Hession-free 的共轭梯度法的高效计算版本的部分代码(pytorch实现,实现一阶求导的一次计算重复使用)
Hession-free 的共轭梯度法的高效计算版本的部分代码(pytorch实现,实现一阶求导的一次计算重复使用)
Hession-free 的共轭梯度法在求解 H*v 的时候是先求一阶导,即雅可比向量,然后雅可比向量与向量v乘积后再求二导数,这样可以避免Hession矩阵在内存中的完全展开,减少内存消耗,使大规模矩阵的计算实现可行;但是该种传统的计算过程中会出现大量重复的对相同计算图的一阶求导,而这部分求导是在整个共轭梯度算法中保持不变的,我们完全可以避免掉这部分计算的重复进行,因此在pytorch版本中对一阶计算图求导时使用create_graph=True参数,而在二阶求导时使用retain_graph=True参数,这样我们就可以对一阶计算图进行重复使用。
给出部分代码,H*v部分代码:
import torch
w=torch.tensor([1.],requires_grad=True) # w=1
x=torch.tensor([2.],requires_grad=True) # x=2
a=torch.add(w,x) # a = w+x
b=torch.add(w,1) # b = w+1
y=torch.mul(a,b) # y = w**2+w*x+w+x
# w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y, [w, x], retain_graph=True, create_graph=True)
w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y, [w, x], create_graph=True)
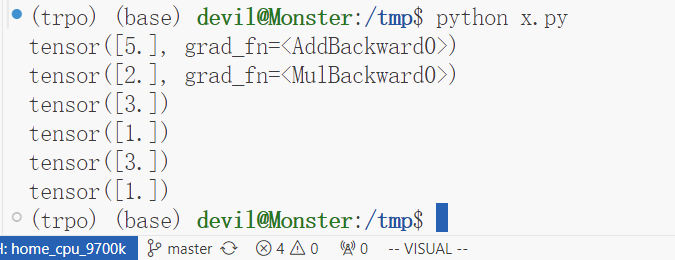
print(w_grad) # 2w+x+1 = 5
print(x_grad) # w+1 = 2
z = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z, [w, x], retain_graph=True)
print(w_grad2) # 3
print(x_grad2) # 1
z2 = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z2, [w, x])
print(w_grad2) # 3
print(x_grad2) # 1
计算结果:
性能比较:一个简单例子
import torch
import numpy as np
import time
w=torch.tensor(torch.randn(10000), requires_grad=True) # w=1
x=torch.tensor(torch.randn(10000), requires_grad=True) # x=2
a=torch.add(w,x) # a = w+x
b=torch.add(w,1) # b = w+1
y=torch.mul(a,b) # y = w**2+w*x+w+x
# w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y, [w, x], retain_graph=True, create_graph=True)
w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y.mean(), [w, x], create_graph=True)
# print(w_grad) # 2w+x+1 = 5
# print(x_grad) # w+1 = 2
z = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z.mean(), [w, x], retain_graph=True)
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
z2 = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z2.mean(), [w, x])
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
##########################################
a=torch.add(w,x) # a = w+x
b=torch.add(w,1) # b = w+1
y=torch.mul(a,b) # y = w**2+w*x+w+x
a_t = time.time()
# w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y, [w, x], retain_graph=True, create_graph=True)
w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y.mean(), [w, x], create_graph=True)
# print(w_grad) # 2w+x+1 = 5
# print(x_grad) # w+1 = 2
z = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z.mean(), [w, x], retain_graph=True)
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
z2 = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z2.mean(), [w, x])
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
b_t = time.time()
a=torch.add(w,x) # a = w+x
b=torch.add(w,1) # b = w+1
y=torch.mul(a,b) # y = w**2+w*x+w+x
b2_t = time.time()
# w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y, [w, x], retain_graph=True, create_graph=True)
w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y.mean(), [w, x], create_graph=True)
# print(w_grad) # 2w+x+1 = 5
# print(x_grad) # w+1 = 2
z = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z.mean(), [w, x], retain_graph=True)
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
z2 = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z2.mean(), [w, x])
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
c_t = time.time()
print(b_t - a_t)
print(c_t - b2_t)
运行结果:

可以看到,使用该种方法可以避免一次求导的重复进行,可以提速10%,虽然没有因为避免一阶求导的重复进行而省掉较大的计算时间,但是提速10%也算是不错的表现了,当然这个例子只是使用CPU进行的。
给出GPU版本:
点击查看代码
import torch
import numpy as np
import time
w=torch.tensor(torch.randn(10000), requires_grad=True).to("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") # w=1
x=torch.tensor(torch.randn(10000), requires_grad=True).to("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") # x=2
a=torch.add(w,x) # a = w+x
b=torch.add(w,1) # b = w+1
y=torch.mul(a,b) # y = w**2+w*x+w+x
# w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y, [w, x], retain_graph=True, create_graph=True)
w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y.mean(), [w, x], create_graph=True)
# print(w_grad) # 2w+x+1 = 5
# print(x_grad) # w+1 = 2
z = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z.mean(), [w, x], retain_graph=True)
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
z2 = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z2.mean(), [w, x])
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
##########################################
a=torch.add(w,x) # a = w+x
b=torch.add(w,1) # b = w+1
y=torch.mul(a,b) # y = w**2+w*x+w+x
a_t = time.time()
# w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y, [w, x], retain_graph=True, create_graph=True)
w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y.mean(), [w, x], create_graph=True)
# print(w_grad) # 2w+x+1 = 5
# print(x_grad) # w+1 = 2
z = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z.mean(), [w, x], retain_graph=True)
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
z2 = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z2.mean(), [w, x])
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
b_t = time.time()
a=torch.add(w,x) # a = w+x
b=torch.add(w,1) # b = w+1
y=torch.mul(a,b) # y = w**2+w*x+w+x
b2_t = time.time()
# w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y, [w, x], retain_graph=True, create_graph=True)
w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y.mean(), [w, x], create_graph=True)
# print(w_grad) # 2w+x+1 = 5
# print(x_grad) # w+1 = 2
z = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z.mean(), [w, x], retain_graph=True)
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
z2 = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z2.mean(), [w, x])
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
c_t = time.time()
print(b_t - a_t)
print(c_t - b2_t)
运行结果:
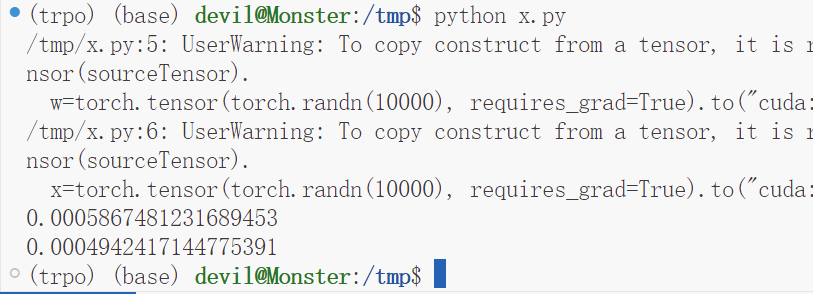
可以看到,性能提升了15%左右。
更正:
上面的测评标准不是很正确,下面给出更正后的测评代码和性能表现:
import torch
import numpy as np
import time
w=torch.tensor(torch.randn(10000000), requires_grad=True).to("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") # w=1
x=torch.tensor(torch.randn(10000000), requires_grad=True).to("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu") # x=2
a=torch.add(w,x) # a = w+x
b=torch.add(w,1) # b = w+1
y=torch.mul(a,b) # y = w**2+w*x+w+x
# w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y, [w, x], retain_graph=True, create_graph=True)
w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y.mean(), [w, x], create_graph=True)
# print(w_grad) # 2w+x+1 = 5
# print(x_grad) # w+1 = 2
z = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z.mean(), [w, x], retain_graph=True)
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
z2 = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z2.mean(), [w, x])
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
##########################################
##########################################
a_t = time.time()
def f():
a=torch.add(w,x) # a = w+x
b=torch.add(w,1) # b = w+1
y=torch.mul(a,b) # y = w**2+w*x+w+x
# w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y, [w, x], retain_graph=True, create_graph=True)
w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y.mean(), [w, x], create_graph=True)
# print(w_grad) # 2w+x+1 = 5
# print(x_grad) # w+1 = 2
z = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z.mean(), [w, x])
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
for i in range(5):
f()
###################################
###################################
b_t = time.time()
a=torch.add(w,x) # a = w+x
b=torch.add(w,1) # b = w+1
y=torch.mul(a,b) # y = w**2+w*x+w+x
# w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y, [w, x], retain_graph=True, create_graph=True)
w_grad, x_grad = torch.autograd.grad(y.mean(), [w, x], create_graph=True)
# print(w_grad) # 2w+x+1 = 5
# print(x_grad) # w+1 = 2
def f2():
z = w_grad + x_grad
w_grad2, x_grad2 = torch.autograd.grad(z.mean(), [w, x], retain_graph=True)
# print(w_grad2) # 3
# print(x_grad2) # 1
for i in range(5):
f2()
c_t = time.time()
print(b_t - a_t)
print(c_t - b_t)
性能表现:
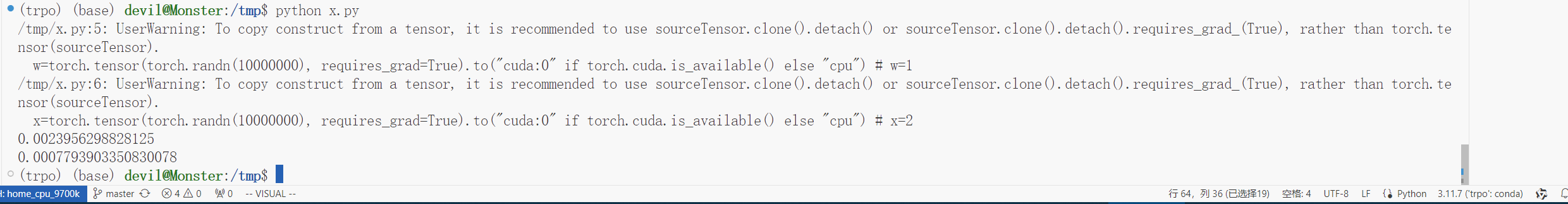

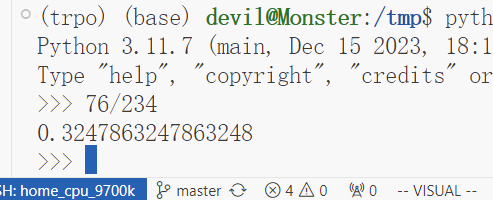
可以看到,用时为之前的32%,可以说提速了70%左右,可以看到在更正后的测评中本文提出的Hession-free的共轭梯度加速计算方法可以有不错的性能表现。
本博客是博主个人学习时的一些记录,不保证是为原创,个别文章加入了转载的源地址,还有个别文章是汇总网上多份资料所成,在这之中也必有疏漏未加标注处,如有侵权请与博主联系。
如果未特殊标注则为原创,遵循 CC 4.0 BY-SA 版权协议。
posted on 2024-02-27 11:33 Angry_Panda 阅读(85) 评论(0) 收藏 举报




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号