凸优化: 回溯线搜索(Backtracking line search)
声明:
本文大量摘录 https://www.cnblogs.com/kemaswill/p/3416231.html 内容。
======================================
回溯线搜索(Backtracking line search)
预备知识:
函数的梯度--最快上升方向。下降方向则是负梯度。
给出 回溯线搜索(Backtracking line search)的算法流程描述:

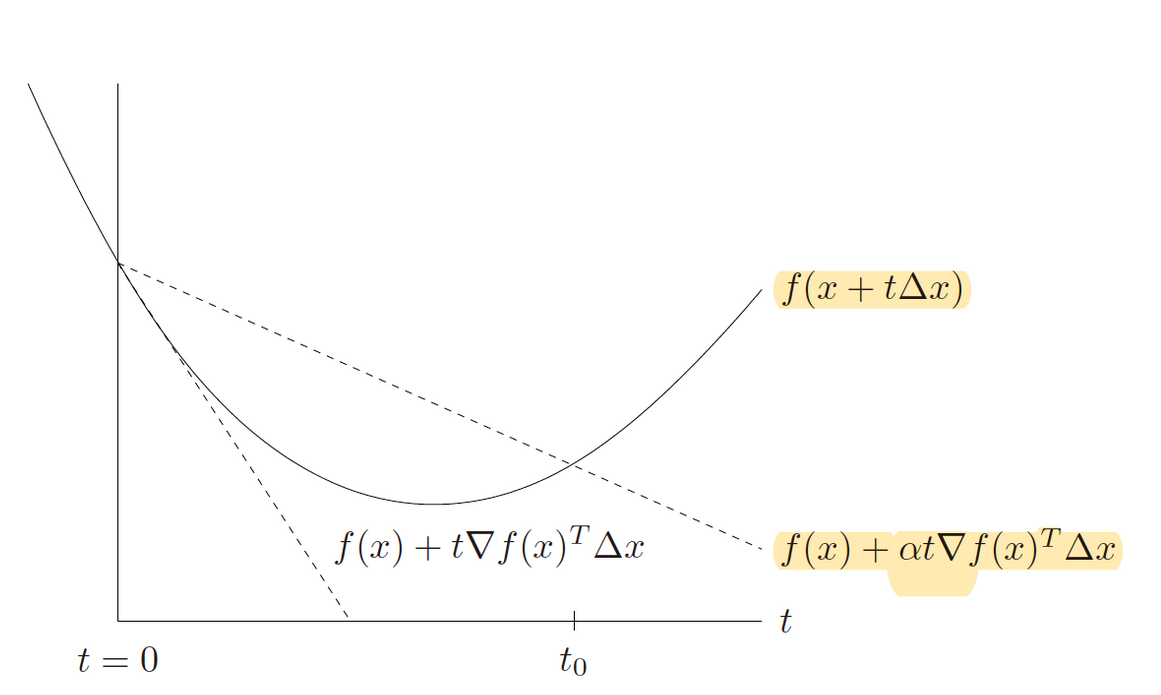
===================================================
下面内容摘录自:
https://www.cnblogs.com/kemaswill/p/3416231.html
个人推荐阅读上面这个链接的内容,这个内容比较易懂,而且讲的也比较透彻。

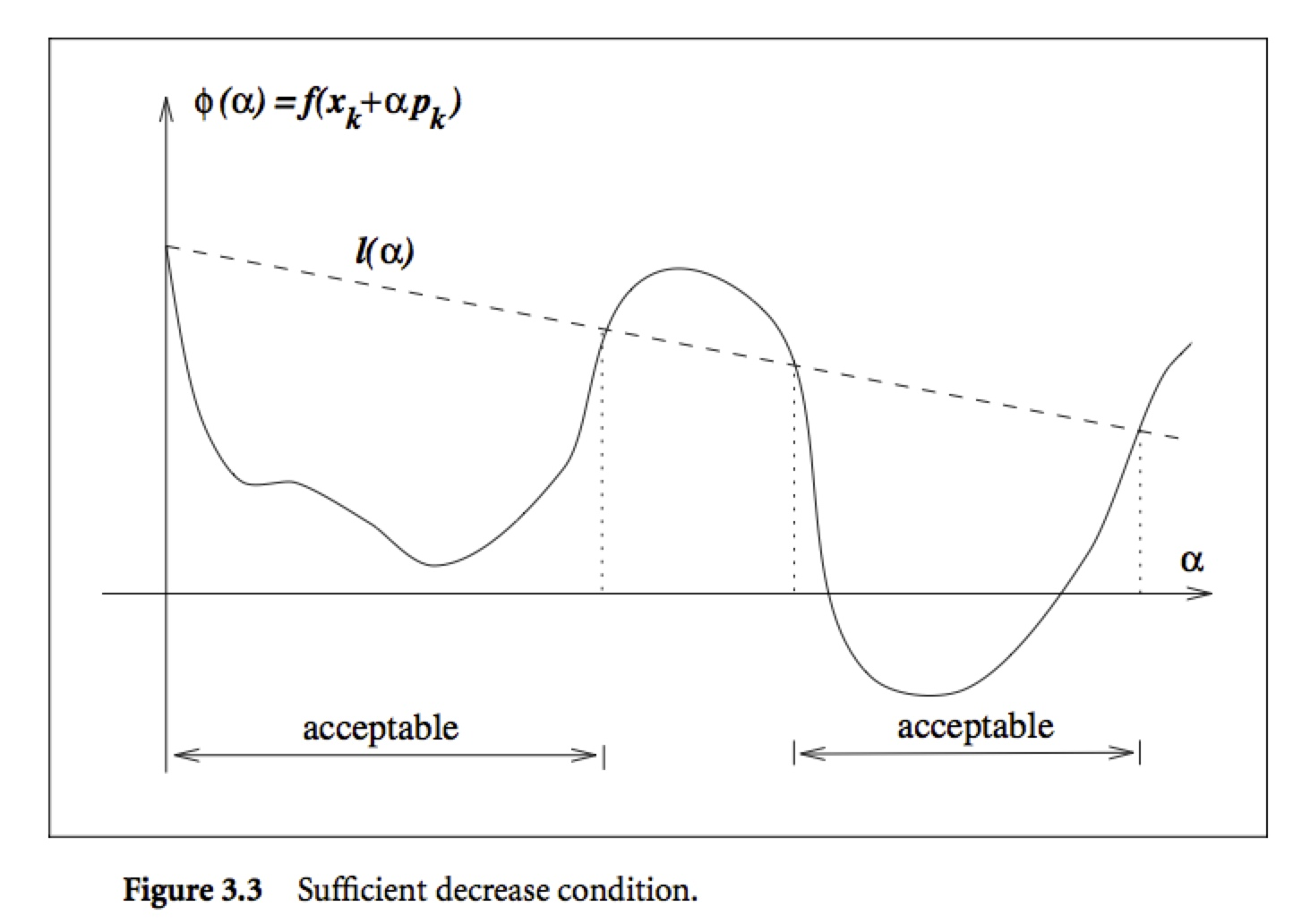

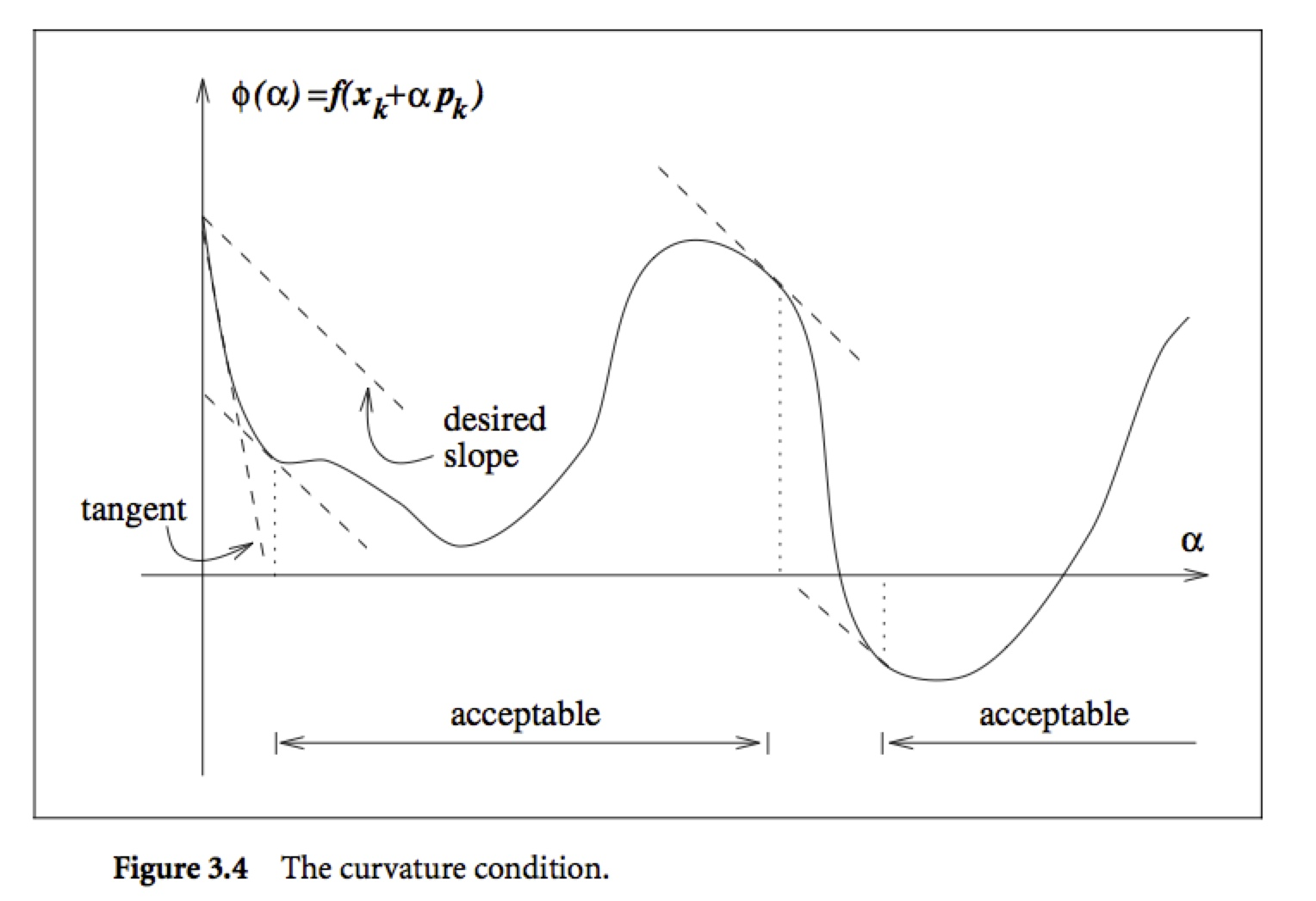

===================================================
根据 https://www.cnblogs.com/kemaswill/p/3416231.html 中的理论,我们可以得到下面的demo代码:
import random import numpy as np from scipy.linalg import orth import torch seed = 9999 random.seed(seed) np.random.seed(seed) torch.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed) torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True class Data_Gen(): def __init__(self, N, positive_definite=True): self.N = N # 不变的矩阵 B = np.random.rand(N, 1) # 数据集,数据B矩阵 self.B = torch.tensor(B, dtype=torch.float32) if positive_definite==True: # 正定矩阵的生成, A_ X = np.diag(np.abs(np.random.rand(N))+1) U = orth(np.random.rand(N, N)) A = np.dot(np.dot(U.T, X), U) else: # 非正定矩阵的生成,A M = np.random.rand(N, N) A = np.dot(M.T, M) + 0.01*np.eye(N) self.A = torch.tensor(A, dtype=torch.float32) def data_gen(self, x: torch.FloatTensor): """ 数据生成 """ # 训练数据,x_data, x # x = torch.randn(N, requires_grad=True) N = x.size()[0] assert N==self.N, "向量长度不匹配" # 构建训练数据,非正定数据矩阵生成的y_data y=self.object_fun(self.A, self.B, x) return y def object_fun(self, A: torch.FloatTensor, B: torch.FloatTensor, x: torch.FloatTensor): if x.dim() == 1: x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1) ans = torch.mm(x.T, torch.mm(A, x)) + torch.mm(x.T, B) # print( torch.mm(A, x) ) # print( torch.mm(x.T, torch.mm(A, x)) ) # print( torch.mm(x.T, B) ) return torch.squeeze(ans) ##################################################### # 随机梯度法 def sgd(x: torch.FloatTensor, data_gen: Data_Gen, step=0.00001): # x = torch.randn(N, device="cuda:0", requires_grad=True) y = data_gen.data_gen(x) iter_num = 0 while True: g = torch.autograd.grad(y, x, retain_graph=False, create_graph=False)[0] x.data.add_( -step*g ) y_new = data_gen.data_gen(x) iter_num += 1 print("iter_num: ", iter_num, "y_old: ", y.item(), "y_new: ", y_new.item()) if abs(y_new.item()-y.item()) < 0.00001: break else: y = y_new ##################################################### # 回溯线搜索(Backtracking line search) def bls(x: torch.FloatTensor, data_gen: Data_Gen): iter_num = 0 c = 0.25 beta = 0.8 while True: iter_num += 1 y0 = data_gen.data_gen(x) g = torch.autograd.grad(y0, x, retain_graph=False, create_graph=False)[0] p = -1.0*g # 求最小值,梯度下降,使用负梯度 delta_f = g search_time = 0 alpha_step = 1.0 while True: y_new = data_gen.data_gen(x.detach() + alpha_step*p) y_up = y0 + c*alpha_step*torch.dot(delta_f, p) if y_new.item() > y_up.item(): search_time += 1 alpha_step *= beta else: break x.data.add_( alpha_step*p ) print("iter_num: ", iter_num, "search_time: ", search_time, " y_old: ", y0.item(), "y_new: ", y_new.item()) if abs(y_new.item()-y0.item()) < 0.00001: break if __name__ == '__main__': # 数据生成 N = 500 data_gen = Data_Gen(N) x = torch.randn(N, requires_grad=True) ##################################################### # 对凸二次函数进行求解,正定矩阵,求解最小值 ##################################################### # data_gen = Data_Gen(N) # 随机梯度法 sgd(x, data_gen) # bls算法 bls(x, data_gen) ##################################################### # 对非凸二次函数进行求解,非正定矩阵,求解最小值 ##################################################### """ data_gen = Data_Gen(N, positive_definite=False) # 随机梯度法 sgd(x, data_gen) # bls算法 bls(x, data_gen) """
对于二阶正定矩阵所形成的凸优化问题,我们使用随机梯度下降,代码:

import random import numpy as np from scipy.linalg import orth import torch seed = 9999 random.seed(seed) np.random.seed(seed) torch.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed) torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True class Data_Gen(): def __init__(self, N, positive_definite=True): self.N = N # 不变的矩阵 B = np.random.rand(N, 1) # 数据集,数据B矩阵 self.B = torch.tensor(B, dtype=torch.float32) if positive_definite==True: # 正定矩阵的生成, A_ X = np.diag(np.abs(np.random.rand(N))+1) U = orth(np.random.rand(N, N)) A = np.dot(np.dot(U.T, X), U) else: # 非正定矩阵的生成,A M = np.random.rand(N, N) A = np.dot(M.T, M) + 0.01*np.eye(N) self.A = torch.tensor(A, dtype=torch.float32) def data_gen(self, x: torch.FloatTensor): """ 数据生成 """ # 训练数据,x_data, x # x = torch.randn(N, requires_grad=True) N = x.size()[0] assert N==self.N, "向量长度不匹配" # 构建训练数据,非正定数据矩阵生成的y_data y=self.object_fun(self.A, self.B, x) return y def object_fun(self, A: torch.FloatTensor, B: torch.FloatTensor, x: torch.FloatTensor): if x.dim() == 1: x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1) ans = torch.mm(x.T, torch.mm(A, x)) + torch.mm(x.T, B) # print( torch.mm(A, x) ) # print( torch.mm(x.T, torch.mm(A, x)) ) # print( torch.mm(x.T, B) ) return torch.squeeze(ans) ##################################################### # 随机梯度法 def sgd(x: torch.FloatTensor, data_gen: Data_Gen, step=0.00001): # x = torch.randn(N, device="cuda:0", requires_grad=True) y = data_gen.data_gen(x) iter_num = 0 while True: g = torch.autograd.grad(y, x, retain_graph=False, create_graph=False)[0] x.data.add_( -step*g ) y_new = data_gen.data_gen(x) iter_num += 1 print("iter_num: ", iter_num, "y_old: ", y.item(), "y_new: ", y_new.item()) if abs(y_new.item()-y.item()) < 0.00001: break else: y = y_new ##################################################### # 回溯线搜索(Backtracking line search) def bls(x: torch.FloatTensor, data_gen: Data_Gen): iter_num = 0 c = 0.25 beta = 0.8 while True: iter_num += 1 y0 = data_gen.data_gen(x) g = torch.autograd.grad(y0, x, retain_graph=False, create_graph=False)[0] p = -1.0*g # 求最小值,梯度下降,使用负梯度 delta_f = g search_time = 0 alpha_step = 1.0 while True: y_new = data_gen.data_gen(x.detach() + alpha_step*p) y_up = y0 + c*alpha_step*torch.dot(delta_f, p) if y_new.item() > y_up.item(): search_time += 1 alpha_step *= beta else: break x.data.add_( alpha_step*p ) print("iter_num: ", iter_num, "search_time: ", search_time, " y_old: ", y0.item(), "y_new: ", y_new.item()) if abs(y_new.item()-y0.item()) < 0.00001: break if __name__ == '__main__': # 数据生成 N = 500 data_gen = Data_Gen(N) x = torch.randn(N, requires_grad=True) ##################################################### # 对凸二次函数进行求解,正定矩阵,求解最小值 ##################################################### # data_gen = Data_Gen(N) # 随机梯度法 sgd(x, data_gen) # bls算法 # bls(x, data_gen) ##################################################### # 对非凸二次函数进行求解,非正定矩阵,求解最小值 ##################################################### """ data_gen = Data_Gen(N, positive_definite=False) # 随机梯度法 sgd(x, data_gen) # bls算法 bls(x, data_gen) """
运行结果:
iter_num: 109598 y_old: -24.1126766204834 y_new: -24.11280059814453
iter_num: 109599 y_old: -24.11280059814453 y_new: -24.11285972595215
iter_num: 109600 y_old: -24.11285972595215 y_new: -24.112972259521484
iter_num: 109601 y_old: -24.112972259521484 y_new: -24.113067626953125
iter_num: 109602 y_old: -24.113067626953125 y_new: -24.113168716430664
iter_num: 109603 y_old: -24.113168716430664 y_new: -24.113237380981445
iter_num: 109604 y_old: -24.113237380981445 y_new: -24.11332130432129
iter_num: 109605 y_old: -24.11332130432129 y_new: -24.113388061523438
iter_num: 109606 y_old: -24.113388061523438 y_new: -24.11349868774414
iter_num: 109607 y_old: -24.11349868774414 y_new: -24.11361312866211
iter_num: 109608 y_old: -24.11361312866211 y_new: -24.113622665405273
对于二阶正定矩阵所形成的凸优化问题,我们使用bls算法,代码:

import random import numpy as np from scipy.linalg import orth import torch seed = 9999 random.seed(seed) np.random.seed(seed) torch.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed) torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True class Data_Gen(): def __init__(self, N, positive_definite=True): self.N = N # 不变的矩阵 B = np.random.rand(N, 1) # 数据集,数据B矩阵 self.B = torch.tensor(B, dtype=torch.float32) if positive_definite==True: # 正定矩阵的生成, A_ X = np.diag(np.abs(np.random.rand(N))+1) U = orth(np.random.rand(N, N)) A = np.dot(np.dot(U.T, X), U) else: # 非正定矩阵的生成,A M = np.random.rand(N, N) A = np.dot(M.T, M) + 0.01*np.eye(N) self.A = torch.tensor(A, dtype=torch.float32) def data_gen(self, x: torch.FloatTensor): """ 数据生成 """ # 训练数据,x_data, x # x = torch.randn(N, requires_grad=True) N = x.size()[0] assert N==self.N, "向量长度不匹配" # 构建训练数据,非正定数据矩阵生成的y_data y=self.object_fun(self.A, self.B, x) return y def object_fun(self, A: torch.FloatTensor, B: torch.FloatTensor, x: torch.FloatTensor): if x.dim() == 1: x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1) ans = torch.mm(x.T, torch.mm(A, x)) + torch.mm(x.T, B) # print( torch.mm(A, x) ) # print( torch.mm(x.T, torch.mm(A, x)) ) # print( torch.mm(x.T, B) ) return torch.squeeze(ans) ##################################################### # 随机梯度法 def sgd(x: torch.FloatTensor, data_gen: Data_Gen, step=0.00001): # x = torch.randn(N, device="cuda:0", requires_grad=True) y = data_gen.data_gen(x) iter_num = 0 while True: g = torch.autograd.grad(y, x, retain_graph=False, create_graph=False)[0] x.data.add_( -step*g ) y_new = data_gen.data_gen(x) iter_num += 1 print("iter_num: ", iter_num, "y_old: ", y.item(), "y_new: ", y_new.item()) if abs(y_new.item()-y.item()) < 0.00001: break else: y = y_new ##################################################### # 回溯线搜索(Backtracking line search) def bls(x: torch.FloatTensor, data_gen: Data_Gen): iter_num = 0 c = 0.25 beta = 0.8 while True: iter_num += 1 y0 = data_gen.data_gen(x) g = torch.autograd.grad(y0, x, retain_graph=False, create_graph=False)[0] p = -1.0*g # 求最小值,梯度下降,使用负梯度 delta_f = g search_time = 0 alpha_step = 1.0 while True: y_new = data_gen.data_gen(x.detach() + alpha_step*p) y_up = y0 + c*alpha_step*torch.dot(delta_f, p) if y_new.item() > y_up.item(): search_time += 1 alpha_step *= beta else: break x.data.add_( alpha_step*p ) print("iter_num: ", iter_num, "search_time: ", search_time, " y_old: ", y0.item(), "y_new: ", y_new.item()) if abs(y_new.item()-y0.item()) < 0.00001: break if __name__ == '__main__': # 数据生成 N = 500 data_gen = Data_Gen(N) x = torch.randn(N, requires_grad=True) ##################################################### # 对凸二次函数进行求解,正定矩阵,求解最小值 ##################################################### # data_gen = Data_Gen(N) # 随机梯度法 # sgd(x, data_gen) # bls算法 bls(x, data_gen) ##################################################### # 对非凸二次函数进行求解,非正定矩阵,求解最小值 ##################################################### """ data_gen = Data_Gen(N, positive_definite=False) # 随机梯度法 sgd(x, data_gen) # bls算法 bls(x, data_gen) """
运行结果:
iter_num: 1 search_time: 4 y_old: 741.302490234375 y_new: 61.191226959228516
iter_num: 2 search_time: 4 y_old: 61.191226959228516 y_new: -6.580791473388672
iter_num: 3 search_time: 5 y_old: -6.580791473388672 y_new: -24.848424911499023
iter_num: 4 search_time: 5 y_old: -24.848424911499023 y_new: -25.728652954101562
iter_num: 5 search_time: 5 y_old: -25.728652954101562 y_new: -25.78291893005371
iter_num: 6 search_time: 5 y_old: -25.78291893005371 y_new: -25.786640167236328
iter_num: 7 search_time: 5 y_old: -25.786640167236328 y_new: -25.786869049072266
iter_num: 8 search_time: 3 y_old: -25.786869049072266 y_new: -25.786916732788086
iter_num: 9 search_time: 5 y_old: -25.786916732788086 y_new: -25.786951065063477
iter_num: 10 search_time: 3 y_old: -25.786951065063477 y_new: -25.78696060180664
可以看到,对于凸优化问题,我们使用随机梯度下降和bls算法相差不大,甚至bls算法的结果要由于随机梯度下降,但是最为重要的是运算的迭代次数,我们可以看到随机梯度下降算法共进行了109608次迭代,而bls算法只进行了10次迭代,虽然bls算法在每次迭代的过程中都会进行search操作,但是每次迭代过程中search次数都没有超过5。
可以看到对于凸优化问题,bls算法在总体表现上要优与随机梯度sgd算法。
对于非凸优化问题,给出demo代码:
非凸优化问题,随机梯度下降算法,sgd:

import random import numpy as np from scipy.linalg import orth import torch seed = 9999 random.seed(seed) np.random.seed(seed) torch.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed) torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True class Data_Gen(): def __init__(self, N, positive_definite=True): self.N = N # 不变的矩阵 B = np.random.rand(N, 1) # 数据集,数据B矩阵 self.B = torch.tensor(B, dtype=torch.float32) if positive_definite==True: # 正定矩阵的生成, A_ X = np.diag(np.abs(np.random.rand(N))+1) U = orth(np.random.rand(N, N)) A = np.dot(np.dot(U.T, X), U) else: # 非正定矩阵的生成,A M = np.random.rand(N, N) A = np.dot(M.T, M) + 0.01*np.eye(N) self.A = torch.tensor(A, dtype=torch.float32) def data_gen(self, x: torch.FloatTensor): """ 数据生成 """ # 训练数据,x_data, x # x = torch.randn(N, requires_grad=True) N = x.size()[0] assert N==self.N, "向量长度不匹配" # 构建训练数据,非正定数据矩阵生成的y_data y=self.object_fun(self.A, self.B, x) return y def object_fun(self, A: torch.FloatTensor, B: torch.FloatTensor, x: torch.FloatTensor): if x.dim() == 1: x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1) ans = torch.mm(x.T, torch.mm(A, x)) + torch.mm(x.T, B) # print( torch.mm(A, x) ) # print( torch.mm(x.T, torch.mm(A, x)) ) # print( torch.mm(x.T, B) ) return torch.squeeze(ans) ##################################################### # 随机梯度法 def sgd(x: torch.FloatTensor, data_gen: Data_Gen, step=0.00001): # x = torch.randn(N, device="cuda:0", requires_grad=True) y = data_gen.data_gen(x) iter_num = 0 while True: g = torch.autograd.grad(y, x, retain_graph=False, create_graph=False)[0] x.data.add_( -step*g ) y_new = data_gen.data_gen(x) iter_num += 1 print("iter_num: ", iter_num, "y_old: ", y.item(), "y_new: ", y_new.item()) if abs(y_new.item()-y.item()) < 0.00001: break else: y = y_new ##################################################### # 回溯线搜索(Backtracking line search) def bls(x: torch.FloatTensor, data_gen: Data_Gen): iter_num = 0 c = 0.25 beta = 0.8 while True: iter_num += 1 y0 = data_gen.data_gen(x) g = torch.autograd.grad(y0, x, retain_graph=False, create_graph=False)[0] p = -1.0*g # 求最小值,梯度下降,使用负梯度 delta_f = g search_time = 0 alpha_step = 1.0 while True: y_new = data_gen.data_gen(x.detach() + alpha_step*p) y_up = y0 + c*alpha_step*torch.dot(delta_f, p) if y_new.item() > y_up.item(): search_time += 1 alpha_step *= beta else: break x.data.add_( alpha_step*p ) print("iter_num: ", iter_num, "search_time: ", search_time, " y_old: ", y0.item(), "y_new: ", y_new.item()) if abs(y_new.item()-y0.item()) < 0.00001: break if __name__ == '__main__': # 数据生成 N = 500 x = torch.randn(N, requires_grad=True) """ ##################################################### # 对凸二次函数进行求解,正定矩阵,求解最小值 ##################################################### # data_gen = Data_Gen(N) # 随机梯度法 # sgd(x, data_gen) # bls算法 bls(x, data_gen) """ ##################################################### # 对非凸二次函数进行求解,非正定矩阵,求解最小值 ##################################################### data_gen = Data_Gen(N, positive_definite=False) # 随机梯度法 sgd(x, data_gen) # bls算法 # bls(x, data_gen)
运算结果:
iter_num: 18261 y_old: 29.948509216308594 y_new: 29.945993423461914
iter_num: 18262 y_old: 29.945993423461914 y_new: 29.94289207458496
iter_num: 18263 y_old: 29.94289207458496 y_new: 29.940031051635742
iter_num: 18264 y_old: 29.940031051635742 y_new: 29.93958282470703
iter_num: 18265 y_old: 29.93958282470703 y_new: 29.936599731445312
iter_num: 18266 y_old: 29.936599731445312 y_new: 29.932973861694336
iter_num: 18267 y_old: 29.932973861694336 y_new: 29.930309295654297
iter_num: 18268 y_old: 29.930309295654297 y_new: 29.92643165588379
iter_num: 18269 y_old: 29.92643165588379 y_new: 29.92643928527832
非凸优化问题,bls算法,代码:

import random import numpy as np from scipy.linalg import orth import torch seed = 9999 random.seed(seed) np.random.seed(seed) torch.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed) torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True class Data_Gen(): def __init__(self, N, positive_definite=True): self.N = N # 不变的矩阵 B = np.random.rand(N, 1) # 数据集,数据B矩阵 self.B = torch.tensor(B, dtype=torch.float32) if positive_definite==True: # 正定矩阵的生成, A_ X = np.diag(np.abs(np.random.rand(N))+1) U = orth(np.random.rand(N, N)) A = np.dot(np.dot(U.T, X), U) else: # 非正定矩阵的生成,A M = np.random.rand(N, N) A = np.dot(M.T, M) + 0.01*np.eye(N) self.A = torch.tensor(A, dtype=torch.float32) def data_gen(self, x: torch.FloatTensor): """ 数据生成 """ # 训练数据,x_data, x # x = torch.randn(N, requires_grad=True) N = x.size()[0] assert N==self.N, "向量长度不匹配" # 构建训练数据,非正定数据矩阵生成的y_data y=self.object_fun(self.A, self.B, x) return y def object_fun(self, A: torch.FloatTensor, B: torch.FloatTensor, x: torch.FloatTensor): if x.dim() == 1: x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1) ans = torch.mm(x.T, torch.mm(A, x)) + torch.mm(x.T, B) # print( torch.mm(A, x) ) # print( torch.mm(x.T, torch.mm(A, x)) ) # print( torch.mm(x.T, B) ) return torch.squeeze(ans) ##################################################### # 随机梯度法 def sgd(x: torch.FloatTensor, data_gen: Data_Gen, step=0.00001): # x = torch.randn(N, device="cuda:0", requires_grad=True) y = data_gen.data_gen(x) iter_num = 0 while True: g = torch.autograd.grad(y, x, retain_graph=False, create_graph=False)[0] x.data.add_( -step*g ) y_new = data_gen.data_gen(x) iter_num += 1 print("iter_num: ", iter_num, "y_old: ", y.item(), "y_new: ", y_new.item()) if abs(y_new.item()-y.item()) < 0.00001: break else: y = y_new ##################################################### # 回溯线搜索(Backtracking line search) def bls(x: torch.FloatTensor, data_gen: Data_Gen): iter_num = 0 c = 0.25 beta = 0.8 while True: iter_num += 1 y0 = data_gen.data_gen(x) g = torch.autograd.grad(y0, x, retain_graph=False, create_graph=False)[0] p = -1.0*g # 求最小值,梯度下降,使用负梯度 delta_f = g search_time = 0 alpha_step = 1.0 while True: y_new = data_gen.data_gen(x.detach() + alpha_step*p) y_up = y0 + c*alpha_step*torch.dot(delta_f, p) if y_new.item() > y_up.item(): search_time += 1 alpha_step *= beta else: break x.data.add_( alpha_step*p ) print("iter_num: ", iter_num, "search_time: ", search_time, " y_old: ", y0.item(), "y_new: ", y_new.item()) if abs(y_new.item()-y0.item()) < 0.00001: break if __name__ == '__main__': # 数据生成 N = 500 x = torch.randn(N, requires_grad=True) """ ##################################################### # 对凸二次函数进行求解,正定矩阵,求解最小值 ##################################################### # data_gen = Data_Gen(N) # 随机梯度法 # sgd(x, data_gen) # bls算法 bls(x, data_gen) """ ##################################################### # 对非凸二次函数进行求解,非正定矩阵,求解最小值 ##################################################### data_gen = Data_Gen(N, positive_definite=False) # 随机梯度法 # sgd(x, data_gen) # bls算法 bls(x, data_gen)
运算结果:
iter_num: 12931 search_time: 50 y_old: 21.942323684692383 y_new: 21.939422607421875
iter_num: 12932 search_time: 49 y_old: 21.939422607421875 y_new: 21.936918258666992
iter_num: 12933 search_time: 51 y_old: 21.936918258666992 y_new: 21.934120178222656
iter_num: 12934 search_time: 47 y_old: 21.934120178222656 y_new: 21.93170738220215
iter_num: 12935 search_time: 51 y_old: 21.93170738220215 y_new: 21.92693519592285
iter_num: 12936 search_time: 48 y_old: 21.92693519592285 y_new: 21.924362182617188
iter_num: 12937 search_time: 51 y_old: 21.924362182617188 y_new: 21.922771453857422
iter_num: 12938 search_time: 45 y_old: 21.922771453857422 y_new: 21.919511795043945
iter_num: 12939 search_time: 51 y_old: 21.919511795043945 y_new: 21.914203643798828
iter_num: 12940 search_time: 49 y_old: 21.914203643798828 y_new: 21.911758422851562
iter_num: 12941 search_time: 51 y_old: 21.911758422851562 y_new: 21.9085693359375
iter_num: 12942 search_time: 48 y_old: 21.9085693359375 y_new: 21.904415130615234
iter_num: 12943 search_time: 89 y_old: 21.904415130615234 y_new: 21.904300689697266
iter_num: 12944 search_time: 90 y_old: 21.904300689697266 y_new: 21.904294967651367
可以看到,对于非凸优化问题,bls算法虽然依旧获得由于sgd算法的结果,但是在运算迭代次数上却远远高于sgd算法;上面的非凸优化问题,随机梯度下降共迭代18296次,而bls算法迭代12944次,但是bls算法在每次迭代过程中都进行了50次左右的search,因此bls算法对于非凸优化问题在运行时间上是不占优势的。
不过对于bls算法,我们可以通过对其参数的修改优化其运算性能,比如将 c 设置为: c = 0.5
代码:

import random import numpy as np from scipy.linalg import orth import torch seed = 9999 random.seed(seed) np.random.seed(seed) torch.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed) torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True class Data_Gen(): def __init__(self, N, positive_definite=True): self.N = N # 不变的矩阵 B = np.random.rand(N, 1) # 数据集,数据B矩阵 self.B = torch.tensor(B, dtype=torch.float32) if positive_definite==True: # 正定矩阵的生成, A_ X = np.diag(np.abs(np.random.rand(N))+1) U = orth(np.random.rand(N, N)) A = np.dot(np.dot(U.T, X), U) else: # 非正定矩阵的生成,A M = np.random.rand(N, N) A = np.dot(M.T, M) + 0.01*np.eye(N) self.A = torch.tensor(A, dtype=torch.float32) def data_gen(self, x: torch.FloatTensor): """ 数据生成 """ # 训练数据,x_data, x # x = torch.randn(N, requires_grad=True) N = x.size()[0] assert N==self.N, "向量长度不匹配" # 构建训练数据,非正定数据矩阵生成的y_data y=self.object_fun(self.A, self.B, x) return y def object_fun(self, A: torch.FloatTensor, B: torch.FloatTensor, x: torch.FloatTensor): if x.dim() == 1: x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1) ans = torch.mm(x.T, torch.mm(A, x)) + torch.mm(x.T, B) # print( torch.mm(A, x) ) # print( torch.mm(x.T, torch.mm(A, x)) ) # print( torch.mm(x.T, B) ) return torch.squeeze(ans) ##################################################### # 随机梯度法 def sgd(x: torch.FloatTensor, data_gen: Data_Gen, step=0.00001): # x = torch.randn(N, device="cuda:0", requires_grad=True) y = data_gen.data_gen(x) iter_num = 0 while True: g = torch.autograd.grad(y, x, retain_graph=False, create_graph=False)[0] x.data.add_( -step*g ) y_new = data_gen.data_gen(x) iter_num += 1 print("iter_num: ", iter_num, "y_old: ", y.item(), "y_new: ", y_new.item()) if abs(y_new.item()-y.item()) < 0.00001: break else: y = y_new ##################################################### # 回溯线搜索(Backtracking line search) def bls(x: torch.FloatTensor, data_gen: Data_Gen): iter_num = 0 c = 0.5 beta = 0.8 while True: iter_num += 1 y0 = data_gen.data_gen(x) g = torch.autograd.grad(y0, x, retain_graph=False, create_graph=False)[0] p = -1.0*g # 求最小值,梯度下降,使用负梯度 delta_f = g search_time = 0 alpha_step = 1.0 while True: y_new = data_gen.data_gen(x.detach() + alpha_step*p) y_up = y0 + c*alpha_step*torch.dot(delta_f, p) if y_new.item() > y_up.item(): search_time += 1 alpha_step *= beta else: break x.data.add_( alpha_step*p ) print("iter_num: ", iter_num, "search_time: ", search_time, " y_old: ", y0.item(), "y_new: ", y_new.item()) if abs(y_new.item()-y0.item()) < 0.00001: break if __name__ == '__main__': # 数据生成 N = 500 x = torch.randn(N, requires_grad=True) """ ##################################################### # 对凸二次函数进行求解,正定矩阵,求解最小值 ##################################################### # data_gen = Data_Gen(N) # 随机梯度法 # sgd(x, data_gen) # bls算法 bls(x, data_gen) """ ##################################################### # 对非凸二次函数进行求解,非正定矩阵,求解最小值 ##################################################### data_gen = Data_Gen(N, positive_definite=False) # 随机梯度法 # sgd(x, data_gen) # bls算法 bls(x, data_gen)
运算结果:
iter_num: 3676 search_time: 53 y_old: 29.511341094970703 y_new: 29.50807762145996
iter_num: 3677 search_time: 34 y_old: 29.50807762145996 y_new: 29.432992935180664
iter_num: 3678 search_time: 53 y_old: 29.432992935180664 y_new: 29.379230499267578
iter_num: 3679 search_time: 47 y_old: 29.379230499267578 y_new: 29.374101638793945
iter_num: 3680 search_time: 51 y_old: 29.374101638793945 y_new: 29.368497848510742
iter_num: 3681 search_time: 62 y_old: 29.368497848510742 y_new: 29.3680362701416
iter_num: 3682 search_time: 70 y_old: 29.3680362701416 y_new: 29.367828369140625
iter_num: 3683 search_time: 82 y_old: 29.367828369140625 y_new: 29.367551803588867
iter_num: 3684 search_time: 90 y_old: 29.367551803588867 y_new: 29.367528915405273
iter_num: 3685 search_time: 98 y_old: 29.367528915405273 y_new: 29.367528915405273
将 c 设置为: c = 0.5, 将 beta 设置为:beta=0.1
代码:

import random import numpy as np from scipy.linalg import orth import torch seed = 9999 random.seed(seed) np.random.seed(seed) torch.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed) torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed) torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True class Data_Gen(): def __init__(self, N, positive_definite=True): self.N = N # 不变的矩阵 B = np.random.rand(N, 1) # 数据集,数据B矩阵 self.B = torch.tensor(B, dtype=torch.float32) if positive_definite==True: # 正定矩阵的生成, A_ X = np.diag(np.abs(np.random.rand(N))+1) U = orth(np.random.rand(N, N)) A = np.dot(np.dot(U.T, X), U) else: # 非正定矩阵的生成,A M = np.random.rand(N, N) A = np.dot(M.T, M) + 0.01*np.eye(N) self.A = torch.tensor(A, dtype=torch.float32) def data_gen(self, x: torch.FloatTensor): """ 数据生成 """ # 训练数据,x_data, x # x = torch.randn(N, requires_grad=True) N = x.size()[0] assert N==self.N, "向量长度不匹配" # 构建训练数据,非正定数据矩阵生成的y_data y=self.object_fun(self.A, self.B, x) return y def object_fun(self, A: torch.FloatTensor, B: torch.FloatTensor, x: torch.FloatTensor): if x.dim() == 1: x = torch.unsqueeze(x, 1) ans = torch.mm(x.T, torch.mm(A, x)) + torch.mm(x.T, B) # print( torch.mm(A, x) ) # print( torch.mm(x.T, torch.mm(A, x)) ) # print( torch.mm(x.T, B) ) return torch.squeeze(ans) ##################################################### # 随机梯度法 def sgd(x: torch.FloatTensor, data_gen: Data_Gen, step=0.00001): # x = torch.randn(N, device="cuda:0", requires_grad=True) y = data_gen.data_gen(x) iter_num = 0 while True: g = torch.autograd.grad(y, x, retain_graph=False, create_graph=False)[0] x.data.add_( -step*g ) y_new = data_gen.data_gen(x) iter_num += 1 print("iter_num: ", iter_num, "y_old: ", y.item(), "y_new: ", y_new.item()) if abs(y_new.item()-y.item()) < 0.00001: break else: y = y_new ##################################################### # 回溯线搜索(Backtracking line search) def bls(x: torch.FloatTensor, data_gen: Data_Gen): iter_num = 0 c = 0.5 beta = 0.1 while True: iter_num += 1 y0 = data_gen.data_gen(x) g = torch.autograd.grad(y0, x, retain_graph=False, create_graph=False)[0] p = -1.0*g # 求最小值,梯度下降,使用负梯度 delta_f = g search_time = 0 alpha_step = 1.0 while True: y_new = data_gen.data_gen(x.detach() + alpha_step*p) y_up = y0 + c*alpha_step*torch.dot(delta_f, p) if y_new.item() > y_up.item(): search_time += 1 alpha_step *= beta else: break x.data.add_( alpha_step*p ) print("iter_num: ", iter_num, "search_time: ", search_time, " y_old: ", y0.item(), "y_new: ", y_new.item()) if abs(y_new.item()-y0.item()) < 0.00001: break if __name__ == '__main__': # 数据生成 N = 500 x = torch.randn(N, requires_grad=True) """ ##################################################### # 对凸二次函数进行求解,正定矩阵,求解最小值 ##################################################### # data_gen = Data_Gen(N) # 随机梯度法 # sgd(x, data_gen) # bls算法 bls(x, data_gen) """ ##################################################### # 对非凸二次函数进行求解,非正定矩阵,求解最小值 ##################################################### data_gen = Data_Gen(N, positive_definite=False) # 随机梯度法 # sgd(x, data_gen) # bls算法 bls(x, data_gen)
运算结果:
iter_num: 1838 search_time: 6 y_old: 83.01563262939453 y_new: 82.85948181152344
iter_num: 1839 search_time: 6 y_old: 82.85948181152344 y_new: 82.74000549316406
iter_num: 1840 search_time: 6 y_old: 82.74000549316406 y_new: 82.64784240722656
iter_num: 1841 search_time: 6 y_old: 82.64784240722656 y_new: 82.57584381103516
iter_num: 1842 search_time: 6 y_old: 82.57584381103516 y_new: 82.52399444580078
iter_num: 1843 search_time: 6 y_old: 82.52399444580078 y_new: 82.48124694824219
iter_num: 1844 search_time: 6 y_old: 82.48124694824219 y_new: 82.44764709472656
iter_num: 1845 search_time: 6 y_old: 82.44764709472656 y_new: 82.42279815673828
iter_num: 1846 search_time: 6 y_old: 82.42279815673828 y_new: 82.40233612060547
iter_num: 1847 search_time: 6 y_old: 82.40233612060547 y_new: 82.38795471191406
iter_num: 1848 search_time: 6 y_old: 82.38795471191406 y_new: 82.37630462646484
iter_num: 1849 search_time: 6 y_old: 82.37630462646484 y_new: 82.36550903320312
iter_num: 1850 search_time: 6 y_old: 82.36550903320312 y_new: 82.35576629638672
iter_num: 1851 search_time: 11 y_old: 82.35576629638672 y_new: 82.35576629638672
可以看到,对于非凸优化问题,如果使用bls算法,在追求运算速度的情况下必然要舍弃最终的运算结果性能,而追求运算结果的性能必然要花费大量的运算时间,因此可以说bls算法更适合于凸优化问题,而对于非凸问题,bls算法往往难以得到很好的性能表现。
===================================================
参考:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/590013413
https://blog.csdn.net/jianti9962/article/details/121739041
https://www.cnblogs.com/fstang/p/4192735.html
posted on 2023-06-20 15:19 Angry_Panda 阅读(1326) 评论(0) 收藏 举报





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号