN=40 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=128 ID=43974 DF PROTO=TCP SPT=9844 DPT=22 WINDOW=4102 RES=0x00 ACK URGP=0 Mar 19 18:41:07 centos8 kernel: new connections: IN=eth0 OUT= MAC=00:0c:29:f8:5d:b7:00:50:56:c0:00:08:08:00 SRC=10.0.0.1 DST=10.0.0.8 LEN=40 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=128 ID=43975 DF PROTO=TCP SPT=9844 DPT=22 WINDOW=4102 RES=0x00 ACK URGP=0 Mar 19 18:41:08 centos8 kernel: new connections: IN=eth0 OUT=
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#iptables -R INPUT 2 -p tcp --dport 21 -m state --state NEW -j LOG --log-prefix "ftp new link: " [root@centos8 ~]#tail -f /var/log/messages Dec 21 10:02:31 centos8 kernel: ftp new link: IN=eth0 OUT= MAC=00:0c:29:f9:8d:90:00:0c:29:10:8a:b1:08:00 SRC=192.168.39.6 DST=192.168.39.8 LEN=60 TOS=0x00 PREC=0x00 TTL=64 ID=15556 DF PROTO=TCP SPT=53706 DPT=21 WINDOW=14600 RES=0x00 SYN URGP=0
2.5规则优化最佳实践
2、谨慎放行入站的新请求
3、有特殊目的限制访问功能,要在放行规则之前加以拒绝
4、同类规则(访问同一应用,比如:http ),匹配范围小的放在前面,用于特殊处理
5、不同类的规则(访问不同应用,一个是http,另一个是mysql ),匹配范围大的放在前面,效率更高
-s 10.0.0.6 -p tcp --dport 3306 -j REJECT -s 172.16.0.0/16 -p tcp --dport 80 -j REJECT
7、设置默认策略,建议白名单(只放行特定连接)
iptables -P,不建议,容易出现“自杀现象”
规则的最后定义规则做为默认策略,推荐使用,放在最后一条
使用iptables命令定义的规则,手动删除之前,其生效期限为kernel存活期限
持久保存规则:
iptables-save > /PATH/TO/SOME_RULES_FILE
CentOS 6
#将规则覆盖保存至/etc/sysconfig/iptables文件中
service iptables save
iptables-restore < /PATH/FROM/SOME_RULES_FILE
iptables-restore选项
-n, --noflush:不清除原有规则
-t, --test:仅分析生成规则集,但不提交
CentOS 6:
#会自动从/etc/sysconfig/iptables 重新载入规则
service iptables restart
iptables-restore < /PATH/FROM/IPTABLES_RULES_FILE
[root@centos8 ~]#yum -y install iptables-services [root@centos8 ~]#cp /etc/sysconfig/iptables{,.bak} #保存现在的规则到文件中方法1 [root@centos8 ~]#/usr/libexec/iptables/iptables.init save #保存现在的规则到文件中方法2 iptables-save > /etc/sysconfig/iptables #开机启动 [root@centos8 ~]#systemctl enable iptables.service [root@centos8 ~]#systemctl mask firewalld.service nftables.service
2.7网络防火墙
iptables/netfilter 利用filter表的FORWARD链,可以充当网络防火墙:
注意的问题:
(1) 请求-响应报文均会经由FORWARD链,要注意规则的方向性
(2) 如果要启用conntrack机制,建议将双方向的状态为ESTABLISHED的报文直接放行
范例:
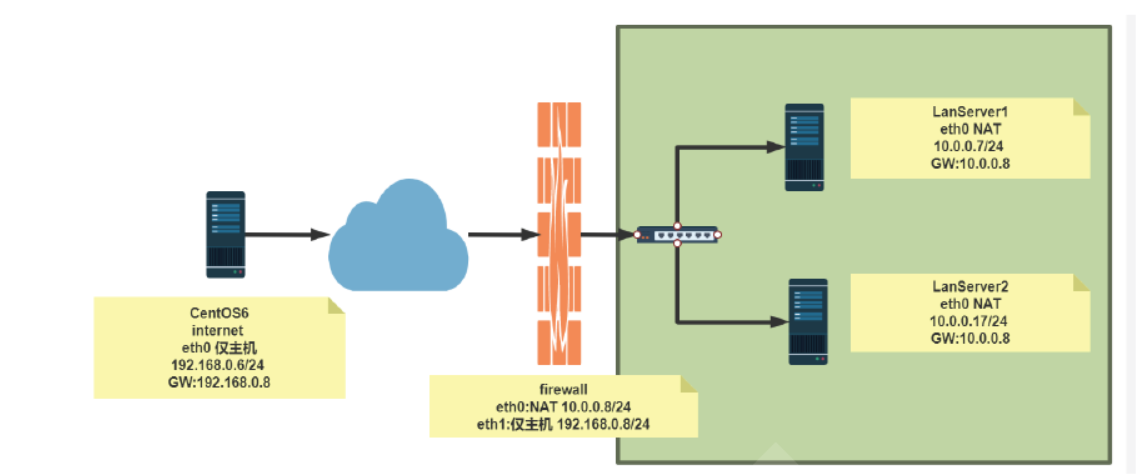
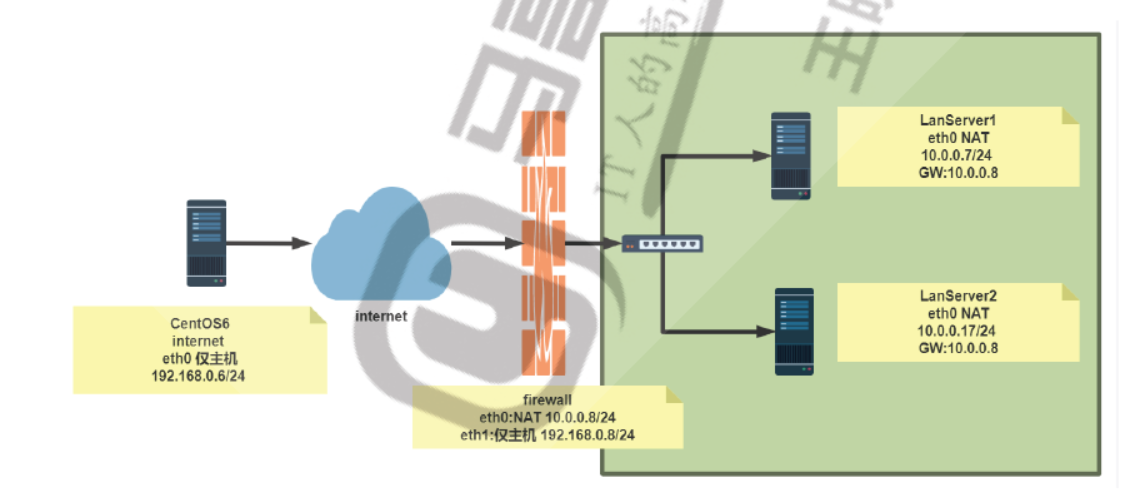
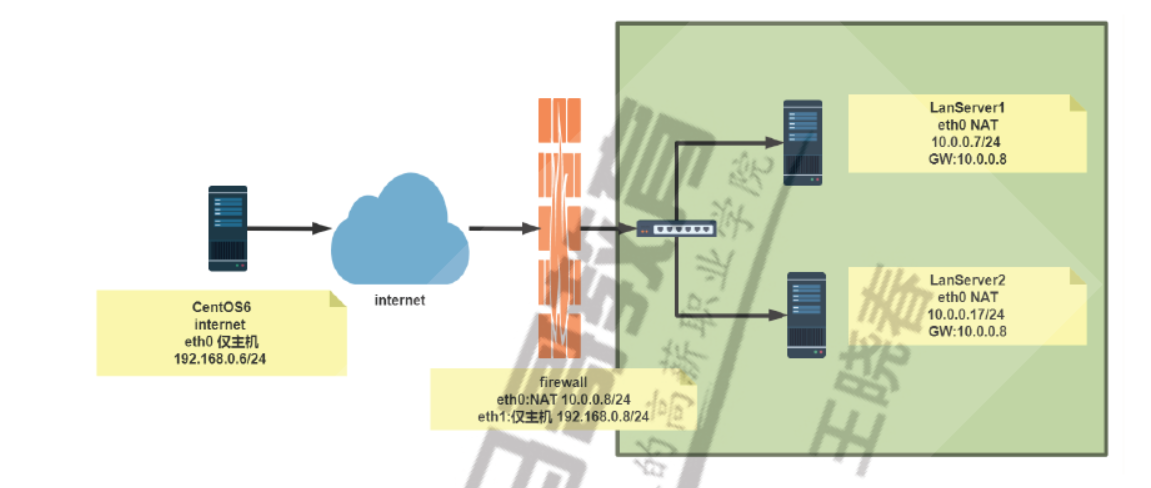
#环境准备 [root@internet ~]#hostname -I 192.168.0.6 [root@internet ~]#route -n Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 192.168.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 eth0 169.254.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.0.0 U 1002 0 0 eth0 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.8 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 [root@firewall ~]#hostname -I 10.0.0.8 192.168.0.8 [root@firewall ~]#cat /etc/sysctl.conf net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 [root@lanserver1 ~]#hostname -I 10.0.0.7 [root@lanserver1 ~]#route -n Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.8 0.0.0.0 UG 100 0 0 eth0 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 100 0 0 eth0 [root@lanserver2 ~]#hostname -I 10.0.0.17 [root@lanserver2 ~]#route -n Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.8 0.0.0.0 UG 100 0 0 eth0 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 100 0 0 eth0 #方法1 通过标准模块实现内网访问外网,反之禁止 [root@firewall ~]#iptables -A FORWARD -j REJECT [root@firewall ~]#iptables -I FORWARD -s 10.0.0.0/24 -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT [root@firewall ~]#iptables -I FORWARD -d 10.0.0.0/24 -p tcp --sport 80 -j ACCEPT [root@firewall ~]#iptables -I FORWARD -s 10.0.0.0/24 -p icmp --icmp-type 8 -j ACCEPT [root@firewall ~]#iptables -I FORWARD -d 10.0.0.0/24 -p icmp --icmp-type 0 -j ACCEPT [root@firewall ~]#iptables -vnL --line-numbers Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 174 14616 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 10.0.0.0/24 icmptype 0 2 218 18312 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 10.0.0.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 icmptype 8 3 10 1084 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 10.0.0.0/24 tcp spt:80 4 31 1938 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 10.0.0.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:80 5 312 25632 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination #方法2 利用state模块实现内网访问可以访问外网,反之禁止 [root@firewall ~]#iptables -DFORWARD 1 [root@firewall ~]#iptables -DFORWARD 2 [root@firewall ~]#iptables -vnL --line-numbers Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 342 28728 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 10.0.0.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 icmptype 8 2 47 2898 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 10.0.0.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:80 3 462 37608 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination [root@firewall ~]#iptables -IFORWARD -m state --state RELATED,ESTABLISHED -j ACCEPT [root@firewall ~]#iptables -vnL --line-numbers Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 40 3429 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED 2 443 37212 ACCEPT icmp -- * * 10.0.0.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 icmptype 8 3 49 3018 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 10.0.0.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:80 4 563 46068 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination [root@lanserver1 ~]#ping 192.168.0.6 -c1 PING 192.168.0.6 (192.168.0.6) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.0.6: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=2.20 ms [root@lanserver2 ~]#curl 192.168.0.6 internet [root@internet ~]#ping 10.0.0.7 -c1 PING 10.0.0.7 (10.0.0.7) 56(84) bytes of data. From 192.168.0.8 icmp_seq=1 Destination Port Unreachable [root@internet ~]#curl 10.0.0.7 curl: (7) couldn't connect to host #利用state模块实现允许内网可以访问外网所有资源 [root@firewall ~]#iptables -DFORWARD 2 [root@firewall ~]#iptables -DFORWARD 2 [root@firewall ~]#iptables -IFORWARD 2 -s 10.0.0.0/24 -m state --state NEW -j ACCEPT [root@firewall ~]#iptables -vnL --line-numbers Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 134 15209 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED 2 3 204 ACCEPT all -- * * 10.0.0.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW 3 572 46680 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination [root@lanserver1 ~]#ping 192.168.0.6 -c1 PING 192.168.0.6 (192.168.0.6) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 192.168.0.6: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=2.26 ms [root@lanserver2 ~]#curl 192.168.0.6 internet [root@lanserver2 ~]#ssh 192.168.0.6 The authenticity of host '192.168.0.6 (192.168.0.6)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is SHA256:ldHMw3UFehPuE3bgtMHIX5IxRRTM7fwC4iZ0Qqglcys. RSA key fingerprint is MD5:8c:44:d9:3d:22:54:62:d8:27:77:d5:06:09:58:76:92. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? [root@internet ~]#curl 10.0.0.7 curl: (7) couldn't connect to host [root@internet ~]#ping 10.0.0.7 -c1 PING 10.0.0.7 (10.0.0.7) 56(84) bytes of data. From 192.168.0.8 icmp_seq=1 Destination Port Unreachable [root@internet ~]#ssh 10.0.0.7 ssh: connect to host 10.0.0.7 port 22: Connection refused
#允许内网指定主机被外网访问 [root@firewall ~]#iptables -IFORWARD 3 -d 10.0.0.7 -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT [root@firewall ~]#iptables -vnL --line-numbers Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 63 12862 ACCEPT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 state RELATED,ESTABLISHED 2 9 612 ACCEPT all -- * * 10.0.0.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 state NEW 3 1 60 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 10.0.0.7 tcp dpt:80 4 586 47464 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 reject-with icmp-port-unreachable Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination [root@internet ~]#curl 10.0.0.7 lanserver1 [root@internet ~]#ping 10.0.0.7 -c1 PING 10.0.0.7 (10.0.0.7) 56(84) bytes of data. From 192.168.0.8 icmp_seq=1 Destination Port Unreachable [root@internet ~]#curl 10.0.0.17 curl: (7) couldn't connect to host
范例:
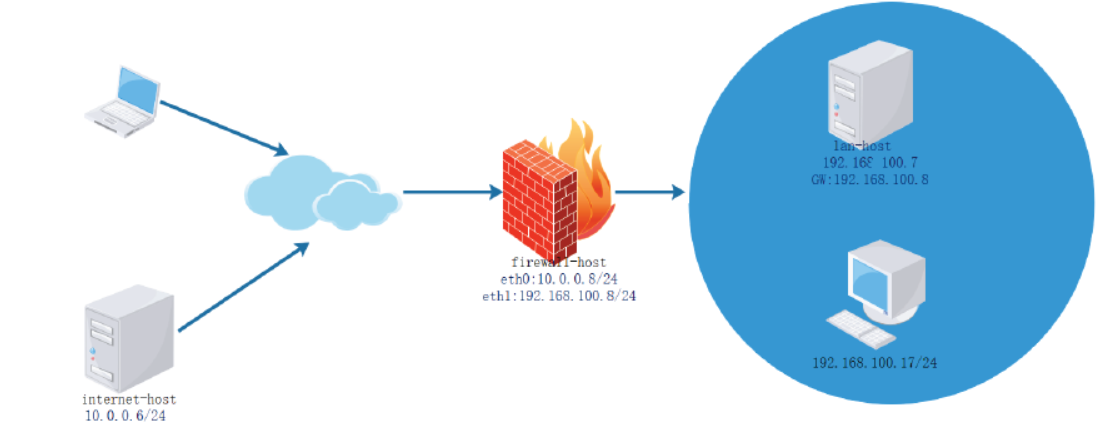
[root@internet-host ~]#hostname -I 10.0.0.6 [root@internet-host ~]#route -n Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 1 0 0 eth0 0.0.0.0 10.0.0.8 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 eth0 [root@firewall-host ~]#hostname -I 10.0.0.8 192.168.100.8 [root@lan-host ~]#hostname -I 192.168.100.7 [root@lan-host ~]#route -n Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 0.0.0.0 1 92.168.100.8 0.0.0.0 UG 100 0 0 eth0 192.168.100.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 100 0 0 eth0 [root@firewall-host ~]#vim /etc/sysctl.conf net.ipv4.ip_forward=1 [root@firewall-host ~]#sysctl -p [root@firewall-host ~]#iptables -A FORWARD -d 192.168.100.0/24 -m state --state NEW -j REJECT
针对内部的特定服务可以允许外部访问,其它服务禁止访问
[root@firewall-host ~]#iptables -I FORWARD -d 192.168.100.0/24 -p tcp --dport 80 -j ACCEPT [root@firewall-host ~]#iptables -vnL FORWARD --line-numbers Chain FORWARD (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) num pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 6 486 ACCEPT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.100.0/24 tcp dpt:80 2 3 228 REJECT all -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 192.168.100.0/24 state NEW reject-with icmp-port-unreachable
NAT: network address translation,支持PREROUTING,INPUT,OUTPUT,POSTROUTING四个链
1、SNAT:source NAT ,支持POSTROUTING, INPUT,让本地网络中的主机通过某一特定地址访问 外部网络,实现地址伪装,请求报文:修改源IP
2、DNAT:destination NAT 支持PREROUTING , OUTPUT,把本地网络中的主机上的某服务开放给 外部网络访问(发布服务和端口映射),但隐藏真实IP,请求报文:修改目标IP
3、PNAT: port nat,端口和IP都进行修改
思考题
在单位内部使用未经申请的公网地址,如:6.0.0.0/8网段,进行内部网络通讯,并利用SNAT连接Internet,是否可以? 答案:可以,在访问互联网的时候,在出口其源ip会做nat地址转换
SNAT:基于nat表的target,适用于固定的公网IP SNAT选项:
--to-source
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s LocalNET ! -d LocalNet -j SNAT --to-source ExtIP
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.0.1.0/24 ! –d 10.0.1.0/24 -j SNAT --tosource 172.18.1.6-172.18.1.9 #当源ip为10.0.1.0/24网段的地址来访问的目标地址不是10.0.1.0/24网段,其源ip会转换为172.18.1.6-172.18.1.9中的某一个地址
2.7.2.2、MASQUERADE:
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s LocalNET ! -d LocalNet -j MASQUERADE
范例:
iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.0.1.0/24 ! –d 10.0.1.0/24 -j MASQUERADE
范例:查看本地主机访问公网时使用的IP
[root@centos8 ~]#curl http://ip.sb 111.199.191.204 [root@centos8 ~]#curl http://ipinfo.io/ip/ 111.199.191.204 [root@centos8 ~]#curl http://ifconfig.me 111.199.191.204 [root@centos8 ~]#curl -L http://tool.lu/ip 当前IP: 111.199.191.204 归属地: 中国 北京 北京 [root@centos8 ~]#curl -sS --connect-timeout 10 -m 60 https://www.bt.cn/Api/getIpAddress 111.199.189.164
范例: SNAT
#针对专线静态公共IP [root@firewall ~]#iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.0.0.0/24 -j SNAT --tosource 192.168.0.8 #针对拨号网络和专线静态公共IP [root@firewall ~]#iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.0.0.0/24 -j MASQUERADE #查看监听端口 [root@firewall ~]#ss -ntl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:* LISTEN 0 100 [::1]:25 [::]:* #内网可以访问外网 [root@lanserver1 ~]#curl 192.168.0.6 internet #外网不可以访问内网 [root@internet ~]#curl 10.0.0.7 curl: (7) Failed to connect to 10.0.0.7: Network is unreachable #在外网服务器查看到是firewalld的地址在访问 [root@internet ~]#tail -f /var/log/httpd/access_log 192.168.0.8 - - [08/Jul/2020:17:36:54 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 9 "-" "curl/7.29.0" #查看转换状态信息 [root@firewall ~]#cat /proc/net/nf_conntrack ipv4 2 tcp 6 112 TIME_WAIT src=10.0.0.7 dst=192.168.0.6 sport=58384 dport=80 src=192.168.0.6 dst=192.168.0.8 sport=80 dport=58384 [ASSURED] mark=0 zone=0 use=2
[root@internet-host ~]#hostname -I 10.0.0.6 [root@internet-host ~]#route -n Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 10.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 1 0 0 eth0 [root@firewall-host ~]#hostname -I 10.0.0.8 192.168.100.8 [root@firewall-host ~]#sysctl -a |grep net.ipv4.ip_forward net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1 [root@lan-host ~]#hostname -I 192.168.100.7 [root@lan-host ~]#route -n Kernel IP routing table Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface 0.0.0.0 192.168.100.8 0.0.0.0 UG 100 0 0 eth0 192.168.100.0 0.0.0.0 255.255.255.0 U 100 0 0 eth0 [root@firewall-host ~]#iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 192.168.100.0/24 -j SNAT --to-source 10.0.0.8 [root@firewall-host ~]#iptables -vnL -t nat Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 0 0 SNAT all -- * * 192.168.100.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 to:10.0.0.8 Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination [root@lan-host ~]#curl 10.0.0.6 internet Server [root@internet-host ~]#curl 192.168.100.7 curl: (7) Failed to connect to 192.168.100.7: Network is unreachable [root@internet-host ~]#tail /var/log/httpd/access_log 10.0.0.8 - - [21/Mar/2020:16:31:35 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 16 "-" "curl/7.29.0" [root@lan-host ~]#ping 10.0.0.6 PING 10.0.0.6 (10.0.0.6) 56(84) bytes of data. 64 bytes from 10.0.0.6: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=0.989 ms 64 bytes from 10.0.0.6: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=0.544 ms [root@internet-host ~]#tcpdump -i eth0 -nn icmp tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 65535 bytes 16:34:30.171222 IP 10.0.0.8 > 10.0.0.6: ICMP echo request, id 24718, seq 120, length 64 16:34:30.171255 IP 10.0.0.6 > 10.0.0.8: ICMP echo reply, id 24718, seq 120, length 64 [root@firewall-host ~]#iptables -t nat -R POSTROUTING 1 -s 192.168.100.0/24 -j MASQUERADE [root@firewall-host ~]#iptables -t nat -nvL Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 0 0 MASQUERADE all -- * * 192.168.100.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination [root@firewall-host ~]#cat /proc/net/nf_conntrack ipv4 2 tcp 6 32 TIME_WAIT src=192.168.100.7 dst=10.0.0.6 sport=39430 dport=80 src=10.0.0.6 dst=10.0.0.8 sport=80 dport=39430 [ASSURED] mark=0 zone=0 use=2
[root@firewall-host ~]#man iptables-extensions --to-destination [ipaddr[-ipaddr]][:port[-port]] which can specify a single new destination IP address, an inclusive range of IP addresses. Optionally a port range, if the rule also specifies one of the following protocols: tcp, udp, dccp or sctp. If no port range is specified, then the destination port will never be modi-fied. If no IP address is specified then only the destination port will be modified. In Ker-nels up to 2.6.10 you can add several --to-destination options. For those kernels, if you specify more than one destination address, either via an address range or multiple -- to-des-tination options, a simple round-robin (one after another in cycle) load balancing takes place between these addresses. Later Kernels (>= 2.6.11- rc1) don't have the ability to NAT to multiple ranges anymore.
DNAT 格式:
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d ExtIP -p tcp|udp --dport PORT -j DNAT --todestination InterSeverIP[:PORT]
范例: DNAT
[root@firewall ~]#iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 192.168.0.8 -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 10.0.0.7:8080 [root@firewall ~]#ss -ntl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:* LISTEN 0 100 [::1]:25 [::]:* [root@internet ~]#curl 192.168.0.8 lanserver1 [root@lanserver1 ~]#tail /var/log/httpd/access_log 192.168.0.6 - - [08/Jul/2020:18:10:37 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 11 "-" "curl/7.19.7 (x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu) libcurl/7.19.7 NSS/3.27.1 zlib/1.2.3 libidn/1.18 libssh2/1.4.2" [root@firewall ~]#cat /proc/net/nf_conntrack ipv4 2 tcp 6 117 TIME_WAIT src=192.168.0.6 dst=192.168.0.8 sport=58170 dport=80 src=10.0.0.7 dst=192.168.0.6 sport=8080 dport=58170 [ASSURED] mark=0 zone=0 use=2
范例:
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -s 0/0 -d 172.18.100.6 -p tcp --dport 22 -j DNAT --to-destination 10.0.1.22 iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -s 0/0 -d 172.18.100.6 -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 10.0.1.22:8080
范例:
[root@firewall-host ~]#iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 10.0.0.8 -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.100.7 [root@firewall-host ~]#iptables -t nat -vnL PREROUTING Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 0 0 DNAT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 10.0.0.8 tcp dpt:80 to:192.168.100.7 [root@firewall-host ~]#ss -ntl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 128 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:* [root@internet-host ~]#curl 10.0.0.8 lan server [root@internet-host ~]#telnet 10.0.0.8 Trying 10.0.0.8... telnet: connect to address 10.0.0.8: Connection refused [root@lan-host ~]#tail -f /var/log/httpd/access_log 10.0.0.6 - - [21/Mar/2020:17:32:37 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 200 11 "-" "curl/7.19.7 (x86_64-redhat-linux-gnu) libcurl/7.19.7 NSS/3.27.1 zlib/1.2.3 libidn/1.18 libssh2/1.4.2" [root@firewall-host ~]#tail -f /proc/net/nf_conntrack ipv4 2 tcp 6 81 TIME_WAIT src=10.0.0.6 dst=10.0.0.8 sport=59426 dport=80 src=192.168.100.7 dst=10.0.0.6 sport=80 dport=59426 [ASSURED] mark=0 zone=0 use=2 [root@lan-host ~]#vim /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf listen 8000 [root@lan-host ~]#systemctl restart httpd [root@lan-host ~]#ss -ntl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:* LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* LISTEN 0 128 [::]:23 [::]:* LISTEN 0 100 [::1]:25 [::]:* LISTEN 0 128 [::]:8000 [::]:* LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:* [root@firewall-host ~]#iptables -t nat -R PREROUTING 1 -d 10.0.0.8 -p tcp --dport 80 -j DNAT --to-destination 192.168.100.7:8000 [root@firewall-host ~]#iptables -t nat -vnL Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 0 0 DNAT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 10.0.0.8 tcp dpt:80 to:192.168.100.7:8000 Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 11 816 MASQUERADE all -- * * 192.168.100.0/24 0.0.0.0/0 Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
2.7.2.4REDIRECT 转发(端口转发)
REDIRECT,是NAT表的 target,通过改变目标IP和端口,将接受的包转发至同一个主机的不同端口, 可用于PREROUTING OUTPUT链
REDIRECT选项: --to-ports port[-port]
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -d 172.16.100.10 -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 8080
范例:
[root@lan-host ~]#ss -ntl State Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address:Port Peer Address:Port LISTEN 0 100 127.0.0.1:25 *:* LISTEN 0 128 *:22 *:* LISTEN 0 128 [::]:23 [::]:* LISTEN 0 100 [::1]:25 [::]:* LISTEN 0 128 [::]:80 [::]:* LISTEN 0 128 [::]:22 [::]:* [root@lan-host ~]#iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 8000 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 80 [root@lan-host ~]#iptables -vnL -t nat Chain PREROUTING (policy ACCEPT 0 packets, 0 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination 1 60 REDIRECT tcp -- * * 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:8000 redir ports 80 Chain INPUT (policy ACCEPT 1 packets, 60 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain OUTPUT (policy ACCEPT 1 packets, 120 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination Chain POSTROUTING (policy ACCEPT 1 packets, 120 bytes) pkts bytes target prot opt in out source destination
# Generated by iptables-save v1.4.7 on Wed May 18 09:22:34 2016 *filter :INPUT ACCEPT [85890:4530430] :FORWARD ACCEPT [76814:55698470] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [166620:238017546] -A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.100/32 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.200/32 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.67/32 -j ACCEPT #WANG ADD NEXT LINE IN 20170627 #-A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.0/16 -j ACCEPT #WANG ADD NEXT LINE IN 20170704 #-A FORWARD -s 172.18.0.0/16 -j ACCEPT #-A FORWARD -s 172.18.0.0/16 -j REJECT #-A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.68/32 -j ACCEPT #-A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.69/32 -j ACCEPT #-A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.6/32 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -s 172.17.200.200/32 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -s 172.17.136.136/32 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -s 172.17.0.100/32 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -s 172.18.100.1/32 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -s 172.18.0.100/32 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -s 172.18.200.2/32 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -s 172.18.200.3/32 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -s 172.18.211.211/32 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -s 172.18.212.212/32 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -m iprange --src-range 172.16.0.100-172.16.0.110 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -m iprange --src-range 172.17.0.100-172.17.0.110 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -m iprange --src-range 172.18.0.100-172.18.0.110 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -m iprange --src-range 172.17.100.6-172.17.100.16 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -m iprange --src-range 172.18.100.61-172.18.100.70 -j ACCEPT -A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.0/16 -m string --string "verycd.com" --algo kmp --to 65535 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.0/16 -m string --string "tudou.com" --algo kmp --to 65535 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.0/16 -m string --string "youku.com" --algo kmp --to 65535 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.0/16 -m string --string "iqiyi.com" --algo kmp --to 65535 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.0/16 -m string --string "pptv.com" --algo kmp --to 65535 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.0/16 -m string --string "letv.com" --algo kmp --to 65535 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.0/16 -m string --string "xunlei.com" --algo kmp --to 65535 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.18.0.0/16 -m string --string "verycd.com" --algo kmp --to 65535 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.18.0.0/16 -m string --string "tudou.com" --algo kmp --to 65535 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.18.0.0/16 -m string --string "youku.com" --algo kmp --to 65535 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.18.0.0/16 -m string --string "iqiyi.com" --algo kmp --to 65535 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.18.0.0/16 -m string --string "pptv.com" --algo kmp --to 65535 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.18.0.0/16 -m string --string "letv.com" --algo kmp --to 65535 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.18.0.0/16 -m string --string "xunlei.com" --algo kmp --to 65535 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable #-A FORWARD -s 172.18.0.0/16 -j REJECT #-A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.0/16 -j REJECT #-A FORWARD -i ppp0 -m string --string ".exe" --algo bm --to 65535 -j REJECT -- reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.18.0.0/16 -m time --timestart 08:50:00 --timestop 18:00:00 -- weekdays Mon,Wed,Fri --datestop 2038-01-19T11:14:07 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.17.0.0/16 -m time --timestart 08:50:00 --timestop 18:00:00 -- weekdays Mon,Wed,Fri --datestop 2038-01-19T11:14:07 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.0/16 -m time --timestart 08:50:00 --timestop 12:30:00 -- weekdays Tue,Thu,Sat --datestop 2038-01-19T11:14:07 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable -A FORWARD -s 172.16.0.0/16 -m time --timestart 13:50:00 --timestop 18:00:00 -- weekdays Tue,Thu,Sat --datestop 2038-01-19T11:14:07 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable #wang next 2 lines changed in 20170619 #-A FORWARD -s 172.17.0.0/16 -m time --timestart 08:50:00 --timestop 12:30:00 -- weekdays Mon,Wed,Fri --datestop 2038-01-19T11:14:07 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable #-A FORWARD -s 172.17.0.0/16 -m time --timestart 13:30:00 --timestop 18:10:00 -- weekdays Mon,Wed,Fri --datestop 2038-01-19T11:14:07 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable #-A FORWARD -s 172.18.0.0/16 -m time --timestart 08:50:00 --timestop 18:10:00 -- weekdays Mon,Wed,Fri --datestop 2038-01-19T11:14:07 -j REJECT --reject-with icmp-port-unreachable #-A FORWARD -s 172.18.0.0/16 -m time --timestart 08:50:00 --timestop 18:10:00 -- weekdays Tue,Thu --datestop 2038-01-19T11:14:07 -j REJECT --reject-with icmpport- unreachable COMMIT # Completed on Wed May 18 09:22:34 2016 # Generated by iptables-save v1.4.7 on Wed May 18 09:22:34 2016 *nat :PREROUTING ACCEPT [1429833:65427211] :POSTROUTING ACCEPT [850518:35452195] :OUTPUT ACCEPT [120198:9146655] -A POSTROUTING -s 172.16.0.100/32 -j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -s 172.18.0.100/32 -j MASQUERADE #-A POSTROUTING -s 172.16.0.200/32 -j MASQUERADE #wang add next 1 line in 20170619 #wang add next 1 line in 20170704 -A POSTROUTING -s 172.16.0.69/32 -j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -s 172.17.200.200/32 -j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -s 172.17.136.136/32 -j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -s 172.17.0.100/32 -j MASQUERADE #-A POSTROUTING -s 172.18.0.0/16 -j MASQUERADE #-A POSTROUTING -s 172.16.0.6/32 -j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -m iprange --src-range 172.16.0.100-172.16.0.110 -j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -m iprange --src-range 172.17.0.100-172.17.0.110 -j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -m iprange --src-range 172.18.0.100-172.18.0.110 -j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -s 172.16.0.0/16 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,443,53,22,6666 - j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -s 172.16.0.0/16 -p udp -m multiport --dports 22 -j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -s 172.17.0.0/16 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,443,53,22,6666 - j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -s 172.17.0.0/16 -p udp -m multiport --dports 22 -j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -s 172.18.0.0/16 -p tcp -m multiport --dports 80,443,53,22,6666,1206,5938,1949 -j MASQUERADE -A POSTROUTING -s 172.18.0.0/16 -p udp -m multiport --dports 22,1206,5938,1949 - j MASQUERADE COMMIT # Completed on Wed May 18 09:22:34 2016
三、firewalld服务
firewalld是CentOS 7.0新推出的管理netfilter的用户空间软件工具
firewalld是配置和监控防火墙规则的系统守护进程。
可以实iptables,ip6tables,ebtables的功能
firewalld服务由firewalld包提供
firewalld支持划分区域zone,每个zone可以设置独立的防火墙规则
1、先根据数据包中源地址,将其纳为某个zone 2、纳为网络接口所属zone 3、纳入默认zone,默认为public zone,管理员可以改为其它zone 4、网卡默认属于public zone,lo网络接口属于trusted zone
firewalld zone 分类
trusted: 允许所有流量 home: 拒绝除和传出流量相关的,以及ssh,mdsn,ipp-client,samba-client,dhcpv6-client预定义服务之外其它所有传入流量 internal: 和home相同 work: 拒绝除和传出流量相关的,以及ssh,ipp-client,dhcpv6-client预定义服务之外的其它所有传入流量 public: 拒绝除和传出流量相关的,以及ssh,dhcpv6-client预定义服务之外的其它所有传入流量,新加的网卡默认属于public zone external: 拒绝除和传出流量相关的,以及ssh预定义服务之外的其它所有传入流量,属于external zone的传出ipv4流量的源地址将被伪装为传出网卡的地址。 dmz: 拒绝除和传出流量相关的,以及ssh预定义服务之外的其它所有传入流量 block: 拒绝除和传出流量相关的所有传入流量 drop: 拒绝除和传出流量相关的所有传入流量(甚至不以ICMP错误进行回应)
预定义服务
ssh: Local SSH server. Traffic to 22/tcp dhcpv6-client: Local DHCPv6 client. Traffic to 546/udp on the fe80::/64 IPv6 network ippclient: Local IPP printing. Traffic to 631/udp. sambaclient: Local Windows file and print sharing client. Traffic to 137/udp and 138/udp. mdns: Multicast DNS (mDNS) local-link name resolution. Traffic to 5353/udp to the224.0.0.251 (IPv4) or ff02::fb (IPv6) multicast addresses.
firewalld预定义服务配置firewall-cmd --get-services 查看预定义服务列表/usr/lib/firewalld/services/*.xml预定义服务的配置firewalld 三种配置方法 1)firewall-config 图形工具: 需安装 firewall-config包 3)/etc/firewalld/ 配置文件,一般不建议,如:/etc/firewalld/zones/public.xml
3.2、firewall-cmd 命令
firewall-cmd 格式
Usage: firewall-cmd [OPTIONS...]
常见选项
--get-zones 列出所有可用区域 --get-default-zone 查询默认区域 --set-default-zone=<ZONE> 设置默认区域 --get-active-zones 列出当前正使用的区域 --add-source=<CIDR>[--zone=<ZONE>] 添加源地址的流量到指定区域,如果无--zone= 选项,使用默认区域 --remove-source=<CIDR> [--zone=<ZONE>] 从指定区域删除源地址的流量,如无--zone= 选项,使用默认区域 --add-interface=<INTERFACE>[--zone=<ZONE>] 添加来自于指定接口的流量到特定区域,如果无--zone= 选项,使用默认区域 --change-interface=<INTERFACE>[--zone=<ZONE>] 改变指定接口至新的区域,如果无--zone=选项,使用默认区域 --add-service=<SERVICE> [--zone=<ZONE>] 允许服务的流量通过,如果无--zone= 选项,使用默认区域 --add-port=<PORT/PROTOCOL>[--zone=<ZONE>] 允许指定端口和协议的流量,如果无--zone= 选项,使用默认区域 --remove-service=<SERVICE> [--zone=<ZONE>] 从区域中删除指定服务,禁止该服务流量,如果无--zone= 选项,使用默认区域 --remove-port=<PORT/PROTOCOL>[--zone=<ZONE>] 从区域中删除指定端口和协议,禁止该端口的流量,如果无--zone= 选项,使用默认区域 --reload 删除当前运行时配置,应用加载永久配置 --list-services 查看开放的服务 --list-ports 查看开放的端口 --list-all [--zone=<ZONE>] 列出指定区域的所有配置信息,包括接口,源地址,端口,服务等,如果无--zone= 选项,使用默认区域
范例:
#查看默认zone firewall-cmd --get-default-zone #默认zone设为dmz firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=dmz #在internal zone中增加源地址192.168.0.0/24的永久规则 firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=internal --add-source=192.168.0.0/24 #在internal zone中增加协议mysql的永久规则 firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=internal --add-service=mysql #加载新规则以生效 firewall-cmd --reload
范例:
[root@centos8 ~]#firewall-cmd --get-zones block dmz drop external home internal public trusted work [root@centos7 ~]#firewall-cmd --get-service RH-Satellite-6 amanda-client amanda-k5-client amqp amqps apcupsd audit bacula bacula-client bgp bitcoin bitcoin-rpc bitcoin-testnet bitcoin-testnet-rpc ceph ceph-mon cfengine condor-collector ctdb dhcp dhcpv6 dhcpv6-client distcc dns docker-registry docker-swarm dropbox-lansync elasticsearch etcd-client etcdserver finger freeipa-ldap freeipa-ldaps freeipa-replication freeipa-trust ftp ganglia-client ganglia-master git gre high-availability http https imap imaps ipp ipp-client ipsec irc ircs iscsi-target isns jenkins kadmin kerberos kibana klogin kpasswd kprop kshell ldap ldaps libvirt libvirt-tls lightning-network llmnr managesieve matrix mdns minidlna mongodb mosh mountd mqtt mqtt-tls ms-wbt mssql murmur mysql nfs nfs3 nmea-0183 nrpe ntp nut openvpn ovirt-imageio ovirtstorageconsole ovirt-vmconsole plex p
mcd pmproxy pmwebapi pmwebapis pop3 pop3s postgresql privoxy proxy-dhcp ptp pulseaudio puppetmaster quassel radius redis rpc-bind rsh rsyncd rtsp salt-master samba samba-client samba-dc sane sip sips slp smtp smtp-submission smtps snmp snmptrap spideroak-lansync squid ssh steamstreaming svdrp svn syncthing syncthing-gui synergy syslog syslog-tls telnet tftp tftp-client tinc tor-socks transmission-client upnp-client vdsm vnc-server wbem-http wbem-https wsman wsmans xdmcp xmpp-bosh xmpp-client xmpp-local xmppserver zabbix-agent zabbix-server
范例:配置firewalld
systemctl mask iptables systemctl mask ip6tables systemctl status firewalld systemctl enable firewalld systemctl start firewalld firewall-cmd --get-default-zone firewall-cmd --set-default-zone=public firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --list-all firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-port 8080/tcp firewall-cmd ---reload
3.3、其它规则
当基本firewalld语法规则不能满足要求时,可以使用以下更复杂的规则1、rich-rules 富规则,功能强,表达性语言2、Direct configuration rules 直接规则,灵活性差, 帮助:man 5 firewalld.direct
3.3.1、管理rich规则
规则实施顺序:
1、该区域的端口转发,伪装规则 2、该区域的日志规则 3、该区域的允许规则 4、该区域的拒绝规则
每个匹配的规则生效,所有规则都不匹配,该区域默认规则生效
rule [source] [destination] service|port|protocol|icmp-block|masquerade|forward-port [log] [audit] [accept|reject|drop]
man 5 firewalld.richlanguage
rich规则选项
--add-richrule='' Add to the specified zone, or the default zone if no zone is specified. #添加到指定区域,或如果没有指定区域,则添加到默认区域。 --removerichrule='' Remove to the specified zone, or the default zone if no zone is specified. #移到指定区域,或如果没有指定区域,移到默认区域。 --queryrichrule='' Query if has been added to the specified zone, or the default zone if no zoneis specified. Returns 0 if the rule is present, otherwise 1. #查询是否已添加到指定区域,或如果未指定区域,则为默认区域。如果规则存在,则返回0,否则返回1。 --list-richrules Outputs all rich rules for the specified zone, or the default zone if no zone is specified.4.3.2 #输出指定区域的所有富规则,如果没有指定区域,则为默认区域specified.4.3.2
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-rich-rule='rule family=ipv4 source address=192.168.0.100/32 reject'
限制每分钟只有两个连接到ftp服务
firewall-cmd --add-rich-rule=‘rule service name=ftp limit value=2/m accept’
抛弃esp( IPsec 体系中的一种主要协议)协议的所有数据包
firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule='rule protocol value=esp drop'
接受所有192.168.1.0/24子网端口5900-5905范围的TCP流量
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=vnc --add-rich-rule='rule family=ipv4 source address=192.168.1.0/24 port port=5900-5905 protocol=tcp accept'
rich日志规则
log [prefix="<PREFIX TEXT>" [level=<LOGLEVEL>] [limit value="<RATE/DURATION>"] <LOGLEVEL> 可以是emerg,alert, crit, error, warning, notice, info, debug. <DURATION> s:秒, m:分钟, h:小时, d:天 audit [limit value="<RATE/DURATION>"]
范例
#接受ssh新连接,记录日志到syslog的notice级别,每分钟最多三条信息 firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=work --add-rich-rule='rule service name="ssh" log prefix="ssh level="notice" limit value="3/m" accept #从2001:db8::/64子网的DNS连接在5分钟内被拒绝,并记录到日志到audit,每小时最大记录一条信息 firewall-cmd --add-rich-rule='rule family=ipv6 source address="2001:db8::/64" service name="dns" audit limit value="1/h" reject' --timeout=300 firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule='rule family=ipv4 source ddress=172.25.X.10/32 service name="http" log level=notice prefix="NEW HTTP " limit value="3/s" accept' firewall-cmd --reload tail -f /var/log/messages curl http://serverX.example.com
NAT网络地址转换,firewalld支持伪装和端口转发两种NAT方式
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=<ZONE> --add-masquerade firewall-cmd --query-masquerade #检查是否允许伪装 firewall-cmd --add-masquerade #允许防火墙伪装IP firewall-cmd --remove-masquerade #禁止防火墙伪装IP
范例:
firewall-cmd --add-rich-rule='rule family=ipv4 source address=192.168.0.0/24 masquerade'
端口转发:将发往本机的特定端口的流量转发到本机或不同机器的另一个端口。通常要配合地址伪装才能实现
firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=<ZONE> --add-forward-port=port=<PORTNUMBER>:proto=<PROTOCOL>[:toport=<PORTNUMBER>][:toaddr=]
#转发传入的连接9527/TCP,到防火墙的80/TCP到public zone 的192.168.0.254 firewall-cmd --add-masquerade 启用伪装 firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-forwardport=port=9527:proto=tcp:toport=80:toaddr=192.168.0.254
rich规则的port转发语法:
forward-port port=<PORTNUM> protocol=tcp|udp [to-port=<PORTNUM>] [to-addr=<ADDRESS>]
范例:
#转发从192.168.0.0/24来的,发往80/TCP的流量到防火墙的端口8080/TCP firewall-cmd --zone=work --add-rich-rule='rule family=ipv4 source address=192.168.0.0/24 forward-port port=80 protocol=tcp to-port=8080' firewall-cmd --permanent --add-rich-rule 'rule family=ipv4 source address=172.25.X.10/32 forward-port port=443 protocol=tcp to-port=22' firewall-cmd --reload ssh -p 443 serverX.example.com
范例:限制ssh服务非标准端口访问
cp /usr/lib/firewalld/services/ssh.xml /etc/firewalld/services/ssh.xml vim /etc/firewalld/services/ssh.xml <port protocol="tcp" port="999"/> systemctl restart sshd.service systemctl status -l sshd.service sealert -a /var/log/audit/audit.log semanage port -a -t ssh_port_t -p tcp 999 systemctl restart sshd.service ss -tulpn | grep sshd firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=work --add-source=172.25.X.0/24 firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=work --add-port=999/tcp firewall-cmd --reload
firewalld zone 分类




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号