软考系统分析师·每日学习卡 | [日期:2025-07-01] | [今日主题:系统设计-结构型设计模式]
一、今日学了啥?
- 结构型设计模式(7 种)P476
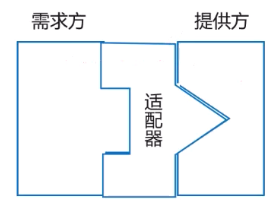
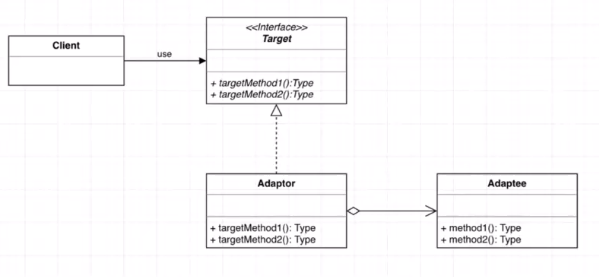
- 适配器模式(Adapter):讲一个类的接口转换成用户希望得到的另一种接口,使原本不相容的接口得以协同工作
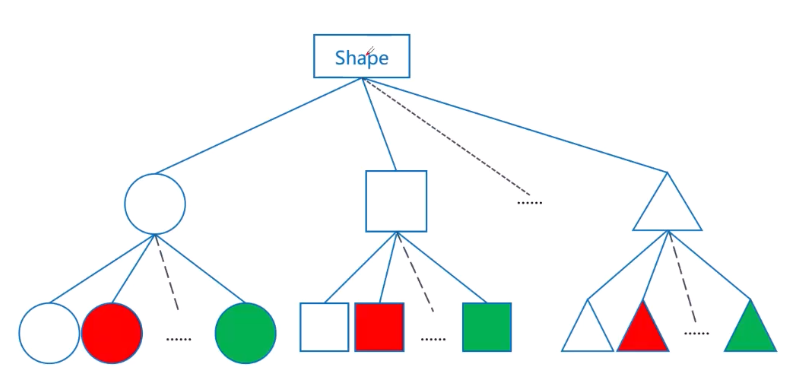
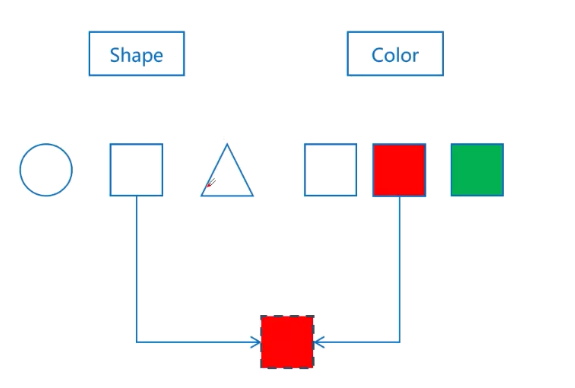
- 桥接模式(Bridge):将类的抽象部分与它的实现部分分离,使它们都可以独立地变化
- 组合模式(Composite):将对象组合成树形结构以表示“部分-整体”的层次结构,使用户对单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性
- 装饰模式(Decorator):动态地给一个对象添加一些额外的职责,提供了用子类扩展功能的一个灵活替代,比派生一个子类更为灵活
- 外观模式(Facade):定义一个高层接口,为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,简化该子系统的使用
- 享元模式(Flyweight):运用共享技术有效地支持大量细粒度的对象
- 代理模式(Proxy):为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问
二、重点/要记住的!
-
🔺 适配器模式:转换、兼容接口
-
🔺 桥接模式:抽象与实现分离、用聚合或组合来替换类的集成(避免类爆炸)
->
-
🔺 组合模式:整体-部分、树形结构
-
🔺 装饰模式:在不改变对象功能基础上附加职责
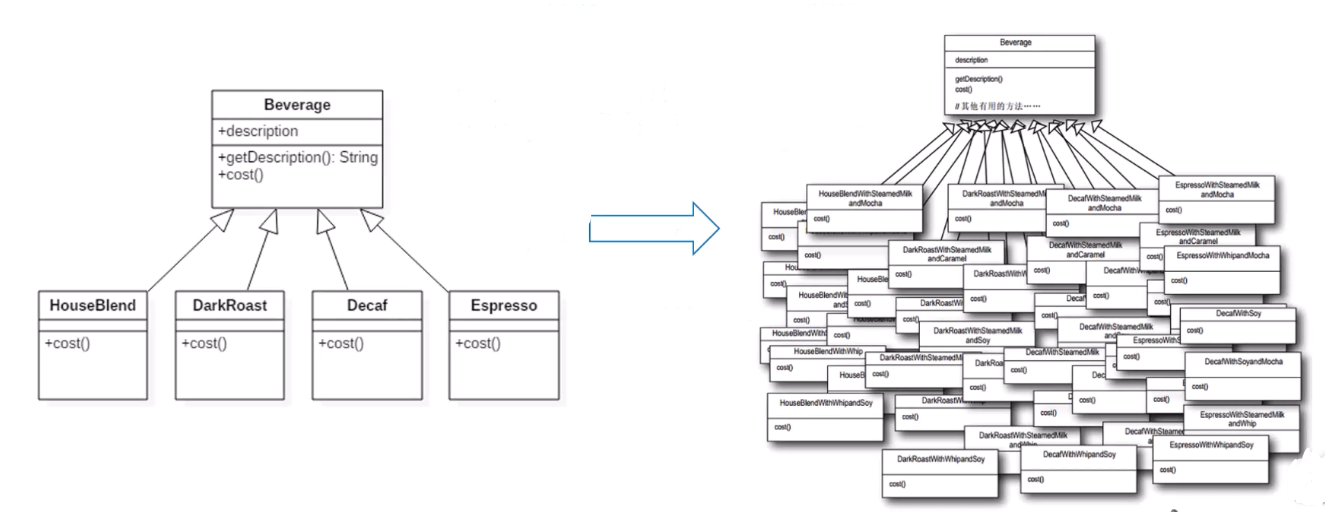
-
🔺 外观模式:对外统一接口
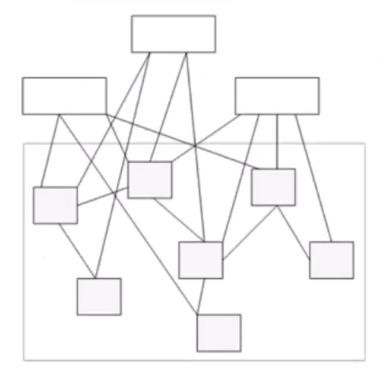
-
🔺 享元模式:细粒度、共享
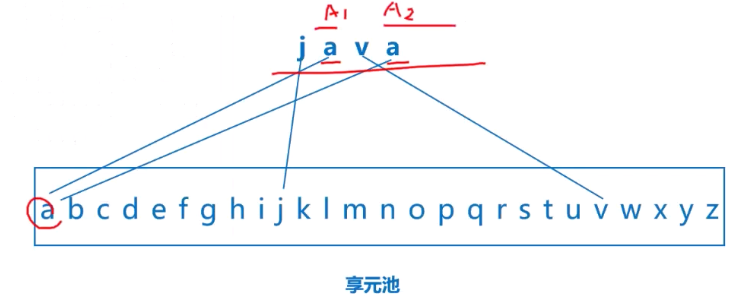
-
🔺 代理模式:代理控制
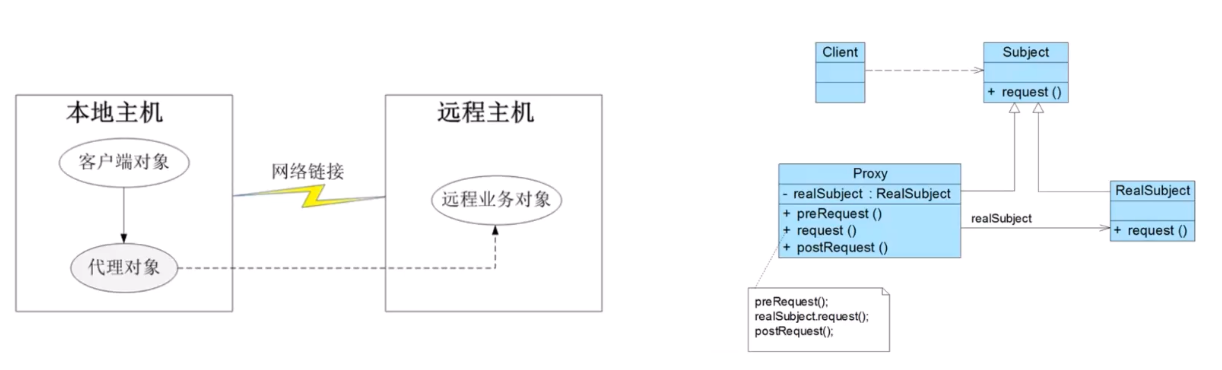
三、今天的小收获/卡住的地方
-
卡住:今天视频教程里面缺失,用AI以python结合举例帮助理解
- 适配器模式(Adapter):比如将旧有的支付接口适配成新系统需要的接口。Python中可以用类继承或组合来实现。
- 桥接模式(Bridge):比如不同形状(圆形、方形)与颜色(红色、蓝色)的组合,避免类爆炸。
- 组合模式(Composite):文件系统结构,目录包含文件和其他目录,统一处理。
- 装饰模式(Decorator):比如咖啡加料(牛奶、糖)的费用计算,动态添加功能。
- 外观模式(Facade):简化家庭影院系统的操作,提供一个统一的接口。
- 享元模式(Flyweight):管理大量相似对象,比如围棋中的棋子,共享颜色和形状。
- 代理模式(Proxy):远程调用代理,或者权限控制,比如访问受保护资源。
以下是7种模式的详细解析:
-
适配器模式(Adapter) - 支付接口兼容
class OldPayment: def legacy_pay(self, amount): print(f"旧系统支付 {amount} 元") class NewPayment: def pay(self, amount): print(f"新系统支付 {amount} 元") class PaymentAdapter: def __init__(self, payment): self.payment = payment def pay(self, amount): if hasattr(self.payment, 'pay'): self.payment.pay(amount) else: # 适配旧接口 self.payment.legacy_pay(amount) # 使用示例 old_adapter = PaymentAdapter(OldPayment()) old_adapter.pay(100) # 输出:旧系统支付 100 元现实案例:银行系统升级时保持原有支付接口的兼容性
-
桥接模式(Bridge) - 形状与颜色组合
class Color: def apply_color(self): pass class Red(Color): def apply_color(self): return "红色" class Blue(Color): def apply_color(self): return "蓝色" class Shape: def __init__(self, color): self.color = color def draw(self): pass class Circle(Shape): def draw(self): print(f"圆形填充{self.color.apply_color()}") class Square(Shape): def draw(self): print(f"方形填充{self.color.apply_color()}") # 使用示例 red_circle = Circle(Red()) red_circle.draw() # 输出:圆形填充红色现实案例:图形界面库中形状与颜色的自由组合
-
组合模式(Composite) - 文件系统结构
class FileSystemItem: def get_size(self): pass class File(FileSystemItem): def __init__(self, size): self.size = size def get_size(self): return self.size class Directory(FileSystemItem): def __init__(self): self.items = [] def add(self, item): self.items.append(item) def get_size(self): return sum(item.get_size() for item in self.items) # 使用示例 root = Directory() root.add(File(100)) sub_dir = Directory() sub_dir.add(File(50)) root.add(sub_dir) print(root.get_size()) # 输出:150现实案例:操作系统文件管理器中的目录树管理
-
装饰模式(Decorator) - 咖啡加料
class Coffee: def cost(self): return 5 class MilkDecorator: def __init__(self, coffee): self._coffee = coffee def cost(self): return self._coffee.cost() + 2 class SugarDecorator: def __init__(self, coffee): self._coffee = coffee def cost(self): return self._coffee.cost() + 1 # 使用示例 my_coffee = MilkDecorator(SugarDecorator(Coffee())) print(my_coffee.cost()) # 输出:8现实案例:Java IO流的功能增强(BufferedReader包装InputStream)
-
外观模式(Facade) - 家庭影院系统
class Amplifier: def on(self): print("功放开启") def set_volume(self, level): print(f"设置音量到{level}") class Projector: def on(self): print("投影仪开启") def set_mode(self, mode): print(f"设置模式为{mode}") class HomeTheater: def __init__(self): self.amp = Amplifier() self.proj = Projector() def watch_movie(self): self.amp.on() self.amp.set_volume(5) self.proj.on() self.proj.set_mode("影院模式") # 使用示例 theater = HomeTheater() theater.watch_movie()现实案例:智能家电控制系统的一键观影模式
-
享元模式(Flyweight) - 围棋棋子
class ChessPiece: def __init__(self, color, shape): self.color = color self.shape = shape def display(self, position): print(f"{self.color} {self.shape} @ {position}") class PieceFactory: _pieces = {} @staticmethod def get_piece(color, shape): key = (color, shape) if key not in PieceFactory._pieces: PieceFactory._pieces[key] = ChessPiece(color, shape) return PieceFactory._pieces[key] # 使用示例 factory = PieceFactory() black_dot = factory.get_piece("黑", "圆形") white_dot = factory.get_piece("白", "圆形") black_dot.display("A1") # 输出:黑 圆形 @ A1现实案例:游戏引擎中大量相似对象的内存优化
-
代理模式(Proxy) - 远程调用代理
class RealSubject: def request(self): print("真实请求执行") class Proxy: def __init__(self): self._real_subject = None def request(self): if self._real_subject is None: self._real_subject = RealSubject() self._real_subject.request() # 使用示例 proxy = Proxy() proxy.request() # 输出:真实请求执行现实案例:分布式系统中的远程服务代理(如RPC框架)
四、明天学啥?
明天学习行为型设计模式
像实干家一样思考问题,像思想家一样付诸行动。
愿你我共同进步!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号