Codeforces Round #852(Div. 2)
A
核心思路
这个过程还是有点绕的,但是想清楚了很简单。首先把那m+1捆在一起买,然后看还剩下多少。乘上a和b的最小值就好了。
// Problem: A. Yet Another Promotion
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round #852 (Div. 2)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/contest/1793/problem/0
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define IOS std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define NO {puts("NO") ; return ;}
#define YES {puts("YES") ; return ;}
#define endl "\n"
#define int long long
void solve()
{
int a,b,cnt,m;
cin>>a>>b>>cnt>>m;
int ans1=cnt*b;
int x=(cnt)/(m+1);
//cout<<x<<endl;
int ans2=a*m*x+(cnt-(m+1)*x)*min(a,b);
cout<<min(ans1,ans2)<<endl;
return;
}
signed main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
}
B
核心思路
就按照递增构造就好了,然后碰到我们想要的值就拐弯就好了。但是需要注意的是一定要选好我们构造的数列的起点。
// Problem: B. Fedya and Array
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round #852 (Div. 2)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/contest/1793/problem/B
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define IOS std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define NO {puts("NO") ; return ;}
#define YES {puts("YES") ; return ;}
#define endl "\n"
#define int long long
void solve()
{
int x,y;
cin>>x>>y;
vector<int> ans;
int start=y+1;
for(int i=start;i<=x;i++)
{
ans.push_back(i);
}
for(int i=x-1;i>=y;i--)
ans.push_back(i);
for(int i=y+1;i<start;i++)
ans.push_back(i);
cout<<ans.size()<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<ans.size();i++)
cout<<ans[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
}
signed main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
}
C
这个题目咋一看是线段树,但是其实利用好性质就方便解题了。因为我们排列有那么一个性质就是我们可以很方便的知道一个排列的最大值和最小值。
所以这个题目我们可以采用双指针,最开始我们排列的最大值和最小值肯定是1和n。如果这个值是最大值或者最小值那么就把我们指针做出相应的移动。
这个做法还是很巧妙的。
// Problem: C. Dora and Search
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round #852 (Div. 2)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/contest/1793/problem/C
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 1000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define IOS std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define NO {puts("NO") ; return ;}
#define YES {puts("YES") ; return ;}
#define endl "\n"
#define int long long
void solve()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int> a(n+1);
int mx=-0x3f3f3f3f;
int mn=0x3f3f3f3f;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
cin>>a[i];
mn=1,mx=n;
int l=1,r=n;
while(l<r)
{
if(a[l]==mx)
{
l++;
mx--;
}
else if(a[l]==mn)
{
l++;
mn++;
}
else if(a[r]==mx)
{
r--;
mx--;
}
else if(a[r]==mn)
{
mn++;
r--;
}
else
{
cout<<l<<" "<<r<<endl;
return;
}
}
cout<<-1<<endl;
}
signed main()
{
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
}
D
核心思路
其实类似于这种mex的题目,我们需要采取从底部往上面的构造方式,也就是\(1,2,3,....n\).的方式。首先想下怎么样可以构造出来1,由图可知。
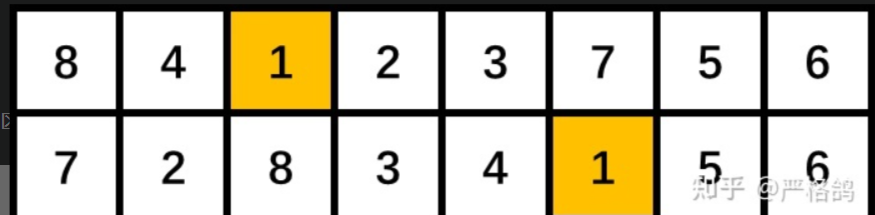
我们肯定是不可以选择包含1的部分的,所以也就是有了三部分的可选择位置,对于每一部分使用排列组合公式就好了。
接下来就是mex=2的情况。
这种情况的不同之处在于我们需要选择包含了一的区间。
我们把pa作为a数组里面2的位置,pb作为b数组里面2的位置。
L和R表示的是我们1的一个位置。
于是就有了一下几组分类情况。
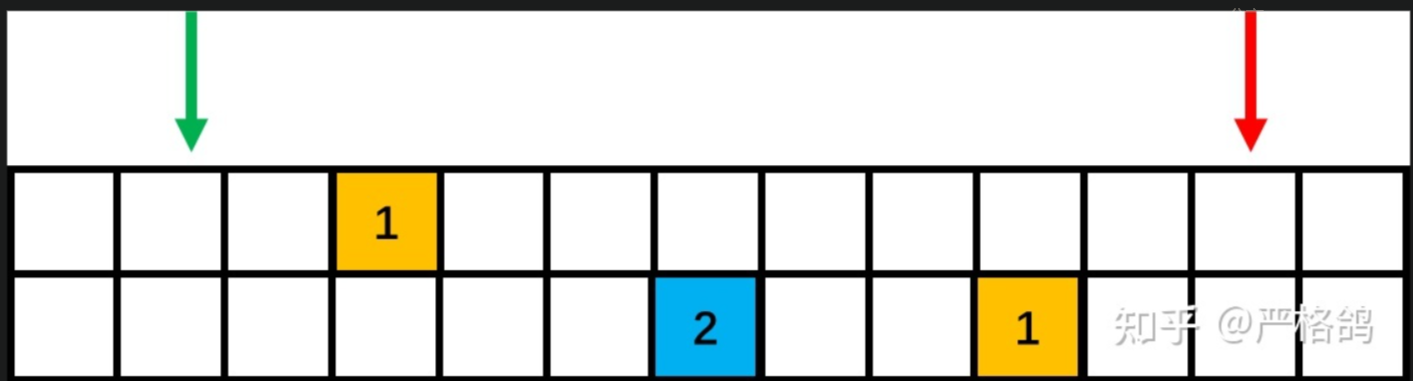
首先这种情况是肯定不可以的,因为其实我们是需要取a里面包含1的区间和b里面包含1的区间一个并值,a和b区间的端点就是我们选择的那个点。但是这样是肯定是取到2的。所以是不可以取的。
接下来就是pb<L
也就是pb和pa都在L的左侧的情况。
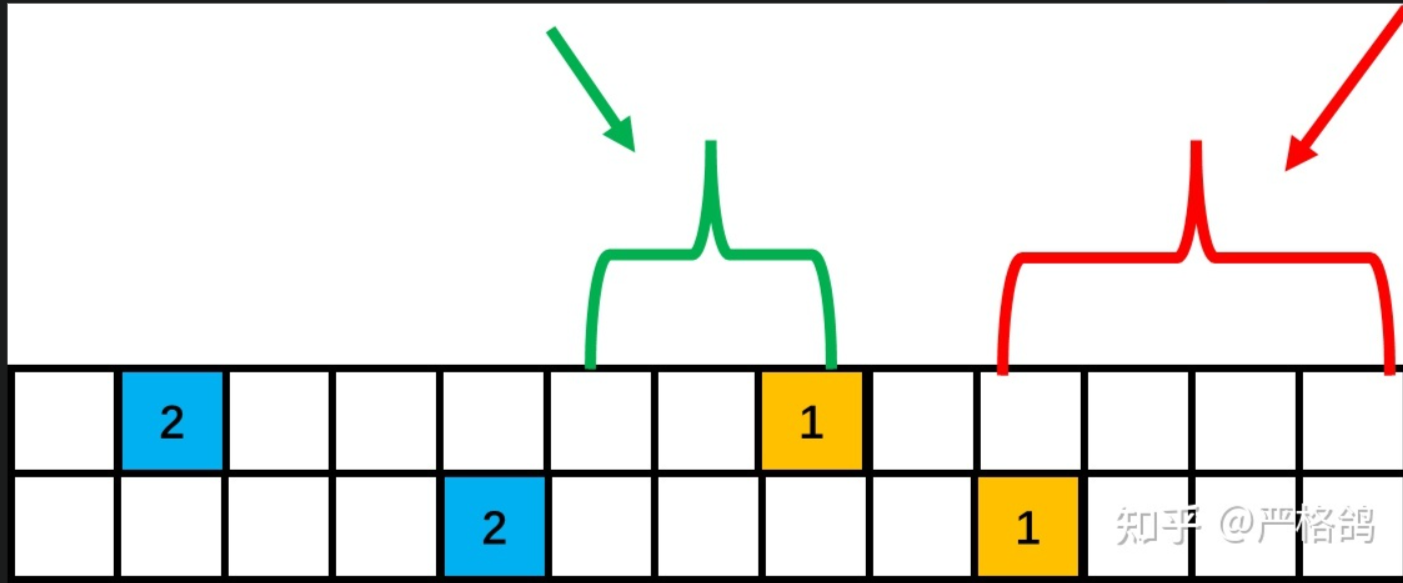
这里可能会有疑惑:为什么中间那段不需要考虑呢,其实中间那段的贡献是1,也就是取L这个点,但是这种情况已经枚举过了,所以不需要考虑了。一定要仔细看下上面的黄字。
还有一种情况就是都在右边的情况,和上面是一样的。
最后一种是\(pa\le L\le R \le pb\)
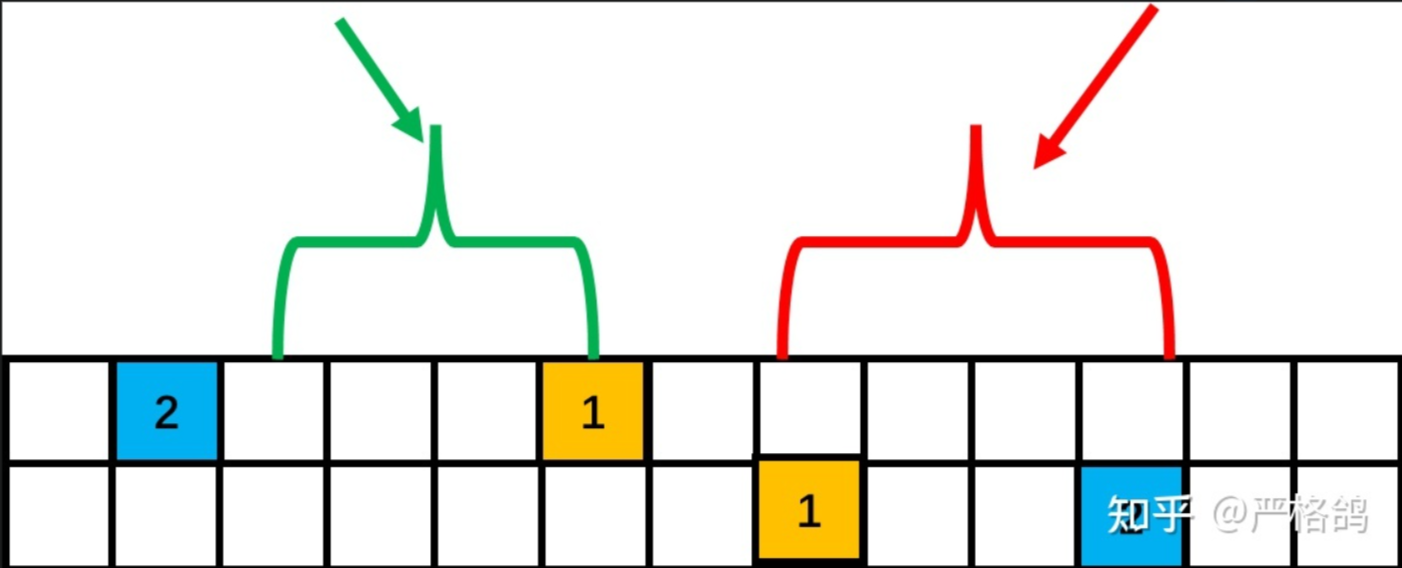
也比较好分析。
一定要注意考虑边界问题。也就是区间长度需不需要加1.
// Problem: D. Moscow Gorillas
// Contest: Codeforces - Codeforces Round #852 (Div. 2)
// URL: https://codeforces.com/contest/1793/problem/D
// Memory Limit: 256 MB
// Time Limit: 2000 ms
//
// Powered by CP Editor (https://cpeditor.org)
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
#define IOS std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0)
#define NO {puts("NO") ; return ;}
#define YES {puts("YES") ; return ;}
#define endl "\n"
#define int long long
const int N=1e6+10;
int pos_a[N],pos_b[N];
void solve()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<int> a(n+1);
vector<int> b(n+1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>a[i];
pos_a[a[i]]=i;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>b[i];
pos_b[b[i]]=i;
}
auto C2=[](int n) {return n*(n+1)/2;};
int L=min(pos_a[1],pos_b[1]);
int R=max(pos_a[1],pos_b[1]);
int ans=0;
ans+=C2(L-1)+C2(max(0ll,R-L-1))+C2(n-R);
for(int mex=2;mex<=n;mex++)
{
int pa=pos_a[mex];
int pb=pos_b[mex];
if(pa>pb)
swap(pa,pb);
if(pa>=L&&pa<=R||pb>=L&&pb<=R)
{}
else if(pb<L)
{
ans+=-(pb-L)*(n-R+1);
}
else if(pa>R)
{
ans+=(L)*(pa-R);
}
else if(pa<=L&&pb>=R)
{
ans+=(L-pa)*(pb-R);
}
L=min(L,pa);
R=max(R,pb);
}
cout<<ans+1<<endl;
}
signed main()
{
int T;
T=1;
while(T--)
{
solve();
}
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号