实验7
实验任务1:
1 // 文件读写操作:格式化读、写文本文件 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 4 #define N 80 5 #define M 100 6 7 typedef struct { 8 char name[N]; // 书名 9 char author[N]; // 作者 10 } Book; 11 12 void write(); 13 void read(); 14 15 int main() { 16 printf("测试1: 把图书信息写入文本文件\n"); 17 write(); 18 19 printf("\n测试2: 从文本文件读取图书信息, 打印输出到屏幕\n"); 20 read(); 21 22 return 0; 23 } 24 25 void write() { 26 Book x[] = { {"《雕塑家》", "斯科特.麦克劳德"}, 27 {"《灯塔》", "克里斯多夫.夏布特"}, 28 {"《人的局限性》", "塞缪尔.约翰生"}, 29 {"《永不停步:玛格丽特.阿特伍德传》", "罗斯玛丽.沙利文"}, 30 {"《大地之上》", "罗欣顿·米斯特里"}, 31 {"《上学记》", "何兆武"}, 32 {"《命运》", "蔡崇达"} }; 33 int n, i; 34 FILE *fp; 35 36 // 计算数组x中元素个数 37 n = sizeof(x) / sizeof(x[0]); 38 39 // 以写的方式打开文本文件data1.txt 40 fp = fopen("data1.txt", "w"); 41 42 // 如果打开文件失败,输出提示信息并返回 43 if(fp == NULL) { 44 printf("fail to open file to write\n"); 45 return; 46 } 47 48 // 将结构体数组x中的图书信息格式化写到fp指向的文件data1.txt 49 for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) 50 fprintf(fp, "%-40s %-20s\n", x[i].name, x[i].author); 51 52 fclose(fp); 53 } 54 55 void read() { 56 Book x[M]; 57 int i, n; 58 59 FILE *fp; 60 61 // 以读的方式打开文本文件data1.txt 62 fp = fopen("data1.txt", "r"); 63 64 // 如果打开文件失败,输出提示信息并返回 65 if(fp == NULL) { 66 printf("fail to open file to read\n"); 67 return; 68 } 69 70 // 从文件中读取图书信息,保存到结构体数组x中 71 i = 0; 72 while(fscanf(fp, "%s%s", x[i].name, x[i].author) != EOF) 73 ++i; 74 75 // 将图书信息打印输出到屏幕上 76 n = i; 77 for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) 78 printf("%d. %-40s%-20s\n", i+1, x[i].name, x[i].author); 79 80 fclose(fp); 81 }
运行结果截图:

实验任务2:
1 // 文件读写操作:以数据块方式读、写二进制文件 2 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 5 #define N 80 6 #define M 100 7 8 typedef struct { 9 char name[N]; // 书名 10 char author[N]; // 作者 11 } Book; 12 13 void write(); 14 void read(); 15 16 int main() { 17 printf("测试1: 把图书信息以数据块方式写入二进制文件\n"); 18 write(); 19 20 printf("\n测试2: 从二进制文件读取图书信息, 打印输出到屏幕\n"); 21 read(); 22 23 return 0; 24 } 25 26 void write() { 27 Book x[] = { {"《雕塑家》", "斯科特.麦克劳德"}, 28 {"《灯塔》", "克里斯多夫.夏布特"}, 29 {"《人的局限性》", "塞缪尔.约翰生"}, 30 {"《永不停步:玛格丽特.阿特伍德传》", "罗斯玛丽.沙利文"}, 31 {"《大地之上》", "罗欣顿·米斯特里"}, 32 {"《上学记》", "何兆武"}, 33 {"《命运》", "蔡崇达"} }; 34 int n, i; 35 FILE *fp; 36 37 // 计算数组x中元素个数 38 n = sizeof(x) / sizeof(x[0]); 39 40 // 以写的方式打开二进制文件data2.dat 41 fp = fopen("data2.dat", "wb"); 42 43 // 如果打开文件失败,输出提示信息并返回 44 if(fp == NULL) { 45 printf("fail to open file to write\n"); 46 return; 47 } 48 49 // 将结构体数组x中的图书信息以数据块方式写入二进制文件data2.dat 50 fwrite(x, sizeof(Book), n, fp); 51 52 fclose(fp); 53 } 54 55 void read() { 56 Book x[M]; 57 int i, n; 58 59 FILE *fp; 60 61 // 以读的方式打开二进制文件data2.dat 62 fp = fopen("data2.dat", "rb"); 63 64 // 如果打开文件失败,输出提示信息并返回 65 if(fp == NULL) { 66 printf("fail to open file to read\n"); 67 return; 68 } 69 70 // 从二进制文件data2.dat以数据块方式读取图书信息存储到结构体数组x 71 i = 0; 72 while(fread(&x[i], sizeof(Book), 1, fp) == 1) 73 ++i; 74 75 // 在屏幕上打印输出 76 n = i; 77 for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) 78 printf("%d. %-40s%-20s\n", i+1, x[i].name, x[i].author); 79 80 fclose(fp); 81 }
运行结果截图:

实验任务3:
1 // 文件读写操作:以字符、字符串形式读、写 2 3 #include <stdio.h> 4 #define N 100 5 #define M 80 6 7 void write(); 8 void read_str(); 9 void read_char(); 10 11 int main() { 12 printf("测试1: 把一组字符信息以字符串方式写入文本文件\n"); 13 write(); 14 15 printf("\n测试2: 从文件以字符串方式读取, 输出到屏幕\n"); 16 read_str(); 17 18 printf("\n测试3: 从文件以单个字符方式读取, 输出到屏幕\n"); 19 read_char(); 20 21 return 0; 22 } 23 24 void write() { 25 char *ptr[] = { "Working\'s Blues", 26 "Everything Will Flow", 27 "Streets of London", 28 "Perfect Day", 29 "Philadelphia"}; 30 int i, n; 31 FILE *fp; 32 33 fp = fopen("data3.txt", "w"); 34 if(fp == NULL) { 35 printf("fail to open file to write\n"); 36 return; 37 } 38 39 n = sizeof(ptr)/sizeof(ptr[0]); 40 41 for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) { 42 fputs(ptr[i], fp); 43 fputs("\n", fp); 44 } 45 46 fclose(fp); 47 } 48 49 void read_str() { 50 char songs[N][M]; 51 int i, n; 52 FILE *fp; 53 54 fp = fopen("data3.txt", "r"); 55 if(fp == NULL) { 56 printf("fail to open file to read\n"); 57 return; 58 } 59 60 i = 0; 61 while(i < N && (fgets(songs[i], M, fp) != NULL)) 62 ++i; 63 64 n = i; 65 for(i = 0; i < n; ++i) 66 printf("%d. %s", i+1, songs[i]); 67 68 fclose(fp); 69 } 70 71 void read_char() { 72 int ch; 73 FILE *fp; 74 75 fp = fopen("data3.txt", "r"); 76 if(fp == NULL) { 77 printf("fail to open file to read\n"); 78 return; 79 } 80 81 while((ch = fgetc(fp)) != EOF) 82 putchar(ch); 83 84 fclose(fp); 85 }
运行结果截图:

实验任务4:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 3 int main() { 4 FILE *fp; 5 char ch; 6 int line = 1; 7 int count = 0; 8 9 fp = fopen("data4.txt", "r"); 10 if (fp == NULL) { 11 perror("data4.txt"); 12 return 1; 13 } 14 15 while ((ch = fgetc(fp)) != EOF) { 16 if (ch == '\n') { 17 line++; 18 } 19 else 20 count++; 21 22 } 23 24 printf("data4.txt统计结果:\n"); 25 printf("行数:%d\n", line); 26 printf("字符数(不计空白字符):%d\n", count); 27 28 fclose(fp);
运行结果截图:

实验任务5:
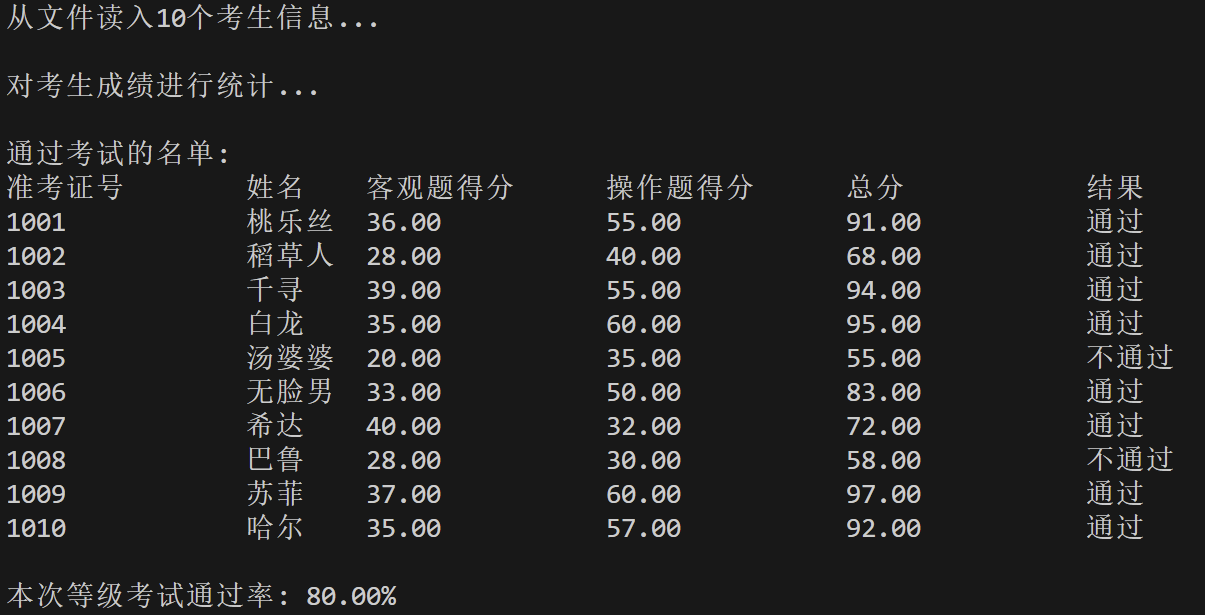
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <string.h> 3 4 #define N 10 5 6 typedef struct { 7 long id; // 准考证号 8 char name[20]; // 姓名 9 float objective; // 客观题得分 10 float subjective; // 操作题得分 11 float sum; // 总分 12 char result[10]; // 考试结果 13 } STU; 14 15 // 函数声明 16 void read(STU st[], int n); 17 void write(STU st[], int n); 18 void output(STU st[], int n); 19 int process(STU st[], int n, STU st_pass[]); 20 21 int main() { 22 STU stu[N], stu_pass[N]; 23 int cnt; 24 double pass_rate; 25 26 printf("从文件读入%d个考生信息...\n", N); 27 read(stu, N); 28 29 printf("\n对考生成绩进行统计...\n"); 30 cnt = process(stu, N, stu_pass); 31 32 printf("\n通过考试的名单:\n"); 33 output(stu, N); // 输出所有考生完整信息到屏幕 34 write(stu, N); // 输出考试通过的考生信息到文件 35 36 pass_rate = 1.0 * cnt / N; 37 printf("\n本次等级考试通过率: %.2f%%\n", pass_rate*100); 38 39 return 0; 40 } 41 42 // 把所有考生完整信息输出到屏幕上 43 // 准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分,总分,结果 44 void output(STU st[], int n) { 45 int i; 46 47 printf("准考证号\t姓名\t客观题得分\t操作题得分\t总分\t\t结果\n"); 48 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) 49 printf("%ld\t\t%s\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%s\n", st[i].id, st[i].name, st[i].objective, st[i].subjective, st[i].sum, st[i].result); 50 } 51 52 // 从文本文件examinee.txt读入考生信息:准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分 53 void read(STU st[], int n) { 54 int i; 55 FILE *fin; 56 57 fin = fopen("examinee.txt", "r"); 58 if (!fin) { 59 printf("fail to open file\n"); 60 return; 61 } 62 63 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) 64 fscanf(fin, "%ld %s %f %f", &st[i].id, st[i].name, &st[i].objective, &st[i].subjective); 65 66 fclose(fin); 67 } 68 69 // 把通过考试的考生完整信息写入文件list_pass.txt 70 // 准考证号,姓名,客观题得分,操作题得分,总分,结果 71 void write(STU s[], int n) { 72 int i; 73 FILE *fp; 74 75 fp = fopen("list_pass.txt", "w"); 76 if (!fp) { 77 perror("list_pass.txt"); 78 } 79 80 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { 81 fprintf(fp, "%ld\t%s\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t\t%.2f\t%s\n", 82 s[i].id, s[i].name, s[i].objective, 83 s[i].subjective, s[i].sum, s[i].result); 84 } 85 fclose(fp); 86 } 87 88 // 对考生信息进行处理:计算每位考生考试总分、结果;统计考试通过的人数 89 int process(STU st[], int n, STU st_pass[]) { 90 int i, cnt = 0; 91 double pass = 60.0; 92 93 for (i = 0; i < n; i++) { 94 st[i].sum = st[i].objective + st[i].subjective; 95 if (st[i].sum >= pass) { 96 strcpy(st[i].result, "通过"); 97 st_pass[cnt++] = st[i]; 98 } else { 99 strcpy(st[i].result, "不通过"); 100 } 101 } 102 103 return cnt; 104 }
运行结果截图:
实验任务6:
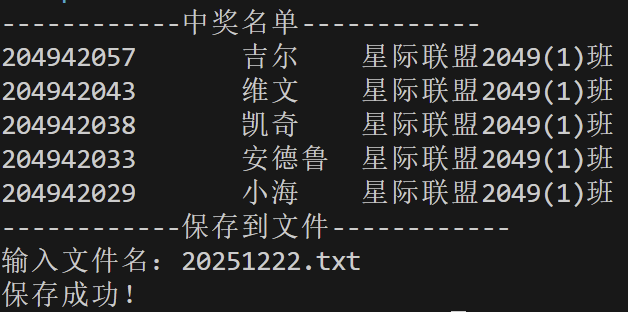
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #define N 100 3 #define M 5 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 #include <time.h> 6 #include <string.h> 7 8 int main(){ 9 10 char s[N][N]; 11 int i=0,n,lucky_i; 12 int has_hit[N] = {0}; 13 char hit[N][N]; 14 char filename[80]; 15 16 FILE *fp,*fout; 17 18 fp = fopen("list.txt","r"); 19 20 if (!fp){ 21 perror("list.txt"); 22 return 1; 23 } 24 while(fgets(s[i],N,fp)!=NULL) 25 i++; 26 n=i; 27 srand(time(0)); 28 printf("------------中奖名单------------\n"); 29 for(i=0;i<M;){ 30 lucky_i=rand()%n; 31 32 if (has_hit[lucky_i]) 33 continue; 34 35 has_hit[lucky_i]=1; 36 strcpy(hit[i],s[lucky_i]); 37 printf("%s", hit[i]); 38 ++i; 39 } 40 printf("------------保存到文件------------\n"); 41 printf("输入文件名:"); 42 scanf("%s", filename); 43 44 fout = fopen(filename,"w"); 45 for (i = 0; i < M; i++) { 46 fprintf(fout, "%s", hit[i]); 47 } 48 fclose(fout); 49 50 printf("保存成功!"); 51 return 0; 52 }
运行结果截图:




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号