hystrix 源码分析以及属性的配置
一.feign与hystix结合
1.1测试环境搭建
架构如图:
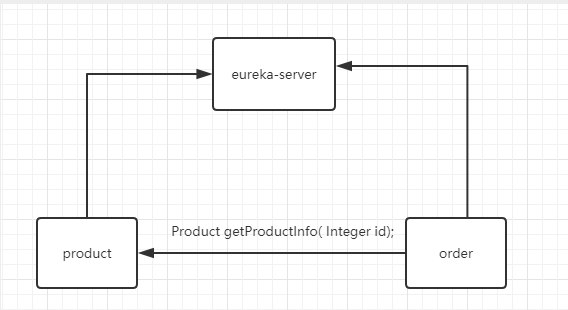
非常简单,就是Order服务通过feign调用product服务的一个获取商品信息的一个接口:
package com.yang.xiao.hui.order.controller; import org.springframework.cloud.openfeign.FeignClient; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @FeignClient(name ="product",fallback =ProductHystrix.class) @Primary public interface ProductService { @RequestMapping("/info/{id}") Product getProductInfo(@PathVariable("id") Integer id); }
@Component public class ProductHystrix implements ProductService{ @Override public Product getProductInfo(Integer id) { System.out.println("被熔断;了"); Product product = new Product(); product.setName("熔断了。。。。。"); return product; } }
我们在order服务引入feign的依赖:
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId> <artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId> </dependency>
通过下面的依赖关系图可见,已经引入了hystrix相关依赖:
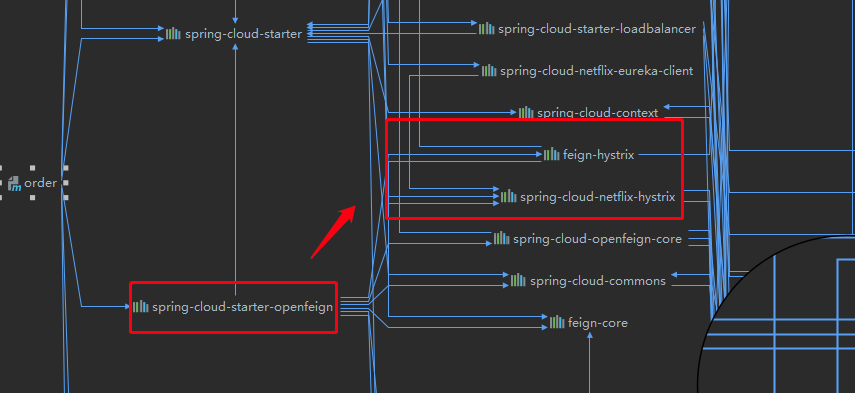
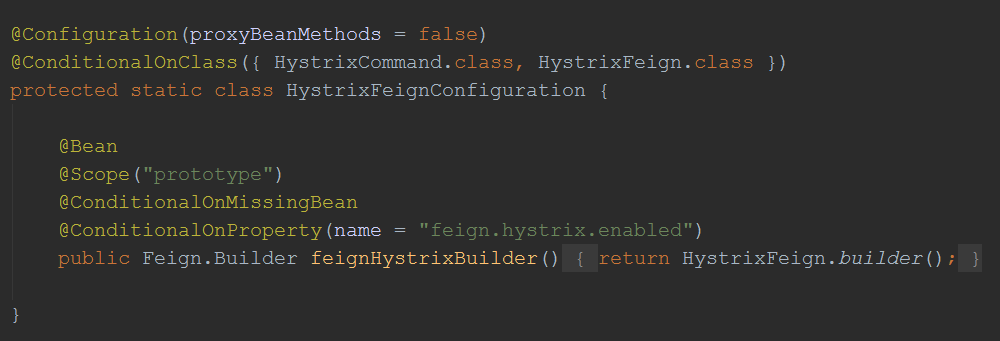
根据FeignClientsConfiguration这个配置类的一个方法feignHystrixBuilder(),可以知道,要让feign跟hystrix结合,需要在application.yml配置一个feign.hystrix.enabled =true的属性
1.2 debug调试feignClient客户端的创建:
.根据上次feign的调用源码分析,可以知道,带有@FeignClient的接口都会被封装成FeignClientFactoryBean类,通过该类的getObject()方法可以获取对应的代理对象,具体源码分析,参考https://www.cnblogs.com/yangxiaohui227/p/12965340.html
断点打在FeignClientFactoryBean的getObject()方法,然后启动Order服务:(因为我的order服务的Controller注入ProductSerivce,所以启动时,会调用FeignClientFactoryBean的getObject()获取实例)
@Controller public class OrderContorller { @Autowired private ProductService productService; @ResponseBody @RequestMapping("/info/{id}") @MyLogAnnotation public Product getProductInfo(@PathVariable Integer id){ return productService.getProductInfo(id); } }

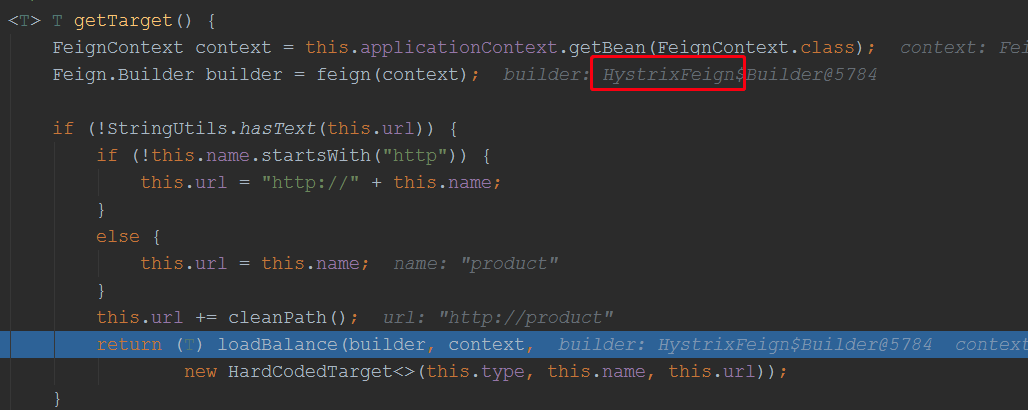
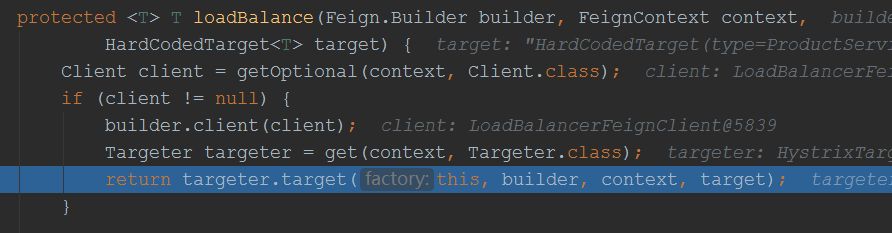
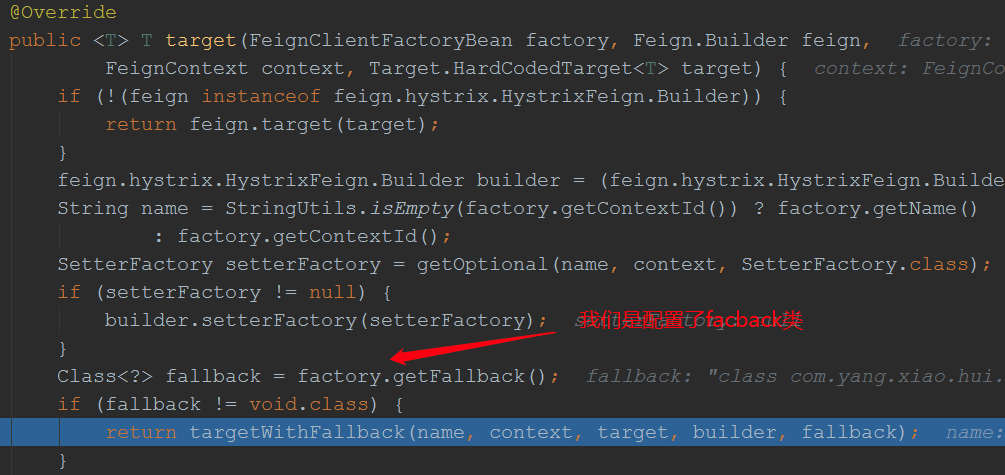
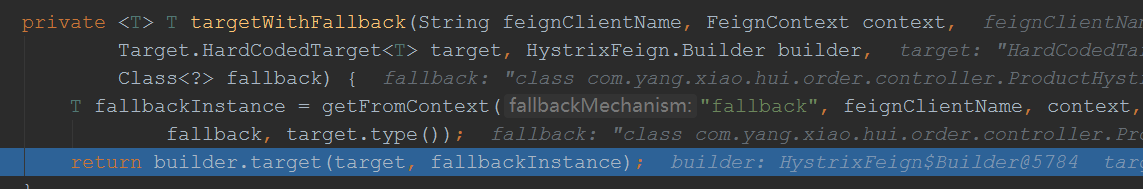
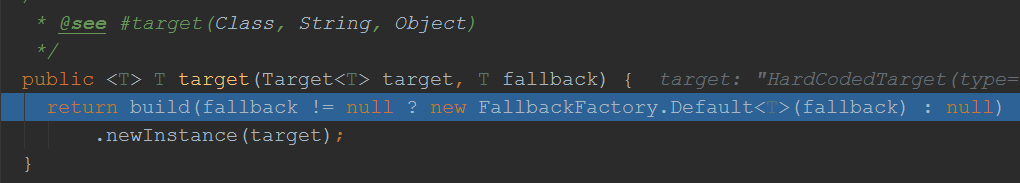
上面先调用build,在调用newInstance来创建代理对象,先看build方法:
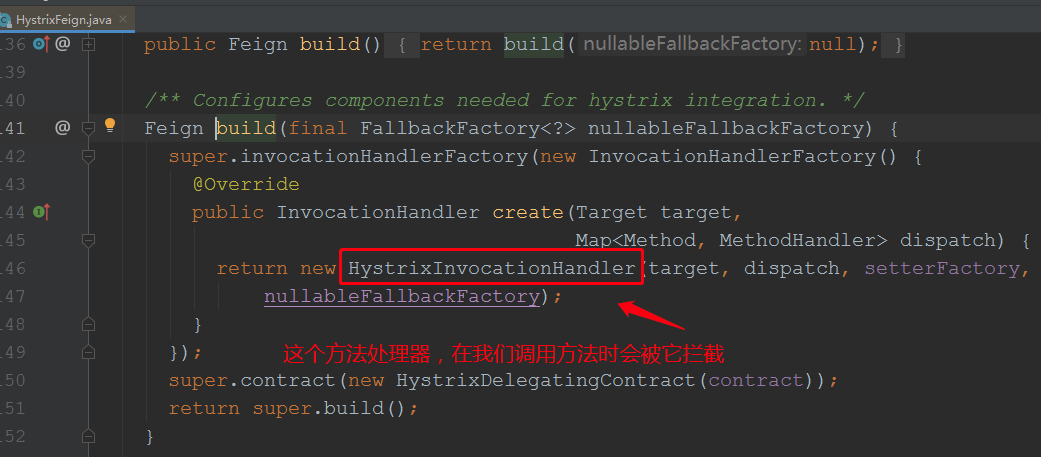
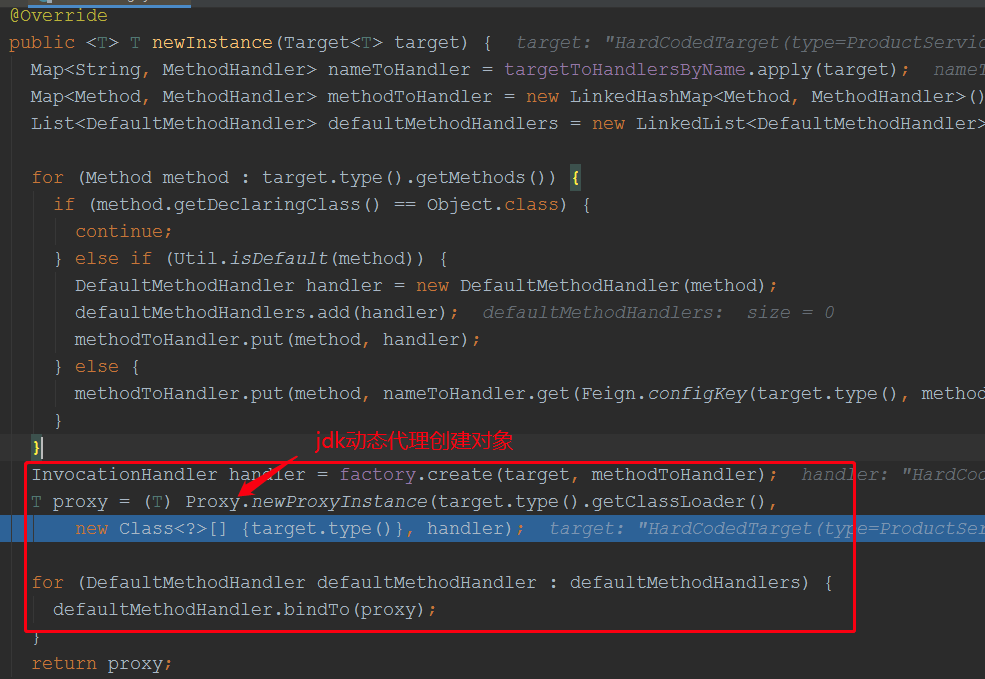
至此代理对象创建完毕,我们看到了方法处理器是:HystrixInvocationHandler
1.3 debug调试feign调用第三方接口:
在浏览器输入http://localhost:8674/info/3,调用order服务的getProductInfo方法:
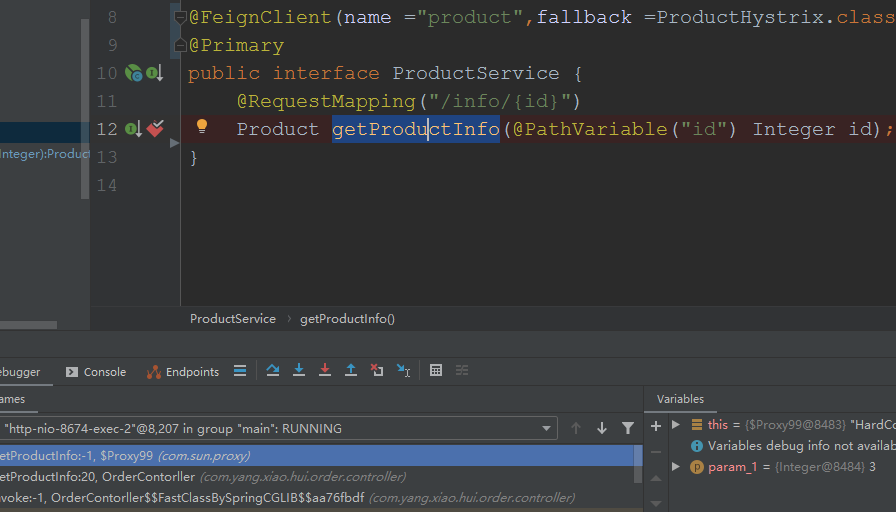
debug跟踪进去:
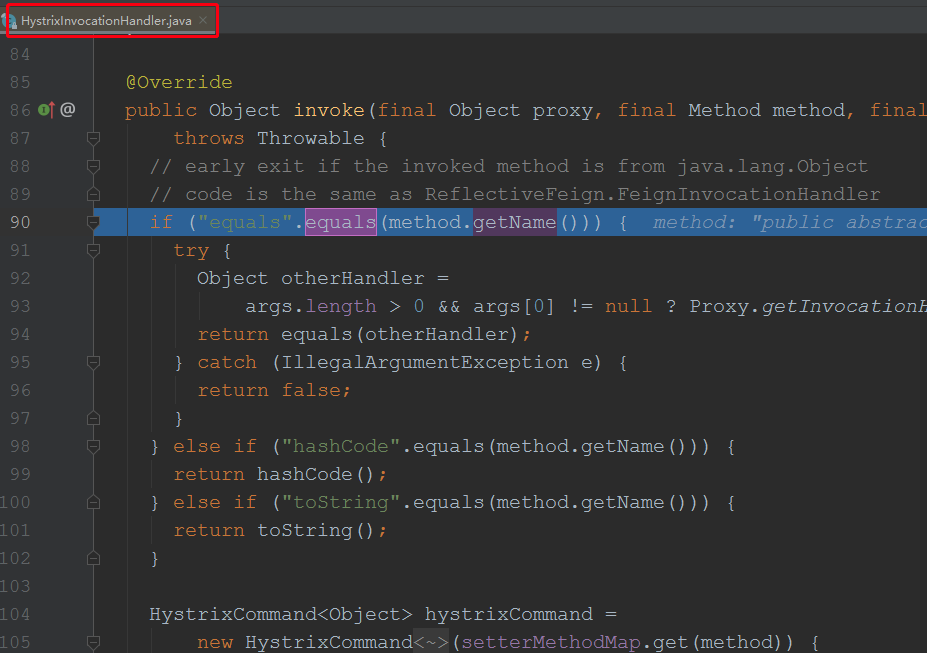
可见,最终是进入了HystrixInvocationHandler类的invoke方法: 方法具体如下:
@Override public Object invoke(final Object proxy, final Method method, final Object[] args) throws Throwable { // early exit if the invoked method is from java.lang.Object // code is the same as ReflectiveFeign.FeignInvocationHandler if ("equals".equals(method.getName())) { try { Object otherHandler = args.length > 0 && args[0] != null ? Proxy.getInvocationHandler(args[0]) : null; return equals(otherHandler); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { return false; } } else if ("hashCode".equals(method.getName())) { return hashCode(); } else if ("toString".equals(method.getName())) { return toString(); }
//这里创建一个command命令对象,里面实现了2个方法,一个是执行我们目标方法的run()方法,一个是执行目标方法失败后,调用我们的服务降级方法getFallcack() HystrixCommand<Object> hystrixCommand = new HystrixCommand<Object>(setterMethodMap.get(method)) { @Override protected Object run() throws Exception { try { return HystrixInvocationHandler.this.dispatch.get(method).invoke(args); } catch (Exception e) { throw e; } catch (Throwable t) { throw (Error) t; } } @Override protected Object getFallback() { if (fallbackFactory == null) { return super.getFallback(); } try { Object fallback = fallbackFactory.create(getExecutionException()); Object result = fallbackMethodMap.get(method).invoke(fallback, args); if (isReturnsHystrixCommand(method)) { return ((HystrixCommand) result).execute(); } else if (isReturnsObservable(method)) { // Create a cold Observable return ((Observable) result).toBlocking().first(); } else if (isReturnsSingle(method)) { // Create a cold Observable as a Single return ((Single) result).toObservable().toBlocking().first(); } else if (isReturnsCompletable(method)) { ((Completable) result).await(); return null; } else if (isReturnsCompletableFuture(method)) { return ((Future) result).get(); } else { return result; } } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { // shouldn't happen as method is public due to being an interface throw new AssertionError(e); } catch (InvocationTargetException | ExecutionException e) { // Exceptions on fallback are tossed by Hystrix throw new AssertionError(e.getCause()); } catch (InterruptedException e) { // Exceptions on fallback are tossed by Hystrix Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); throw new AssertionError(e.getCause()); } } }; if (Util.isDefault(method)) { return hystrixCommand.execute(); } else if (isReturnsHystrixCommand(method)) { return hystrixCommand; } else if (isReturnsObservable(method)) { // Create a cold Observable return hystrixCommand.toObservable(); } else if (isReturnsSingle(method)) { // Create a cold Observable as a Single return hystrixCommand.toObservable().toSingle(); } else if (isReturnsCompletable(method)) { return hystrixCommand.toObservable().toCompletable(); } else if (isReturnsCompletableFuture(method)) { return new ObservableCompletableFuture<>(hystrixCommand); } return hystrixCommand.execute(); //最终调用了命令行的execute方法 }
小结:这里创建一个command命令对象,里面实现了2个方法,一个是执行我们目标方法的run()方法,一个是执行目标方法失败后,调用我们的服务降级方法getFallcack(),直接调用了命令对象的execute方法:1.4 我们跟进命令对象的创建看看有哪些属性:
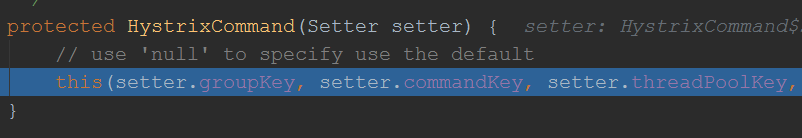
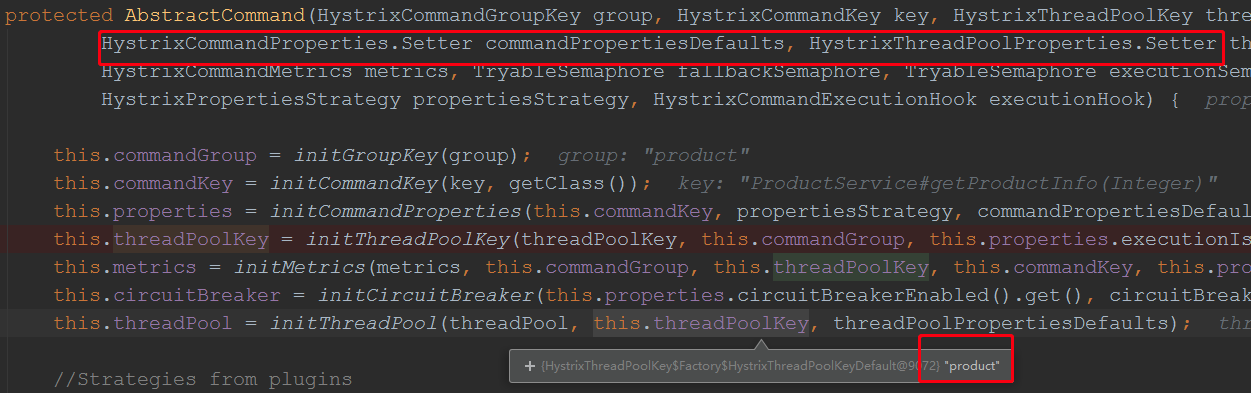
这里一大堆初始化属性,我们主要关注2个:HystrixCommandProperties.Setter 和 HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter,以及线程池的初始化
我们看到线程池的初始化,有个threadPoolkey,该值为服务的名称,也就是@FeignClient注解的name 值,初始化时,同时传入了一个线程池的默认配置:

那么我们先看HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter的属性有哪些值:
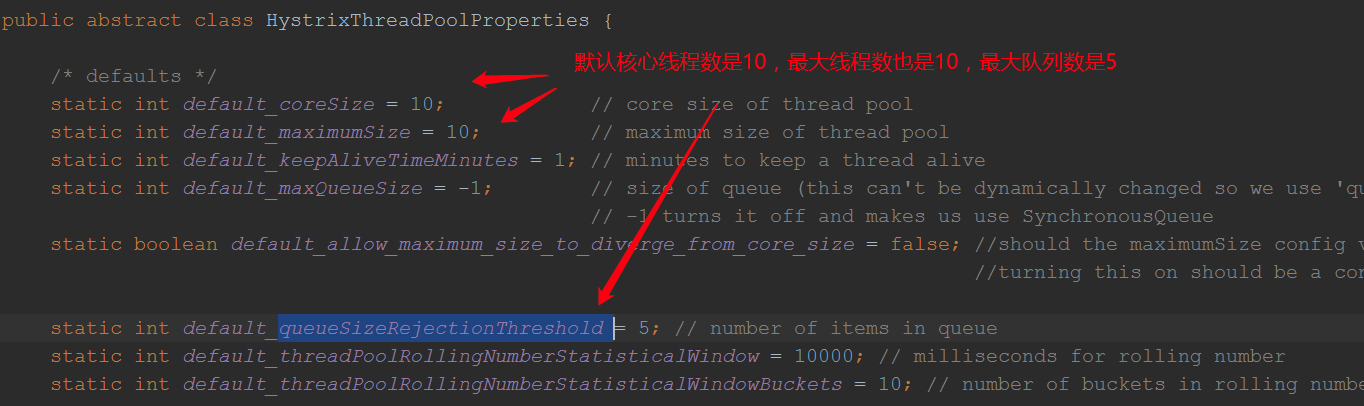

线程池属性初始化前缀是hystrix,通过上面我们可以知道,Hystrix有默认的线程参数,超过对应的线程参数就会被拒绝,那么我们就可以用该特征来做服务限流了,真对某个方法给其设置相应的最大队列属性;
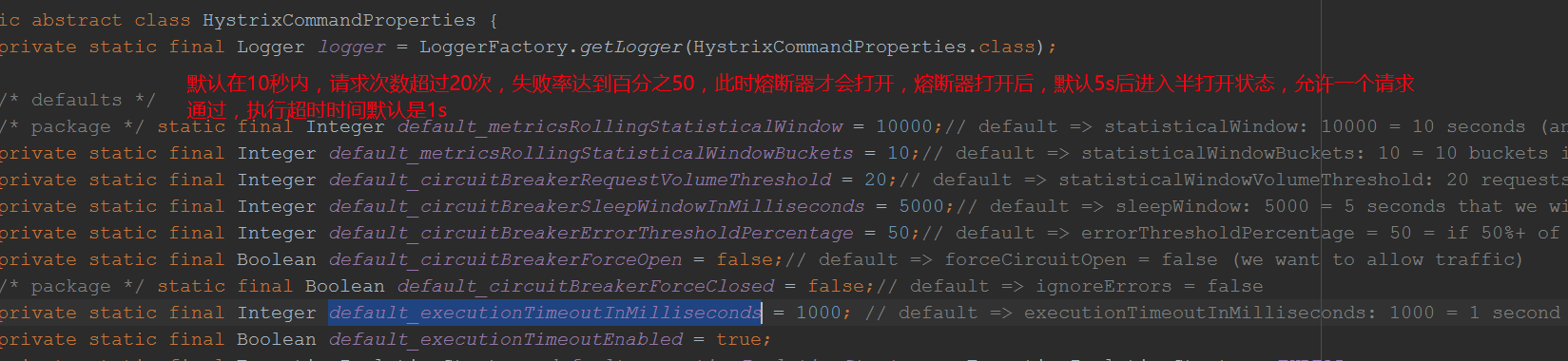
直接我们查看HystrixCommandProperties的属性值:
命令创建分析完后,我们跟踪执行逻辑:hystrixCommand.execute();
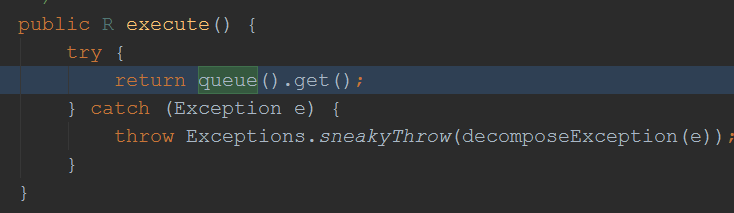
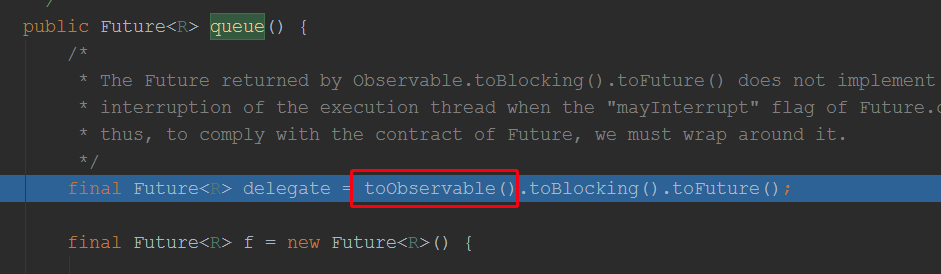
这里用到了大量的RXJava相关知识,从上面代码可以知道,该方法是阻塞的:
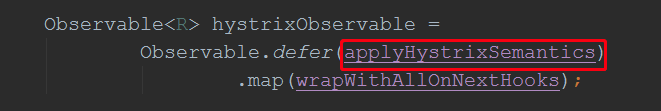
跟进toObservable(),我们找到核心代码:
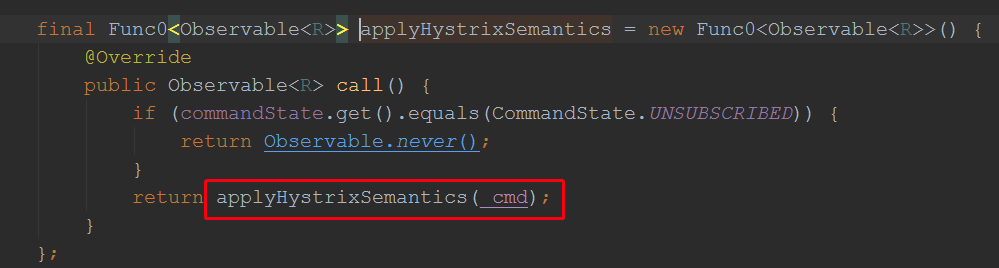
private Observable<R> applyHystrixSemantics(final AbstractCommand<R> _cmd) { // mark that we're starting execution on the ExecutionHook // if this hook throws an exception, then a fast-fail occurs with no fallback. No state is left inconsistent executionHook.onStart(_cmd); /* determine if we're allowed to execute */ if (circuitBreaker.allowRequest()) { //这里判断是否允许执行目标方法,如果不允许,那就执行fallbcak方法 final TryableSemaphore executionSemaphore = getExecutionSemaphore(); final AtomicBoolean semaphoreHasBeenReleased = new AtomicBoolean(false); final Action0 singleSemaphoreRelease = new Action0() { @Override public void call() { if (semaphoreHasBeenReleased.compareAndSet(false, true)) { executionSemaphore.release(); } } }; final Action1<Throwable> markExceptionThrown = new Action1<Throwable>() { @Override public void call(Throwable t) { eventNotifier.markEvent(HystrixEventType.EXCEPTION_THROWN, commandKey); } }; if (executionSemaphore.tryAcquire()) { try { /* used to track userThreadExecutionTime */ executionResult = executionResult.setInvocationStartTime(System.currentTimeMillis()); return executeCommandAndObserve(_cmd)//这里是执行目标方法 .doOnError(markExceptionThrown) .doOnTerminate(singleSemaphoreRelease) .doOnUnsubscribe(singleSemaphoreRelease); } catch (RuntimeException e) { return Observable.error(e); } } else { return handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback();//处理fallback方法 } } else { return handleShortCircuitViaFallback();//处理fallback方法 } }
重点三个方法:circuitBreaker.allowRequest() /executeCommandAndObserve(_cmd) / handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback()
先看熔断器核心业务方法:circuitBreaker.allowRequest()
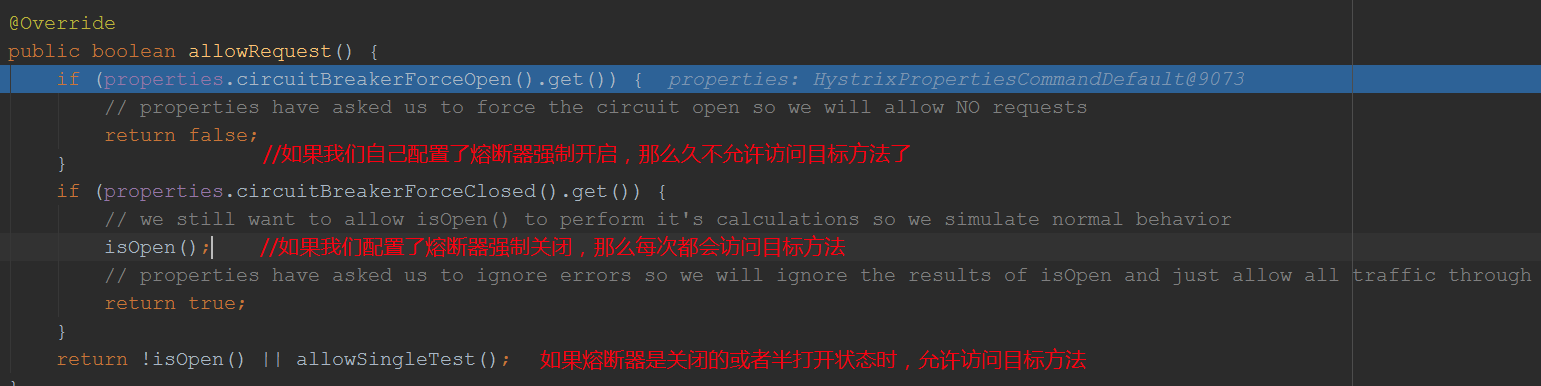
我们看看isOpen()方法的逻辑:
@Override public boolean isOpen() { if (circuitOpen.get()) { //如果已经是打开的,那就返回true // if we're open we immediately return true and don't bother attempting to 'close' ourself as that is left to allowSingleTest and a subsequent successful test to close return true; } // we're closed, so let's see if errors have made us so we should trip the circuit open HealthCounts health = metrics.getHealthCounts(); //获取统计对象,每个command对象的key值就会有一个统计对象,也就是每个请求方法对应一个对象 // check if we are past the statisticalWindowVolumeThreshold if (health.getTotalRequests() < properties.circuitBreakerRequestVolumeThreshold().get()) { //在一个时间窗口内,默认10s,请求总次数要达到配置的最小请求数(默认20次) // we are not past the minimum volume threshold for the statisticalWindow so we'll return false immediately and not calculate anything return false; } if (health.getErrorPercentage() < properties.circuitBreakerErrorThresholdPercentage().get()) { /在一个时间窗口内,默认10s,请求失败率要达到最小配置百分比(默认50%) return false; } else { // our failure rate is too high, trip the circuit //执行到这里说明失败率过高 if (circuitOpen.compareAndSet(false, true)) { // if the previousValue was false then we want to set the currentTime //即使之前是关闭状态也要将其改为打开状态 circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime.set(System.currentTimeMillis());//设置最近打开时间,用于半打开状态的设置 return true; } else { // How could previousValue be true? If another thread was going through this code at the same time a race-condition could have // caused another thread to set it to true already even though we were in the process of doing the same // In this case, we know the circuit is open, so let the other thread set the currentTime and report back that the circuit is open return true; } } } }
小结:isOpen()在默认情况下,如果10s内请求次数达到20次,失败率达到百分之50,则熔断器将会打开
接着我们分析半打开方法:allowSingleTest();
public boolean allowSingleTest() { long timeCircuitOpenedOrWasLastTested = circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime.get(); //上次最近打开熔断器的时间 // 1) if the circuit is open // 2) and it's been longer than 'sleepWindow' since we opened the circuit
//熔断器如果是打开状态,并且最近打开时间距离当前时间已经超过了设置的时间(默认5s)
if (circuitOpen.get() && System.currentTimeMillis() > timeCircuitOpenedOrWasLastTested + properties.circuitBreakerSleepWindowInMilliseconds().get()) { // We push the 'circuitOpenedTime' ahead by 'sleepWindow' since we have allowed one request to try. // If it succeeds the circuit will be closed, otherwise another singleTest will be allowed at the end of the 'sleepWindow'. if (circuitOpenedOrLastTestedTime.compareAndSet(timeCircuitOpenedOrWasLastTested, System.currentTimeMillis())) { //更新最近打开时间,方便下一个5s进行判断 // if this returns true that means we set the time so we'll return true to allow the singleTest // if it returned false it means another thread raced us and allowed the singleTest before we did return true; } } return false; }
一张图总结:
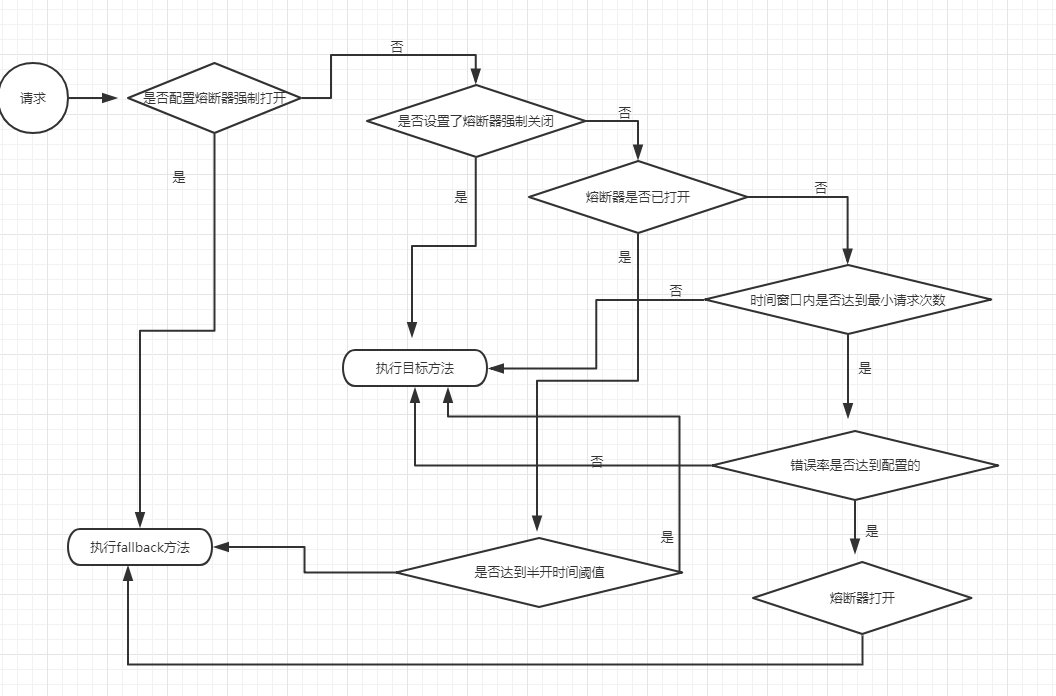
至此,熔断器核心逻辑分析完毕了,我们回到之前目标方法的逻辑,继续跟踪executeCommandAndObserve(_cmd);
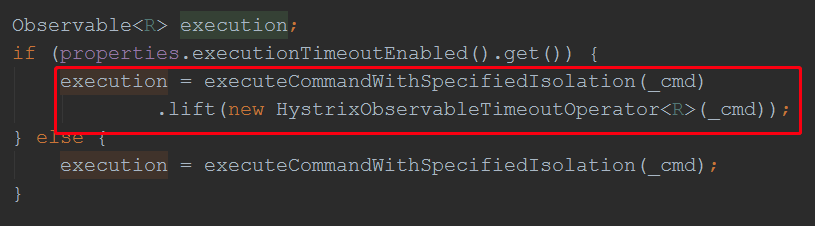
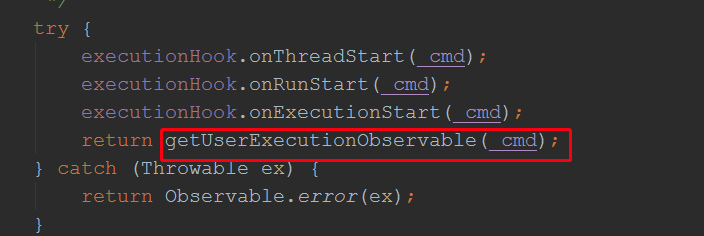
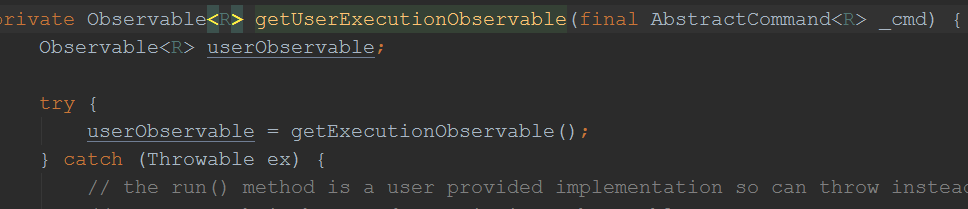
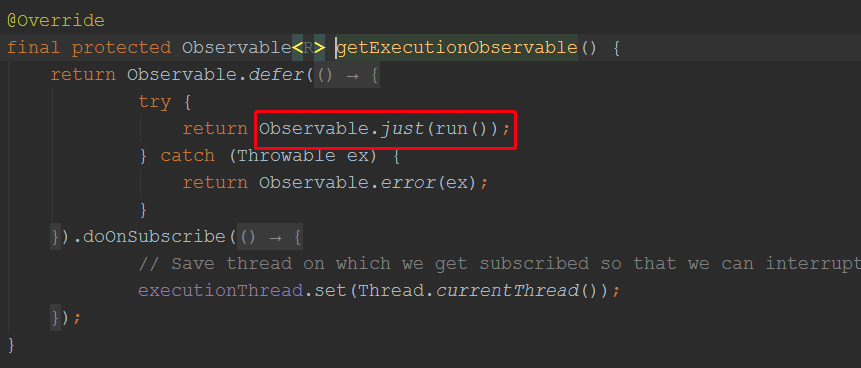
前面我们分析过,创建Command对象时,实现了run方法,和getFallback()方法,上图可见,run方法被调用了,而run方法里面有我们的目标方法
接着我们分析执行目标方法失败后,是如何调用getFallback方法的: handleSemaphoreRejectionViaFallback():

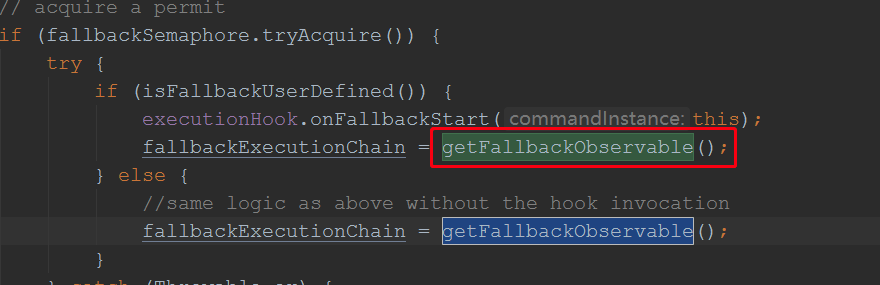
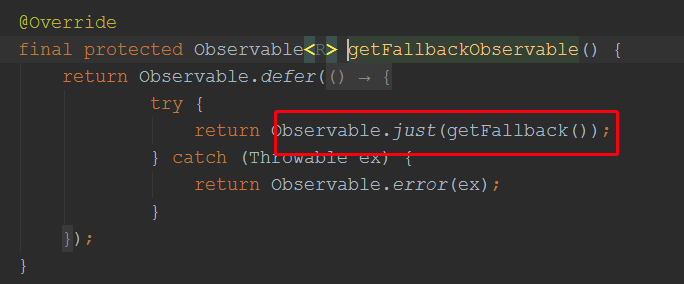
由此可见,这里最终调用了Command对象的getFallback()方法;
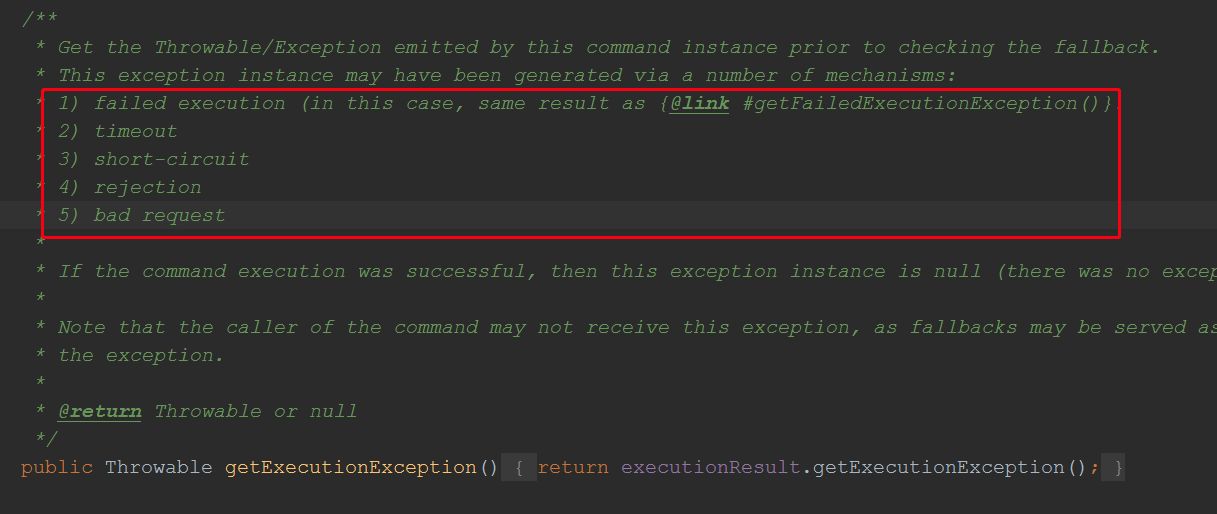
执行失败的原因有:执行异常,超时,熔断器打开,线程数超过最大限制,请求异常
1.4 如何修改默认的参数配置:如,我想更改线程池的配置,或者滑动窗口时间,@FeignClient注解里面并没有更改hystrix的相关配置,那么我们回顾下ProductService接口的创建过程: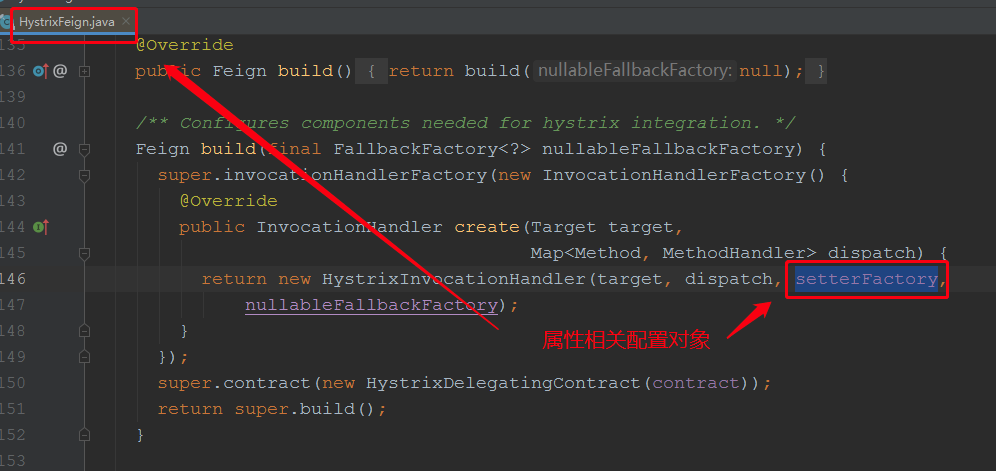
我们创建命令对象时:
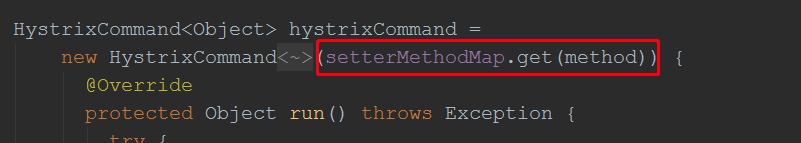
由此可知,我们创建的HystrixCommand时,要用到一个属性配置对象,该对象其实就是创建代理对象时,由HystrixFeign提供,但该属性是直接new出来的,所以我们唯有替换掉HystrixFeign
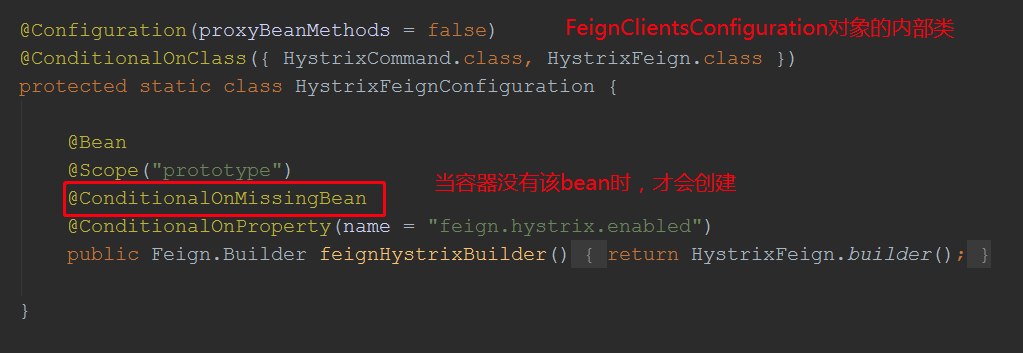
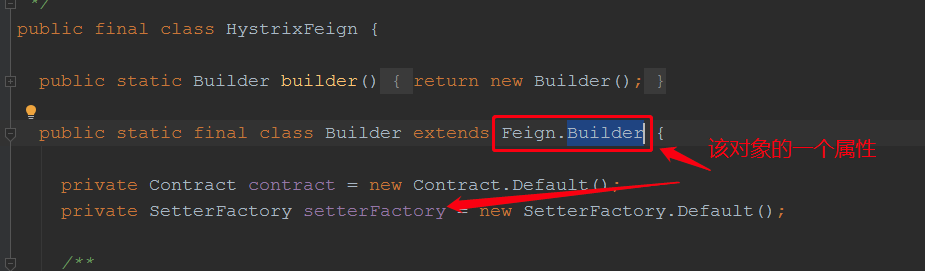
我们发现,容器中没有HystrixFeign.Builder对象时就才会创建Feign.Builder,那么我们就给他注入一股Feign.Builder,在里面给它设置setterFactory属性:
package com.yang.xiao.hui.order.controller; import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommand; import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommandGroupKey; import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommandKey; import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixThreadPoolProperties; import feign.Feign; import feign.Target; import feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign; import feign.hystrix.SetterFactory; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope; import java.lang.reflect.Method; @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnClass({ HystrixCommand.class, HystrixFeign.class }) public class FeignConfig { @Bean @Scope("prototype") @ConditionalOnProperty(name = "feign.hystrix.enabled") public Feign.Builder feignHystrixBuilder() { HystrixFeign.Builder builder = HystrixFeign.builder(); SetterFactory setterFactory= new SetterFactory(){ @Override public HystrixCommand.Setter create(Target<?> target, Method method) { String groupKey = target.name(); String commandKey = Feign.configKey(target.type(), method); return HystrixCommand.Setter .withGroupKey(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey(groupKey)) .andCommandKey(HystrixCommandKey.Factory.asKey(commandKey)) .andThreadPoolPropertiesDefaults(HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter().withCoreSize(100).withMaxQueueSize(200)); } }; builder.setterFactory(setterFactory); return builder; } }
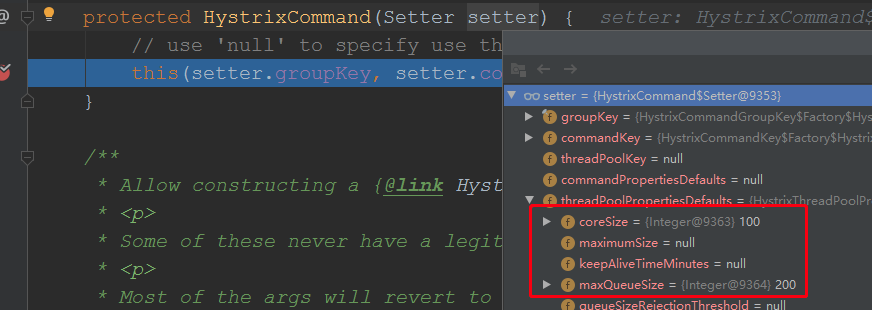
//需要更改任何属性就在HystrixCommand.Setter对象加,我们这里更改了线程池的核心线程数为100,最大队列数为200,启动order服务,重新调用方法:
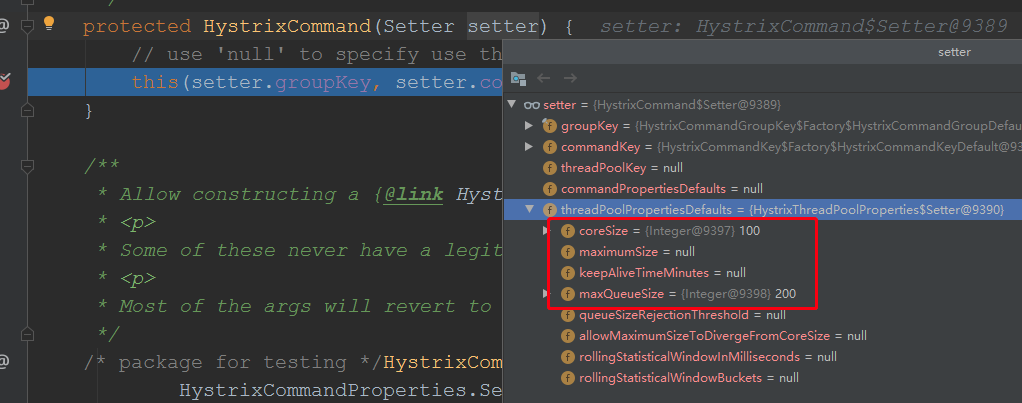
已经变更了;
思考: 上面的配置是对所有的服务都起效的,如果我们需要对不同的服务,如库存服务,客户服务,等有不同的配置,如何处理:
方案一,在主启动类中,将上面的配置类的扫描排除,然后在@FeignClient注解中添加该配置,原理在feign源码里说过,在创建feign对象时,如果子容器不存在某个bean,会到父,容器中找;那么我们的思路是让父容器扫描不到:
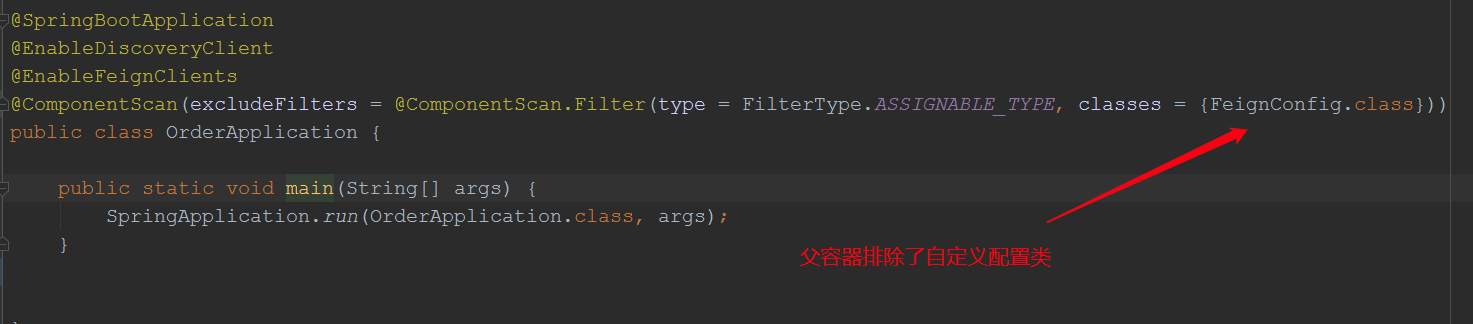
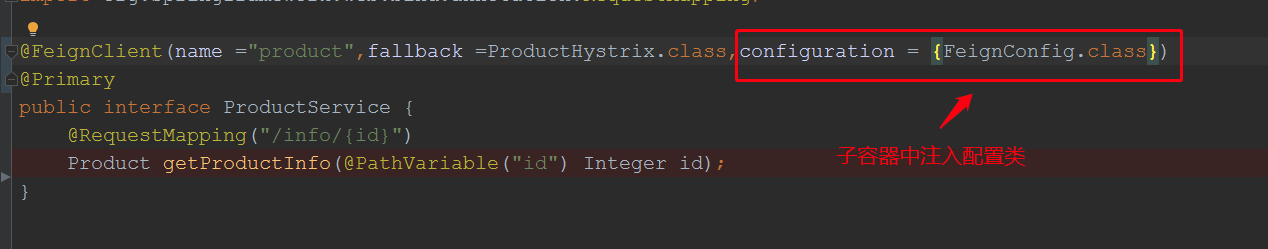
此时再次测试:
方案二:在配置类那里根据不同服务返回不同设置,甚至可以根据不同方法返回不同设置,因为Feign.Builder对象是多例的:
package com.yang.xiao.hui.order.controller; import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommand; import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommandGroupKey; import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCommandKey; import com.netflix.hystrix.HystrixThreadPoolProperties; import feign.Feign; import feign.Target; import feign.hystrix.HystrixFeign; import feign.hystrix.SetterFactory; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope; import java.lang.reflect.Method; @Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) @ConditionalOnClass({ HystrixCommand.class, HystrixFeign.class }) public class FeignConfig { @Bean @Scope("prototype") @ConditionalOnProperty(name = "feign.hystrix.enabled") public Feign.Builder feignHystrixBuilder() { HystrixFeign.Builder builder = HystrixFeign.builder(); SetterFactory setterFactory= new SetterFactory(){ @Override public HystrixCommand.Setter create(Target<?> target, Method method) { String groupKey = target.name(); String commandKey = Feign.configKey(target.type(), method); HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter setter = HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter().withCoreSize(100).withMaxQueueSize(200); if("product".equals(groupKey)){ //如果是商品服务就用下面配置 setter=HystrixThreadPoolProperties.Setter().withCoreSize(50).withMaxQueueSize(50); } return HystrixCommand.Setter .withGroupKey(HystrixCommandGroupKey.Factory.asKey(groupKey)) .andCommandKey(HystrixCommandKey.Factory.asKey(commandKey)) .andThreadPoolPropertiesDefaults(setter); } }; builder.setterFactory(setterFactory); return builder; } }
二.hystix用于controller层
前面分析的是feign与hystrix结合的源码,hystix还可以用于controller层:
2.1 添加依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-hystrix</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.2 修改controller
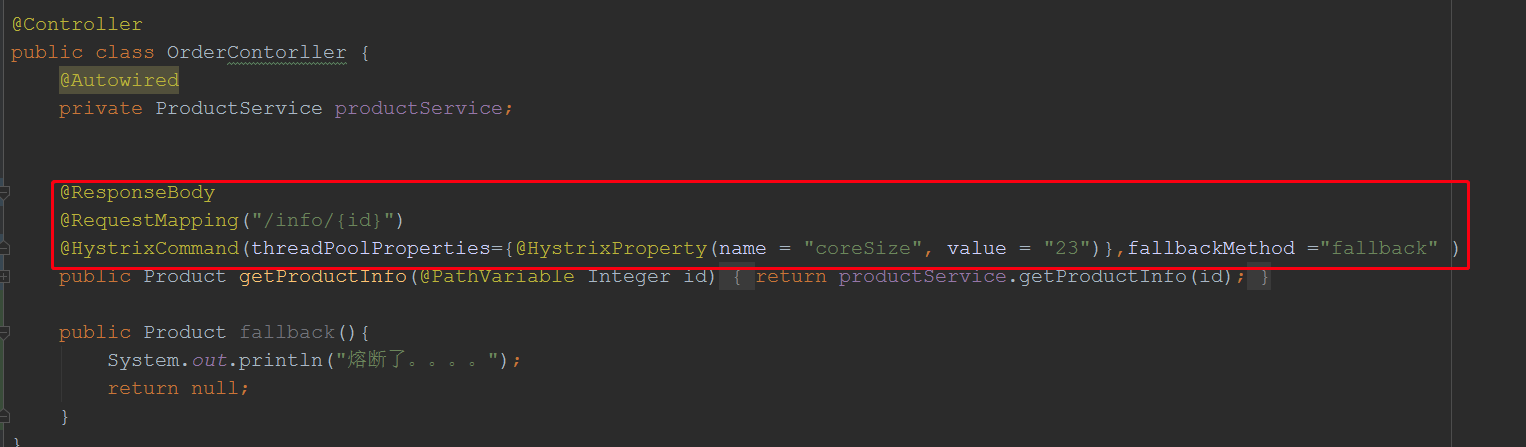
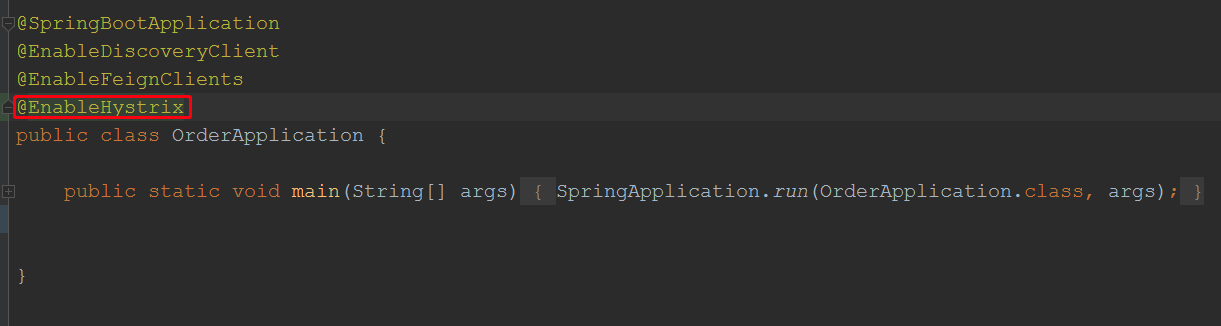
2.3.主启动类添加@EnableHystrix或@EnableCircuitBreaker @EnableHystrix注解里面包含了@EnableCircuitBreaker所以他们功能一致
2.4 源码分析:
从EnableHystrix注解开始:
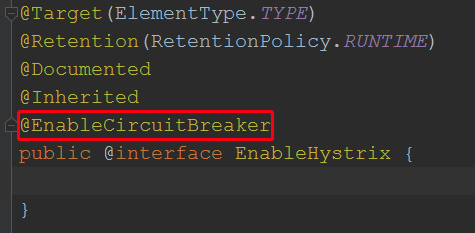
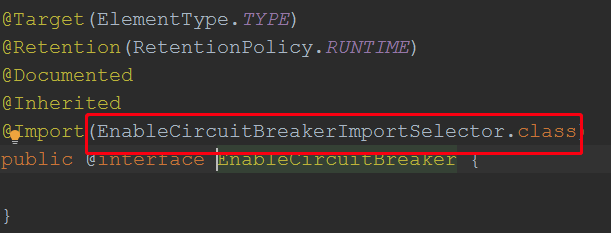
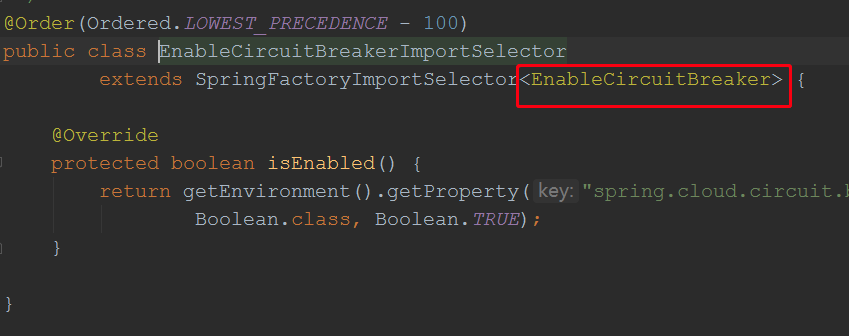

根据上面分析,springboot会加载类路径下,META-INF/spring.factories文件,找到key为org.springframework.cloud.client.circuitbreaker.EnableCircuitBreaker的类
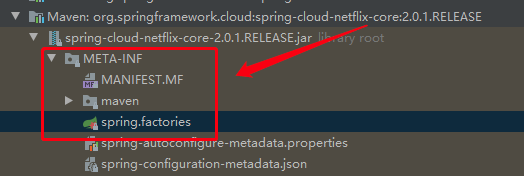
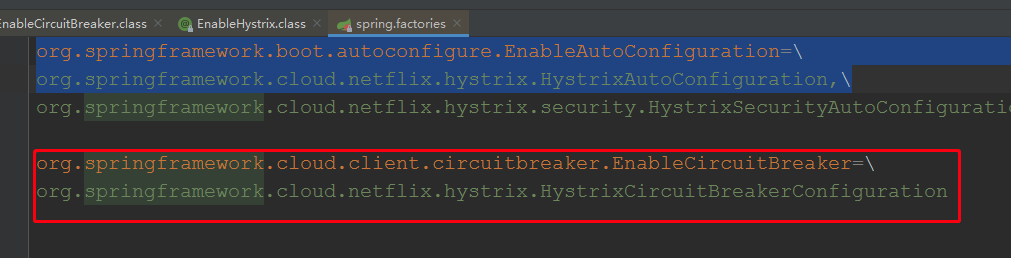
由此可见org.springframework.cloud.netflix.hystrix.HystrixCircuitBreakerConfiguration这个是我们要找的配置类
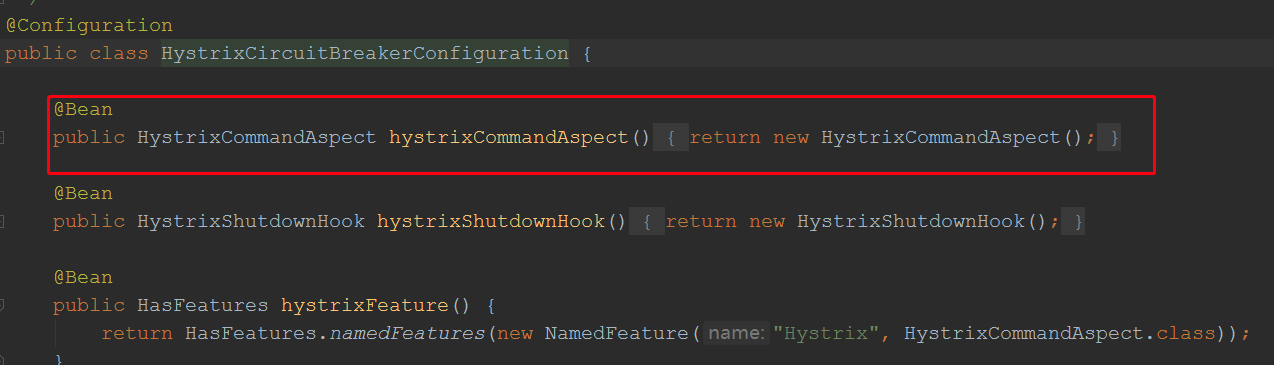
跟踪到此,我们看到了最终会注入一个切面类HystrixCommandAspect,我们根进看看
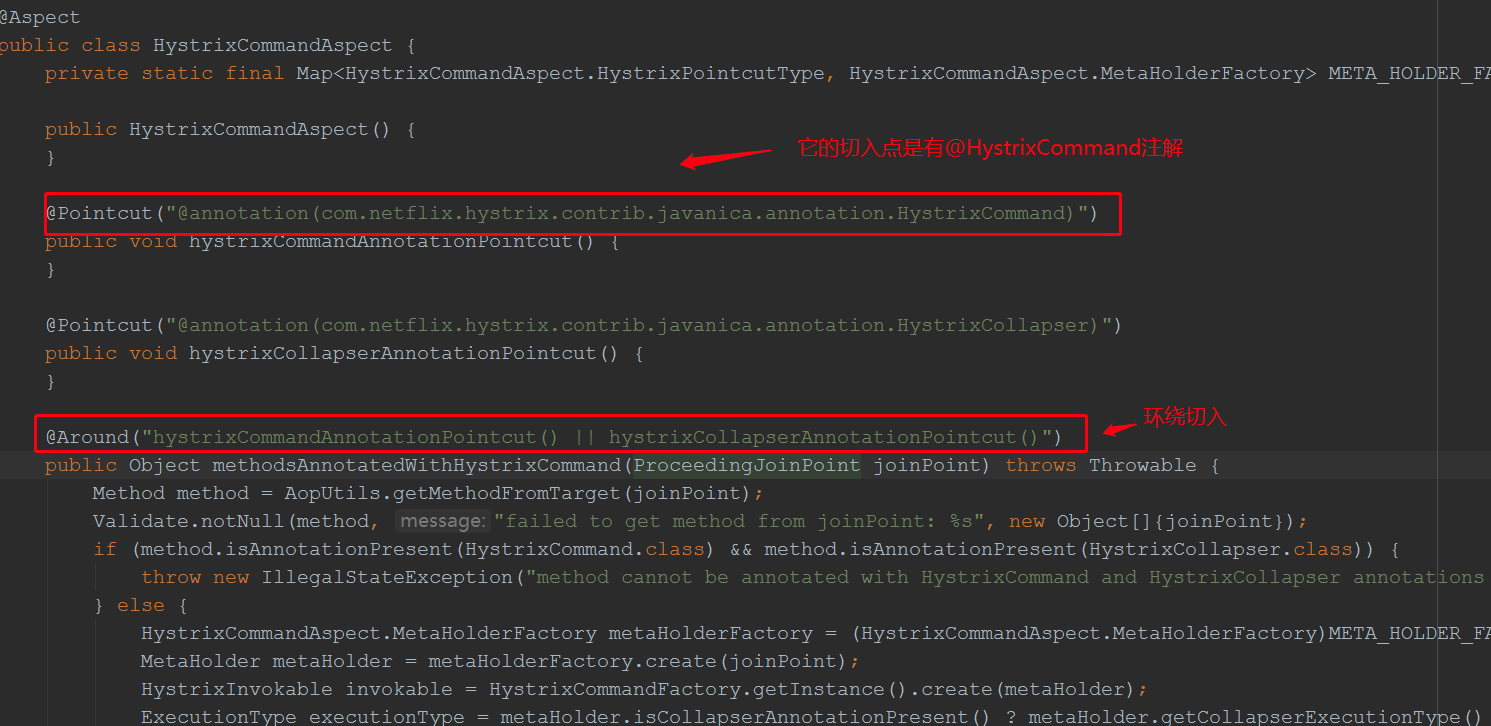
调用contorller方法,debug跟踪:
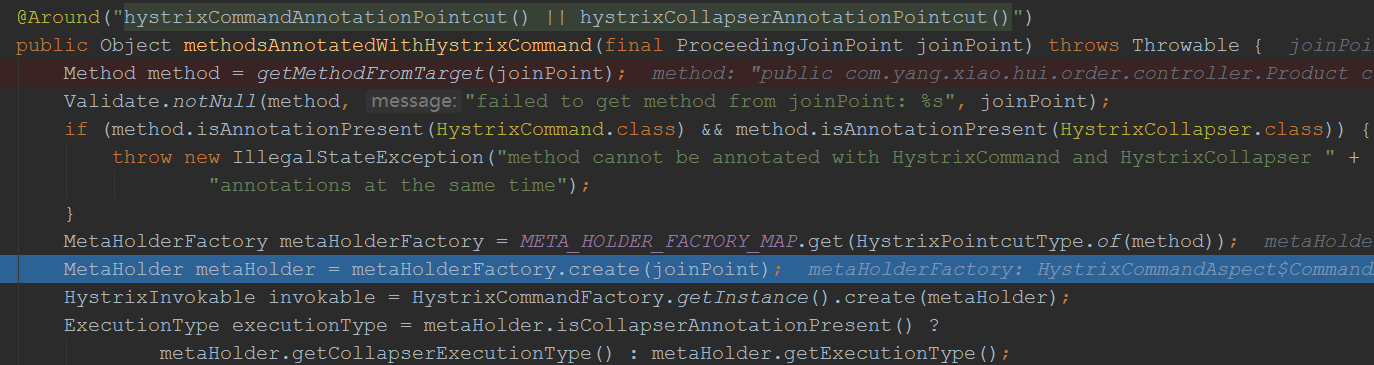
进入create方法:
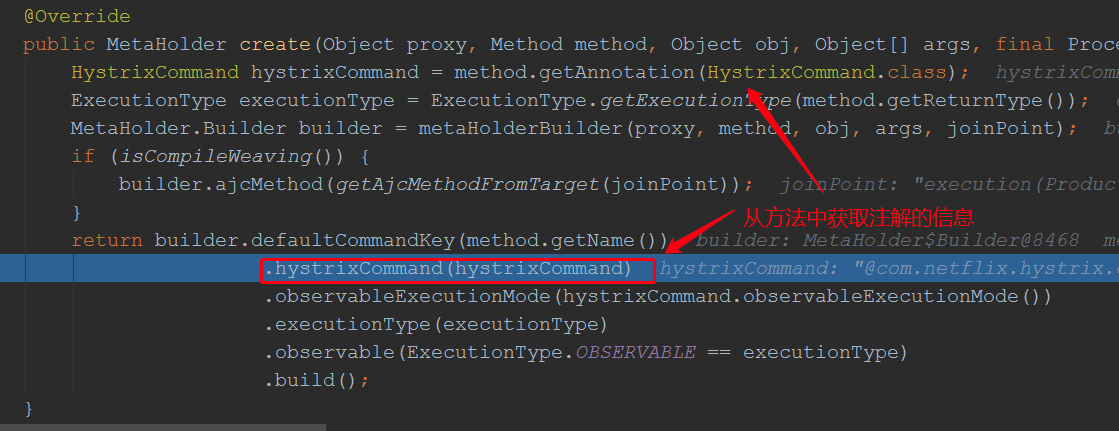
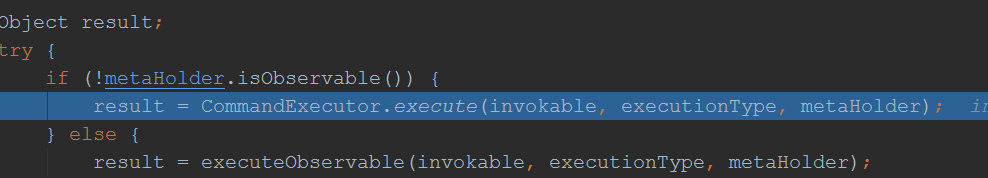
继续跟进HystrixCommandFactory.getInstance().create(metaHolder);
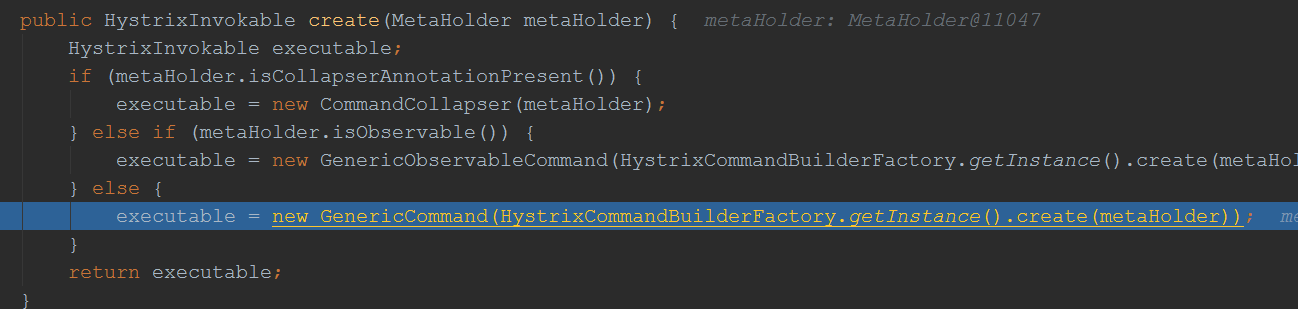
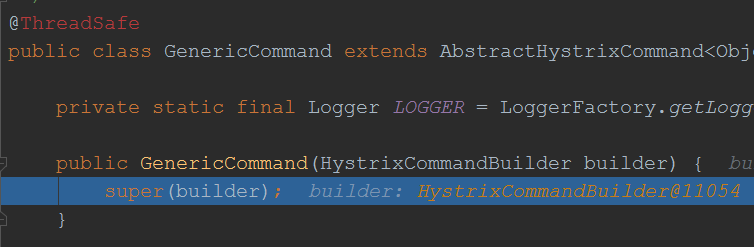
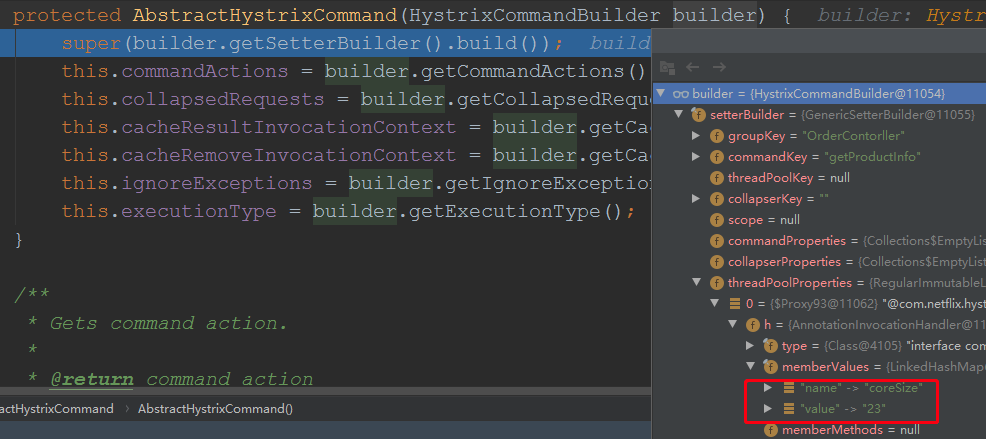
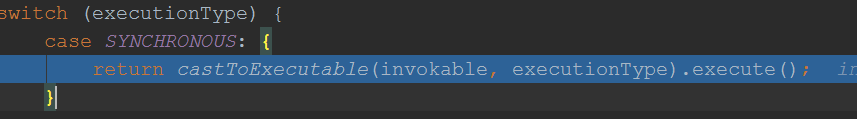
由此可见,最终也是将一个方法封装成了一个Command对象,跟前面分析feign的调用逻辑基本一致了
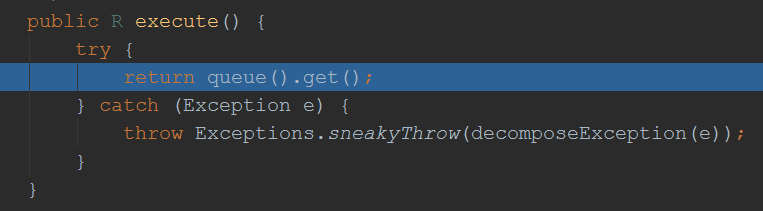
至此,调用逻辑跟之前feign结合hystrix时已经一致了,因此不再重复分分析
既然controller可以使用hystrix,如果feign调用过程也使用了hystirx,那么我们可以通过在application.yml配置文件中设置feign.hystrix.enabled=false,保留controller层的hystrix逻辑
总结: Hystix 可以实现熔断,服务降级,限流三大功能;
1.熔断的理解:就是前面判断断路器是否开还是关,跟保险丝作用一样
2. 服务降级的理解: 就是服务熔断后,执行fallback方法,这就是服务降级了
3. 限流的理解:就是里面的线程池最大队列数
=




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号