python-内置函数
python的内置函数包含了68个。它们就是python提供给你直接可以拿来使用的所有函数。
可以将这些内置的函数分为:
- 作用域相关的(2)
- 基础数据类型相关(38)
- 反射相关的(4)
- 面向对象的相关的(9)
- 迭代器/生成器相关的(3)
- 其他(12)
作用域相关的
locals :函数会以字典的类型返回当前位置的全部局部变量。
globals:函数以字典的类型返回全部全局变量
a = 12
b = 20
print(globals()) # 两者打印的都一样 都是全局变量
print(locals())
'''
{'__name__': '__main__', '__doc__': None, '__package__': None, '__loader__': <_frozen_importlib_external.SourceFileLoader object at 0x0000028B3D907940>, '__spec__': None, '__annotations__': {}, '__builtins__': <module 'builtins' (built-in)>, '__file__': 'F:/oldboy_code/day_12/内置函数.py', '__cached__': None, 'a': 12, 'b': 20}
{'__name__': '__main__', '__doc__': None, '__package__': None, '__loader__': <_frozen_importlib_external.SourceFileLoader object at 0x0000028B3D907940>, '__spec__': None, '__annotations__': {}, '__builtins__': <module 'builtins' (built-in)>, '__file__': 'F:/oldboy_code/day_12/内置函数.py', '__cached__': None, 'a': 12, 'b': 20}
'''
def func():
a = 10
b = 20
print(globals()) # {'__name__': '__main__', '__doc__': None, '__package__': None, '__loader__': <_frozen_importlib_external.SourceFileLoader object at 0x000001DCB44C7940>, '__spec__': None, '__annotations__': {}, '__builtins__': <module 'builtins' (built-in)>, '__file__': 'F:/oldboy_code/day_12/内置函数.py', '__cached__': None, 'func': <function func at 0x000001DCB4593AE8>}
print(locals()) # {'b': 20, 'a': 10}
func()
其他相关的
字符串类型代码的执行eval,exec,complie。
eval
执行字符串类型的代码,并返回结果。
a = "1+2*3"
print(eval(a)) # 7
a = "a"
b = "b"
c = "c"
# 有返回值 eval
res = eval('a + b +c')
print(res) # abc
s = 'for i in range(10):print(i,end=" ")'
# 没有返回值 exec
ret = exec(s) # 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
print(ret) # None
# compile:将字符串类型的代码编译。代码对象能够通过exec语句来执行或者eval()进行求值。
# compile
'''
参数说明:
compile(source,filename,mode)
1. 参数source:字符串或者AST(Abstract Syntax Trees)对象。即需要动态执行的代码段。
2. 参数 filename:代码文件名称,如果不是从文件读取代码则传递一些可辨认的值。当传入了source参数时,filename参数传入空字符即可。
3. 参数model:指定编译代码的种类,可以指定为 ‘exec’,’eval’,’single’。当source中包含流程语句时,model应指定为‘exec’;
当source中只包含一个简单的求值表达式,model应指定为‘eval’;当source中包含了交互式命令语句,model应指定为'single'。
'''
input_name = 'name = input("name:")'
s = 'for i in range(10):print(i,end=" ")'
code1 = compile(s, '', 'exec')
exec(code1) # 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
exec(input_name)
print(name)
'''
name:Yang
Yang
'''
输入输出相关 input,print
input:函数接受一个标准输入数据,返回为 string 类型。
print:打印输出。
print(111,222,333,sep='*') # 111*222*333
print(111,end='')
print(222) #两行的结果 111222
f = open('log','w',encoding='utf-8')
print('写入文件',file=f,flush=True)
内存相关 hash id
hash
hash:获取一个对象(可哈希对象:int,str,Bool,tuple)的哈希值。
print(hash(123))
print(hash("a"))
print(hash(78.1))
print(hash(bool))
print(hash(tuple))
'''
123
-2110688139077058015
230584300921356366
123273748
123277059
'''
查看变量的内存地址id###
>>> a = 10
>>> id(a)
1955032832
>>> id("str")
1326756325280
>>> id({"a":"b"})
1326757792792
>>> id((a,))
1326757861472
>>> id([1,2])
1326760439624
文件操作相关open####
open:函数用于打开一个文件,创建一个 file 对象,相关的方法才可以调用它进行读写。
with open("a.txt", "w", encoding="utf-8") as file:
file.write("测试")
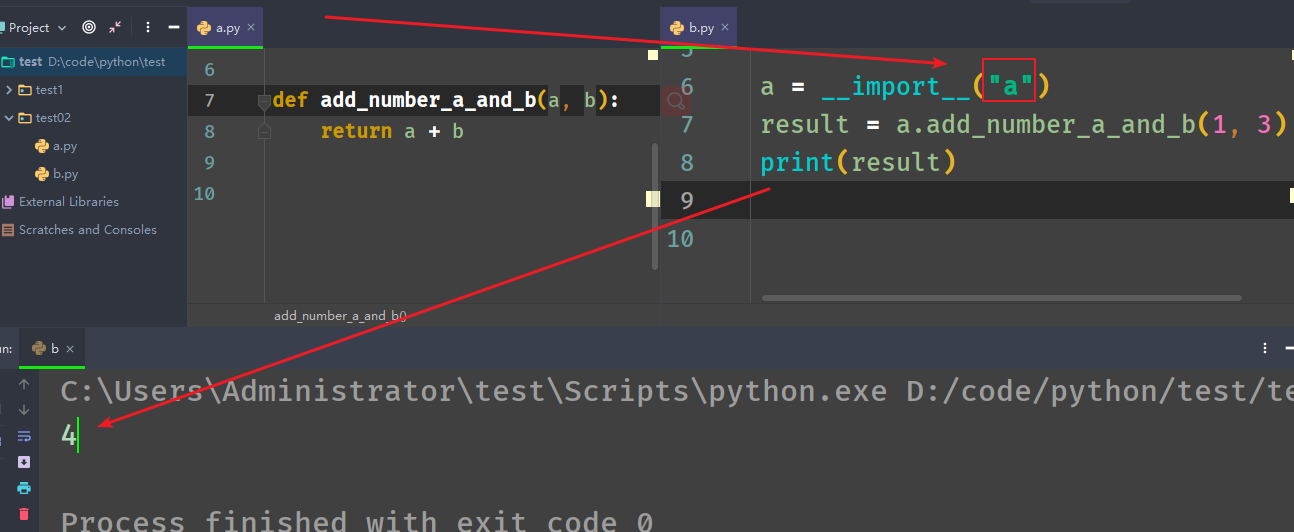
模块相关__import__###
__import__:函数用于动态加载类和函数 。
In [6]: import os
In [7]: os1 = __import__("os")
In [8]: os1
Out[8]: <module 'os' from 'G:\\sofeware\\Anaconda3\\lib\\os.py'>
In [9]: os
Out[9]: <module 'os' from 'G:\\sofeware\\Anaconda3\\lib\\os.py'>
In [10]: os.path
Out[10]: <module 'ntpath' from 'G:\\sofeware\\Anaconda3\\lib\\ntpath.py'>
In [11]: os1.path
Out[11]: <module 'ntpath' from 'G:\\sofeware\\Anaconda3\\lib\\ntpath.py'>
In [12]: os1.path.abspath(".")
Out[12]: 'C:\\Users\\Administrator'
帮助help
help:函数用于查看函数或模块用途的详细说明
>>> help(list) # 查看list的方法
Help on class list in module builtins:
class list(object)
| list() -> new empty list
| list(iterable) -> new list initialized from iterable's items
|
| Methods defined here:
|
| __add__(self, value, /)
| Return self+value.
|
| __contains__(self, key, /)
| Return key in self.
|
| __delitem__(self, key, /)
| Delete self[key].
|
| __eq__(self, value, /)
| Return self==value.
|
| __ge__(self, value, /)
| Return self>=value.
|
| __getattribute__(self, name, /)
| Return getattr(self, name).
|
| __getitem__(...)
| x.__getitem__(y) <==> x[y]
|
| __gt__(self, value, /)
| Return self>value.
|
| __iadd__(self, value, /)
-- More --
调用相关callable###
def func():
print("测试")
a = 10
print(callable(a)) # False
print(callable(func)) # True
print(callable(bool)) # True
print(callable(callable)) # True
class A:
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
def show(self):
print(f"{self.name}")
a = A("Yang")
print(callable(A)) # True
print(callable(A.show)) # True
print(callable(a)) # False
查看内置属性dir
dir:函数不带参数时,返回当前范围内的变量、方法和定义的类型列表;带参数时,返回参数的属性、方法列表。如果参数包含方法__dir__(),该方法将被调用。如果参数不包含__dir__(),该方法将最大限度地收集参数信息。
>>> dir(list) # 查看列表的方法
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__delitem__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__iadd__', '__imul__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__reversed__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__setitem__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'append', 'clear', 'copy', 'count', 'extend', 'index', 'insert', 'pop', 'remove', 'reverse', 'sort']
>>> dir(str) # 查看字符串的方法
['__add__', '__class__', '__contains__', '__delattr__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__getnewargs__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__len__', '__lt__', '__mod__', '__mul__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__rmod__', '__rmul__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', 'capitalize', 'casefold', 'center', 'count', 'encode', 'endswith', 'expandtabs', 'find', 'format', 'format_map', 'index', 'isalnum', 'isalpha', 'isdecimal', 'isdigit', 'isidentifier', 'islower', 'isnumeric', 'isprintable', 'isspace', 'istitle', 'isupper', 'join', 'ljust', 'lower', 'lstrip', 'maketrans', 'partition', 'replace', 'rfind', 'rindex', 'rjust', 'rpartition', 'rsplit', 'rstrip', 'split', 'splitlines', 'startswith', 'strip', 'swapcase', 'title', 'translate', 'upper', 'zfill']
迭代器和生成器相关的
range:函数可创建一个整数对象,一般用在 for 循环中。
__next__:内部实际使用了__next__方法,返回迭代器的下一个项目。
for i in range(10):
print(i, end=' ') # 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
lis = iter([1, 2, 3, 4])
print(lis) # <list_iterator object at 0x000001FB2DCE9B38>
for i in lis:
print(i, end=" ") # 1 2 3 4
while 1:
try:
print(lis.__next__(), end=" ") # 1 2 3 4
except StopIteration as e:
break
基础数据类型相关
数字类型
数据类型
bool :用于将给定参数转换为布尔类型,如果没有参数,返回 False。
int:函数用于将一个字符串或数字转换为整型
float:函数用于将整数和字符串转换成浮点数。
complex:函数用于创建一个值为 real + imag * j 的复数或者转化一个字符串或数为复数。如果第一个参数为字符串,则不需要指定第二个参数。
>>> int("12")
12
>>> int(3.6)
3
>>> int("0100",base=2)
4
ple
0
>>> float(3.6)
3.6
>>> float(3.004)
3.004
>>> complex(1,2)
(1+2j)
>>> complex(1)
(1+0j)
进制转换
bin:将十进制转换成二进制并返回。
oct:将十进制转化成八进制字符串并返回。
hex:将十进制转化成十六进制字符串并返回。
>>> bin(10)
'0b1010'
>>> oct(10)
'0o12'
>>> hex(10)
'0xa'
数学运算
abs:函数返回数字的绝对值。
divmod:计算除数与被除数的结果,返回一个包含商和余数的元组(a // b, a % b)。
round:保留浮点数的小数位数,默认保留整数。
pow:求x**y次幂。(三个参数为x**y的结果对z取余)
>>> abs(0)
0
>>> abs(-10)
10
>>> abs(10)
10
>>> divmod(10,3)
(3, 1)
>>> divmod(7,2)
(3, 1)
>>> round(1.002, 2)
1.0
>>> round(45.12345, 4)
45.1234
>>> pow(2,3,2) # 3个数,则就是 (2 ** 3) % 2
0
>>> pow(2,3,3)
2
>>> pow(17,3,1)
0
>>> pow(2,3) # 2个参数 则是2 ** 3
8
>>> pow(2,4)
16
sum:对可迭代对象进行求和计算(可设置初始值)。
min:返回可迭代对象的最小值(可加key,key为函数名,通过函数的规则,返回最小值)。
max:返回可迭代对象的最大值(可加key,key为函数名,通过函数的规则,返回最大值)
>>> sum(1,2,3)
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: sum expected at most 2 arguments, got 3
>>> sum([1,2,3])
6
>>> sum((1,2,3))
6
>>> min(1,2,3)
1
>>> min([1,2,3])
1
>>> max([1,2,3])
3
>>> max(1,2,3)
3
和数据结构相关的
列表和元组
list:将一个可迭代对象转化成列表(如果是字典,默认将key作为列表的元素)。
tuple:将一个可迭代对象转化成元祖(如果是字典,默认将key作为元祖的元素)。
>>> list([1,2,3,4])
[1, 2, 3, 4]
>>> list({'k1':1,'k2':2})
['k1', 'k2']
>>> tuple((1,2,3))
(1, 2, 3)
>>> tuple({'k1':1,'k2':2})
('k1', 'k2')
相关内置函数
reversed:将一个序列翻转,并返回此翻转序列的迭代器。
slice:构造一个切片对象,用于列表的切片。
>>> list(reversed(['a',2,3,'c',4,2]))
[2, 4, 'c', 3, 2, 'a']
>>> list(reversed(range(10)))
[9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]
>>> li = ['a','b','c','d','e','f','g']
>>> slice(3)
slice(None, 3, None)
>>> slice(0, 7, 3)
slice(0, 7, 3)
>>> li[slice(0,7,3)]
['a', 'd', 'g']
字符串相关
str:将数据转化成字符串。
format:与具体数据相关,用于计算各种小数,精算等。
数据集合
#字符串可以提供的参数,指定对齐方式,<是左对齐, >是右对齐,^是居中对齐
print(format('test', '<20'))
print(format('test', '>20'))
print(format('test', '^20'))
#整形数值可以提供的参数有 'b' 'c' 'd' 'o' 'x' 'X' 'n' None
>>> format(3,'b') #转换成二进制
'11'
>>> format(97,'c') #转换unicode成字符
'a'
>>> format(11,'d') #转换成10进制
'11'
>>> format(11,'o') #转换成8进制
'13'
>>> format(11,'x') #转换成16进制 小写字母表示
'b'
>>> format(11,'X') #转换成16进制 大写字母表示
'B'
>>> format(11,'n') #和d一样
'11'
>>> format(11) #默认和d一样
'11'
#浮点数可以提供的参数有 'e' 'E' 'f' 'F' 'g' 'G' 'n' '%' None
>>> format(314159267,'e') #科学计数法,默认保留6位小数
'3.141593e+08'
>>> format(314159267,'0.2e') #科学计数法,指定保留2位小数
'3.14e+08'
>>> format(314159267,'0.2E') #科学计数法,指定保留2位小数,采用大写E表示
'3.14E+08'
>>> format(314159267,'f') #小数点计数法,默认保留6位小数
'314159267.000000'
>>> format(3.14159267000,'f') #小数点计数法,默认保留6位小数
'3.141593'
>>> format(3.14159267000,'0.8f') #小数点计数法,指定保留8位小数
'3.14159267'
>>> format(3.14159267000,'0.10f') #小数点计数法,指定保留10位小数
'3.1415926700'
>>> format(3.14e+1000000,'F') #小数点计数法,无穷大转换成大小字母
'INF'
#g的格式化比较特殊,假设p为格式中指定的保留小数位数,先尝试采用科学计数法格式化,得到幂指数exp,如果-4<=exp<p,则采用小数计数法,并保留p-1-exp位小数,否则按小数计数法计数,并按p-1保留小数位数
>>> format(0.00003141566,'.1g') #p=1,exp=-5 ==》 -4<=exp<p不成立,按科学计数法计数,保留0位小数点
'3e-05'
>>> format(0.00003141566,'.2g') #p=1,exp=-5 ==》 -4<=exp<p不成立,按科学计数法计数,保留1位小数点
'3.1e-05'
>>> format(0.00003141566,'.3g') #p=1,exp=-5 ==》 -4<=exp<p不成立,按科学计数法计数,保留2位小数点
'3.14e-05'
>>> format(0.00003141566,'.3G') #p=1,exp=-5 ==》 -4<=exp<p不成立,按科学计数法计数,保留0位小数点,E使用大写
'3.14E-05'
>>> format(3.1415926777,'.1g') #p=1,exp=0 ==》 -4<=exp<p成立,按小数计数法计数,保留0位小数点
'3'
>>> format(3.1415926777,'.2g') #p=1,exp=0 ==》 -4<=exp<p成立,按小数计数法计数,保留1位小数点
'3.1'
>>> format(3.1415926777,'.3g') #p=1,exp=0 ==》 -4<=exp<p成立,按小数计数法计数,保留2位小数点
'3.14'
>>> format(0.00003141566,'.1n') #和g相同
'3e-05'
>>> format(0.00003141566,'.3n') #和g相同
'3.14e-05'
>>> format(0.00003141566) #和g相同
'3.141566e-05'
bytes:用于不同编码之间的转化。
s = "中国"
bs = s.encode('utf-8')
print(bs) # b'\xe4\xb8\xad\xe5\x9b\xbd'
str_ = bs.decode('utf-8')
print(str_) # 中国
bs1 = bytes(s, encoding='utf-8')
print(bs1) # b'\xe4\xb8\xad\xe5\x9b\xbd'
bytearry:返回一个新字节数组。这个数组里的元素是可变的,并且每个元素的值范围: 0 <= x < 256。
>>> bytearray("abcdefg",encoding='utf-8')
bytearray(b'abcdefg')
>>> a = bytearray("abcdefg",encoding='utf-8')
>>> a[0], a[1]
(97, 98)
>>> a[1::2]
bytearray(b'bdf')
>>> a[1::2][0]
98
>>> a[1::2][1]
100
ret = memoryview(bytes('你好',encoding='utf-8'))
print(len(ret)) # 6
print(ret) # <memory at 0x00000202C598B348>
print(bytes(ret[:3]).decode('utf-8')) # 你
print(bytes(ret[3:]).decode('utf-8')) # 好
ord:输入字符找该字符编码的位置
chr:输入位置数字找出其对应的字符
ascii:是ascii码中的返回该值,不是就返回/u...
>>> ord("a")
97
>>> ord("输")
36755
>>> chr(97)
'a'
>>> chr(36755)
'输'
>>> ascii('a')
"'a'"
>>> ascii('输')
"'\\u8f93
repr:返回一个对象的string形式(原形毕露)
str_ = 'abc'
print(str_) # abc
print(repr(str_)) # 'abc' 字符串完全的显示
数据集合
dict:创建一个字典。
set:创建一个集合。
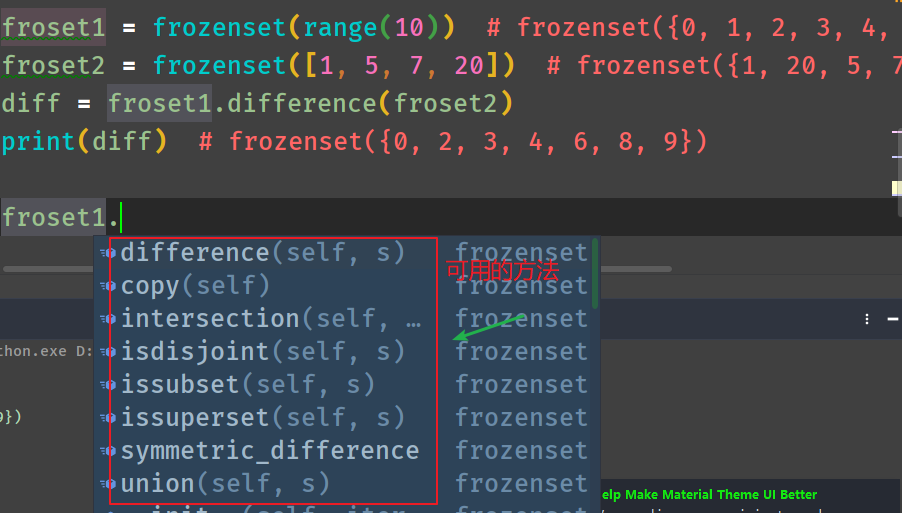
frozenset:返回一个冻结的集合,冻结后集合不能再添加或删除任何元素。
froset1 = frozenset(range(10)) # frozenset({0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9})
froset2 = frozenset([1, 5, 7, 20]) # frozenset({1, 20, 5, 7}
diff = froset1.difference(froset2)
print(diff) # frozenset({0, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9})
# 和set进行操作
froset3 = frozenset(range(4))
set1 = set([4, 1, 2])
diff1 = set1.difference(froset3) # 集合的difference方法
print(diff1) # {4}
diff2 = froset3.difference(set1)
print(diff2) # frozenset({0, 3})
相关内置函数
len:返回一个对象中元素的个数。
sorted:对所有可迭代的对象进行排序操作。
>>> a = "abcdef"
>>> len(a)
6
>>> len(["a", 'b'])
2
>>> len(dict(a=1,b=2))
2
>>> sorted([1, 3, 1, 4])
[1, 1, 3, 4]
>>> sorted([1, 3, 1, 4], reverse=True)
[4, 3, 1, 1]
>>> sorted(['a', 'c', 'b'])
['a', 'b', 'c']
L = [('a', 1), ('c', 3), ('d', 4), ('b', 2), ]
data = sorted(L, key=lambda x: x[1]) #
print(data) # [('a', 1), ('b', 2), ('c', 3), ('d', 4)]
students = [('john', 'A', 15), ('jane', 'B', 12), ('dave', 'B', 10)]
data = sorted(students, key=lambda x:x[2], reverse=True) # reverse反转
print(data) # [('john', 'A', 15), ('jane', 'B', 12), ('dave', 'B', 10)]
enumerate:枚举,返回一个枚举对象。
for index, em in enumerate("ABC"): # 默认的索引位置为0
print(index,em)
'''
0 A
1 B
2 C
'''
for index, em in enumerate("ABC", 10): # 设置索引位置
print(index,em)
'''
10 A
11 B
12 C
'''
all:可迭代对象中,全都是True才是True
any:可迭代对象中,有一个True 就是True
print(all([1, 2, 3])) # True
print(all([1, 2, 3, 0])) # False
print(all([])) # True
print(all("7777")) # True
print(any([1, 2, 3])) # True
print(any([1, 2, 3, 0])) # True
print(any([])) # False
print(any("7777")) # True
zip:函数用于将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表。如果各个迭代器的元素个数不一致,则返回列表长度与最短的对象相同。
l1 = [1, 2, 3, 4]
l2 = ["a", "b", 'c', 'd', 'e']
l3 = ["A", "B", "C", "D", "E"]
data = zip(l1, l2, l3)
print(list(data)) # [(1, 'a', 'A'), (2, 'b', 'B'), (3, 'c', 'C'), (4, 'd', 'D')]
filter:过滤·
ret = filter(lambda x: x > 3, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(list(ret)) # [4, 5, 6, 7]
def func(x):
if x > 3:
return x
ret = filter(func, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
print(list(ret)) # [4, 5, 6, 7]
map:会根据提供的函数对指定序列做映射。
ret = map(func, list(range(5)))
print(list(ret)) # [0, 1, 4, 9, 16]
ret1 = map(lambda x: x ** 2, list(range(5)))
print(list(ret1)) # [0, 1, 4, 9, 16]
data =map(lambda x, y: x + y, [1, 3, 5, 7, 9], [2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
print(list(data)) # [3, 7, 11, 15, 19]
匿名函数
匿名函数:为了解决那些功能很简单的需求而设计的一句话函数。

res = filter(lambda x: x > 10, [5, 8, 11, 9, 15])
for i in res:
print(i, end=" ") # 11 15


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号