linux运维、架构之路-git版本管理
一、常见版本管理系统
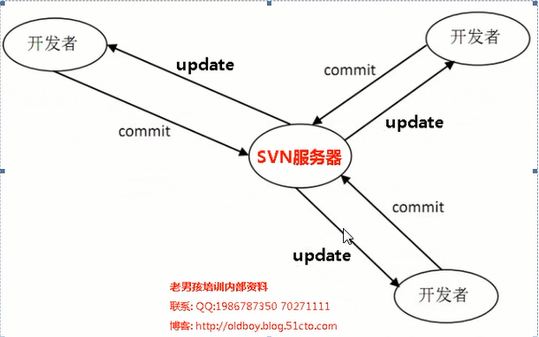
1、SVN
集中式的版本控制系统,只有一个中央数据仓库,如果中央数据仓库挂了或者不能访问,所有的使用者无法使用svn,无法进行提交或者备份文件
2、Git
分布式的版本控制系统,在每个使用者电脑上就有一个完整的数据仓,没有网络依然可以使用Git,当然为了习惯及团队协作,会将本地数据同步到Git服务器或者GitHub等代码仓库

二、Git的工作模式
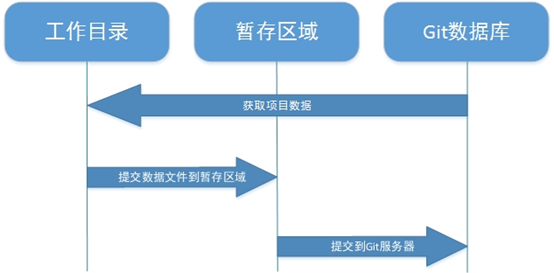
1、在工作目录中修改数据文件。
2、将文件的快照放入暂存区域。
3、将暂存区域的文件快照提交到Git仓库中
三、Git安装部署
1、环境准备
[root@gitlab ~]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS Linux release 7.2.1511 (Core) [root@gitlab ~]# uname -r 3.10.0-327.el7.x86_64 [root@gitlab ~]# systemctl status firewalld.service ● firewalld.service - firewalld - dynamic firewall daemon Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/firewalld.service; disabled; vendor preset: enabled) Active: inactive (dead) [root@gitlab ~]# getenforce Disabled [root@gitlab ~]# hostname -I 172.19.5.63 172.16.1.63
2、Git安装配置
①安装Git、全局配置
yum install git -y
[root@gitlab ~]# git config --global user.name "yan xinjiang" # 配置git使用用户 [root@gitlab ~]# git config --global user.email "774181401@qq.com" # 配置git使用邮箱 [root@gitlab ~]# git config --global color.ui true # 语法高亮 [root@gitlab ~]# git config --list # 查看全局配置 user.name=yan xinjiang user.email=774181401@qq.com color.ui=true
②新建并初始化Git工作目录
[root@gitlab ~]# mkdir git_data [root@gitlab ~]# cd git_data/ [root@gitlab git_data]# git init 初始化空的 Git 版本库于 /root/git_data/.git/ [root@gitlab git_data]# git status # 位于分支 master # # 初始提交 # 无文件要提交(创建/拷贝文件并使用 "git add" 建立跟踪)
③Git基本使用

④创建数据、提交数据
[root@gitlab git_data]# touch README [root@gitlab git_data]# git status # 位于分支 master # # 初始提交 # # 未跟踪的文件: # (使用 "git add <file>..." 以包含要提交的内容) # # README 提交为空,但是存在尚未跟踪的文件(使用 "git add" 建立跟踪) [root@gitlab git_data]# git add README #添加文件到暂存区域 [root@gitlab git_data]# git status #查看git状态 # 位于分支 master # # 初始提交 # # 要提交的变更: # (使用 "git rm --cached <file>..." 撤出暂存区) # # 新文件: README # [root@gitlab git_data]# git commit -m "README first commit" #git commit 提交暂存区文件README到git仓库 [master(根提交) 86bc282] README first commit 1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-) create mode 100644 README
⑤删除暂存区数据
[root@gitlab git_data]# touch database [root@gitlab git_data]# git add database [root@gitlab git_data]# git status # 位于分支 master # 要提交的变更: # (使用 "git reset HEAD <file>..." 撤出暂存区) # # 新文件: database # [root@gitlab git_data]# git reset HEAD database #将git暂存区的追踪列表删除,并不会删除工作目录的数据文件 [root@gitlab git_data]# git rm --cached database#撤出暂存区文件的另一种写法,-f参数git暂存区和工作目录数据一起删除 [root@gitlab git_data]# git status # 位于分支 master # 未跟踪的文件: # (使用 "git add <file>..." 以包含要提交的内容) # # database 提交为空,但是存在尚未跟踪的文件(使用 "git add" 建立跟踪)
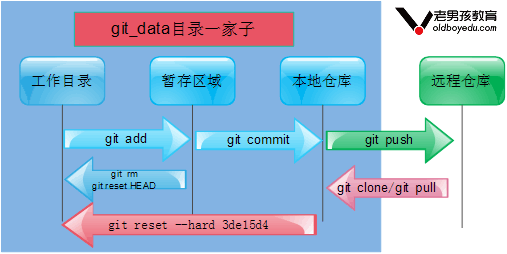
3、Git历史记录
①查看历史记录相关命令
git log #查看提交历史记录 git log -2 #查看最近几条记录 git log -p -1 #显示每次提交的内容差异,例如仅查看最近一次差异 git log --stat -2 #简要显示数据增改行数,这样能够看到提交中修改过的内容,对文件添加或移动的行数,并在最后列出所有增减行的概要信息 git log --pretty=oneline #根据不同的格式展示提交的历史信息 git log --pretty=fuller -2 #以更详细的模式输出提交的历史记录 git log --pretty=fomat:"%h %cn" #查看当前所有提交记录的简短SHA-1哈希字串与提交者的姓名,其他格式见备注
format参数指定具体输出格式
%s 提交说明。 %cd 提交日期。 %an 作者的名字。 %cn 提交者的姓名。 %ce 提交者的电子邮件。 %H 提交对象的完整SHA-1哈希字串。 %h 提交对象的简短SHA-1哈希字串。 %T 树对象的完整SHA-1哈希字串。 %t 树对象的简短SHA-1哈希字串。 %P 父对象的完整SHA-1哈希字串。 %p 父对象的简短SHA-1哈希字串。 %ad 作者的修订时间
②还原历史数据
#模拟提交了三次数据 [root@gitlab git_data]# git log commit e92dc47b6e2d4972e45fb7be557a6bcfebd3fd2e Author: yan xinjiang <774181401@qq.com> Date: Mon Dec 18 13:57:35 2017 +0800 README three commit commit a3950f561fc74803d8a4dba7e4980f19a87a85e9 Author: yan xinjiang <774181401@qq.com> Date: Mon Dec 18 13:56:14 2017 +0800 README second commit commit 86bc282a6c90e332e516a289c7c92282bdc425ac Author: yan xinjiang <774181401@qq.com> Date: Mon Dec 18 13:24:51 2017 +0800 README first commit
此时查看README数据内容
[root@gitlab git_data]# cat README
heoll
word
还原历史提交版本到上一次
[root@gitlab git_data]# git reset --hard HEAD^ #还原历史提交版本上一次 [root@gitlab git_data]# git reset --hard a3950f #根据SHA-1值,还原 HEAD 现在位于 a3950f5 README second commit [root@gitlab git_data]# cat README #查看数据文件已经还原到上一次 heoll HEAD^ 还原到上次 HEAD^^还原到上上次 HEAD^^^ HEAD~5还原到上5次
说明:上面的操作实际上就是改变了一个HEAD版本指针的位置,你将HEAD指针放在哪里,你的当前工作版本就会定位在哪里,要想把内容再还原到最新提交的版本,先查看提交版本号
③还原未来数据
未来数据指的是还原到历史数据了,突然后悔了,想撤销更改,但是git log已经找不到这个版本了
#查看未来历史更新点 [root@gitlab git_data]# git reflog a3950f5 HEAD@{0}: reset: moving to a3950f e92dc47 HEAD@{1}: reset: moving to e92dc4 a3950f5 HEAD@{2}: reset: moving to HEAD^ e92dc47 HEAD@{3}: commit: README three commit a3950f5 HEAD@{4}: commit: README second commit 86bc282 HEAD@{5}: commit (initial): README first commit
4、标签使用
#前面回滚使用的是一串字符串,又长又难记
git tag v1.0 #当前提交内容打一个标签(方便快速回滚),每次提交都可以打个tag。
git tag #查看当前所有的标签
git show v1.0 #查看当前1.0版本的详细信息
git tag v1.2 -m "version 1.2 release is test" #创建带有说明的标签,-a指定标签名字,-m指定说明文字
git tag -d v1.0 #我们为同一个提交版本设置了两次标签,删除之前的v1.0
[root@gitlab git_data]# git tag v20171218 [root@gitlab git_data]# git tag v20171218 #这样还原起来方便很多,根据tag标记即可以还原# [root@gitlab git_data]# git reset --hard v20171218 HEAD 现在位于 a3950f5 README second commit [root@gitlab git_data]# cat README heoll
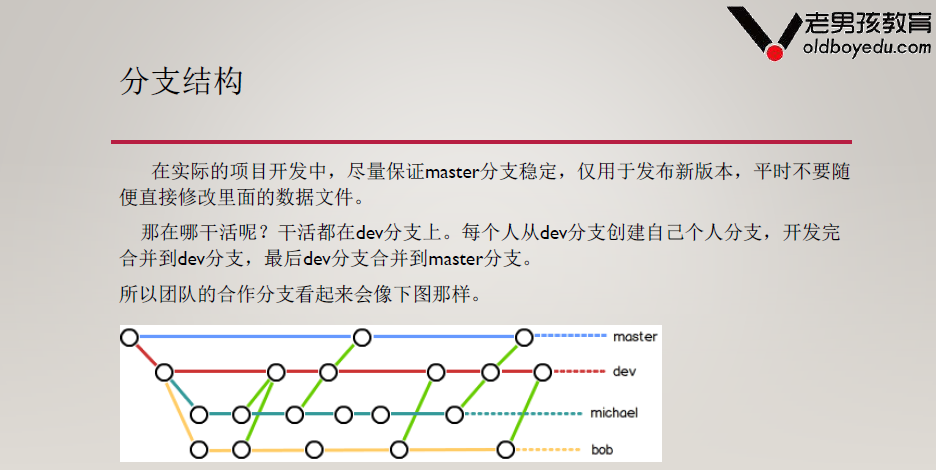
四、Git分支结构管理
1、分支结构
2、创建分支
[root@gitlab git_data]# git branch linux #创建分支 [root@gitlab git_data]# git status # 位于分支 master 无文件要提交,干净的工作区 [root@gitlab git_data]# git checkout linux #切换分支 切换到分支 'linux' [root@gitlab git_data]# git branch #查看当前分支情况,当前分支前面有* * linux master
3、合并分支
[root@gitlab git_data]# git checkout master #把分支linux的工作成果合并到master上,先切换到master 已经位于 'master' [root@gitlab git_data]# git merge linux #合并linux分支到master Already up-to-date. [root@gitlab git_data]# git branch -d linux #查看合并文件,确认合并完成后,可以删除分支linux 已删除分支 linux(曾为 b578156)。
4、合并分支冲突
①自动合并:文件没有冲突,就可以自动合并
②合并失败:文件冲突——文件的同一行有不同的内容
5、Windows客户端使用
①安装Git-2.10.0-64-bit
②windows的git,本质是window上的linux系统

五、Git服务器
1、常见Git仓库
①使用GitHub或者码云等公共代码仓库
②使用GitLab私有仓库
2、搭建私有仓库GitLab
安装文档 https://about.gitlab.com/downloads/#centos7 https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/gitlab-ce/yum/
①安装
[root@gitlab ~]# cd /server/tools/ [root@gitlab tools]# rz #上传gitlab-ce-9.1.4-ce.0.el7.x86_64.rpm [root@gitlab tools]# ls gitlab-ce-9.1.4-ce.0.el7.x86_64.rpm [root@gitlab tools]# rpm -ivh gitlab-ce-9.1.4-ce.0.el7.x86_64.rpm 准备中... ################################# [100%] 正在升级/安装... 1:gitlab-ce-9.1.4-ce.0.el7 ################################# [100%] [root@gitlab tools]# gitlab-ctl reconfigure #初始化,执行一次即可
②启动服务,浏览器输入172.19.5.63访问
gitlab-ctl status/stop/start
创建项目
项目名称
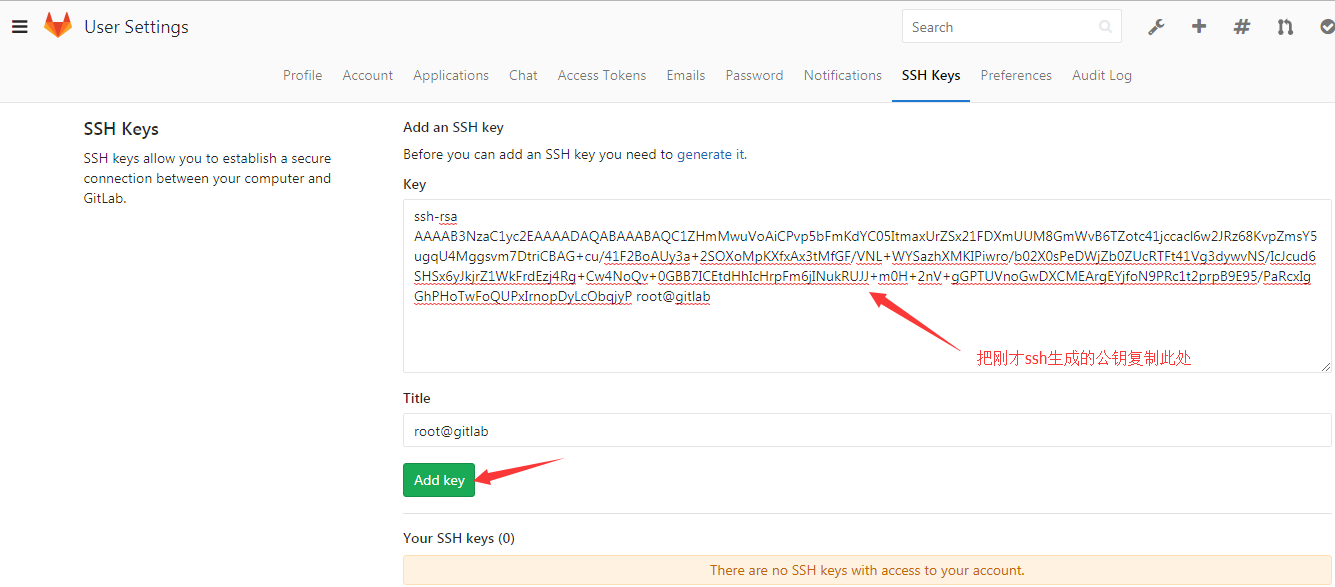
创建SSH秘钥认证
[root@gitlab git_data]# ssh-keygen [root@gitlab git_data]# cat /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQC1ZHmMwuVoAiCPvp5bFmKdYC05ItmaxUrZSx21FDXmUUM8GmWvB6TZotc41jccacl6w2JRz68KvpZmsY5ugqU4Mggsvm7DtriCBAG+cu/41F2BoAUy3a+2SOXoMpKXfxAx3tMfGF/VNL+WYSazhXMKIPiwro/b02X0sPeDWjZb0ZUcRTFt41Vg3dywvNS/IcJcud6SHSx6yJkjrZ1WkFrdEzj4Rg+Cw4NoQv+0GBB7ICEtdHhIcHrpFm6jINukRUJJ+m0H+2nV+gGPTUVnoGwDXCMEArgEYjfoN9PRc1t2prpB9E95/PaRcxIgGhPHoTwFoQUPxIrnopDyLcObqjyP root@gitlab
命令使用说明
Command line instructions #Git global setup# git config --global user.name "Administrator" git config --global user.email "admin@example.com" #Create a new repository# git clone git@gitlab.example.com:root/Nginx_conf.git cd Nginx_conf touch README.md git add README.md git commit -m "add README" git push -u origin master #Existing folder# cd existing_folder git init git remote add origin git@gitlab.example.com:root/Nginx_conf.git git add . git commit git push -u origin master #Existing Git repository# cd existing_repo git remote add origin git@gitlab.example.com:root/Nginx_conf.git git push -u origin --all git push -u origin --tags
③同步Gitlab服务器项目到本地工作目录
[root@gitlab git_data]# git clone git@172.19.5.63:root/Nginx_conf.git#克隆服务端项目到本地 正克隆到 'Nginx_conf'... The authenticity of host '172.19.5.63 (172.19.5.63)' can't be established. ECDSA key fingerprint is 9c:aa:0b:01:a4:48:3f:50:0a:2d:50:41:57:e2:5a:7d. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added '172.19.5.63' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts. warning: 您似乎克隆了一个空版本库。 [root@gitlab git_data]# ls linux.txt Nginx_conf README
④推送本地数据到Gitlab服务器
[root@gitlab git_data]# cd Nginx_conf/ #进入Nginx_conf项目下 [root@gitlab Nginx_conf]# git add nginx.conf #把Nginx配置文件放于此处 [root@gitlab Nginx_conf]# git commit -m "this is Blog Nginx configfile" #提交nginx.conf到git仓库 [master(根提交) 9478a0f] this is Blog Nginx configfile 1 file changed, 28 insertions(+) create mode 100644 nginx.conf [root@gitlab Nginx_conf]# git push -u origin master #将本地代码仓库推送到gitlab服务器master分支下,第一次加上参数-u,代表关联本地与远程 Counting objects: 3, done. Compressing objects: 100% (2/2), done. Writing objects: 100% (3/3), 582 bytes | 0 bytes/s, done. Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0) To git@172.19.5.63:root/Nginx_conf.git * [new branch] master -> master 分支 master 设置为跟踪来自 origin 的远程分支 master。
Gitlab服务端查看
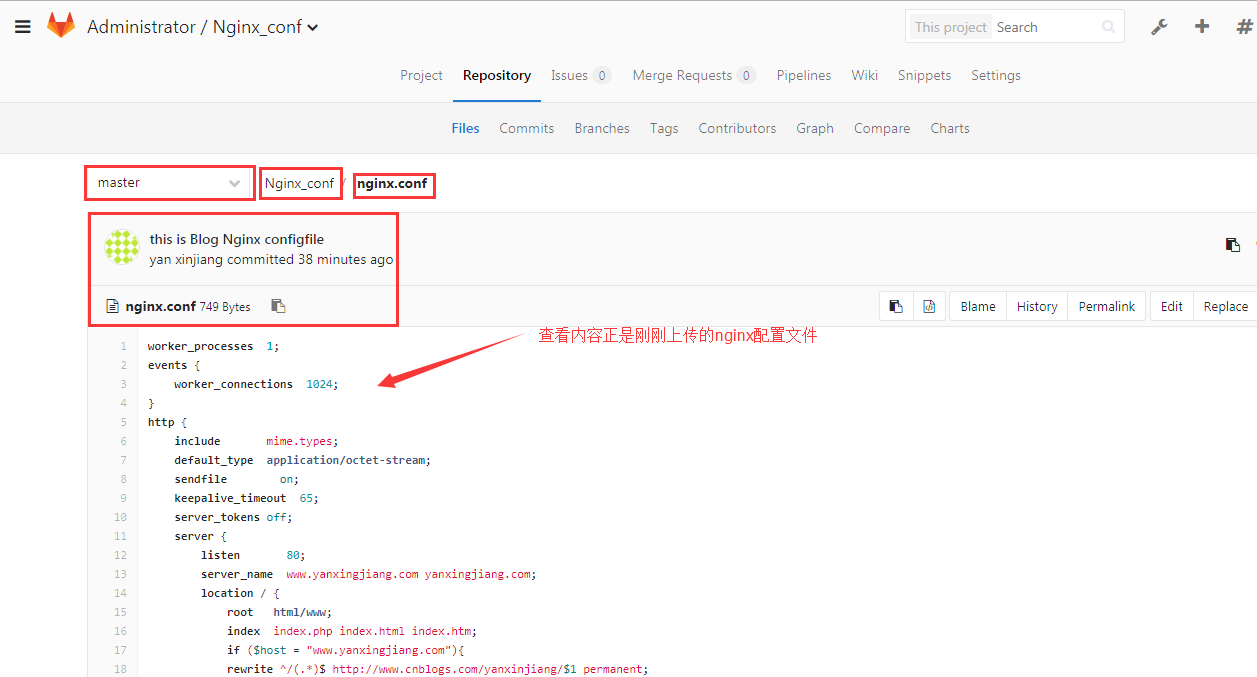
⑤服务端创建测试数据,拉取到本地工作目录
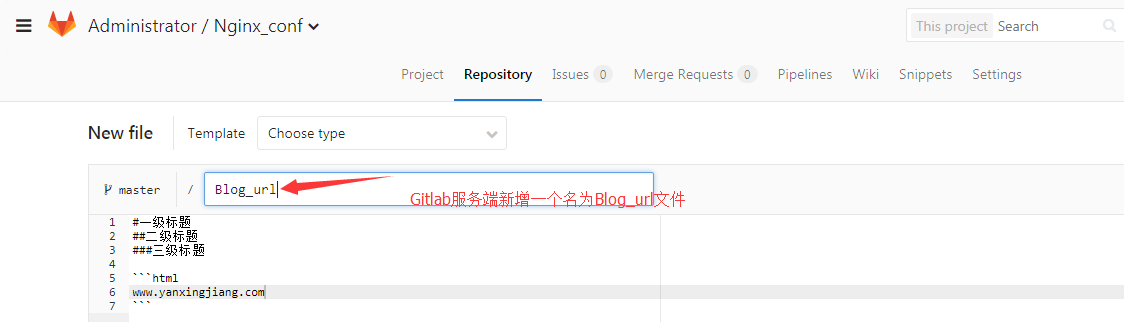
[root@gitlab Nginx_conf]# git pull #拉取服务端数据到本地 remote: Counting objects: 3, done. remote: Compressing objects: 100% (3/3), done. remote: Total 3 (delta 0), reused 0 (delta 0) Unpacking objects: 100% (3/3), done. 来自 172.19.5.63:root/Nginx_conf 9478a0f..af55ef9 master -> origin/master 更新 9478a0f..af55ef9 Fast-forward Blog_url | 7 +++++++ 1 file changed, 7 insertions(+) create mode 100644 Blog_url [root@gitlab Nginx_conf]# ls #查看刚才拉取服务端的数据 Blog_url nginx.conf



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号