python多进程通信 —— 两进程通信 —— Pipe与Queue的通信性能对比
运行代码:
点击查看代码
import time
from multiprocessing import Process, Pipe, Queue
def reader_pipe(pipe):
output_p, input_p = pipe
input_p.close()
while True:
try:
msg = output_p.recv()
except EOFError:
break
def writer_pipe(count, input_p):
for i in range(0, count):
input_p.send(i)
def reader_queue(queue):
while True:
msg = queue.get()
if msg == 'DONE':
break
def writer_queue(count, queue):
for i in range(0, count):
queue.put(i)
queue.put('DONE')
if __name__ == '__main__':
print("testing for pipe")
for count in [10**3, 10**4, 10**5]:
output_p, input_p = Pipe()
reader_p = Process(target=reader_pipe, args=((output_p, input_p), ))
reader_p.start()
output_p.close()
_start = time.time()
writer_pipe(count, input_p)
input_p.close()
reader_p.join()
_end = time.time()
print("Sending %s numbers to Pipe() took %s seconds" % (count, _end - _start))
print("testing for queue")
for count in [10**3, 10**4, 10**5]:
queue = Queue()
reader_q = Process(target=reader_queue, args=(queue,))
reader_q.start()
_start = time.time()
writer_queue(count, queue)
queue.close()
reader_q.join()
_end = time.time()
print("Sending %s numbers to Queue() took %s seconds" % (count, _end - _start))
运行效果:
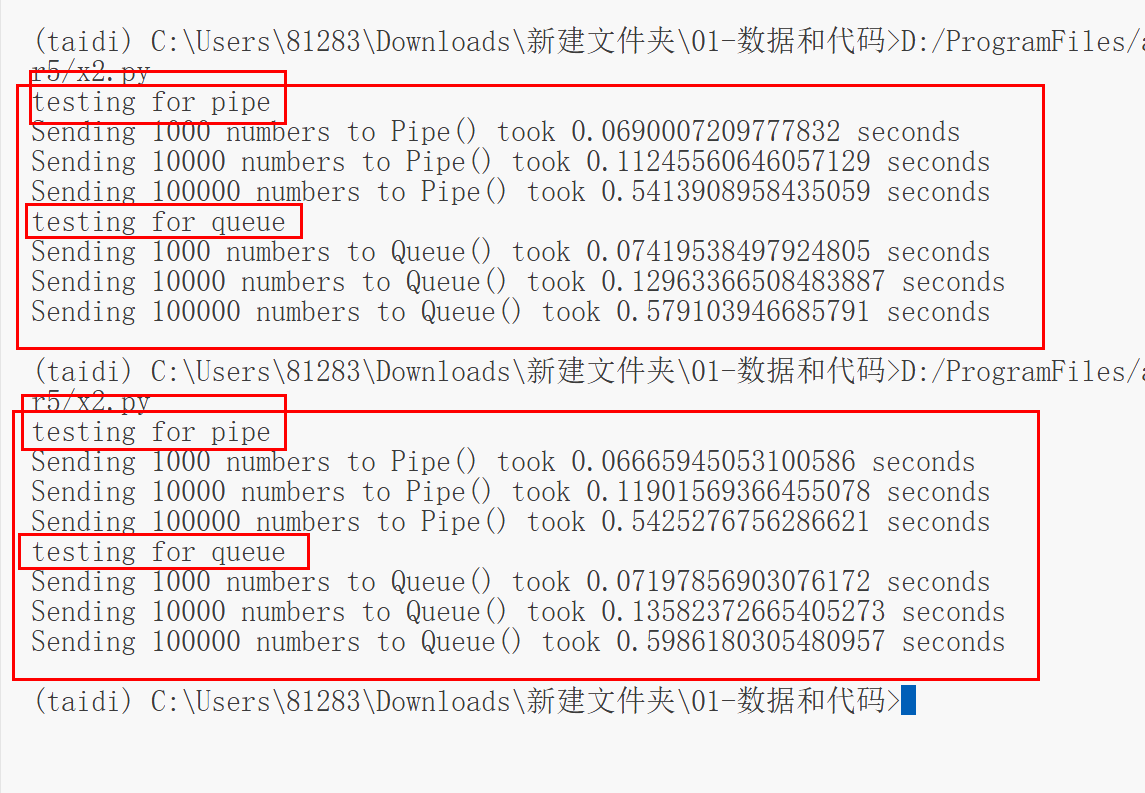
可以看到,两个进程进行单向通信是,Pipe的性能会略微的高于Queue,其原因是Pipe是Queue的底层实现,其中Queue是Pipe的基础上加入了锁机制以及缓存机制。
需要注意的是:
由于Pipe并没有像Queue那边加入了锁机制,因此Pipe在进行多进程(多于两个进程)(两个进程的同时进行双方向)的通信时,会可能出现数据损坏的问题。
Pipe在进行两个进程的通信时,由于Pipe可以进行双向通信,因此为了防止两个进程同时的读或写导致数据损坏,因此示例中的代码都是使用的单方向的(主进程只能写,子进程只能读)。
本博客是博主个人学习时的一些记录,不保证是为原创,个别文章加入了转载的源地址,还有个别文章是汇总网上多份资料所成,在这之中也必有疏漏未加标注处,如有侵权请与博主联系。
如果未特殊标注则为原创,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议。
posted on 2025-11-16 20:14 Angry_Panda 阅读(19) 评论(1) 收藏 举报



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号