汇编语言实验4 汇编应用编程和c语言程序反汇编分析
四、实验结论
1. 实验任务1
附上源程序代码
1 ; task1.asm 2 assume cs:code, ds:data 3 data segment 4 db 'welcome to masm!', 0 5 color db 2, 24h, 71h ; store color attributes here 6 data ends 7 code segment 8 start: 9 mov ax, data 10 mov ds, ax 11 mov bx, 720h ; 11(line)*160(bytes/line)+32(column)*2(bytes/column) 12 mov cx, 3 ; loop 3 times for 3 lines 13 mov di, 0 ; offset of color attributes in color segment 14 mov si, 0 15 16 s: mov ah, color[di] ; store color attribute in ah, and character in al 17 call print ; print the string at position es:[bx+si] 18 add bx, 0a0h ; switch to next line (+160bytes) 19 inc di ; switch to next color attribute 20 loop s 21 22 mov ah, 4ch 23 int 21h 24 25 print: 26 push es ; push registers so that they can be used in subprogram 27 push dx 28 push di 29 push si 30 push ax 31 mov dx, 0b800h ; video memory 32 mov es, dx 33 mov di, 0 34 35 sprint: mov al, ds:[si] ; store color attribute in ah, and character in al 36 cmp al, 0 ; if string ends, then return 37 je ed 38 mov es:[bx+di], ax ; print the character 39 inc si 40 add di, 2 41 jmp sprint 42 43 ed: pop ax 44 pop si 45 pop di 46 pop dx 47 pop es 48 ret 49 50 code ends 51 end start
附上运行结果截图
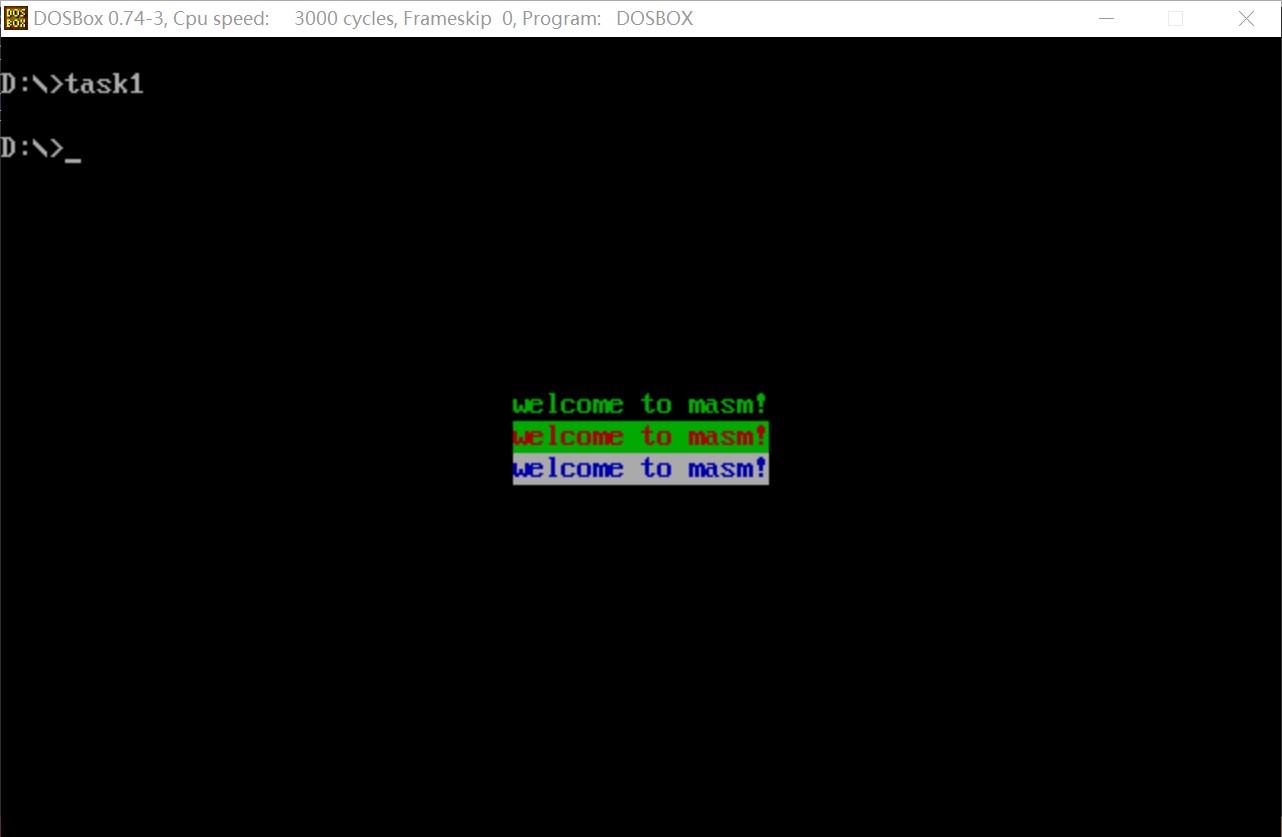
2. 实验任务2
附上源程序代码
1 assume cs:code, ds:data 2 data segment 3 str db 'try', 0 4 data ends 5 6 code segment 7 start: 8 mov ax, data 9 mov ds, ax 10 11 mov si, offset str 12 mov al, 2 13 call printStr 14 15 mov ah, 4ch 16 int 21h 17 18 printStr: 19 push bx 20 push cx 21 push si 22 push di 23 24 mov bx, 0b800H 25 mov es, bx 26 mov di, 0 27 s: mov cl, [si] 28 mov ch, 0 29 jcxz over 30 mov ch, al 31 mov es:[di], cx 32 inc si 33 add di, 2 34 jmp s 35 36 over: pop di 37 pop si 38 pop cx 39 pop bx 40 ret 41 42 code ends 43 end start
附上运行结果截图

修改Line3与Line12后运行结果截图:
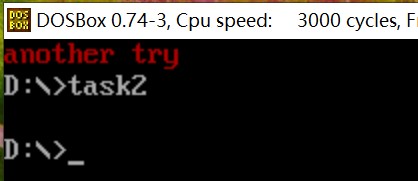
line19-22, line36-39,这组对称使用的push、pop,这样用的目的是什么?
在子程序执行之前将寄存器的数据保存至栈中,子程序执行结束返回之前再将寄存器的数据从栈中恢复,可以保护主程序在栈中存放的数据不被修改。
line30的功能是什么?
将要显示的数据移动至显存区域,以在屏幕上显示。
3. 实验任务3
附上子任务1的反汇编截图
程序运行前首先查看内存,再反汇编
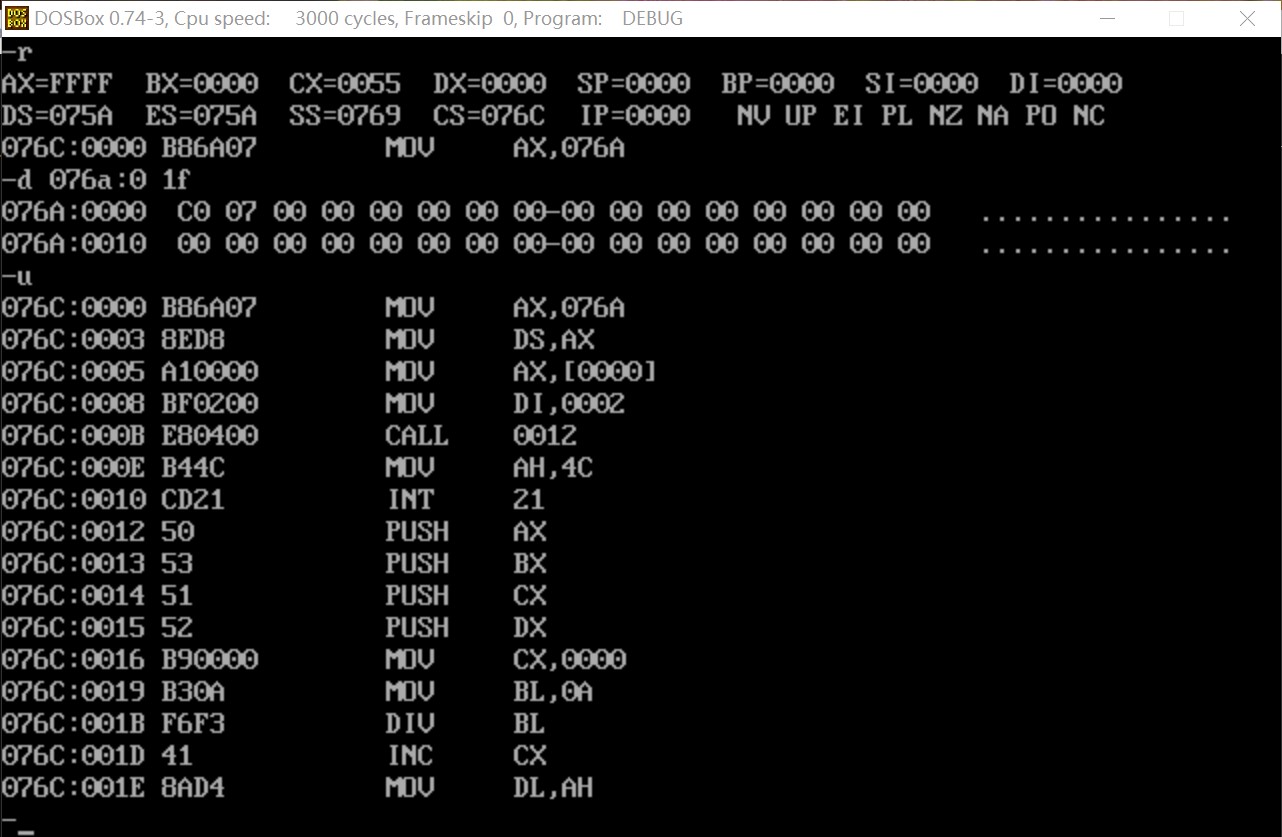
可以看出此时内存中数据为0,程序结束前的指令地址为076c:000e。使用g命令执行至程序结束前
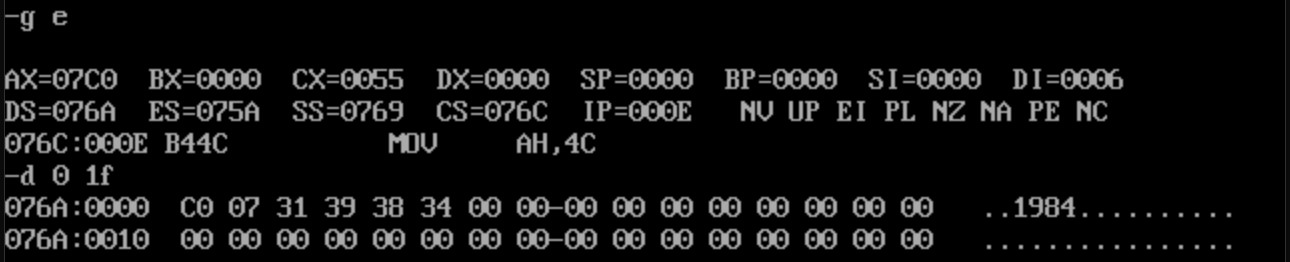
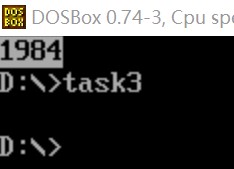
可以看出1984被成功存放在数据段中str标号后面的单元。
附上子任务2修改、完善后的完整汇编源代码,及,运行测试截图
将task2.asm中的printStr添加至task3.asm后
1 assume cs:code, ds:data 2 data segment 3 x dw 1984 4 str db 16 dup(0) 5 data ends 6 7 code segment 8 start: 9 mov ax, data 10 mov ds, ax 11 mov ax, x 12 mov di, offset str 13 call num2str 14 15 mov si, offset str 16 mov al, 70h 17 call printStr 18 19 mov ah, 4ch 20 int 21h 21 22 num2str: 23 push ax 24 push bx 25 push cx 26 push dx 27 28 mov cx, 0 29 mov bl, 10 30 s1: 31 div bl 32 inc cx 33 mov dl, ah 34 push dx 35 mov ah, 0 36 cmp al, 0 37 jne s1 38 s2: 39 pop dx 40 or dl, 30h 41 mov [di], dl 42 inc di 43 loop s2 44 45 pop dx 46 pop cx 47 pop bx 48 pop ax 49 50 ret 51 52 printStr: 53 push bx 54 push cx 55 push si 56 push di 57 58 mov bx, 0b800H 59 mov es, bx 60 mov di, 0 61 s: mov cl, [si] 62 mov ch, 0 63 jcxz over 64 mov ch, al 65 mov es:[di], cx 66 inc si 67 add di, 2 68 jmp s 69 70 over: pop di 71 pop si 72 pop cx 73 pop bx 74 ret 75 code ends 76 end start
运行结果:
4. 实验任务4
附上程序源代码
1 ; task4.asm 2 assume cs:code, ds:data 3 data segment 4 str db 80 dup(?) 5 data ends 6 7 code segment 8 start: 9 mov ax, data 10 mov ds, ax 11 mov si, 0 12 13 s1: 14 mov ah, 1 15 int 21h 16 mov [si], al 17 cmp al, '#' 18 je next 19 inc si 20 jmp s1 21 next: 22 mov cx, si 23 mov si, 0 24 s2: mov ah, 2 25 mov dl, [si] 26 int 21h 27 inc si 28 loop s2 29 30 mov ah, 4ch 31 int 21h 32 code ends 33 end start
附上运行测试截图

line13-20实现的功能是?
从键盘中读取字符存入data segment中,直到遇到'#'结束。
line22-28实现的功能是?
将用户输入的串在屏幕上打印。
5. 实验任务5
1 // task5.c 2 #include <stdio.h> 3 4 int sum(int, int); 5 6 int main() { 7 int a = 2, b = 7, c; 8 c = sum(a, b); 9 return 0; 10 } 11 12 int sum(int x, int y) { 13 return (x + y); 14 }
由于我的电脑上未安装Visual Studio环境,下面使用gcc环境进行反汇编等操作。使用gcc命令进行编译得到task5.o文件,然后使用objdump命令进行反汇编。
(base) PS D:\> gcc -g -c task5.c (base) PS D:\> objdump -d -M intel -S task5.o >> task5.s
使用这种方式得到的.s文件同时包含.c文件源代码以及反汇编指令代码,阅读起来较为方便,使用以下命令同样也可以进行反汇编,但是得到的.s文件仅有反汇编指令代码。
gcc -S task5.c
查看task5.s中的内容
1 task5.o: file format pe-i386 2 3 4 Disassembly of section .text: 5 6 00000000 <_main>: 7 // task5.c 8 #include <stdio.h> 9 10 int sum(int, int); 11 12 int main() { 13 0: 55 push ebp 14 1: 89 e5 mov ebp,esp 15 3: 83 e4 f0 and esp,0xfffffff0 16 6: 83 ec 20 sub esp,0x20 17 9: e8 00 00 00 00 call e <_main+0xe> 18 int a = 2, b = 7, c; 19 e: c7 44 24 1c 02 00 00 mov DWORD PTR [esp+0x1c],0x2 20 15: 00 21 16: c7 44 24 18 07 00 00 mov DWORD PTR [esp+0x18],0x7 22 1d: 00 23 c = sum(a, b); 24 1e: 8b 44 24 18 mov eax,DWORD PTR [esp+0x18] 25 22: 89 44 24 04 mov DWORD PTR [esp+0x4],eax 26 26: 8b 44 24 1c mov eax,DWORD PTR [esp+0x1c] 27 2a: 89 04 24 mov DWORD PTR [esp],eax 28 2d: e8 0b 00 00 00 call 3d <_sum> 29 32: 89 44 24 14 mov DWORD PTR [esp+0x14],eax 30 return 0; 31 36: b8 00 00 00 00 mov eax,0x0 32 } 33 3b: c9 leave 34 3c: c3 ret 35 36 0000003d <_sum>: 37 38 int sum(int x, int y) { 39 3d: 55 push ebp 40 3e: 89 e5 mov ebp,esp 41 return (x + y); 42 40: 8b 55 08 mov edx,DWORD PTR [ebp+0x8] 43 43: 8b 45 0c mov eax,DWORD PTR [ebp+0xc] 44 46: 01 d0 add eax,edx 45 48: 5d pop ebp 46 49: c3 ret 47 4a: 90 nop 48 4b: 90 nop
- 参数传递:Line24-27可以看出在调用sum子函数前,main函数将两个参数放在了栈顶上方,即[esp]与[esp+0x4],在sum子函数里,再从[esp+0x8]与[esp+0xc]处取得。这里猜测是调用sum函数时,将CS与EIP压入了栈中,所以ESP减小了0x8。
- 返回值传递:Line29与Line44可以看出返回值存放在EAX寄存器中。
- 参数顺序:比较Line19-21与Line24-27可以看出,在调用c=sum(a, b)时,b首先被存至栈顶上方一个int处,接着a再被存至栈顶处。所以参数的处理顺序为从右至左。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号