MySQL----语法篇
IFNULL
SELECT
a.`id`,
a.`name`,
b.`id`,
IFNULL(b.`name`,'/') //如果查询为null,可以设置一个默认值
FROM
tb_content_category AS a
LEFT JOIN tb_content_category AS b
ON a.`parent_id` = b.`id`
EXISTS和select配饰使用
(执行student.length次)对于下面的sql语句首先执行的语句是select * from student s,在根据表的每一条记录,执行以下语句(EXISTS(select stuid from score ss where ss.stuid = s.stuid)),依次去判断where后面的条件是否成立:如果成立则返回true不成立则返回false。如果返回的是true的话,则该行结果保留,如果返回的是false的话,则删除该行,最后将得到的结果返回
select * from student s where EXISTS(select stuid from score ss where ss.stuid = s.stuid)
EXISTS和update配饰使用
update actor set name='1' where id=1 and exists(1=1);
EXISTS和Insert配合使用
有问题?参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/chucklu/p/10482311.html
IF NOT EXISTS (SELECT * FROM logininfo WHERE username="stdf")
BEGIN
INSERT INTO logininfo(username,PASSWORD) VALUES("xx","xx")
END
<insert id="insertSelection" parameterType="net.microcarystal.sport.pojo.master.CourseStudentSelection">
<selectKey keyProperty="id" order="AFTER" resultType="long">
select LAST_INSERT_ID();
</selectKey>
insert into course_student_selection
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="id != null">
id,
</if>
<if test="status != null">
status,
</if>
<if test="schoolId != null">
schoolId,
</if>
<if test="stuId != null">
stuId,
</if>
<if test="yearId != null">
yearId,
</if>
<if test="courseId != null">
courseId,
</if>
<if test="scheduleId != null">
scheduleId,
</if>
<if test="sportStageId != null">
sportStageId,
</if>
<if test="sportItemId != null">
sportItemId,
</if>
<if test="updateTime != null">
updateTime,
</if>
<if test="createTime != null">
createTime,
</if>
<if test="createUser != null">
createUser,
</if>
<if test="updateUser != null">
updateUser,
</if>
</trim>
select
<trim suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="id != null">
#{id,jdbcType=BIGINT},
</if>
<if test="status != null">
#{status,jdbcType=INTEGER},
</if>
<if test="schoolId != null">
#{schoolId,jdbcType=BIGINT},
</if>
<if test="stuId != null">
#{stuId,jdbcType=BIGINT},
</if>
<if test="yearId != null">
#{yearId,jdbcType=BIGINT},
</if>
<if test="courseId != null">
#{courseId,jdbcType=BIGINT},
</if>
<if test="scheduleId != null">
#{scheduleId,jdbcType=BIGINT},
</if>
<if test="sportStageId != null">
#{sportStageId,jdbcType=BIGINT},
</if>
<if test="sportItemId != null">
#{sportItemId,jdbcType=BIGINT},
</if>
<if test="updateTime != null">
#{updateTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
</if>
<if test="createTime != null">
#{createTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP},
</if>
<if test="createUser != null">
#{createUser,jdbcType=BIGINT},
</if>
<if test="updateUser != null">
#{updateUser,jdbcType=BIGINT},
</if>
</trim>
from DUAL where 1=(SELECT count(1) FROM course_schedule a
left join user_info b on b.id=#{stuId}
left join course_student_selection c on c.stuId=b.id and c.scheduleId = a.id and c.`status`=1
WHERE c.id is null and a.id = #{scheduleId} and a.lastLim>0 and (a.genderLim!=3 or (a.genderLim=3 and b.userSex=0 AND (femaleScale-femaleCount)>0) or (genderLim=3 AND b.userSex=1 AND (maleScale-maleCount)>0)))
</insert>
插入加where条件
INSERT INTO f (id,name, num) VALUES (4,'1', 10) WHERE 1=1;#报错 INSERT INTO f (id,name, num) select 5,'1', 10 from dual WHERE 0=(select count(id) from f where id=5);#不报错
上面直接使用where条件1=1来判断,如果使用not exists
mysql>
->INSERT INTO test_book1
-> SELECT 1, 'TEST', 'ABC' FROM dual #从前台传递进来的值 select #{id},#{xx},#{xx} from dual
-> WHERE NOT EXISTS( SELECT 1 FROM test_book1 WHERE id = 1);
IN
(只执行一次),in在查询的时候,首先查询子查询的表,然后将内表和外表做一个笛卡尔积,然后按照条件进行筛选。所以相对内表比较小的时候,in的速度较快。
首先会执行from语句找出student表,然后执行 in 里面的子查询,再然后将查询到的结果和原有的user表做一个笛卡尔积,再根据我们的student.stuid IN score.stuid的条件,将结果进行筛选(既比较stuid列的值是否相等,将不相等的删除)。最后,得到符合条件的数据。
select * from student s where s.stuid in(select stuid from score ss where ss.stuid <1005)
使用UNION替代IN
select id from user where id in (1,2); #替换成 select id from user where id = 1 union select id from user where id=2;
EXISTS和In选择
select * from A where id in (select id from B)
如果B查询结果集较少,A有索引,使用in
select * from student A where EXISTS(select id from score B where B.id = A.d)
如果A没有索引,B有索引,并且A的结果集少,使用exists
- in 和 exists的区别: 如果子查询得出的结果集记录较少,主查询中的表较大且又有索引时应该用in, 反之如果外层的主查询记录较少,子查询中的表大,又有索引时使用exists。
- in 是把外表和内表作hash 连接,而exists是对外表作loop循环,每次loop循环再对内表进行查询。一直以来认为exists比in效率高的说法是不准确的。
- 如果查询语句使用了not in 那么内外表都进行全表扫描,没有用到索引;而not extsts 的子查询依然能用到表上的索引。所以无论那个表大,用not exists都比not in要快。
Unique
首先建表的时候给name设置为unique
不存在则插入,存在则更新(on duplicate key update)
如果数据库中有一条数据name = “jack”(因为name设置了unique,插入数据会造成冲突),那么我们继续update操作,更新年龄是19,否则就正常插入操作
INSERT INTO `student`(`name`, `age`) VALUES('Jack', 19) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE `age`=19;
先删除旧数据再插入最新的数据(replace into)
REPLACE INTO `student`(`name`, `age`) VALUES('Jack', 18);
避免重复插入(insert ignore into)
INSERT IGNORE INTO `student`(`name`, `age`) VALUES('Jack', 18);
Group By
group By 和聚合函数:https://blog.csdn.net/u014717572/article/details/80687042
当使用group By的时候,sql首先执行Group 在进行条件判断,如果希望group By的时候对某些字段不进行group By可以在条件中进行判断
比如:这种startYear=2019的数据就不会查出来
SELECT * FROM school_year WHERE STATUS = 1 AND schoolId = 1 AND (startYear != 2019) GROUP BY startYear ORDER BY startYear DESC
我们就可以使用or方法并添加条件来将startYear的数据查询出来
SELECT * FROM school_year WHERE STATUS = 1 AND schoolId = 1 AND (startYear != 2019 OR isThisYear=1) GROUP BY startYear ORDER BY startYear DESC
Order by
如果order by的字段包括多个表 select * from (select * from xx,xx) order by $(xx) desc
Case
如果字段中没有#{},比如genderLim,就会从数据库中的字段来查
And (CASE genderLim WHEN 1 THEN #{userSex} = 1 WHEN 2 THEN #{userSex} = 0 ELSE 1=1 END)
select
a.id as id,
d.courseName as courseName,
(case b.weekTimes when 1 then '星期一'
when 2 then '星期二'
when 3 then '星期三'
when 4 then '星期四'
when 5 then '星期五'
when 6 then '星期六'
when 7 then '星期日'
else null end)
as weekTimes,
b.beginTimes as beginTimes,
from attend_calendar
IF
IF(expr1,expr2,expr3),如果expr1的值为true,则返回expr2的值,如果expr1的值为false
and if((`v`.`rangeTYPE`= '2'),(`v`.`rangeID`= `s`.`SCHOOL_ID`),(`v`.`parentId`= `s`.`SCHOOL_ID`))
代替IF
#性别是1名字是liming,性别是2,名字是xx and (sex='1' and name="liming") or (sex='2' and name="xx")
concat
可以将返回的字段进行拼接
SELECT CONCAT(user_info.`userCode`,'-',user_info.`userName`) AS userCodeAndUserName FROM user_info WHERE user_info.`status`=1 AND user_info.`userType`=2 AND schoolId=1 LIMIT 0,20
update关联
update course_schedule
set totalCount = totalCount+1, lastLim = lastLim-1,
maleCount = maleCount + (select ifnull(count(*),0) as maleCount from user_info where id=#{stuId} and userSex=1),
femaleCount = femaleCount + (select ifnull(count(*),0) as maleCount from user_info where id=#{stuId} and userSex=0)
where id = #{scheduleId,jdbcType=BIGINT}
正则
select * from tb where name regexp ’z’;
on和where的用法
无论LEFT JOIN ON后面什么条件,都不影响主表数据被查询数来(只是关联表没有数据而已)
参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/FENGXUUEILIN/p/10040025.html
SELECT
stu.*
FROM
student stu
LEFT JOIN grade gra on stu.id = gra.c_stuId
WHERE gra.c_fs is NOT null
执行顺序
Where, Group By, Having, Order by
Insert into
https://www.w3school.com.cn/sql/sql_select_into.asp
- 把某些字段插入新表
SELECT colum1,colum2 INTO new_table FROM SYS_BUSINESS_SEQNUM
- 如果在函数里面,可以查询的数据赋值到另一个数据
iseqnum :=1; SELECT SEQNUM INTO iseqnum FROM SYS_BUSINESS_SEQNUM
distinct
select distinct name from xx;
建立临时表,如果name是索引就不会建立临时表,直接在索引树去重,如果要优化,对name建立索引是非要有必要的。
date()
省略时间
更多参考:https://www.w3school.com.cn/sql/sql_dates.asp
select * from DATE(date),date where Date(date)='2020-01-01';
UNION和UNION ALL
- 注意UNION 内部的 SELECT 语句必须拥有相同数量的列。列也必须拥有相似的数据类型。
- 每条 SELECT 语句中的列的顺序必须相同。
- 如果教师1和教师2中的name有重复值,union会去重,而union all不去重
示例
SELECT name FROM Teacher1 UNION ALL SELECT name FROM Teacher2
For update
select 一般情况下不产生锁。如果需要对select加锁,需要在select后面加锁for update。
for update 仅适用于InnoDB,并且必须开启事务,在begin与commit之间才生效。
for update的使用场景
如果遇到存在高并发并且对于数据的准确性很有要求的场景,是需要了解和使用for update的。
比如涉及到金钱、库存等。一般这些操作都是很长一串并且是开启事务的。如果库存刚开始读的时候是1,而立马另一个进程进行了update将库存更新为0了,而事务还没有结束,会将错的数据一直执行下去,就会有问题。所以需要for upate 进行数据加锁防止高并发时候数据出错。
session1:select * from f where id in (1,2) for update; session2:select * from f where id in (1,2) for update;等待,select * from f where id in (1,2);不等待
参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/143866444
四大排名函数
ROW_NUMBER()
定义:ROW_NUMBER()函数作用就是将select查询到的数据进行排序,每一条数据加一个序号,他不能用做于学生成绩的排名,一般多用于分页查询,
比如查询前10个 查询10-100个学生。
实例:
1.1对学生成绩排序
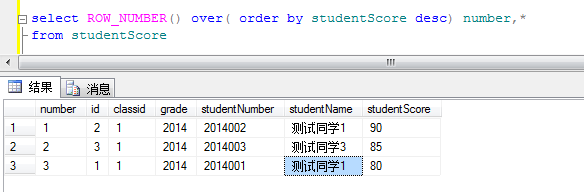
这里number就是每个学生的序号 根据studentScore(分数)进行desc倒序
1.2获取第二个同学的成绩信息
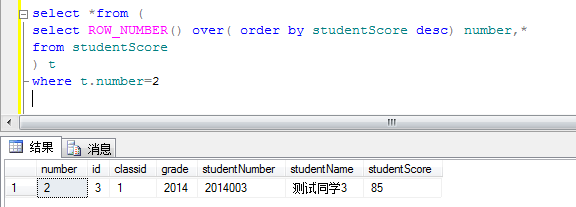
这里用到的思想就是 分页查询的思想 在原sql外再套一层select
where t.number>=1 and t.number<=10 是不是就是获取前十个学生的成绩信息纳。
RANK()
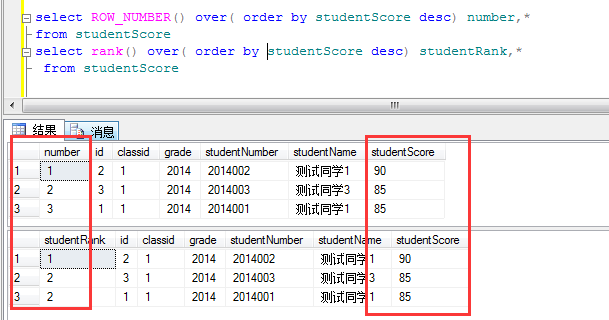
定义:RANK()函数,顾名思义排名函数,可以对某一个字段进行排名,这里为什么和ROW_NUMBER()不一样那,ROW_NUMBER()是排序,当存在相同成绩的学生时,ROW_NUMBER()会依次进行排序,他们序号不相同,而Rank()则不一样出现相同的,他们的排名是一样的。下面看例子:
当出现两个学生成绩相同是里面出现变化。RANK()是 1 2 2,而ROW_NUMBER()则还是1 2 3,这就是RANK()和ROW_NUMBER()的区别了
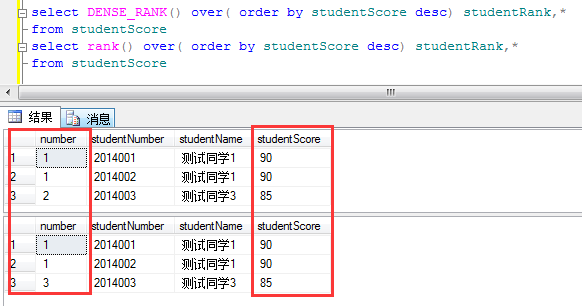
DENSE_RANK()
NTILE()
定义:将数据进行分组
一共13行数据,分三组,第一组就是5;





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号