剑指offer系列——15.反转链表 i-ii
Q:输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出新链表的表头。
C:时间限制:C/C++ 1秒,其他语言2秒 空间限制:C/C++ 32M,其他语言64M
T:
1.常规的反转链表方法
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
ListNode *temp = pHead;
ListNode *target = temp;
if (pHead == nullptr)
return pHead;
while (pHead->next != nullptr) {
temp = pHead->next;
pHead->next = temp->next;
temp->next = target;
target = temp;
}
return target;
}
2.递归:递归的方法其实是非常巧的,它利用递归走到链表的末端,然后再更新每一个node的next 值 ,实现链表的反转。而newhead 的值没有发生改变,为该链表的最后一个结点,所以,反转后,我们可以得到新链表的head.
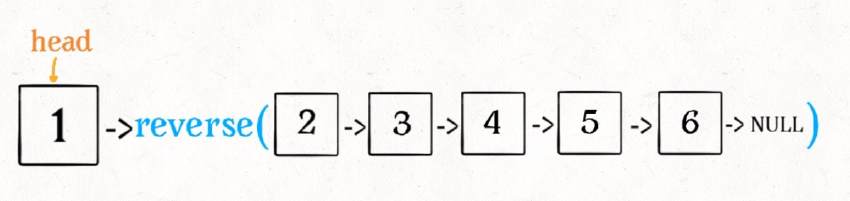
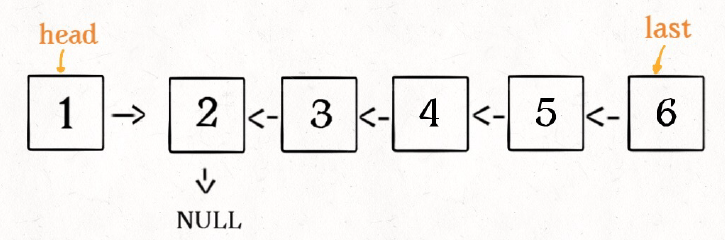
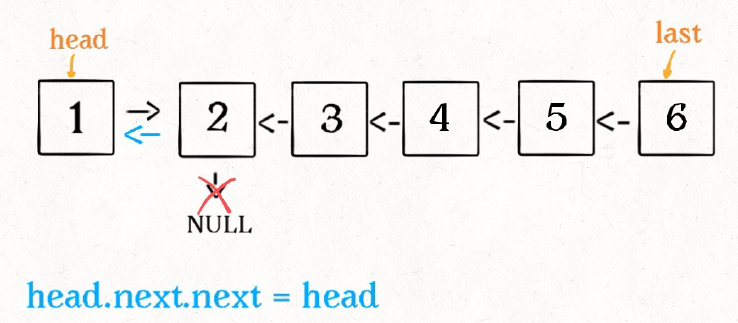
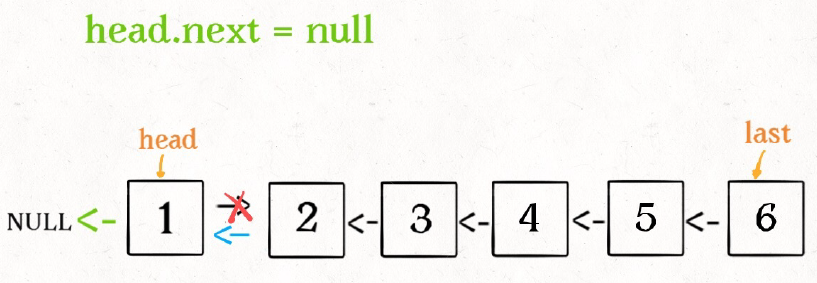
ListNode *ReverseList(ListNode *pHead){
if(pHead == nullptr || pHead->next == nullptr)
return pHead;
ListNode* target = ReverseList(pHead->next);
pHead->next->next = pHead;
pHead->next = nullptr;
return target;
}
3.利用栈:
ListNode* ReverseList(ListNode* pHead) {
stack<int> s;
ListNode* target = pHead;
while(target){
int temp = target->val;
s.push(temp);
target = target->next;
}
target = pHead;
while(!s.empty()){
int t = s.top();
s.pop();
target->val = t;
target = target->next;
}
return pHead;
}
Q:将一个链表m位置到n位置之间的区间反转,要求使用原地算法,并且在一次扫描之内完成反转。
例如:
给出的链表为1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2 ,n = 4,
返回1->4->3->2->5->NULL.
注意:
给出的m,n满足以下条件:
1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 链表长度
A:
1.添加头结点
2.记得记录当前节点前面的那个节点,所以应该分为三个节点:当前节点,当前节点前节点,当前节点后节点。如果不记录前节点,那就断了以后重连。
//断了重连的,很麻烦
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
if (head == null || head.next == null)
return head;
ListNode head0 = new ListNode(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
head0.next = head;
ListNode node = head0;
for (int i = 0; i < m - 1; i++) {
node = node.next;
}
ListNode node1 = node.next;
node.next = null;
ListNode node2 = node1;
for (int j = 0; j < n - m + 1; j++) {
node2 = node1.next;
node1.next = node.next;
node.next = node1;
node1 = node2;
}
while (node.next != null) {
node = node.next;
}
node.next = node2;
return head0.next;
}
//添加前节点的
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode preStart = dummy;
ListNode start = head;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i ++ ) {
preStart = start;
start = start.next;
}
// reverse
for (int i = 0; i < n - m; i ++ ) {
ListNode temp = start.next;
start.next = temp.next;
temp.next = preStart.next;
preStart.next = temp;
}
return dummy.next;
}
使用递归来做:
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
if (m == 1){
return reverseN(head, n);//翻转前N个
}
head.next = reverseBetween(head.next, m - 1, n - 1);
return head;
}
ListNode nextNode = null;
private ListNode reverseN(ListNode head, int n) {
if (n == 1) {
nextNode = head.next;
return head;
}
ListNode last = reverseN(head.next, n - 1);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = nextNode;
return last;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号