cs61b笔记_Lists
2.Lists
2.1 Mystery of the Walrus
海象之谜,主要解释了java是怎么传值的
代码部分
public class IntList {
public int first;
public IntList rest;
//给链表赋值,输入两个参数,值还有下一个
public IntList(int f,IntList r)
{
first=f;
rest=r;
}
//递归调用,返回链表长度
public int size(){
if(rest==null)
{
return 1;
}
return 1+this.rest.size();
}
//不用递归,使用迭代法,返回链表长度
public int iterativeSize(){
IntList p=this;
int totalSize=0;
while (p!=null)
{
totalSize=totalSize+1;
p=p.rest;
}
return totalSize;
}
//返回第i个元素里面有什么(递归)
public int get(int i){
if (i==0)
{
return first;
}
return rest.get(i-1);
}
//主方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//初始化链表
IntList L=new IntList(5,null);
L.rest=new IntList(10,null);
L.rest.rest=new IntList(15,null);
//
System.out.println("L的长度是"+ L.size());
System.out.println("L的长度是"+L.iterativeSize());
System.out.println("L里第二个元素是:"+L.get(1));
}
}
2.2 The SLList
private和public
使用public的时候容易搞出一些幺儿子
比如
L.first.next.next = L.first.next;
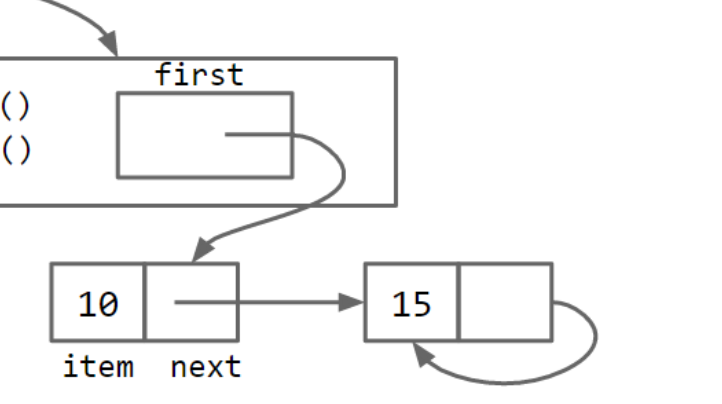
这样子就导致了一个循环
private关键字所做的唯一一件事就是中断原本可以编译的程序。
从系统的角度防止菜鸟程序员乱搞,因为搞了会报错
Nested Classes
嵌套类
就是把一个类放在另外一个类里面
2.3 The DLList
2.4 Arrays
2.5 The AList


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号