Java题目集7-9的总结
一、前言
本次的java学习仍是 3 次题目集,题量减少,难度加大
① 题目集七只有 2 道题,题量少,主要考察继承,多态,接口的应用以及ArrayList泛型的应用方法
② 题目集八只有一道题,但难度较大,考察了类与类之间的调用以及迭代器遍历集合

③ 题目集九也只有一道题,是在题目集八的基础上添加一个功能,考察了继承的应用和对类之间关系的分析

二、题目分析及设计
(1) 图形卡片设计(题目集七(7-1)、(7-2)))
题目描述:为学生所玩的游戏提供正确答案的功能,即根据学生得到的卡片种类与数量,给出 排序前和排序后的卡片顺序,同时给出所有卡片的面积之和 。
题目分析:计算面积并进行排序,需要利用 Comparable 接口中的 CompareTo()方法进行排序。
代码设计: 在之前的题目集写过类似的题目,这道题类结构也与之前的一样,只是排序必须是类排序,根据给出的提示利用compareto对类进行排序,需要解决的就是类排序,直接放代码
1 class DealCardList{ 2 3 ArrayList<Card> cardList= new ArrayList<Card>(); 4 5 public DealCardList() { 6 super(); 7 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 8 } 9 10 public DealCardList(ArrayList<Integer> list) { // 数据读入 11 for(Integer a : list) { 12 if( a==0 ) break; 13 switch(a) { 14 case 1 : 15 Card card1 = new Card(new Circle(Main.input.nextDouble())); 16 card1.getShape().setShapeName("Circle"); 17 if(card1.getShape().validate()) { 18 cardList.add(card1); 19 } 20 else{ 21 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 22 break; 23 } 24 break; 25 case 2 : 26 Card card2 = new Card(new Rectangle(Main.input.nextDouble(),Main.input.nextDouble())); 27 card2.getShape().setShapeName("Rectangle"); 28 if(card2.getShape().validate()) { 29 cardList.add(card2); 30 } 31 else{ 32 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 33 break; 34 } 35 break; 36 case 3: 37 Card card3 = new Card(new Triangle(Main.input.nextDouble(),Main.input.nextDouble(),Main.input.nextDouble())); 38 card3.getShape().setShapeName("Triangle"); 39 if(card3.getShape().validate()) { 40 cardList.add(card3); 41 } 42 else{ 43 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 44 break; 45 } 46 break; 47 case 4: 48 Card card4 = new Card(new Trapezoid(Main.input.nextDouble(),Main.input.nextDouble(),Main.input.nextDouble())); 49 card4.getShape().setShapeName("Trapezoid"); 50 if(card4.getShape().validate()) { 51 cardList.add(card4); 52 // System.out.println("ww "+ card4.getShape().getArea() ); 53 } 54 else{ 55 System.out.println("Wrong Format"); 56 break; 57 } 58 break; 59 } 60 } 61 62 } 63 64 public boolean validate(){ //合法性 65 for (Card c : cardList) { 66 if (!c.getShape().validate()){ 67 return false; 68 } 69 if (!c.getShape().validate()){ 70 break; 71 } 72 } 73 return true; 74 } 75 76 public void cardSort(){ 77 Collections.sort(cardList, new Comparator<Card>(){ //进行排序 78 public int compare(Card user1, Card user2) { 79 Integer id1 = (int) user1.getShape().getArea(); 80 Integer id2 = (int) user2.getShape().getArea(); 81 return id2.compareTo(id1);} 82 }); 83 } 84 85 public double getAllArea(){ // 总面积 86 double sum=0; 87 for (Card card : cardList) { 88 sum+=card.getShape().getArea(); 89 } 90 return sum; 91 } 92 93 public void showResult(){ 94 System.out.println("The original list:"); 95 for (Card card : cardList) { 96 System.out.print(card.getShape()); 97 } 98 System.out.println(); 99 System.out.println("The sorted list:"); 100 cardSort(); 101 for (Card card : cardList) { 102 System.out.print(card.getShape()); 103 } 104 System.out.println(); 105 System.out.printf("Sum of area:%.2f\n",getAllArea()); 106 } 107 108 } 109 110 class Card implements Comparable<Card>{ 111 112 Shape shape; 113 114 public Card() { 115 } 116 117 public Card(Shape shape) { 118 this.shape = shape; 119 } 120 121 public Shape getShape() { 122 return shape; 123 } 124 125 public void setShape(Shape shape) { 126 this.shape = shape; 127 } 128 129 @Override 130 public int compareTo(Card card) { 131 return -(int)(shape.getArea()-card.getShape().getArea()); 132 } 133 }
从代码中可以看到card类实现了Comparable接口,里面实现了compareTo方法。这样我们可以通过比较对象中的area属性进行排序
附上该方法API描述:
compareTo
int compareTo(T o)
比较此对象与指定对象的顺序。如果该对象小于、等于或大于指定对象,则分别返回负整数、零或正整数。
如果没有实现Comparable接口的话,我们也可以我们可以建立一个“比较器”来进行排序。这个“比较器”只需要实现Comparator接口即可
1 Collections.sort(cardList, new Comparator<Card>(){ //进行排序 2 public int compare(Card user1, Card user2) { 3 Integer id1 = (int) user1.getShape().getArea(); 4 Integer id2 = (int) user2.getShape().getArea(); 5 return id2.compareTo(id1);} 6 });
这样我们也可以可以通过比较对象中的area属性进行排序。
题7-1和7-2都需要用到上述方法,不同的是题7-2增加了分类排序,需要我们多设置几个“比较器”完成分类比较,其余类的设计两道题目都是一样的
1 ublic void circleSort(){ 2 Collections.sort(circlesort, new Comparator<Card>(){ //进行排序 3 public int compare(Card user1, Card user2) { 4 Integer id1 = (int) user1.getShape().getArea(); 5 Integer id2 = (int) user2.getShape().getArea(); 6 return id2.compareTo(id1);} 7 }); } 8 public void recSort(){ 9 Collections.sort(rectanglesort, new Comparator<Card>(){ //进行排序 10 public int compare(Card user1, Card user2) { 11 Integer id1 = (int) user1.getShape().getArea(); Integer id2 = (int) user2.getShape().getArea(); 12 return id2.compareTo(id1);} 13 }); } 14 public void triSort(){ 15 Collections.sort(trianglesort, new Comparator<Card>(){ //进行排序 16 public int compare(Card user1, Card user2) { 17 Integer id1 = (int) user1.getShape().getArea(); Integer id2 = (int) user2.getShape().getArea(); 18 return id2.compareTo(id1);} 19 }); } 20 public void traSort(){ 21 Collections.sort(trapezoidsort, new Comparator<Card>(){ //进行排序 22 public int compare(Card user1, Card user2) { 23 Integer id1 = (int) user1.getShape().getArea(); Integer id2 = (int) user2.getShape().getArea(); return id2.compareTo(id1);} 24 }); }
(2)ATM机类结构设计(题目集八、题目集九)
题目描述:编写一个银行 ATM 机的模拟程序,能够完成用户的存款、取款以及查询余额功能。
题目分析:实现取款功能,个人账户信息的存储和查询
代码设计: 本次题目难度较大需要解决的问题比较多,比如每个类之间的关系,如何存储个人账户信息,读取时又如何返回相应的信息。思考良久后决定了用以下方法进行信息存储
1 public static void main(String[] args) { 2 Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in); 3 4 ArrayList<User> list = new ArrayList<User>(); 5 6 list.add(new User("杨过",new Bank("中国建设银行",new ArrayList<Card>()))); 7 list.add(new User("郭靖",new Bank("中国建设银行",new ArrayList<Card>()))); 8 list.add(new User("张无忌",new Bank("中国工商银行",new ArrayList<Card>()))); 9 list.add(new User("韦小宝",new Bank("中国工商银行",new ArrayList<Card>()))); 10 11 list.get(0).getBank().getList().add(new Card("6217000010041315709")); 12 list.get(0).getBank().getList().add(new Card("6217000010041315715")); 13 list.get(0).getBank().getList().add(new Card("6217000010041315718")); 14 15 list.get(1).getBank().getList().add(new Card("6217000010051320007")); 16 17 list.get(2).getBank().getList().add(new Card("6222081502001312389")); 18 list.get(2).getBank().getList().add(new Card("6222081502001312390")); 19 list.get(2).getBank().getList().add(new Card("6222081502001312399")); 20 list.get(2).getBank().getList().add(new Card("6222081502001312400")); 21 22 list.get(3).getBank().getList().add(new Card("6222081502051320785")); 23 list.get(3).getBank().getList().add(new Card("6222081502051320786")); 24 25 String str ; 26 List<String> s = new ArrayList<String>(); 27 str = scan.nextLine(); 28 int cmp = str.compareTo("#"); 29 while(cmp!=0) 30 { 31 s.add(str); 32 str = scan.nextLine(); 33 cmp = str.compareTo("#"); 34 } 35 36 37 for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++) { 38 39 String[] a = s.get(i).split(" "); 40 if(a.length > 1 ) { 41 if(!valid(list , a[0])) { 42 System.out.println("Sorry,this card does not exist."); 43 break; 44 } 45 if(Double.valueOf(a[2]) > 6 || Double.valueOf(a[2]) < 1 ) { 46 System.out.println("Sorry,the ATM's id is wrong."); 47 break; 48 } 49 if(!a[1].equals("88888888")) { 50 System.out.println("Sorry,your password is wrong."); 51 break; 52 } 53 if(!validsurplus( list , a[0] , a[3])) { 54 System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); 55 break; 56 } 57 58 else 59 getmoney( list , a[0] , a[3] ,a[2]); 60 } 61 62 if(a.length == 1) { 63 getsurplus(list, a[0]); 64 } 65 66 } 67 68 69 }
存储信息完成之后,需要解决的是如何读取到个人账户的具体信息,写的时候想到老师讲过的迭代器遍历集合,想利用这种方法解决信息读取的问题,于是写出了以下代码
1 public static void getmoney(List list ,String a , String b,String c){ 2 Iterator<User> itr = list.iterator(); 3 while(itr.hasNext()) { 4 5 Iterator<Card> car = itr.next().getBank().getList().iterator(); 6 while(car.hasNext() ){ 7 Card ca = car.next(); 8 9 if(ca.getCardId().equals(a)) { 10 ca.getAccount().Drawsave(Double.valueOf(b)); 11 if(ca.getAccount().SurplusJudge()&&(Double.valueOf(b)>0)) { 12 System.out.println(c+"号ATM机上存款¥"+String.format("%.2f", Math.abs(Double.valueOf(b)))); 13 System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+String.format("%.2f", ca.getAccount().getSurplus())); 14 } 15 if(ca.getAccount().SurplusJudge()&&(Double.valueOf(b)<0)) { 16 System.out.println(c+"号ATM机上存款¥"+String.format("%.2f", Math.abs(Double.valueOf(b)))); 17 System.out.println("当前余额为¥"+String.format("%.2f", ca.getAccount().getSurplus())); 18 } 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 }
但是还是无法解决个人信息不匹配的问题,只能遗憾放弃。题目集八结束后听老师的讲解之后才知道我的迭代器用错了地方,应该将它放在对应的类中,返回个人账户的信息
1 public static Account getAmountbyCardNO(String cardNO) { 2 Iterator<Card> cardItr = Account.list.iterator(); 3 Card card = null; 4 5 while(cardItr.hasNext()) { 6 card = cardItr.next(); 7 if(card.getCardNO().equals(cardNO)) { 8 return card.getAccount(); 9 } 10 } 11 12 return null; 13 }
像这样通过卡匹配返回卡持有人的账户,这样完美解决了之前困扰我的问题,然后就开始了题目集九orz,题目集九是在题目集八的基础上添加借记卡(即可透支),所以在原来账户的基础上创建两个类继承自账户,一个为信用卡,一个为借记卡。在各自的类中解决是否透支的问题
1 class DebitAccount extends Account{ 2 3 public DebitAccount() { 4 super(); 5 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 6 } 7 8 public DebitAccount(String accountNO, double balance, User user, Bank bank) { 9 super(); 10 this.accountNO = accountNO; 11 this.balance = balance; 12 this.user = user; 13 this.bank = bank; 14 } 15 16 public void withdraw(double amount) { 17 double over = amount - balance; 18 19 if((balance >= 0) && (over>0)) { 20 balance = balance - amount - over*0.05; 21 } 22 else if((balance >= 0) && (over<0)) { 23 balance = balance - amount ; 24 } 25 else if(balance < 0 ) { 26 balance = balance - amount -amount*0.05; 27 } 28 29 if ((balance - amount -amount*0.05) < (-50000)) { 30 System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); 31 System.exit(0); 32 } 33 } 34 35 public void withdraw(double amount, double rate) { 36 double over = amount - balance; 37 38 if((balance >= 0) && (over<0)) { 39 balance = balance - amount-amount*rate ; 40 } 41 else if((balance >= 0) && (over>0)) { 42 balance = balance - amount - amount*rate - over*0.05; 43 } 44 else if(balance < 0 ) { 45 balance = balance - amount -amount*0.05; 46 } 47 48 if ((balance - amount -amount*0.05) < (-50000)) { 49 System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); 50 System.exit(0); 51 } 52 53 } 54 } 55 56 class CreditAccount extends Account{ 57 58 public CreditAccount() { 59 super(); 60 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 61 } 62 63 public CreditAccount(String accountNO, double balance, User user, Bank bank) { 64 super(); 65 this.accountNO = accountNO; 66 this.balance = balance; 67 this.user = user; 68 this.bank = bank; 69 } 70 71 public void withdraw(double amount) { 72 balance = balance - amount ; 73 if (amount > balance) { 74 System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); 75 System.exit(0); 76 } 77 } 78 79 public void withdraw(double amount, double rate) { 80 balance = balance - amount - amount*rate; 81 if (amount > balance) { 82 System.out.println("Sorry,your account balance is insufficient."); 83 System.exit(0); 84 } 85 } 86 }
透支的问题解决完后,新增的问题出现了,在题目集八中无法跨行取款,而在题目集九中跨行只需要支付相应的手续费。所以题目集八中简单的判断跨行要变成精确的判断在哪个银行跨行。利用以下方法就解决了此问题。题目集九也完美完成。
1 if (account.getBank().getBankNO() != aTM.getBank().getBankNO()) { 2 if(aTM.getATMID().matches("(0[1-4])")) { 3 rate = 0.02; 4 account.withdraw(amount , rate); 5 } 6 if(aTM.getATMID().matches("(0[5-6])")) { 7 rate = 0.03; 8 account.withdraw(amount , rate); 9 } 10 if(aTM.getATMID().matches("(0[7-9])|(10)|(11)")) { 11 rate = 0.04; 12 account.withdraw(amount , rate); 13 } 14 }
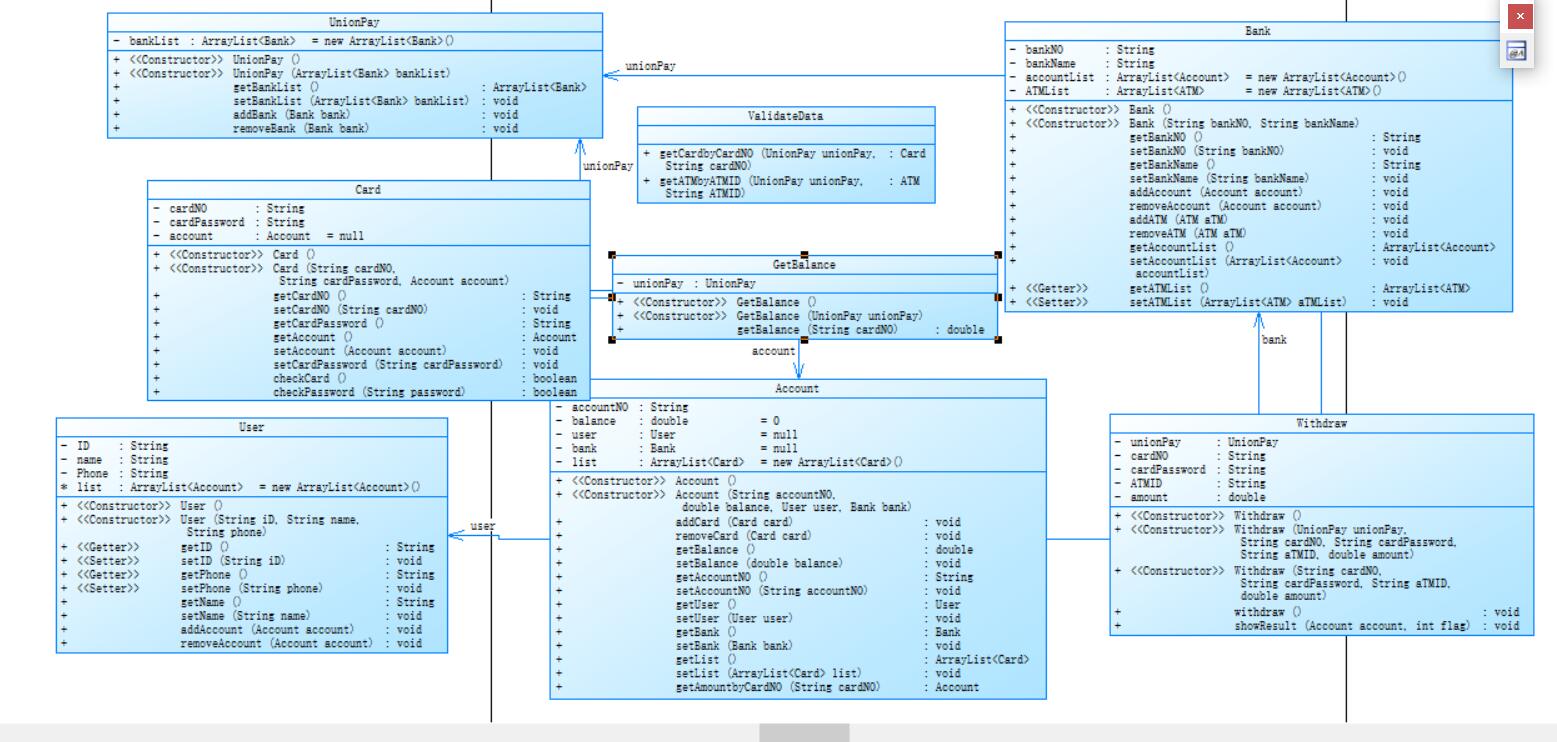
写完之后两道题的类图如下,没有很大的区别

三、学习心得
本阶段的学习好像并没有遇到什么坑,反而是在为各个类的关系纠缠。但本阶段的学习重点也是类的继承,多态关系的运用。不如再理一遍类之间的关系
(1)继承
继承是面向对象最显著的一个特性。继承是从已有的类中派生出新的类,新的类能吸收已有类的数据属性和行为,并能扩展新的能力。
本阶段的作业中都有利用继承关系,例如下
1 class Circle extends Shape{ 2 3 private double radius ; 4 5 public Circle(double radius) { 6 super(); 7 this.radius = radius; 8 } 9 10 public Circle() { 11 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 12 } 13 14 public double getRadius() { 15 return radius; 16 } 17 18 public void setRadius(double radius) { 19 this.radius = radius; 20 } 21 22 public boolean validate() { 23 if(this.radius <= 0 ){ 24 return false; 25 } 26 else 27 return true; 28 } 29 30 public double getArea() { 31 return radius * radius * Math.PI ; 32 } 33 34 35 36 37 } 38 39 class Rectangle extends Shape{ 40 41 private double width ; 42 private double length; 43 44 public Rectangle(double width, double length) { 45 super(); 46 this.width = width; 47 this.length = length; 48 } 49 50 51 public double getWidth() { 52 return width; 53 } 54 55 public void setWidth(double width) { 56 this.width = width; 57 } 58 59 public double getLength() { 60 return length; 61 } 62 63 public void setLength(double length) { 64 this.length = length; 65 } 66 67 public boolean validate() { 68 if(this.length <= 0 || this.width <= 0 ){ 69 return false; 70 } 71 else 72 return true; 73 } 74 75 public double getArea() { 76 return width * length ; 77 } 78 79 80 }
继承的好处是子类即使不扩充父类,也能维持父类的操作。这样可以我们的代码可以更加简便
(2)多态
在题目集中关键的一点就是多态的运用。例如下
1 Account ccbAcc1 = new CreditAccount("3217000010041315709",10000.00,Yangguo,ccb); 2 Account ccbAcc2 = new CreditAccount("3217000010041315715",10000.00,Yangguo,ccb); 3 Account ccbAcc3 = new CreditAccount("3217000010051320007",10000.00,Guojing,ccb); 4 Account ccbAcc4 = new DebitAccount("3640000010045442002",10000.00,zhangsanfeng,ccb); 5 Account icbcAcc1 = new CreditAccount("3222081502001312389",10000.00,Zhangwuji,icbc); 6 Account icbcAcc2 = new CreditAccount("3222081502001312390",10000.00,Zhangwuji,icbc); 7 Account icbcAcc3 = new CreditAccount("3222081502001312399",10000.00,Zhangwuji,icbc); 8 Account icbcAcc4 = new CreditAccount("3222081502051320785",10000.00,Weixiaobao,icbc); 9 Account icbcAcc5 = new CreditAccount("3222081502051320786",10000.00,Weixiaobao,icbc); 10 Account icbcAcc6 = new DebitAccount("360201200513243326",10000.00,linghuchong,icbc); 11 Account abcAcc1 = new DebitAccount("3640000010045442002",10000.00,qiaofeng,abc); 12 Account abcAcc2 = new DebitAccount("3640000010045442002",10000.00,hongqigong,abc);
继承在为多态的实现做了准备。子类CreditAccount和DebitAccount继承父类Account,我们可以编写一个指向子类的父类类型引用,该引用既可以处理父类Account对象,也可以处理子类CreditAccount和DebitAccount对象。当相同的消息发送给子类或者父类对象时,该对象就会根据自己所属的引用而执行不同的行为,这就是多态。即多态性就是相同的消息使得不同的类做出不同的响应。在题目九中就是利用多态解决了判断借记卡,信用卡的问题。
四、改进建议
对于题目集八有遗憾吧,如果我的迭代器运用到位了,题目集就能过了,而不是卡在信息不匹配的问题。对应代码更改后如下:
1 class Account { 2 String accountNO; 3 double balance = 0; 4 User user = null; 5 Bank bank = null; 6 static ArrayList<Card> list = new ArrayList<Card>(); 7 8 public Account() { 9 super(); 10 // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub 11 } 12 13 public Account(String accountNO, double balance, User user, Bank bank) { 14 super(); 15 this.accountNO = accountNO; 16 this.balance = balance; 17 this.user = user; 18 this.bank = bank; 19 } 20 21 public void addCard(Card card) { 22 list.add(card); 23 } 24 25 public void removeCard(Card card) { 26 list.remove(card); 27 } 28 29 public double getBalance() { 30 return balance; 31 } 32 33 public void setBalance(double balance) { 34 this.balance = balance; 35 } 36 37 public String getAccountNO() { 38 return accountNO; 39 } 40 41 public void setAccountNO(String accountNO) { 42 this.accountNO = accountNO; 43 } 44 45 public User getUser() { 46 return user; 47 } 48 49 public void setUser(User user) { 50 this.user = user; 51 } 52 53 public Bank getBank() { 54 return bank; 55 } 56 57 public void setBank(Bank bank) { 58 this.bank = bank; 59 } 60 61 public ArrayList<Card> getList() { 62 return list; 63 } 64 65 public void setList(ArrayList<Card> list) { 66 Account.list = list; 67 } 68 69 public static Account getAmountbyCardNO(String cardNO) { 70 Iterator<Card> cardItr = Account.list.iterator(); 71 Card card = null; 72 73 while(cardItr.hasNext()) { 74 card = cardItr.next(); 75 if(card.getCardNO().equals(cardNO)) { 76 return card.getAccount(); 77 } 78 } 79 80 return null; 81 } 82 83 public void withdraw(double amount , double rate) { 84 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 85 86 } 87 88 public void withdraw(double amount) { 89 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 90 91 } 92 }
五、总结
第三阶段学习到此为止,本次学习对类之间的关系有了更加深刻的印象,做到该用的时候能想起来怎样使用,题目集九多态的应用还是经过同学提醒后才想到可以使用多态解决卡类型的判断,还是当时对多态的理解不够深刻,有了这阶段的学习,相信我对多态有一定的掌握。还是要多加学习,看下课本中得到介绍,多掌握一些专业知识是非常有必要的!



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号