Java第八次作业
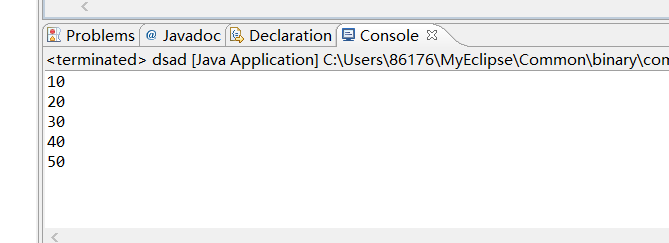
1、编写一个简单程序,要求数组长度为5,分别赋值10,20,30,40,50,在控制台输出该数组的值。(知识点:数组定义和创建、一维数组初始化)[必做题]•
package dsadsa; public class dsad { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int a[]={10,20,30,40,50}; for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.println(a[i]); } } }
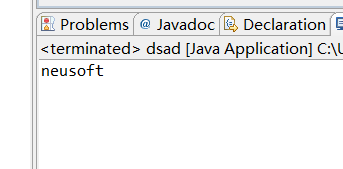
2、将一个字符数组的值(neusofteducation)拷贝到另一个字符数组中。(知识点:数组复制) [必做题]•
package dsadsa; public class dsad { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub char []x={'n','e','u','s','o','f','t'}; char []b=new char[x.length]; System.arraycopy(x, 0, b, 0, x.length); for(char c:b){ System.out.print(c); } } }
3、给定一个有9个整数(1,6,2,3,9,4,5,7,8)的数组,先排序,然后输出排序后的数组的值。(知识点:Arrays.sort排序、冒泡排序)
package dsadsa;public class dsad { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int[] a = { 1, 6, 2, 3, 9, 4, 5, 7, 8 }; for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < a.length - 1 - i; j++) { if (a[j] > a[j + 1]) { int temp = a[j]; a[j] = a[j + 1]; a[j + 1] = temp; } } } for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.println(a[i]); } Arrays.sort(a); for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.println(a[i]); } } }
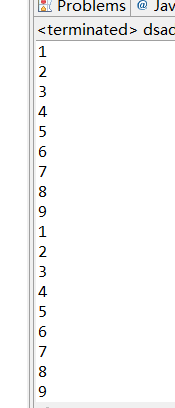
4、 输出一个double型二维数组(长度分别为5、4,值自己设定)的值。(知识点:数组定义和创建、多维数组初始化、数组遍历)
package dsadsa; public class dsad { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub double a[][]=new double[5][4]; for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) { a[i][j]=j; } } for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < a[i].length; j++) { System.out.print(a[i][j]+" "); } System.out.println(" "); } } }

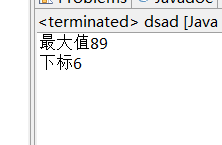
5、 在一个有8个整数(18,25,7,36,13,2,89,63)的数组中找出其中最大的数及其下标。(知识点:数组遍历、数组元素访问) [必做题]•
package dsadsa; public class dsad { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int shuzu[] = new int[]{18,25,7,36,13,2,89,63}; int maxid=0; int c=0; int max = 0; for (int i : shuzu) { if(i>max){ max=i; maxid=c; } c++; } System.out.println("最大值"+max); System.out.println("下标"+maxid); } }
作业
6、将一个数组中的元素逆序存放(知识点:数组遍历、数组元素访问) [选作题]•
package dsadsa; public class dsad { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int num[]={1,2,3,4,5,6}; for (int i = 0; i < num.length/2; i++) { int temp; temp=num[i]; num[i]=num[num.length-1-i]; num[num.length-1-i]=temp; } for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) { System.out.println(num[i]); } } }
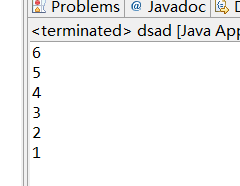
7. 将一个数组中的重复元素保留一个其他的清零。(知识点:数组遍历、数组元素访问) [选作题]课后作业•
package dsadsa; public class dsad { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int[] a = {5,5,7,7,8,8,9,9,4,4,2,2}; for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++) { if (a[i] == a[j] && i != j) { a[j] = 0; } } } for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { System.out.println(a[i]); } } }

8、给定一维数组{ -10,2,3,246,-100,0,5},计算出数组中的平均值、最大值、最小值。(知识点:数组遍历、数组元素访问)
package dsadsa; public class dsad { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int[] a = {-100,-50,0,50,100}; int max = 0; int min = 0; int avg = 0; for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) { if (a[i] > max) { max = a[i]; } if (a[i] < min) { min = a[i]; } avg = avg + a[i]; } System.out.println("这个数组最大数是: " + max); System.out.println("这个数组最小数是: " + min); System.out.println("这个数组平均数是: " + avg /5.0); } }

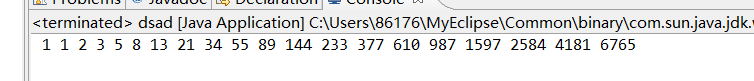
9、使用数组存放裴波那契数列的前20项 ,并输出
package dsadsa; public class dsad { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub int a[]=new int[20]; a[0]=1;a[1]=1; for(int i=2;i<a.length;i++){ a[i]=a[i-1]+a[i-2]; } for(int i=0;i<20;i++){ System.out.print(" "+a[i]); } } }
10、生成一个长度为10的随机整数数组(每个数都是0-100之间),输出,排序后,再输出
package dsadsa; import java.util.Random; import java.util.Scanner; public class dsad { /** * @param args */ public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Random r = new Random(); Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); int m[] = new int[10]; for (int i = 0; i < m.length; i++) { int n = (int) (Math.random() * 100); m[i] = n; System.out.println(m[i]); } System.out.println("排序"); for (int i = 0; i < m.length - 1; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < m.length - 1 - i; j++) { if (m[j] > m[j+1]) { int temp = m[j]; m[j] = m[j + 1]; m[j + 1] = temp; } } } for (int i : m) { System.out.println(i); } } }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号