关于三次pta习题总结
前言
前三次作业内容由浅入深,先是对对程序的输入输出、选择还有字符串进行了考察,而后考察了类与对象、还有正则表达式的使用。由于第一次作业比较简单,因此相比后两次数量较多,但是难度较低,后面题目集的难度依次递增,题量依次递减。
1.初学java的体会
刚开始写题目集1的时候,对于java的语法没有一点了解,虽然现在看来非常简单但是对当时的我来说还是有些挑战的,例如,实现输入输出要用到Scanner,但是Scanner是如何工作的呢?一点都不知道。根据C语言的语法,输出hello word只需要printf("hello word");因此我们可以暂且不管Scanner是否是如何工作的,照葫芦画瓢,将Scanner.out.print类比C语言中的printf;输出hello word只需Scanner.out.print("hello word");
之后学习java,将java中的语法与类比C语言中的语法。刚开始非常不适应Java的语法,在编写程序的时候总是下意识的写成C语言,但是写完这些题目,开始逐渐适应java语言。
2.三次作业遇到的问题
题目集1比较简单,几乎没有遇到什么问题,就是对java的语法很不了解,几乎都是将C语言中的语法套用在这里;因此在编码时总是不经意写成C语言。而第二次题目集相对较难,考察了类与对象;刚开始了解类的时候,很容易联想到C语言中的结构体,类里面多加了一个函数(中的方法);第三次题目集考到正则表达式,我在这里第三题卡了很久,因为写出来的正则表达式总是或多或少有些不符合题意,离提交的时间越来越近,于是没有在继续卡在这里接着去完成下面的内容。更令我烦恼的是,我写了好久的代码突然发现完全是错的,思路完全错误。这个时候是感到很颓废的,看着同学都差不多写好了,而我在这里卡了这么久,本来打算就这样的,及格就行了。之后的几天里我没有碰过一下第三题,但最后我还是继续写了下去,因为我很不服气,凭什么我就会写错,别人就能写好。于是就又开始学呀,写呀......虽然最后成绩也不高,但是我似乎知道java该怎么学了,这个过程却是很难过,但是当你千辛万苦写出的代码通过了测试点,哪怕是一个测试点,都会感到很满足,有些成就在里面。
2.设计与分析
接下来就进入正题了,分别对题目集1的7-8,题目集2的7-4,7-5以及题目集3的7-2,7-3进行解释分析
7-8 判断三角形类型
输入格式:
在一行中输入三角形的三条边的值(实型数),可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔,其中三条边的取值范围均为[1,200]。
输出格式:
(1)如果输入数据非法,则输出“Wrong Format”; (2)如果输入数据合法,但三条边不能构成三角形,则输出“Not a triangle”; (3)如果输入数据合法且能够成等边三角形,则输出“Equilateral triangle”; (3)如果输入数据合法且能够成等腰直角三角形,则输出“Isosceles right-angled triangle”; (5)如果输入数据合法且能够成等腰三角形,则输出“Isosceles triangle”; (6)如果输入数据合法且能够成直角三角形,则输出“Right-angled triangle”; (7)如果输入数据合法且能够成一般三角形,则输出“General triangle”。
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 public class Text178 { 3 public static void main(String[] args){ 4 Scanner input = new Scanner (System.in); 5 double a = input.nextDouble(); 6 double b = input.nextDouble(); 7 double c = input.nextDouble(); 8 if(a<1||a>200||b<1||b>200||c<1||c>200) 9 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 10 else if(a+b<=c||a+c<=b||b+c<=a||a-b>=c||a-c>=b||b-c>=a||b-a>=c||c-a>=b||c-b>=a) 11 System.out.println("Not a triangle"); 12 else if(a==b||b==c||a==c){ 13 if(a==b&&a==c) 14 System.out.println("Equilateral triangle"); 15 else if(a*a+b*b-c*c < 0.0000001||a*a+c*c-b*b < 0.0000001||b*b+c*c-a*a < 0.0000001) 16 System.out.println("Isosceles right-angled triangle"); 17 else if(a==b||a==c||b==c) 18 System.out.println("Isosceles triangle"); 19 } 20 else if(a*a+b*b==c*c||b*b+c*c==a*a||a*a+c*c==b*b) 21 System.out.println("Right-angled triangle"); 22 else 23 System.out.println("General triangle"); 24 25 } 26 }
在判断直角时,有一点要注意
a*a+b*b == c*c//第15行不能这么写
类图
只有一个类
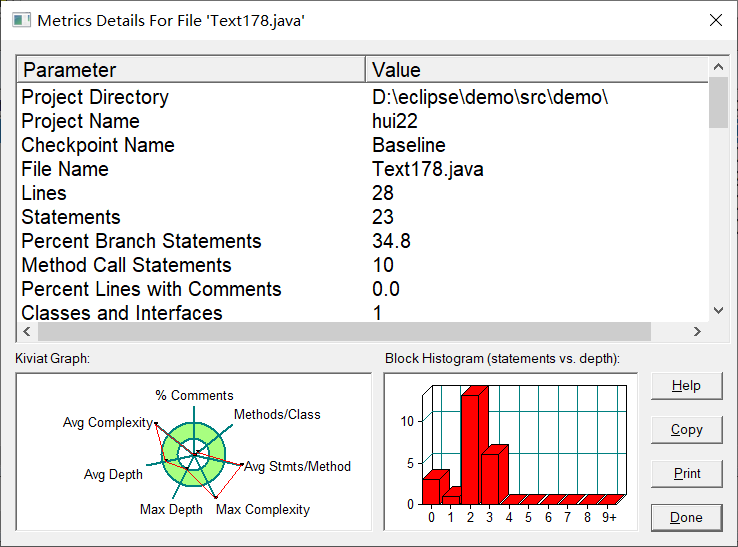
复杂度
7-4 求下一天
输入年月日的值(均为整型数),输出该日期的下一天。 其中:年份的合法取值范围为[1820,2020] ,月份合法取值范围为[1,12] ,日期合法取值范围为[1,31] 。 注意:不允许使用Java中和日期相关的类和方法。
要求:Main类中必须含有如下方法,签名如下:
public static void main(String[] args);//主方法
public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) ;//判断year是否为闰年,返回boolean类型
public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day);//判断输入日期是否合法,返回布尔值
public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day) ; //求输入日期的下一天输入格式:
在一行内输入年月日的值,均为整型数,可以用一到多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
- 当输入数据非法及输入日期不存在时,输出“Wrong Format”;
- 当输入日期合法,输出下一天,格式如下:Next date is:年-月-日
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main{ 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); 6 int y=input.nextInt(); 7 int m=input.nextInt(); 8 int d=input.nextInt(); 9 if(checkInputValidity(y,m,d)){ 10 nextDate(y,m,d); 11 } 12 else{ 13 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 14 } 15 } 16 17 public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) { 18 if(year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0){ 19 return true; 20 } 21 else{ 22 return false; 23 } 24 } 25 public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day){ 26 if(year>=1820&&year<=2020&&month>=1&&month<=12&&day>=1&&day<=31){ 27 if(month==1||month==3||month==5||month==7||month==8||month==10||month==12){ 28 return true; 29 } 30 else if(month==2){ 31 if(isLeapYear(year)){ 32 if(day==31||day==30){ 33 return false; 34 } 35 else{ 36 return true; 37 } 38 } 39 else{ 40 if(day==31||day==30||day==29){ 41 return false; 42 } 43 else{ 44 return true; 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 else{ 49 if(day==31){ 50 return false; 51 } 52 else{ 53 return true; 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 else{ 58 return false; 59 } 60 } 61 public static void nextDate(int year,int month,int day){ 62 day++; 63 if(checkInputValidity(year,month,day)){ 64 System.out.print("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 65 } 66 else{ 67 day=1; 68 if(month==12){ 69 month=1; 70 year++; 71 } 72 else{ 73 month++; 74 } 75 System.out.print("Next date is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 76 } 77 } 78 }
这里要注意的是在求下一天的时候也要进行合法判断,在快要完成题目的时候一定要保持应有的冷静
下面是类图
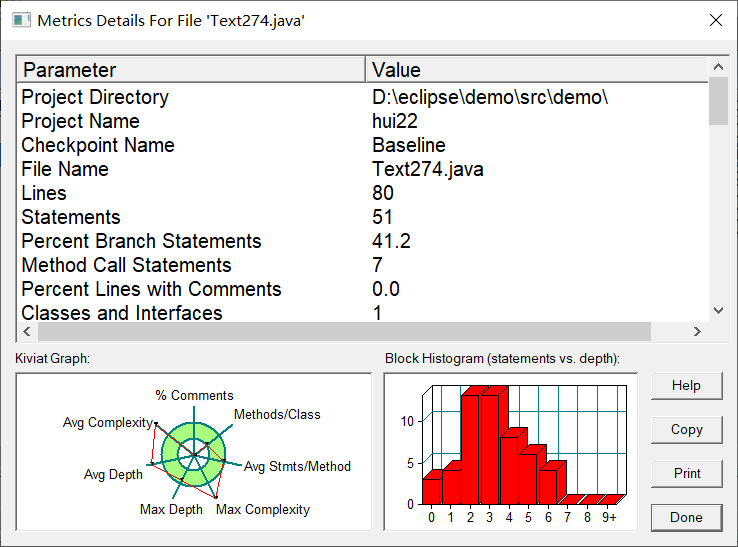
复杂度
输入年月日的值(均为整型数),同时输入一个取值范围在[-10,10] 之间的整型数n,输出该日期的前n天(当n > 0时)、该日期的后n天(当n<0时)。
其中年份取值范围为 [1820,2020] ,月份取值范围为[1,12] ,日期取值范围为[1,31] 。
注意:不允许使用Java中任何与日期有关的类或方法。
输入格式:
在一行中输入年月日的值以及n的值,可以用一个或多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
- 当输入的年、月、日以及n的值非法时,输出“Wrong Format”;
- 当输入数据合法时,输出“n days ago is:年-月-日”
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main{ 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); 6 int y=input.nextInt(); 7 int m=input.nextInt(); 8 int d=input.nextInt(); 9 int n=input.nextInt(); 10 if(checkInputValidity(y,m,d,n)){ 11 nextNDate(y,m,d,n); 12 } 13 else{ 14 System.out.print("Wrong Format"); 15 } 16 } 17 18 public static boolean isLeapYear(int year) { 19 if(year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0){ 20 return true; 21 } 22 else{ 23 return false; 24 } 25 } 26 public static boolean checkInputValidity(int year,int month,int day,int n){ 27 if(year>=1820&&year<=2020&&month>=1&&month<=12&&day>=1&&day<=31&&n>=-10&&n<=10){ 28 if(month==1||month==3||month==5||month==7||month==8||month==10||month==12){ 29 return true; 30 } 31 else if(month==2){ 32 if(isLeapYear(year)){ 33 if(day==31||day==30){ 34 return false; 35 } 36 else{ 37 return true; 38 } 39 } 40 else{ 41 if(day==31||day==30||day==29){ 42 return false; 43 } 44 else{ 45 return true; 46 } 47 } 48 } 49 else{ 50 if(day==31){ 51 return false; 52 } 53 else{ 54 return true; 55 } 56 } 57 } 58 else{ 59 return false; 60 } 61 } 62 public static void nextNDate(int year,int month,int day,int n){ 63 if(checkInputValidity(year,month,day-n,n)){//n等于0时; 64 System.out.print(n+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+(day-n)); 65 } 66 else{ 67 if(n>0){ 68 if(month==1){ 69 year-=1; 70 month=12; 71 day=31+(day-n); 72 } 73 else if(month==3){ 74 if(isLeapYear(year)){ 75 month=2; 76 day=29+(day-n); 77 } 78 else{ 79 month=2; 80 day=28+(day-n); 81 } 82 } 83 else if(month==2||month==4||month==6||month==8||month==9||month==11){ 84 month-=1; 85 day=31+(day-n); 86 } 87 else{ 88 month-=1; 89 day=30+(day-n); 90 } 91 } 92 else if(n<0){ 93 if(month==12){ 94 year+=1; 95 month=1; 96 day=day-n-31; 97 } 98 else if(month==2){ 99 month+=1; 100 if(isLeapYear(year)){ 101 day=(day-n)-29; 102 } 103 else{ 104 day=(day-n)-28; 105 } 106 } 107 else if(month==1||month==3||month==5||month==7||month==8||month==10){ 108 month+=1; 109 day=day-n-31; 110 } 111 else{ 112 month+=1; 113 day=day-n-30; 114 } 115 } 116 System.out.print(n+" days ago is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 117 } 118 } 119 }
类图
复杂度
题目集3,难度有所提升,期限为10天,建议提早做作业
定义一个类Date,包含三个私有属性年(year)、月(month)、日(day),均为整型数,其中:年份的合法取值范围为[1900,2000] ,月份合法取值范围为[1,12] ,日期合法取值范围为[1,31] 。 注意:不允许使用Java中和日期相关的类和方法,否则按0分处理。
要求:Date类结构如下图所示:
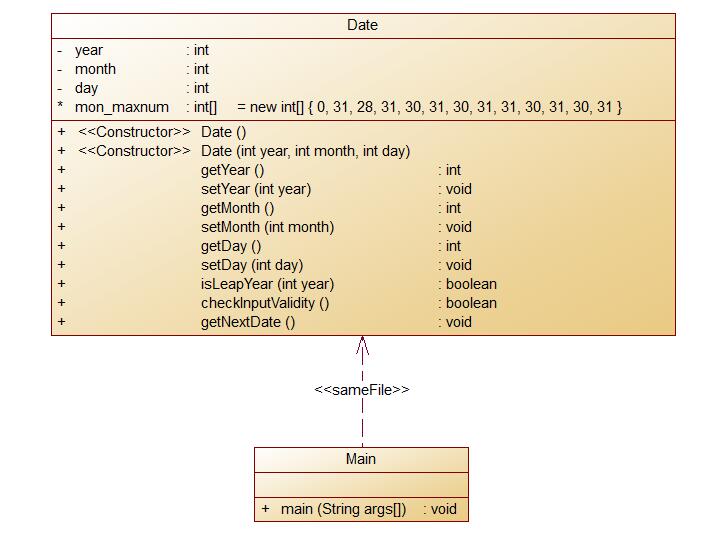
输入格式:
在一行内输入年月日的值,均为整型数,可以用一到多个空格或回车分隔。
输出格式:
- 当输入数据非法及输入日期不存在时,输出“Date Format is Wrong”;
- 当输入日期合法,输出下一天,格式如下:Next day is:年-月-日
1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class Main{ 4 public static void main(String[] args){ 5 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in); 6 int y=input.nextInt(); 7 int m=input.nextInt(); 8 int d=input.nextInt(); 9 Date date = new Date(y,m,d); 10 if(date.checkInputValidity()){ 11 date.nextDate(); 12 } 13 else{ 14 System.out.print("Date Format is Wrong"); 15 } 16 } 17 18 } 19 class Date{ 20 private int year; 21 private int month; 22 private int day; 23 public Date() { 24 } 25 public Date(int year,int month,int day) { 26 this.month = month; 27 this.day = day; 28 this.year = year; 29 } 30 public boolean checkInputValidity(){ 31 if(year>=1900&&year<=2000&&month>=1&&month<=12&&day>=1&&day<=31){ 32 if(month==1||month==3||month==5||month==7||month==8||month==10||month==12){ 33 return true; 34 } 35 else if(month==2){ 36 if(isLeapYear()){ 37 if(day==31||day==30){ 38 return false; 39 } 40 else{ 41 return true; 42 } 43 } 44 else{ 45 if(day==31||day==30||day==29){ 46 return false; 47 } 48 else{ 49 return true; 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 else{ 54 if(day==31){ 55 return false; 56 } 57 else{ 58 return true; 59 } 60 } 61 } 62 else{ 63 return false; 64 } 65 } 66 //判断是否合法 67 public void nextDate(){ 68 day++; 69 if(checkInputValidity()){ 70 System.out.print("Next day is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 71 } 72 else{ 73 day=1; 74 if(month==12){ 75 month=1; 76 year++; 77 } 78 else{ 79 month++; 80 } 81 System.out.print("Next day is:"+year+"-"+month+"-"+day); 82 } 83 } 84 public boolean isLeapYear() { 85 if(year%4==0&&year%100!=0||year%400==0){ 86 return true; 87 } 88 else{ 89 return false; 90 } 91 } 92 }
类图
复杂度




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号