BEVDet-net部分
class FusionLSSFPN(BaseLSSFPN):
...
def forward(self,
sweep_imgs,
mats_dict,
lidar_depth,
timestamps=None,
is_return_depth=False):
"""Forward function.
Args:
sweep_imgs(Tensor): Input images with shape of (B, num_sweeps,
num_cameras, 3, H, W).
mats_dict(dict):
sensor2ego_mats(Tensor): Transformation matrix from
camera to ego with shape of (B, num_sweeps,
num_cameras, 4, 4).
intrin_mats(Tensor): Intrinsic matrix with shape
of (B, num_sweeps, num_cameras, 4, 4).
ida_mats(Tensor): Transformation matrix for ida with
shape of (B, num_sweeps, num_cameras, 4, 4).
sensor2sensor_mats(Tensor): Transformation matrix
from key frame camera to sweep frame camera with
shape of (B, num_sweeps, num_cameras, 4, 4).
bda_mat(Tensor): Rotation matrix for bda with shape
of (B, 4, 4).
lidar_depth (Tensor): Depth generated by lidar.
timestamps(Tensor): Timestamp for all images with the shape of(B,
num_sweeps, num_cameras).
Return:
Tensor: bev feature map.
"""
batch_size, num_sweeps, num_cams, num_channels, img_height, \
img_width = sweep_imgs.shape #[b, 1, 6, 3, 256, 704]
lidar_depth = self.get_downsampled_lidar_depth(lidar_depth) #[b, 1, 6, 1, 16, 44] <-- [b, 1, 6, 256, 704]
key_frame_res = self._forward_single_sweep(
0,
sweep_imgs[:, 0:1, ...], #[b, 1, 6, 3, 256, 704]
mats_dict,
lidar_depth[:, 0, ...],
is_return_depth=is_return_depth)
if num_sweeps == 1:
return key_frame_res
key_frame_feature = key_frame_res[
0] if is_return_depth else key_frame_res
ret_feature_list = [key_frame_feature]
for sweep_index in range(1, num_sweeps):
with torch.no_grad():
feature_map = self._forward_single_sweep(
sweep_index,
sweep_imgs[:, sweep_index:sweep_index + 1, ...],
mats_dict,
lidar_depth[:, sweep_index, ...],
is_return_depth=False)
ret_feature_list.append(feature_map)
if is_return_depth:
return torch.cat(ret_feature_list, 1), key_frame_res[1]
else:
return torch.cat(ret_feature_list, 1)
图像sweep_imgs的shape:batch_size, num_sweeps, num_cams, num_channels, img_height, img_width = sweep_imgs.shape #[b, 1, 6, 3, 256, 704]
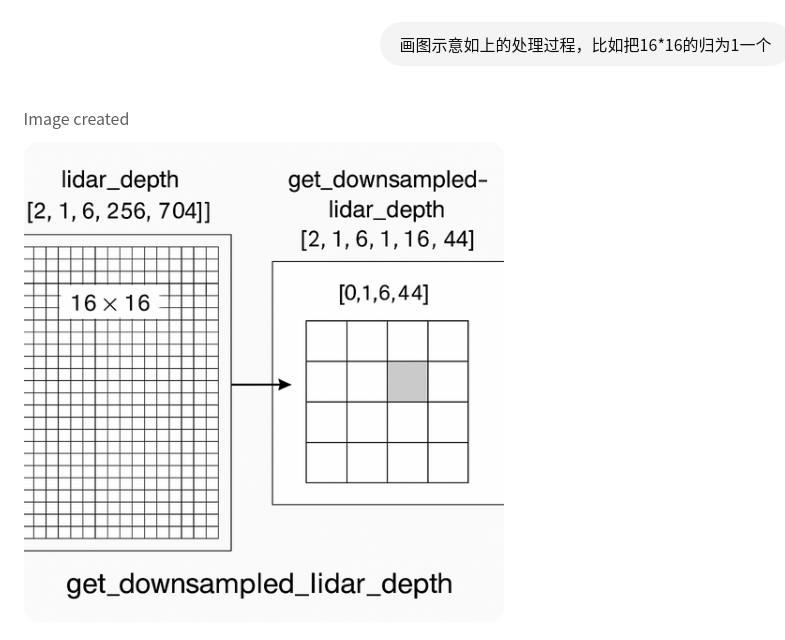
1. lidar特征处理,由 [256, 704]变成[16, 44]
函数get_downsampled_lidar_depth,[B, 1, 6, 256, 704]变成 [b, num_sweeps(1), num_cam(6), ch(1), h(16), w(44)]
lidar_depth的shape是[b,1,6,256,704], 1是num_sweeps,6是num_cams
def get_downsampled_lidar_depth(self, lidar_depth):
batch_size, num_sweeps, num_cams, height, width = lidar_depth.shape # [b, 1, 6, 256, 704]
lidar_depth = lidar_depth.view(
batch_size * num_sweeps * num_cams,
height // self.downsample_factor,
self.downsample_factor,
width // self.downsample_factor,
self.downsample_factor,
1,
) #torch.Size([12, 16, 16, 44, 16, 1])
lidar_depth = lidar_depth.permute(0, 1, 3, 5, 2, 4).contiguous() #torch.Size([12, 16, 44, 1, 16, 16])
lidar_depth = lidar_depth.view(
-1, self.downsample_factor * self.downsample_factor) #torch.Size([8448, 256])
gt_depths_tmp = torch.where(lidar_depth == 0.0, lidar_depth.max(),
lidar_depth)
lidar_depth = torch.min(gt_depths_tmp, dim=-1).values #[8448]
lidar_depth = lidar_depth.view(batch_size, num_sweeps, num_cams, 1,
height // self.downsample_factor,
width // self.downsample_factor) #[2, 1, 6, 1, 16, 44]
lidar_depth = lidar_depth / self.d_bound[1] #self.d_bound[1] 58
return lidar_depth
downsample_factor是16,下面这句是把[256, 704]分成16块,把b和num_cam合并,
view操作,按照16重排
lidar_depth = lidar_depth.view(
batch_size * num_sweeps * num_cams,
height // self.downsample_factor,
self.downsample_factor,
width // self.downsample_factor,
self.downsample_factor,
1,
) #torch.Size([12, 16, 16, 44, 16, 1])
得到的lidar_depth的shape是[b*num_cam, h有多少个16, 16, w有多少个16, 16, 1],即:
【b×num_cam, 16, 16, 44, 16, 1】#256=16x16 704=44x16
permute 改变维度顺序
lidar_depth = lidar_depth.permute(0, 1, 3, 5, 2, 4).contiguous() #torch.Size([12, 16, 44, 1, 16, 16])
原始维度 [B, H_d, 16, W_d, 16, 1] → 调整后:[B, H_d, W_d, 1, 16, 16], 这里的目的是把 (16, 16) 的 patch 作为一个整体,准备拉平为一维。
将每个 patch 展平成一维向量
lidar_depth = lidar_depth.view(
-1, self.downsample_factor * self.downsample_factor) #torch.Size([8448, 256])
每个 downsample patch 拉成一行,共有 8448 个 patch,每个 patch 有 16x16=256 个深度值。
每个patch16x16的只取最小值深度代表该patch
lidar_depth[8448, 256]里面有大量的0,torch.where操作先把0值的地方赋值为最大深度值(后面取最小规避掉0值),有值的地方赋为原本的值。
torch.min操作是8668个256,每个256就取最小值代表该patch
gt_depths_tmp = torch.where(lidar_depth == 0.0, lidar_depth.max(),
lidar_depth)
lidar_depth = torch.min(gt_depths_tmp, dim=-1).values #[8448]
还原shape
lidar_depth = lidar_depth.view(batch_size, num_sweeps, num_cams, 1,
height // self.downsample_factor,
width // self.downsample_factor) #[2, 1, 6, 1, 16, 44]
shape变为[2, 1, 6, 1, 16, 44], 宽和高是16和44,一开始输入进来的宽和高是[256,704],就相当于下采样16倍。
归一化深度值
lidar_depth = lidar_depth / self.d_bound[1] #self.d_bound[1] 58
return lidar_depth #[b(2), num_sweeps(1), num_cam(6), ch(1), h(16), w(44)]
2.图像特征处理,[256,704]变成[16,44]
get_cam_feats() 得到图像特征, img_feats[2, 1, 6, 512, 16, 44] <-- sweep_imgs[2, 1, 6, 3, 256, 704]
函数get_cam_feats()
def get_cam_feats(self, imgs):
"""Get feature maps from images."""
batch_size, num_sweeps, num_cams, num_channels, imH, imW = imgs.shape
imgs = imgs.flatten().view(batch_size * num_sweeps * num_cams,
num_channels, imH, imW) #[12, 3, 256, 704]
img_feats = self.img_neck(self.img_backbone(imgs))[0]
img_feats = img_feats.reshape(batch_size, num_sweeps, num_cams,
img_feats.shape[1], img_feats.shape[2],
img_feats.shape[3])
return img_feats
img_backbone是resnet网络,输出4个不同尺度的特征
输入的shape [12, 3, 256, 704]
输出的shape:
x[0].shape
torch.Size([12, 256, 64, 176])
x[1].shape
torch.Size([12, 512, 32, 88])
x[2].shape
torch.Size([12, 1024, 16, 44])
x[3].shape
torch.Size([12, 2048, 8, 22])
img_neck是叫second_fpn.py
# Copyright (c) OpenMMLab. All rights reserved.
import numpy as np
import torch
from mmcv.cnn import build_conv_layer, build_norm_layer, build_upsample_layer
from mmcv.runner import BaseModule, auto_fp16
from torch import nn as nn
from ..builder import NECKS
@NECKS.register_module()
class SECONDFPN(BaseModule):
"""FPN used in SECOND/PointPillars/PartA2/MVXNet.
Args:
in_channels (list[int]): Input channels of multi-scale feature maps.
out_channels (list[int]): Output channels of feature maps.
upsample_strides (list[int]): Strides used to upsample the
feature maps.
norm_cfg (dict): Config dict of normalization layers.
upsample_cfg (dict): Config dict of upsample layers.
conv_cfg (dict): Config dict of conv layers.
use_conv_for_no_stride (bool): Whether to use conv when stride is 1.
"""
def __init__(self,
in_channels=[128, 128, 256],
out_channels=[256, 256, 256],
upsample_strides=[1, 2, 4],
norm_cfg=dict(type='BN', eps=1e-3, momentum=0.01),
upsample_cfg=dict(type='deconv', bias=False),
conv_cfg=dict(type='Conv2d', bias=False),
use_conv_for_no_stride=False,
init_cfg=None):
# if for GroupNorm,
# cfg is dict(type='GN', num_groups=num_groups, eps=1e-3, affine=True)
super(SECONDFPN, self).__init__(init_cfg=init_cfg)
assert len(out_channels) == len(upsample_strides) == len(in_channels)
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.out_channels = out_channels
self.fp16_enabled = False
deblocks = []
for i, out_channel in enumerate(out_channels):
stride = upsample_strides[i]
if stride > 1 or (stride == 1 and not use_conv_for_no_stride):
upsample_layer = build_upsample_layer(
upsample_cfg,
in_channels=in_channels[i],
out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=upsample_strides[i],
stride=upsample_strides[i])
else:
stride = np.round(1 / stride).astype(np.int64)
upsample_layer = build_conv_layer(
conv_cfg,
in_channels=in_channels[i],
out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=stride,
stride=stride)
deblock = nn.Sequential(upsample_layer,
build_norm_layer(norm_cfg, out_channel)[1],
nn.ReLU(inplace=True))
deblocks.append(deblock)
self.deblocks = nn.ModuleList(deblocks)
if init_cfg is None:
self.init_cfg = [
dict(type='Kaiming', layer='ConvTranspose2d'),
dict(type='Constant', layer='NaiveSyncBatchNorm2d', val=1.0)
]
@auto_fp16()
def forward(self, x):
"""Forward function.
Args:
x (torch.Tensor): 4D Tensor in (N, C, H, W) shape.
Returns:
list[torch.Tensor]: Multi-level feature maps.
"""
assert len(x) == len(self.in_channels)
ups = [deblock(x[i]) for i, deblock in enumerate(self.deblocks)]
if len(ups) > 1:#Yes
out = torch.cat(ups, dim=1) #[12, 512, 16, 44]
else:
out = ups[0]
return [out]
这里输入的x的shape是 [12, 256, 64, 176], [12, 512, 32, 88], [12, 1024, 16, 44], [12, 2048, 8, 22]
ups = [deblock(x[i]) for i, deblock in enumerate(self.deblocks)]
加打印如下:
x[0].shape [12, 256, 64, 176] (self.deblocks[0](x[0])).shape: torch.Size([12, 128, 16, 44])
x[1].shape [12, 512, 32, 88] (self.deblocks[1](x[1])).shape: torch.Size([12, 128, 16, 44])
x[2].shape [12, 1024, 16, 44] (self.deblocks[2](x[2])).shape: torch.Size([12, 128, 16, 44])
x[3].shape [12, 2048, 8, 22] (self.deblocks[3](x[3])).shape: torch.Size([12, 128, 16, 44])
可以看到x[0]、x[1] 是下采样到固定尺寸,x[3]是上采样到固定尺寸
最后cat输出
out = torch.cat(ups, dim=1) #[12, 512, 16, 44]
img_feats = img_feats.reshape(batch_size, num_sweeps, num_cams,
img_feats.shape[1], img_feats.shape[2],
img_feats.shape[3])
恢复原本的shape输出:[b, 1, 6, 512, 16, 44]
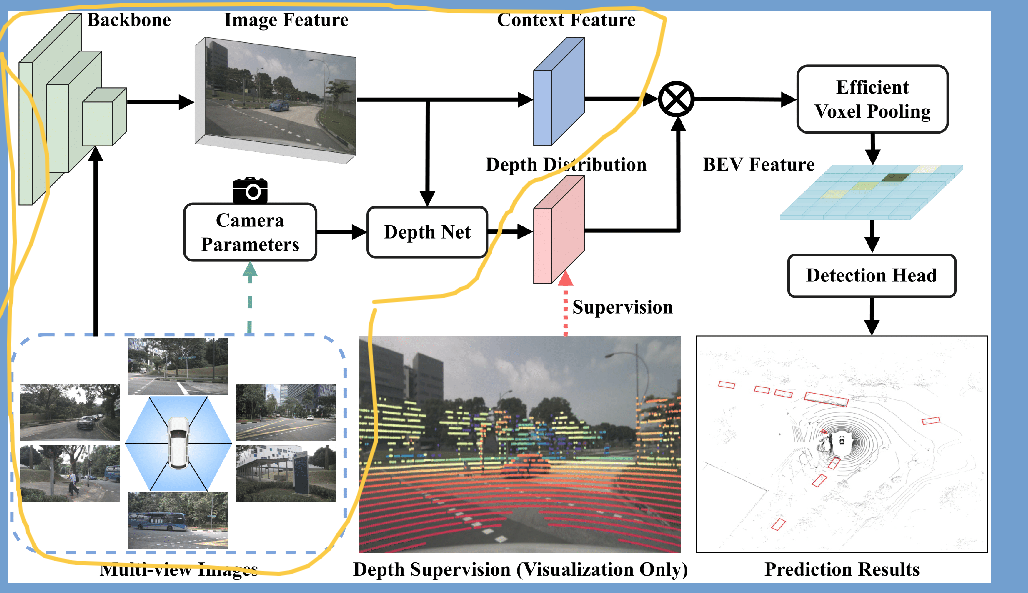
3. _forward_depth_net即DepthNet
DepthNet,图像特征和相机参数和雷达特征融合
输入 #img_feats torch.Size([12, 512, 16, 44]) lidar_depth torch.Size([12, 1, 16, 44])
输出: #[12, 112 + 80, 16, 44] ,112是图像+深度+内参融合的信息, 80单纯是图像
class DepthNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, mid_channels, context_channels,
depth_channels):
super(DepthNet, self).__init__()
self.reduce_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels,
mid_channels,
kernel_size=3,
stride=1,
padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(mid_channels),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
)
self.context_conv = nn.Conv2d(mid_channels,
context_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
self.mlp = Mlp(1, mid_channels, mid_channels)
self.se = SELayer(mid_channels) # NOTE: add camera-aware
self.depth_gt_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, mid_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, mid_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
)
self.depth_conv = nn.Sequential(
BasicBlock(mid_channels, mid_channels),
BasicBlock(mid_channels, mid_channels),
BasicBlock(mid_channels, mid_channels),
)
self.aspp = ASPP(mid_channels, mid_channels)
self.depth_pred = nn.Conv2d(mid_channels,
depth_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
#x(img_feat)torch.Size([12, 512, 16, 44]) lidar_depth torch.Size([12, 1, 16, 44])
def forward(self, x, mats_dict, lidar_depth, scale_depth_factor=1000.0):
x = self.reduce_conv(x) # [12, 512, 16, 44]
context = self.context_conv(x) # [12, 80, 16, 44]
inv_intrinsics = torch.inverse(mats_dict['intrin_mats'][:, 0:1, ...]) # mats_dict['intrin_mats'][b, 1, 6, 4, 4]
pixel_size = torch.norm(torch.stack(
[inv_intrinsics[..., 0, 0], inv_intrinsics[..., 1, 1]], dim=-1),
dim=-1).reshape(-1, 1) #[12,1]
aug_scale = torch.sqrt(mats_dict['ida_mats'][:, 0, :, 0, 0]**2 +
mats_dict['ida_mats'][:, 0, :, 0,
0]**2).reshape(-1, 1)#[12,1]
scaled_pixel_size = pixel_size * scale_depth_factor / aug_scale #[12,1]
x_se = self.mlp(scaled_pixel_size)[..., None, None] ##[12,512,1,1]
x = self.se(x, x_se) #[12,512,16,44]
depth = self.depth_gt_conv(lidar_depth) # [12, 512, 16, 44] <<-- [12, 1, 16, 44]
depth = self.depth_conv(x + depth)
depth = self.aspp(depth) # [12, 512, 16, 44]
depth = self.depth_pred(depth) #[12, 112, 16, 44]
return torch.cat([depth, context], dim=1) #[12, 112 + 80, 16, 44]
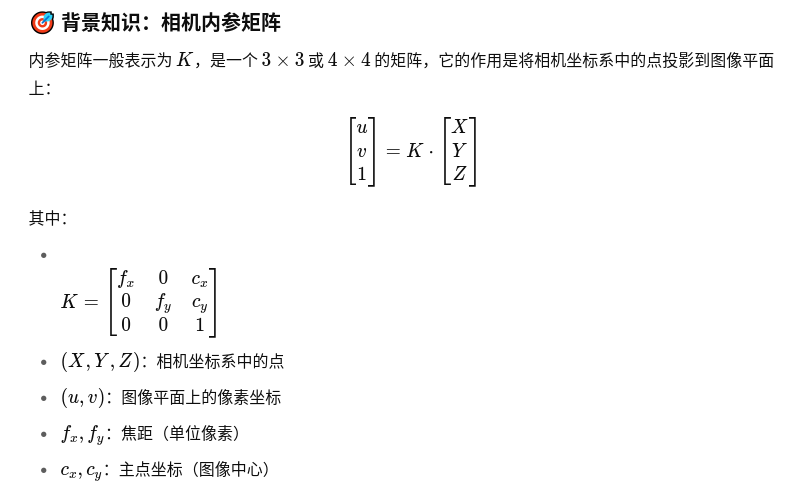
inv_intrinsics = torch.inverse(mats_dict['intrin_mats'][:, 0:1, ...]) # 取逆,用于从像素坐标反推 ray 的方向 mats_dict['intrin_mats'][b, 1, 6, 4, 4]
pixel_size = torch.norm(torch.stack(
[inv_intrinsics[..., 0, 0], inv_intrinsics[..., 1, 1]], dim=-1),
dim=-1).reshape(-1, 1) #[12,1]
inv_intrinsics[..., 0, 0] #[2,1,6], 这里是内参的fx
inv_intrinsics[..., 1, 1] #[2,1,6], 这里是内参的fy
torch.stack([inv_intrinsics[..., 0, 0], inv_intrinsics[..., 1, 1]], dim=-1) #[2, 1, 6, 2]
torch.norm(torch.stack([inv_intrinsics[..., 0, 0], inv_intrinsics[..., 1, 1]], dim=-1),dim=-1) #[2, 1, 6]
reshapr(-1, 1) #[12,1]
inv_intrinsics[..., 0, 0] ~ 1/fx; inv_intrinsics[..., 1, 1] ~ 1/fy
这相当于在估算一个像素在实际物理空间(相机前方)中所对应的大小。这个尺度信息被用来:给网络提供“相机感知能力”,让网络知道某些相机的成像精度更高(比如焦距更大、分辨率更密),某些更粗略。
取逆是为了从像素坐标反推空间尺度,用于计算像素的物理大小,从而做尺度感知的深度预测。
在代码中,inv_intrinsics = torch.inverse(mats_dict['intrin_mats'][:, 0:1, ...]) 这行代码的作用是计算相机内参矩阵的逆矩阵。这里解释其含义和作用:
-
内参矩阵(Intrinsic Matrix):
- 内参矩阵是描述相机固有属性的3x4或4x4矩阵,包含焦距(fx, fy)、光学中心(cx, cy)等参数。
- 通常形式为:
-
-
[fx, 0, cx, 0] [ 0, fy, cy, 0] [ 0, 0, 1, 0]
-
-
取逆(Inverse)的含义:
- 对内参矩阵取逆得到的是从像素坐标到归一化相机坐标的变换矩阵。
- 数学上:如果内参矩阵K将3D点投影到2D像素坐标(x = KX),那么逆矩阵K⁻¹可以将像素坐标反向投影到相机坐标系(X̃ = K⁻¹x)。
-
代码中的具体用途:
- 后续代码用逆矩阵提取了
inv_intrinsics[..., 0, 0]和inv_intrinsics[..., 1, 1],这对应原始内参矩阵中1/fx和1/fy的值。 - 通过计算这两个值的范数(
torch.norm),得到每个像素在相机坐标系中的物理尺寸(pixel_size),用于后续深度估计的尺度校准。
- 后续代码用逆矩阵提取了
-
为什么需要逆矩阵:
- 在深度估计任务中,需要理解像素与实际物理尺寸的关系。由于内参矩阵包含焦距信息(以像素为单位),取其逆可以帮助将像素尺寸转换回物理尺寸(如毫米)。
- 这种转换对多传感器融合(如LIDAR和相机)或跨尺度深度预测至关重要。
总结:内参取逆是为了从像素空间回溯到相机物理空间,从而更准确地建模深度与像素之间的几何关系,尤其在处理多尺度或跨传感器数据时。
#mats_dict['ida_mats'] torch.Size([2, 1, 6, 4, 4])
aug_scale = torch.sqrt(mats_dict['ida_mats'][:, 0, :, 0, 0]**2 +
mats_dict['ida_mats'][:, 0, :, 0,0]**2).reshape(-1, 1)#[12,1]
这里用了2次mats_dict['ida_mats'][:, 0, :, 0,0]有没有问题?
有没有可能是这样:
scale_x = mats_dict['ida_mats'][:, 0, :, 0, 0]
scale_y = mats_dict['ida_mats'][:, 0, :, 1, 1]
aug_scale = torch.sqrt(scale_x**2 + scale_y**2).reshape(-1, 1)
为什么需要计算 aug_scale?
在深度估计任务中,数据增强(如缩放)会影响像素的物理尺寸:
-
如果图像被放大,物体的像素尺寸变大,但实际物理尺寸(如深度)不变。
-
因此,需要补偿增强带来的缩放效应,确保深度预测的物理合理性。
这个 aug_scale 是为了抵消图像缩放对深度估计造成的影响。
图像被缩小了,意味着一个像素覆盖的实际场景更大了;
图像被放大了,像素代表的实际场景更小。
所以我们前面算的 pixel_size 还要除以这个 aug_scale,才能得到真实世界尺度。
ida_mats是在做数据的时候得到的:
def img_transform(img, resize, resize_dims, crop, flip, rotate):
ida_rot = torch.eye(2)
ida_tran = torch.zeros(2)
# adjust image
img = img.resize(resize_dims)
img = img.crop(crop)
if flip:
img = img.transpose(method=Image.FLIP_LEFT_RIGHT)
img = img.rotate(rotate)
# post-homography transformation
ida_rot *= resize
ida_tran -= torch.Tensor(crop[:2])
if flip:
A = torch.Tensor([[-1, 0], [0, 1]])
b = torch.Tensor([crop[2] - crop[0], 0])
ida_rot = A.matmul(ida_rot)
ida_tran = A.matmul(ida_tran) + b
A = get_rot(rotate / 180 * np.pi)
b = torch.Tensor([crop[2] - crop[0], crop[3] - crop[1]]) / 2
b = A.matmul(-b) + b
ida_rot = A.matmul(ida_rot)
ida_tran = A.matmul(ida_tran) + b
ida_mat = ida_rot.new_zeros(4, 4)
ida_mat[3, 3] = 1
ida_mat[2, 2] = 1
ida_mat[:2, :2] = ida_rot
ida_mat[:2, 3] = ida_tran
return img, ida_mat


R2x2 是 ida_mat 中控制图像空间 旋转 / 缩放 / 翻转 的部分,
它是个 2×2 矩阵,作用在像素坐标上,描述了图像如何被几何变换。
scaled_pixel_size = pixel_size * scale_depth_factor / aug_scale # [12, 1]
你问的这一行是整段代码中非常关键的一步,它是为 深度网络提供相机感知能力(camera-aware feature modulation) 的核心计算。
🧠 原代码:
scaled_pixel_size = pixel_size * scale_depth_factor / aug_scale # [B, 1]
✅ 含义分解
🔹 pixel_size
pixel_size = torch.norm(torch.stack(
[inv_intrinsics[..., 0, 0], inv_intrinsics[..., 1, 1]], dim=-1),
dim=-1).reshape(-1, 1)
inv_intrinsics是内参矩阵的逆- ( inv_K[0, 0] ) 和 ( inv_K[1, 1] ) 是分别对应 x 和 y 方向上的像素尺寸(焦距倒数)
- 所以:
[
\text{pixel_size} = \sqrt{(1/f_x)^2 + (1/f_y)^2}
]
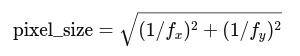
表示图像中一个像素代表的实际物理长度(单位通常是米)
🔹 scale_depth_factor
一个固定的标量(如 1000.0),只是用于把单位从 米 → 毫米 或做数值放大,使得后续的 MLP 更容易训练。
🔹 aug_scale
aug_scale = sqrt(scale_x^2 + scale_y^2)
这个表示图像被增强(resize/crop)后,整体缩放了多少。
🔸 所以 scaled_pixel_size 是什么?
[
\text{scaled_pixel_size} = \frac{\text{pixel size (in real world)}}{\text{image augmentation scale}} \times \text{scale_depth_factor}
]
这是对像素真实物理尺寸的一个矫正结果,并把它缩放到适合网络处理的尺度。

🧩 最终用途
这个值被送入:
x_se = self.mlp(scaled_pixel_size)[..., None, None] # [B, C, 1, 1]
x = self.se(x, x_se) # 调节主干特征
网络根据不同的
scaled_pixel_size,用一个 MLP 学出一个适配当前相机参数的特征缩放向量(像 squeeze-excitation 模块那样),以实现 相机感知(camera-aware)特征调节。
📝 总结一句话:
scaled_pixel_size是对 相机内参 + 图像增强尺度 综合考虑后的、代表“一个像素在真实世界中代表多大范围”的标量,
它用于让网络感知不同视角、相机和增广后的几何关系,从而提升深度估计的泛化能力。
#scaled_pixel_size 【12,1】
x_se = self.mlp(scaled_pixel_size)[..., None, None] ##[12,512,1,1]
class Mlp(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
in_features,
hidden_features=None,
out_features=None,
act_layer=nn.ReLU,
drop=0.0):
super().__init__()
out_features = out_features or in_features
hidden_features = hidden_features or in_features
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(in_features, hidden_features)
self.act = act_layer()
self.drop1 = nn.Dropout(drop)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(hidden_features, out_features)
self.drop2 = nn.Dropout(drop)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.fc1(x)
x = self.act(x)
x = self.drop1(x)
x = self.fc2(x)
x = self.drop2(x)
return x
# x[12, 512, 16, 44] x_se#[12,512,1,1]
x = self.se(x, x_se) #out x[12,512,16,44]
class SELayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, act_layer=nn.ReLU, gate_layer=nn.Sigmoid):
super().__init__()
self.conv_reduce = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, 1, bias=True)
self.act1 = act_layer()
self.conv_expand = nn.Conv2d(channels, channels, 1, bias=True)
self.gate = gate_layer()
def forward(self, x, x_se):
x_se = self.conv_reduce(x_se)
x_se = self.act1(x_se) #[12, 512, 1, 1]
x_se = self.conv_expand(x_se)#[12, 512, 1, 1]
return x * self.gate(x_se) ## [12, 512, 16, 44] = [12, 512, 16, 44] * [12, 512, 1, 1]
depth = self.depth_gt_conv(lidar_depth) # [12, 512, 16, 44] <<-- [12, 1, 16, 44]
self.depth_gt_conv = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(1, mid_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.Conv2d(mid_channels, mid_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=1),
)
#in x[12, 512, 16, 44] depth [12, 512, 16, 44]
depth = self.depth_conv(x + depth) #[12, 512, 16, 44]
self.depth_conv = nn.Sequential(
BasicBlock(mid_channels, mid_channels),
BasicBlock(mid_channels, mid_channels),
BasicBlock(mid_channels, mid_channels),
)
class BasicBlock(BaseModule):
expansion = 1
def __init__(self,
inplanes,
planes,
stride=1,
dilation=1,
downsample=None,
style='pytorch',
with_cp=False,
conv_cfg=None,
norm_cfg=dict(type='BN'),
dcn=None,
plugins=None,
init_cfg=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__(init_cfg)
assert dcn is None, 'Not implemented yet.'
assert plugins is None, 'Not implemented yet.'
self.norm1_name, norm1 = build_norm_layer(norm_cfg, planes, postfix=1)
self.norm2_name, norm2 = build_norm_layer(norm_cfg, planes, postfix=2)
self.conv1 = build_conv_layer(
conv_cfg,
inplanes,
planes,
3,
stride=stride,
padding=dilation,
dilation=dilation,
bias=False)
self.add_module(self.norm1_name, norm1)
self.conv2 = build_conv_layer(
conv_cfg, planes, planes, 3, padding=1, bias=False)
self.add_module(self.norm2_name, norm2)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
self.stride = stride
self.dilation = dilation
self.with_cp = with_cp
@property
def norm1(self):
"""nn.Module: normalization layer after the first convolution layer"""
return getattr(self, self.norm1_name)
@property
def norm2(self):
"""nn.Module: normalization layer after the second convolution layer"""
return getattr(self, self.norm2_name)
def forward(self, x):
"""Forward function."""
def _inner_forward(x):
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.norm1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.norm2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
return out
if self.with_cp and x.requires_grad:
out = cp.checkpoint(_inner_forward, x)
else:
out = _inner_forward(x)
out = self.relu(out)
return out
depth = self.aspp(depth) # [12, 512, 16, 44] #atrous_conv空洞卷积
class _ASPPModule(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, kernel_size, padding, dilation,
BatchNorm):
super(_ASPPModule, self).__init__()
self.atrous_conv = nn.Conv2d(inplanes,
planes,
kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=1,
padding=padding,
dilation=dilation,
bias=False)
self.bn = BatchNorm(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self._init_weight()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.atrous_conv(x)
x = self.bn(x)
return self.relu(x)
def _init_weight(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
torch.nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
class ASPP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, inplanes, mid_channels=256, BatchNorm=nn.BatchNorm2d):
super(ASPP, self).__init__()
dilations = [1, 6, 12, 18]
self.aspp1 = _ASPPModule(inplanes,
mid_channels,
1,
padding=0,
dilation=dilations[0],
BatchNorm=BatchNorm)
self.aspp2 = _ASPPModule(inplanes,
mid_channels,
3,
padding=dilations[1],
dilation=dilations[1],
BatchNorm=BatchNorm)
self.aspp3 = _ASPPModule(inplanes,
mid_channels,
3,
padding=dilations[2],
dilation=dilations[2],
BatchNorm=BatchNorm)
self.aspp4 = _ASPPModule(inplanes,
mid_channels,
3,
padding=dilations[3],
dilation=dilations[3],
BatchNorm=BatchNorm)
self.global_avg_pool = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)),
nn.Conv2d(inplanes, mid_channels, 1, stride=1, bias=False),
BatchNorm(mid_channels),
nn.ReLU(),
)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(int(mid_channels * 5),
mid_channels,
1,
bias=False)
self.bn1 = BatchNorm(mid_channels)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5)
self._init_weight()
def forward(self, x):
x1 = self.aspp1(x)
x2 = self.aspp2(x)
x3 = self.aspp3(x)
x4 = self.aspp4(x)
x5 = self.global_avg_pool(x)
x5 = F.interpolate(x5,
size=x4.size()[2:],
mode='bilinear',
align_corners=True)
x = torch.cat((x1, x2, x3, x4, x5), dim=1)
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
return self.dropout(x)
def _init_weight(self):
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
torch.nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight)
elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
m.weight.data.fill_(1)
m.bias.data.zero_()
depth = self.depth_pred(depth) #[12, 112, 16, 44] <<--- [12, 512, 16, 44]
self.depth_pred = nn.Conv2d(mid_channels,
depth_channels,
kernel_size=1,
stride=1,
padding=0)
return torch.cat([depth, context], dim=1) #[12, 112 + 80, 16, 44]
这里就是图中圈起来的部分,输出depth和context,
depth [12, 112 , 16, 44]是img_feat和inv_intrinsics和lidar_depth融合的结果,
context[12, 80, 16, 44]是img_feat
4. get_geometry
_forward_depth_net就是上面DepthNet,
def _forward_single_sweep(self,
sweep_index,
sweep_imgs,
mats_dict,
sweep_lidar_depth,
is_return_depth=False):
"""Forward function for single sweep.
Args:
sweep_index (int): Index of sweeps.
sweep_imgs (Tensor): Input images.
mats_dict (dict):
sensor2ego_mats(Tensor): Transformation matrix from
camera to ego with shape of (B, num_sweeps,
num_cameras, 4, 4).
intrin_mats(Tensor): Intrinsic matrix with shape
of (B, num_sweeps, num_cameras, 4, 4).
ida_mats(Tensor): Transformation matrix for ida with
shape of (B, num_sweeps, num_cameras, 4, 4).
sensor2sensor_mats(Tensor): Transformation matrix
from key frame camera to sweep frame camera with
shape of (B, num_sweeps, num_cameras, 4, 4).
bda_mat(Tensor): Rotation matrix for bda with shape
of (B, 4, 4).
sweep_lidar_depth (Tensor): Depth generated by lidar.
is_return_depth (bool, optional): Whether to return depth.
Default: False.
Returns:
Tensor: BEV feature map.
"""
batch_size, num_sweeps, num_cams, num_channels, img_height, \
img_width = sweep_imgs.shape #[b, 1, 6, 3, 256, 704]
img_feats = self.get_cam_feats(sweep_imgs) #img_feats[2, 1, 6, 512, 16, 44] <-- sweep_imgs[2, 1, 6, 3, 256, 704]
sweep_lidar_depth = sweep_lidar_depth.reshape(
batch_size * num_cams, *sweep_lidar_depth.shape[2:]) #[b*6, 1, 16, 44]
source_features = img_feats[:, 0, ...] #[2, 6, 512, 16, 44]
depth_feature = self._forward_depth_net(
source_features.reshape(batch_size * num_cams,
source_features.shape[2],
source_features.shape[3],
source_features.shape[4]), mats_dict,
sweep_lidar_depth) ##[12, 112 + 80, 16, 44] [12, 192, 16, 44]
depth = depth_feature[:, :self.depth_channels].softmax(
dim=1, dtype=depth_feature.dtype) #[12, 112, 16, 44]
geom_xyz = self.get_geometry(
mats_dict['sensor2ego_mats'][:, sweep_index, ...],
mats_dict['intrin_mats'][:, sweep_index, ...],
mats_dict['ida_mats'][:, sweep_index, ...],
mats_dict.get('bda_mat', None),
) #geom_xyz[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 3]
#self.voxel_coord tensor([-50.8000, -50.8000, -1.0000], device='cuda:0')
#self.voxel_size tensor([0.8000, 0.8000, 8.0000], device='cuda:0')
geom_xyz = ((geom_xyz - (self.voxel_coord - self.voxel_size / 2.0)) /
self.voxel_size).int() #[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 3]
if self.training or self.use_da: # [12, 80, 112, 16, 44] #[12, 1, 112, 16, 44] [12, 80, 1, 16, 44]
img_feat_with_depth = depth.unsqueeze(
1) * depth_feature[:, self.depth_channels:(
self.depth_channels + self.output_channels)].unsqueeze(2)
# # [12, 80, 112, 16, 44]
img_feat_with_depth = self._forward_voxel_net(img_feat_with_depth)
#[2,6,80,112,16,44]
img_feat_with_depth = img_feat_with_depth.reshape(
batch_size,
num_cams,
img_feat_with_depth.shape[1],
img_feat_with_depth.shape[2],
img_feat_with_depth.shape[3],
img_feat_with_depth.shape[4],
)
#[2,6,112,16,44,80]
img_feat_with_depth = img_feat_with_depth.permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 5, 2)
#feature_map[b, 80, 128, 128] geom_xyz[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 3] img_feat_with_depth[2,6,112,16,44,80] voxel_num[128, 128,1]
feature_map = voxel_pooling_train(geom_xyz,
img_feat_with_depth.contiguous(),
self.voxel_num.cuda())
else:
feature_map = voxel_pooling_inference(
geom_xyz, depth, depth_feature[:, self.depth_channels:(
self.depth_channels + self.output_channels)].contiguous(),
self.voxel_num.cuda())
if is_return_depth: #False
return feature_map.contiguous(), depth.float()
return feature_map.contiguous()
depth = depth_feature[:, :self.depth_channels].softmax(
dim=1, dtype=depth_feature.dtype) #[12, 112, 16, 44]
注意softmax维度是dim=1; 例如:depth[2,:,3,4].sum(), tensor(1.0000, device='cuda:0', grad_fn=
#depth.shape [12,112,16,44]
#depth.unsqueeze(1).shape [12,1,112,16,44]
#[12, 80, 1, 16, 44]
#depth_feature[:, self.depth_channels:(self.depth_channels+self.output_channels)]
#[12, 80,112,16, 44] = [12, 1,112, 16, 44] x [12, 80, 1, 16, 44]
img_feat_with_depth = depth.unsqueeze(
1) * depth_feature[:, self.depth_channels:(
self.depth_channels + self.output_channels)].unsqueeze(2)
#[2,6,80,112,16,44]
img_feat_with_depth = img_feat_with_depth.reshape(
batch_size,
num_cams,
img_feat_with_depth.shape[1],
img_feat_with_depth.shape[2],
img_feat_with_depth.shape[3],
img_feat_with_depth.shape[4],
)
#[2,6,112,16,44,80]
img_feat_with_depth = img_feat_with_depth.permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 5, 2)
def get_geometry(self, sensor2ego_mat, intrin_mat, ida_mat, bda_mat):
"""Transfer points from camera coord to ego coord.
Args:
rots(Tensor): Rotation matrix from camera to ego.
trans(Tensor): Translation matrix from camera to ego.
intrins(Tensor): Intrinsic matrix.
post_rots_ida(Tensor): Rotation matrix for ida.
post_trans_ida(Tensor): Translation matrix for ida
post_rot_bda(Tensor): Rotation matrix for bda.
Returns:
Tensors: points ego coord.
"""
batch_size, num_cams, _, _ = sensor2ego_mat.shape #[2,6,4,4]
# undo post-transformation
# B x N x D x H x W x 3
points = self.frustum #[112, 16, 44, 4]
ida_mat = ida_mat.view(batch_size, num_cams, 1, 1, 1, 4, 4) #[b, 6, 1,1,1,4, 4] ida_mat[b, 6, 4, 4]
points = ida_mat.inverse().matmul(points.unsqueeze(-1)) #[b, 6, 112, 16, 44, 4, 1] = [b, 6, 1,1,1,4, 4] @ [112, 16, 44, 4, 1]
# cam_to_ego
points = torch.cat(
(points[:, :, :, :, :, :2] * points[:, :, :, :, :, 2:3],
points[:, :, :, :, :, 2:]), 5) #torch.Size([2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 4, 1])
combine = sensor2ego_mat.matmul(torch.inverse(intrin_mat))
points = combine.view(batch_size, num_cams, 1, 1, 1, 4,
4).matmul(points) #[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 4, 1]
if bda_mat is not None:
bda_mat = bda_mat.unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, num_cams, 1, 1).view(
batch_size, num_cams, 1, 1, 1, 4, 4)
points = (bda_mat @ points).squeeze(-1) #[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 4]
else:
points = points.squeeze(-1)
return points[..., :3] #[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 4]
def create_frustum(self):
"""Generate frustum"""
# make grid in image plane
ogfH, ogfW = self.final_dim #256, 704
fH, fW = ogfH // self.downsample_factor, ogfW // self.downsample_factor #[16, 44]
d_coords = torch.arange(*self.d_bound, #self.d_bound [2.0, 58.0, 0.5]
dtype=torch.float).view(-1, 1,
1).expand(-1, fH, fW)
D, _, _ = d_coords.shape #[112, 16, 44] 2, 2.5, 3, 3.5, 4, 4.5,..., 58
x_coords = torch.linspace(0, ogfW - 1, fW, dtype=torch.float).view(
1, 1, fW).expand(D, fH, fW)
y_coords = torch.linspace(0, ogfH - 1, fH,
dtype=torch.float).view(1, fH,
1).expand(D, fH, fW)
paddings = torch.ones_like(d_coords)
# D x H x W x 3 ## x_coords, y_coords, d_coords torch.Size([112, 16, 44])
frustum = torch.stack((x_coords, y_coords, d_coords, paddings), -1) #[112, 16, 44, 4]
return frustum
create_frustum具体参考这个链接
https://blog.csdn.net/yang332233/article/details/147332549?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
create_frustum干的就是和图示左一样:
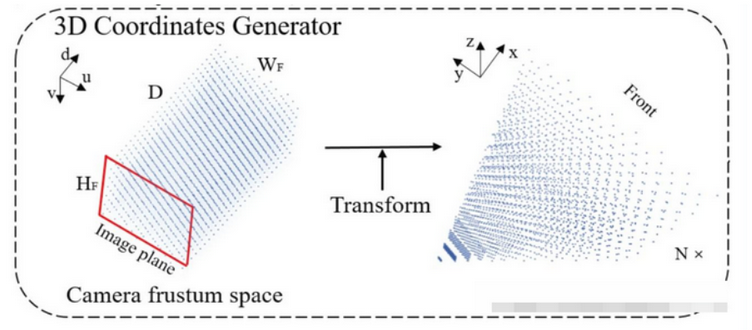
注意这里frustum的shape是[D,H,W,4], 就是[112,16,44,4],D=112,H=16,W=44。
frustum[3][5][9] tensor([147.1395, 85.0000, 3.5000, 1.0000])
frustum[3][5][10] tensor([163.4884, 85.0000, 3.5000, 1.0000])
frustum[3][5][11] tensor([179.8372, 85.0000, 3.5000, 1.0000])
这里可以看到,w维度变化,x的值就是变化,从小到大。
frustum[3:5,0:3,4:8,:3],这里w维度是4:8,对应的值是65,81,98,114这4个值。H维度是0:3,对应的是0,17,34这3个值。
tensor([[[[ 65.3953, 0.0000, 3.5000],
[ 81.7442, 0.0000, 3.5000],
[ 98.0930, 0.0000, 3.5000],
[114.4419, 0.0000, 3.5000]],
[[ 65.3953, 17.0000, 3.5000],
[ 81.7442, 17.0000, 3.5000],
[ 98.0930, 17.0000, 3.5000],
[114.4419, 17.0000, 3.5000]],
[[ 65.3953, 34.0000, 3.5000],
[ 81.7442, 34.0000, 3.5000],
[ 98.0930, 34.0000, 3.5000],
[114.4419, 34.0000, 3.5000]]],
[[[ 65.3953, 0.0000, 4.0000],
[ 81.7442, 0.0000, 4.0000],
[ 98.0930, 0.0000, 4.0000],
[114.4419, 0.0000, 4.0000]],
[[ 65.3953, 17.0000, 4.0000],
[ 81.7442, 17.0000, 4.0000],
[ 98.0930, 17.0000, 4.0000],
[114.4419, 17.0000, 4.0000]],
[[ 65.3953, 34.0000, 4.0000],
[ 81.7442, 34.0000, 4.0000],
[ 98.0930, 34.0000, 4.0000],
[114.4419, 34.0000, 4.0000]]]])
frustum [D,H,W,4], shape是[112,16,44,4], 但是4维度存放的格式是[x,y,z,1]形式。
ida_mat = ida_mat.view(batch_size, num_cams, 1, 1, 1, 4, 4) #[b, 6, 1,1,1,4, 4] ida_mat[b, 6, 4, 4]
points = ida_mat.inverse().matmul(points.unsqueeze(-1)) #[b, 6, 112, 16, 44, 4, 1] = [b, 6, 1,1,1,4, 4] @ [112, 16, 44, 4, 1]
# cam_to_ego
points = torch.cat(
(points[:, :, :, :, :, :2] * points[:, :, :, :, :, 2:3],
points[:, :, :, :, :, 2:]), 5) #torch.Size([2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 4, 1])
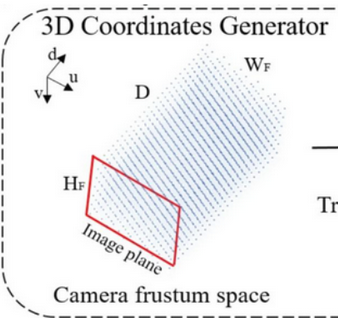
现在图上Image plane就是增强变化之后的图和对应的frustum。需要把它们变化到增强之前的,就需要
ida_mat.inverse().matmul(points.unsqueeze(-1))
# cam_to_ego
points = torch.cat(
(points[:, :, :, :, :, :2] * points[:, :, :, :, :, 2:3],
points[:, :, :, :, :, 2:]), 5) #torch.Size([2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 4, 1])
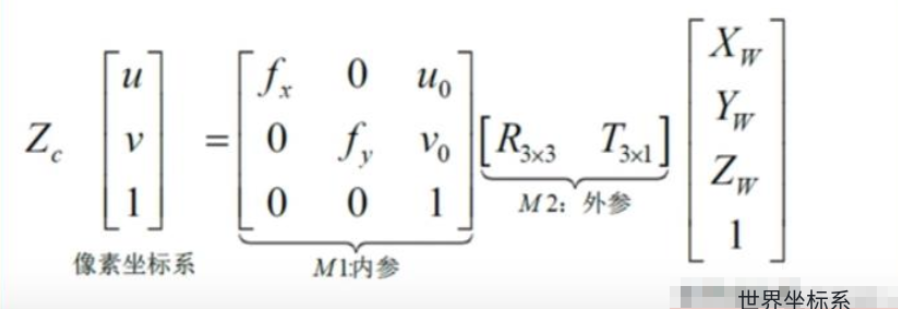
上面cat操作就是式子左边部分。
combine = sensor2ego_mat.matmul(torch.inverse(intrin_mat))
points = combine.view(batch_size, num_cams, 1, 1, 1, 4,
4).matmul(points) #[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 4, 1]
为了转到自车坐标系,需要乘以内参的逆intrin_mat_inv得到相机坐标系,再乘以相机到ego的RT矩阵就转到ego坐标系下了。
BEV增强(整体视角方向变换)
if bda_mat is not None: #bda_mat[2,4,4]
bda_mat = bda_mat.unsqueeze(1).repeat(1, num_cams, 1, 1).view(
batch_size, num_cams, 1, 1, 1, 4, 4)
points = (bda_mat @ points).squeeze(-1) #[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 4]
else:
points = points.squeeze(-1)
return points[..., :3] #[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 4]
对于 BEV 建图,还可能有 BEV 平面上的旋转增强
所以这里要统一做一次 BEV 增强矩阵变换(比如 yaw 方向)
坐标原点转到bev的右下角,体素空间原点在右下角,同时按照x,y0.8米,z8米进行重新划分。
这样就有好多点落在相同的体素格中。
#geom_xyz[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 3]
#self.voxel_coord tensor([-50.8000, -50.8000, -1.0000], device='cuda:0')
#self.voxel_size tensor([0.8000, 0.8000, 8.0000], device='cuda:0')
geom_xyz = ((geom_xyz - (self.voxel_coord - self.voxel_size / 2.0)) /
self.voxel_size).int() #[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 3]
5.voxel_pooling
#[2,6,112,16,44,80]
img_feat_with_depth = img_feat_with_depth.permute(0, 1, 3, 4, 5, 2)
#feature_map[b, 80, 128, 128] geom_xyz[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 3] img_feat_with_depth[2,6,112,16,44,80] voxel_num[128, 128,1]
feature_map = voxel_pooling_train(geom_xyz,
img_feat_with_depth.contiguous(),
self.voxel_num.cuda())
bevdepth/ops/voxel_pooling_train/src/voxel_pooling_train_forward.cpp
// Copyright (c) Megvii Inc. All rights reserved.
#include <ATen/cuda/CUDAContext.h>
#include <cuda.h>
#include <cuda_fp16.h>
#include <cuda_runtime_api.h>
#include <torch/extension.h>
#include <torch/serialize/tensor.h>
#include <vector>
#define CHECK_CUDA(x) \
TORCH_CHECK(x.type().is_cuda(), #x, " must be a CUDAtensor ")
#define CHECK_CONTIGUOUS(x) \
TORCH_CHECK(x.is_contiguous(), #x, " must be contiguous ")
#define CHECK_INPUT(x) \
CHECK_CUDA(x); \
CHECK_CONTIGUOUS(x)
int voxel_pooling_train_forward_wrapper(int batch_size, int num_points,
int num_channels, int num_voxel_x,
int num_voxel_y, int num_voxel_z,
at::Tensor geom_xyz_tensor,
at::Tensor input_features_tensor,
at::Tensor output_features_tensor,
at::Tensor pos_memo_tensor);
void voxel_pooling_train_forward_kernel_launcher(
int batch_size, int num_points, int num_channels, int num_voxel_x,
int num_voxel_y, int num_voxel_z, const int *geom_xyz,
const float *input_features, float *output_features, int *pos_memo,
cudaStream_t stream);
void voxel_pooling_train_forward_kernel_launcher(
int batch_size, int num_points, int num_channels, int num_voxel_x,
int num_voxel_y, int num_voxel_z, const int *geom_xyz,
const half *input_features, half *output_features, int *pos_memo,
cudaStream_t stream);
int voxel_pooling_train_forward_wrapper(int batch_size, int num_points,
int num_channels, int num_voxel_x,
int num_voxel_y, int num_voxel_z,
at::Tensor geom_xyz_tensor,
at::Tensor input_features_tensor,
at::Tensor output_features_tensor,
at::Tensor pos_memo_tensor) {
CHECK_INPUT(geom_xyz_tensor);
CHECK_INPUT(input_features_tensor);
const int *geom_xyz = geom_xyz_tensor.data_ptr<int>();
int *pos_memo = pos_memo_tensor.data_ptr<int>();
cudaStream_t stream = at::cuda::getCurrentCUDAStream().stream();
if (input_features_tensor.dtype() == at::kFloat) {
const float *input_features = input_features_tensor.data_ptr<float>();
float *output_features = output_features_tensor.data_ptr<float>();
voxel_pooling_train_forward_kernel_launcher(
batch_size, num_points, num_channels, num_voxel_x, num_voxel_y,
num_voxel_z, geom_xyz, input_features, output_features, pos_memo,
stream);
}
else if (input_features_tensor.dtype() == at::kHalf) {
assert(num_channels % 2 == 0);
const half *input_features =
(half *)(input_features_tensor.data_ptr<at::Half>());
half *output_features =
(half *)(output_features_tensor.data_ptr<at::Half>());
voxel_pooling_train_forward_kernel_launcher(
batch_size, num_points, num_channels, num_voxel_x, num_voxel_y,
num_voxel_z, geom_xyz, input_features, output_features, pos_memo,
stream);
}
return 1;
}
PYBIND11_MODULE(TORCH_EXTENSION_NAME, m) {
m.def("voxel_pooling_train_forward_wrapper",
&voxel_pooling_train_forward_wrapper,
"voxel_pooling_train_forward_wrapper");
}
bevdepth/ops/voxel_pooling_train/src/voxel_pooling_train_forward_cuda.cu
// Copyright (c) Megvii Inc. All rights reserved.
#include <cuda_fp16.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define THREADS_BLOCK_X 32
#define THREADS_BLOCK_Y 4
#define THREADS_PER_BLOCK THREADS_BLOCK_X *THREADS_BLOCK_Y
#define DIVUP(m, n) ((m) / (n) + ((m) % (n) > 0))
template <typename T>
__global__ void voxel_pooling_train_forward_kernel(
int batch_size, int num_points, int num_channels, int num_voxel_x,
int num_voxel_y, int num_voxel_z, const int *geom_xyz,
const T *input_features, T *output_features, int *pos_memo) {
const int bidx = blockIdx.x;
const int tidx = threadIdx.x;
const int tidy = threadIdx.y;
const int sample_dim = THREADS_PER_BLOCK;
const int idx_in_block = tidy * THREADS_BLOCK_X + tidx;
const int block_sample_idx = bidx * sample_dim;
const int thread_sample_idx = block_sample_idx + idx_in_block;
const int total_samples = batch_size * num_points;
__shared__ int geom_xyz_shared[THREADS_PER_BLOCK * 3];
if (thread_sample_idx < total_samples) {
const int sample_x = geom_xyz[thread_sample_idx * 3 + 0];
const int sample_y = geom_xyz[thread_sample_idx * 3 + 1];
const int sample_z = geom_xyz[thread_sample_idx * 3 + 2];
geom_xyz_shared[idx_in_block * 3 + 0] = sample_x;
geom_xyz_shared[idx_in_block * 3 + 1] = sample_y;
geom_xyz_shared[idx_in_block * 3 + 2] = sample_z;
if ((sample_x >= 0 && sample_x < num_voxel_x) &&
(sample_y >= 0 && sample_y < num_voxel_y) &&
(sample_z >= 0 && sample_z < num_voxel_z)) {
pos_memo[thread_sample_idx * 3 + 0] = thread_sample_idx / num_points;
pos_memo[thread_sample_idx * 3 + 1] = sample_y;
pos_memo[thread_sample_idx * 3 + 2] = sample_x;
}
}
__syncthreads();
for (int i = tidy;
i < THREADS_PER_BLOCK && block_sample_idx + i < total_samples;
i += THREADS_BLOCK_Y) {
const int sample_x = geom_xyz_shared[i * 3 + 0];
const int sample_y = geom_xyz_shared[i * 3 + 1];
const int sample_z = geom_xyz_shared[i * 3 + 2];
if (sample_x < 0 || sample_x >= num_voxel_x || sample_y < 0 ||
sample_y >= num_voxel_y || sample_z < 0 || sample_z >= num_voxel_z) {
continue;
}
const int batch_idx = (block_sample_idx + i) / num_points;
for (int j = tidx; j < num_channels; j += THREADS_BLOCK_X) {
atomicAdd(&output_features[(batch_idx * num_voxel_y * num_voxel_x +
sample_y * num_voxel_x + sample_x) *
num_channels +
j],
input_features[(block_sample_idx + i) * num_channels + j]);
}
}
}
void voxel_pooling_train_forward_kernel_launcher(
int batch_size, int num_points, int num_channels, int num_voxel_x,
int num_voxel_y, int num_voxel_z, const int *geom_xyz,
const float *input_features, float *output_features, int *pos_memo,
cudaStream_t stream) {
cudaError_t err;
dim3 blocks(DIVUP(batch_size * num_points, THREADS_PER_BLOCK));
dim3 threads(THREADS_BLOCK_X, THREADS_BLOCK_Y);
voxel_pooling_train_forward_kernel<<<blocks, threads, 0, stream>>>(
batch_size, num_points, num_channels, num_voxel_x, num_voxel_y,
num_voxel_z, geom_xyz, input_features, output_features, pos_memo);
err = cudaGetLastError();
if (cudaSuccess != err) {
fprintf(stderr, "CUDA kernel failed : %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(err));
exit(-1);
}
}
void voxel_pooling_train_forward_kernel_launcher(
int batch_size, int num_points, int num_channels, int num_voxel_x,
int num_voxel_y, int num_voxel_z, const int *geom_xyz,
const half *input_features, half *output_features, int *pos_memo,
cudaStream_t stream) {
cudaError_t err;
dim3 blocks(DIVUP(batch_size * num_points, THREADS_PER_BLOCK));
dim3 threads(THREADS_BLOCK_X, THREADS_BLOCK_Y);
voxel_pooling_train_forward_kernel<<<blocks, threads, 0, stream>>>(
batch_size, num_points, num_channels, num_voxel_x, num_voxel_y,
num_voxel_z, geom_xyz, input_features, output_features, pos_memo);
err = cudaGetLastError();
if (cudaSuccess != err) {
fprintf(stderr, "CUDA kernel failed : %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(err));
exit(-1);
}
}
单看这行代码:
#feature_map[b, 80, 128, 128] geom_xyz[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 3] img_feat_with_depth[2,6,112,16,44,80] voxel_num值[128, 128,1]
feature_map = voxel_pooling_train(geom_xyz,
img_feat_with_depth.contiguous(),
self.voxel_num.cuda())
| 变量 | Shape | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
geom_xyz |
[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 3] |
每个像素在 voxel 中的整数坐标 (x, y, z) |
img_feat_with_depth |
[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 80] |
每个像素的特征向量(C=80) |
voxel_num |
[3] |
[128, 128, 1]voxel grid 尺寸(W=128, H=128, Z=1) |
目标输出也就是按 BEV 格式展开为 2D 特征图。:feature_map.shape = [2, 80, 128, 128] # [B, C, H, W]
在后续代码中,
geom_xyz = geom_xyz.reshape(B, -1, 3)
即把所有相机图像上的像素点展开成一个大点云序列,每个点在 voxel 中的整数坐标。
input_features = input_features.reshape(B, -1, C)
和 geom_xyz 是一一对应的。也就是说,每个点有一个 (x, y, z) voxel 坐标,对应一个 80 维特征。
这里就是说geom_xyz和img_feat_with_depth的shape一样,img_feat_with_depth是每个像素的特征80维度,geom_xyz里面存放的值是其对应每个像素在voxel空间的整数坐标,每格0.8米。
这里为什么一一对应,因为geom_xyz生成的时候本身就是根据图像对应的像素点转到ego的
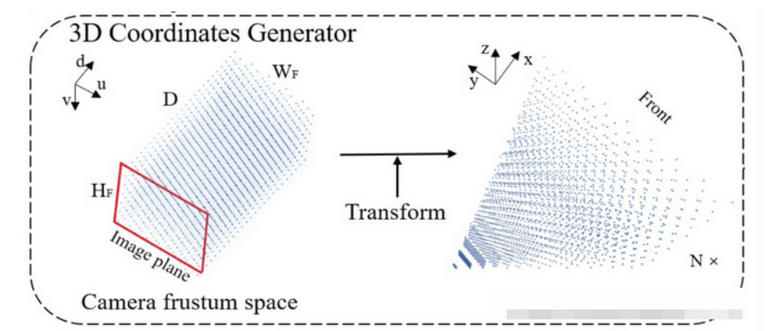
然后调用了 CUDA kernel,执行如下聚合逻辑:
将
(x, y, z)有效范围内的点的input_features(C=80维),累加到output_features[b, y, x, c]上。
feature_map[b, 80, 128, 128], 输出的128并不是128米,是voxel_size的大小×128,一格代表0.8米,128x0.8,self.voxel_size tensor([0.8000, 0.8000, 8.0000], device='cuda:0')
geom_xyz = ((geom_xyz - (self.voxel_coord - self.voxel_size / 2.0)) /self.voxel_size).int() #[2, 6, 112, 16, 44, 3]



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号