EME 09 Risk management
Risk management
- Identify the risks that might affect the project’s success.
- Assess the risks based on cost-effective principal.
- Select appropriate methods to mitigate project’s risks.
- Estimate risks to the schedule using PERT & Critical
Chain technique
Risk
involves “cause vs effects”.
The key role of risk management is considering uncertainty remaining after a plan has been formulated.
Risk Management Process
compare loss & the cost of defraying
- risk identification
- risk assessment
- risk plan
- risk monitoring & control
Risk Identification
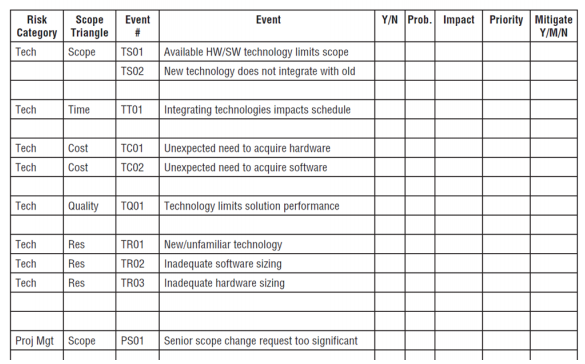
- Technical risks
- Project management risks
- Organizational risks
- External risks
Risk Identification Matrix Template
scope triangle elements:
- scope
- time
- cost
- quality
- resources
![]()
Risk Assessment
risk exposure = (potential damage) × (probability of occurrence)
e.g. 500k*0.1%=500 yuan
level: high>significant>moderate>low
Risk Plan
Contingency planning
- risk accept
- risk avoidance
- risk reduction/mitigation
- transfer
Risk monitoring & control
Risk reduction leverage = (REbefore-REafter)/ cost of risk reduction
- REbefore is the risk exposure, as explained in above, before risk reduction actions have been taken.
- REafter is the risk exposure after taking the risk reduction action.
PERT (Program Evaluation and Review Technique)
Expected duration: 𝑡𝑒 = (𝑎 + 4𝑚 + 𝑏)/6
- Most likely time (a)
- Optimistic time (m)
- Pessimistic time (b)
Case: PERT Application
Activity standard deviations s=(b-a)/6
- Step 1: calculate the standard deviation of each project event
two possible paths: the greater of the two
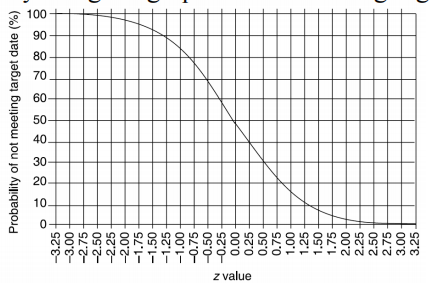
- Step 2: calculate the z value for each event that has a target date
z=(T-𝑡𝑒)/s
- Step 3: Converting z values to probabilities
![]()



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号