二叉树
二叉树
1. 基本概念
1.1 名词定义
-
根节点(Root):树的顶部节点,是整个树的起点
-
父节点(Parent):相对于某个节点来说,其上一级的节点
-
子节点(Child):相对于某个节点来说,其下一级的节点
-
左子节点(Left Child):节点的左边子节点
-
右子节点(Right Child):节点的右边子节点
-
叶节点(Leaf):没有任何子节点的节点
-
兄弟节点(Sibling):具有相同父节点的节点
如在下图,不同的颜色代表不同的层级:粉色表示根节点,蓝色表示内部节点(非叶节点),浅蓝色表示叶节点。箭头表示父子关系,展示了节点之间的层次结构
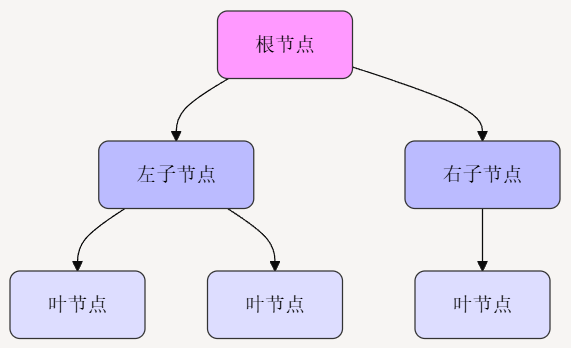
1.2 常见类型
-
满二叉树
- 除叶节点外,每个节点都有左右两个子节点
- 所有叶节点都在最后一层
-
完全二叉树
- 除最后一层外,每一层都是满的
- 最后一层从左到右依次填充
-
空二叉树
- 不包含任何节点的特殊情况
1.3 工作原理
- 存储方式
- 数组存储法:适用于完全二叉树
- 链式存储法:使用指针连接各个节点
- 遍历方法
- 前序遍历(先访问根,再访问左子树,最后右子树):根→左→右
- 中序遍历(先访问左子树,再访问根,最后右子树):左→根→右
- 后序遍历(先访问左右子树,再访问根):左→右→根
- 应用场景
- 文件系统目录结构
- 数据库索引
2. 实现
二叉树例子:
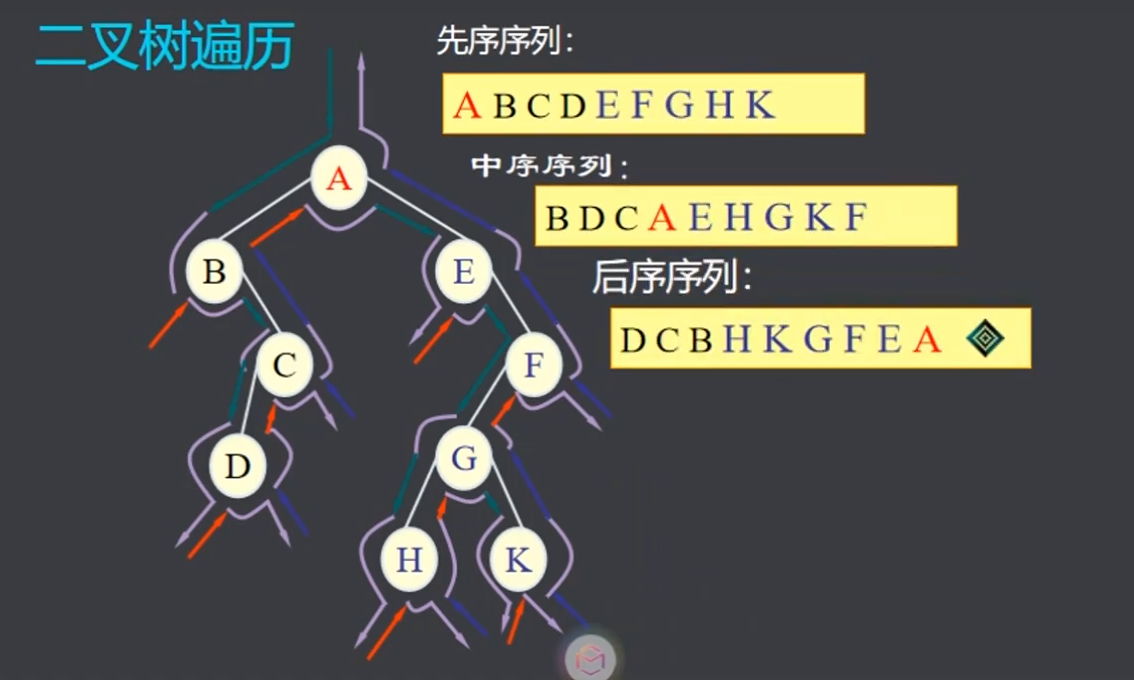
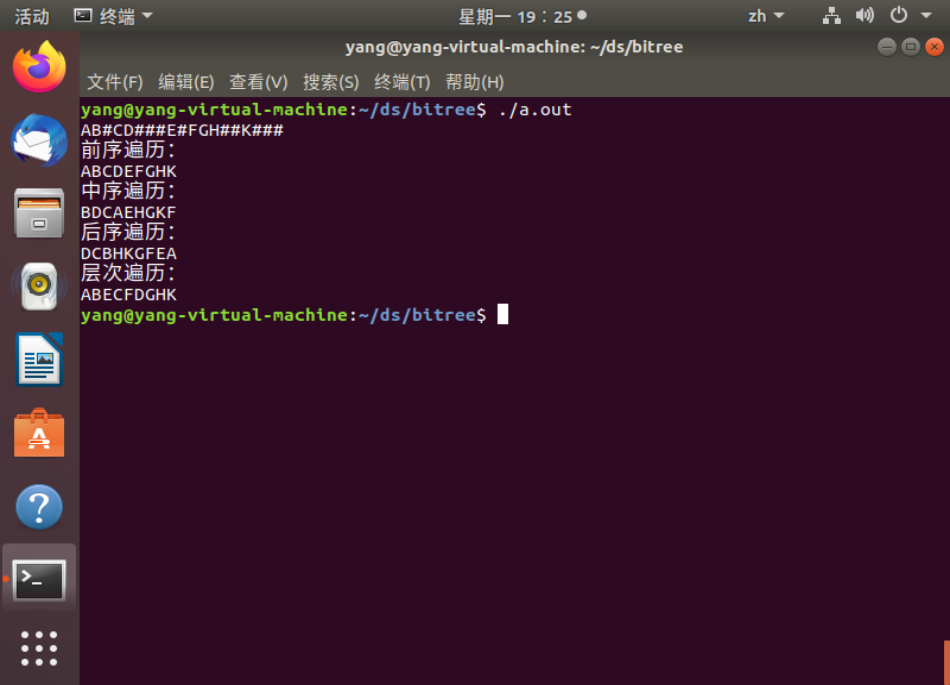
创建二叉树通过前序读入为: AB#CD###E#FGH##K###
实现效果:
main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "bitree.h"
int main()
{
bitree r = create_tree();
printf("前序遍历:\n");
preorder(r);
puts("");
printf("中序遍历:\n");
inorder(r);
puts("");
printf("后序遍历:\n");
postorder(r);
puts("");
printf("层次遍历:\n");
layerorder(r);
return 0;
}
bitree.h
#ifndef BITREE_H
#define BITREE_H
typedef char data_type;
typedef struct Node
{
data_type data;
struct Node *lchild, *rchild;
} treenode, *bitree;
bitree create_tree();
void preorder(bitree r);
void inorder(bitree r);
void postorder(bitree r);
void layerorder(bitree r);
#endif
bitree.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "bitree.h"
#include "linkqueue.h"
bitree create_tree()
{
data_type ch;
bitree r;
scanf("%c", &ch);
if (ch == '#')
return NULL;
if ((r = (bitree)malloc(sizeof(treenode))) == NULL)
{
printf("malloc failed\n ");
return NULL;
}
r->data = ch;
r->lchild = create_tree();
r->rchild = create_tree();
return r;
}
void preorder(bitree r)
{
if (r == NULL)
{
return ;
}
printf("%c", r->data);
preorder(r->lchild);
preorder(r->rchild);
}
void inorder(bitree r)
{
if (r == NULL)
{
return;
}
inorder(r->lchild);
printf("%c", r->data);
inorder(r->rchild);
}
void postorder(bitree r)
{
if (r == NULL)
{
return;
}
postorder(r->lchild);
postorder(r->rchild);
printf("%c", r->data);
}
void layerorder(bitree r)
{
linkqueue lq;
if ((lq = linkqueue_create()) == NULL)
{
printf("malloc linkqueue failed\n");
return;
}
if (r == NULL)
{
return;
}
printf("%c", r->data);
linkqueue_enqueue(lq, r);
while (!linkqueue_empty(lq))
{
r = linkqueue_dequeue(lq);
if (r->lchild)
{
printf("%c", r->lchild->data);
linkqueue_enqueue(lq, r->lchild);
}
if (r->rchild)
{
printf("%c", r->rchild->data);
linkqueue_enqueue(lq, r->rchild);
}
}
puts("");
}
linkqueue.h
#ifndef LINKQUEUE_H
#define LINKQUEUE_H
#include "bitree.h"
typedef bitree data_t;
typedef struct node_t
{
data_t data; // 数据域
struct node_t *next; // 指针域
} queuenode_struct, *queuenode; // 队列结点结构体类型定义
typedef struct
{
queuenode front, rear;
} linkqueue_struct,*linkqueue; // 队列结构体类型定义
linkqueue linkqueue_create(); // 创建队列
int linkqueue_empty(linkqueue q); // 判断队列是否为空
int linkqueue_enqueue(linkqueue q, data_t x); // 入队
data_t linkqueue_dequeue(linkqueue q); // 出队
int linkqueue_show(linkqueue q); // 遍历队列
int linkqueue_free(linkqueue *q); // 释放队列
#endif
linkqueue.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "linkqueue.h"
/**
* @name linkqueue_create()
* @brief 创建链式队列
* @param NULL
* @retval q 队列地址
*/
linkqueue linkqueue_create()
{
// 1. 申请队列头尾指针内存和队列节点内存
linkqueue p = (linkqueue)malloc(sizeof(linkqueue_struct));
if (p == NULL)
{
printf("linkqueue malloc error\n");
return NULL;
}
queuenode newnode = (queuenode)malloc(sizeof(queuenode_struct));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("linknode malloc error\n");
free(p);
return NULL;
}
// 2. 初始化队列头尾指针和队列节点
p->front = p->rear = newnode;
newnode->next = NULL;
newnode->data = NULL;
return p;
}
/**
* @name linkqueue_create()
* @brief p判断链式队列是否为空
* @param q 队列地址
* @retval 0 队列不为空,1 队列为空,-1 队列不存在
*/
int linkqueue_empty(linkqueue q)
{
// 1. 判断队列是否存在
if (q == NULL)
{
printf("linkqueue is invalid\n");
return -1;
}
// 2. 判断队列是否为空
return q->front == q->rear ? 1 : 0;
}
/**
* @name linkqueue_enqueue()
* @brief 入队
* @param q 队列地址
* @retval 0 入队成功,-1 入队失败
*/
int linkqueue_enqueue(linkqueue q, data_t x)
{
// queuenode tem;
// 1. 判断队列是否存在
if (q == NULL)
{
printf("linkqueue is invalid\n");
return -1;
}
// 2. 申请队列节点内存
queuenode newnode = (queuenode)malloc(sizeof(queuenode_struct));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("queuenode malloc error\n");
return -1;
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
// 3. 将新节点插入到队列尾结点之后,并尾指针指向新节点
// tem = q->front;
// while (tem->next != NULL)
// {
// tem = tem->next;
// }
// tem->next = newnode;
q->rear->next = newnode;
q->rear = newnode;
return 0;
}
/**
* @name linkqueue_dequeue()
* @brief 出队
* @param q 队列地址
* @retval 出队元素
*/
data_t linkqueue_dequeue(linkqueue q)
{
// 1. 判断队列是否存在
if (q == NULL)
{
printf("linkqueue is invalid\n");
return NULL;
}
// 2. 判断队列是否为空
if (q->front == q->rear)
{
printf("linkqueue is empty\n");
return NULL;
}
// 3. 出队操作,释放队头结点,并头指针指向头结点下一个结点
queuenode tem = q->front->next;
data_t x = tem->data;
q->front->next = tem->next;
if (q->rear == tem)
{
q->rear = q->front;
}
free(tem);
return x;
}
/**
* @name linkqueue_show()
* @brief 遍历队列,输出队列元素
* @param q 队列地址
* @retval -1 遍历失败,0 遍历成功
*/
int linkqueue_show(linkqueue q)
{
// 1. 判断队列是否存在以及队列是否为空
if (q == NULL)
{
printf("linkqueue is invalid\n");
return -1;
}
if (q->front == q->rear)
{
printf("linkqueue is empty\n");
return -1;
}
// 2. 遍历队列,输出队列元素
queuenode tem = q->front->next;
while (tem != NULL)
{
printf("%d \n", tem->data->data);
tem = tem->next;
}
return 0;
}
/**
* @name linkqueue_free()
* @brief 遍历队列,输出队列元素
* @param q 队列地址
* @retval -1 释放失败,0 释放成功
*/
int linkqueue_free(linkqueue *q)
{
// 1. 判断队列是否存在
if (*q == NULL)
{
printf("linkqueue is invalid\n");
return -1;
}
// 2. 释放队列
queuenode tem = (*q)->front;
while (tem != NULL)
{
queuenode next = tem->next;
free(tem);
tem = next;
}
free(*q);
*q = NULL;
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号