6-视图-2
URL反向解析
1、reverse方法(reverse(viewname,urlconf=None,args=None,kwargs=None,current_app=None))

viewname可以是url模式的名字,也可以是name所指的名字,
urlconf这个属性决定当前的反向解析使用哪一个URLconf模块,默认是URLconf
args用于传递参数,可以是元组或者列表,顺序填充URL中的位置参数
kwargs和args一样,但传递的是字典类型,使用关键字指定参数和参数值。注意args和kwargs不可同时出现
current_app当前执行的视图是哪一个应用的
re_path('msg/(?P<name>[\u4e00-\u9fa5]{0,4})/(?P<year>[0-9]{4})/(?P<month>0[0-9]|1[0-2])/(?P<day>0[1-9]|1[0-9]|2[0-9]|30)/',views.time_time,name='time'),#指定url的name
在shell环境中
>>> from django.urls import reverse >>> reverse('time',args=('诺言',2019,11,20)) '/firstapp/msg/%E8%AF%BA%E8%A8%80/2019/11/20 >>> reverse('time',kwargs={'name':'诺言','year':2019,'month':11,'day':20}) '/firstapp/msg/%E8%AF%BA%E8%A8%80/2019/11/20/'
reverse常常用于视图重定向,reverse中的viewname也可以传递视图对象
from django.urls import reverse from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect def test(request,ceshi): return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('time',kwargs={'name':'诺言','year':2019,'month':11,'day':20}))
2、命名空间
URL命名空间分为两部分 1、app_name:正在部署的应用, 2、区分同一个应用部署的多个不同空间
首先在总项目的urls.py中增加命名空间
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('firstapp/',include('firstApp.urls',namespace='first'))
]
在应用中添加
app_name='first'
最后修改一下reverse方法
from django.urls import reverse from django.http import HttpResponseRedirect def test(request,ceshi): return HttpResponseRedirect(reverse('first:time', kwargs={'name':'诺言','year':2019,'month':11,'day':20}, current_app=request.resolver_match.namespace))
视图重定向
重定向分为两种:临时重定向和永久重定向
HttpResponseRedirect的status_code是302,为临时重定向
HttpResponsePermanentRedirect的status_code是301,为永久重定向
#redirect(to,*args,permanent=False,**kwargs) #*args和**kwargs最终会传递到reverse方法中去,permanent默认为False,实现临时重定向;为True实现永久重定向;to为必填参数,可定义path中的name值,也可用相对路径或者绝对路径来返回一个path
render方法
render(request,template_name,context=None,content_type=None,status=None,using=None) #template_name模板的完整路径 #context通过它来渲染模板 #content_type文档的mime类型 #status响应状态码,默认为200 #using指定加载模板的模板引擎
from django.shortcuts import render def test(request,ceshi): return render(request,'firstApp/templates/ceshi.html')

用于渲染模板的TemplateView
TemplateView(TemplateViewResponseMixin,ContextMixin,View) #TemplateViewResponseMixin定义了两个属性,template_name和render_to_response方法 #ContextMixin定义了一个方法get_context_data,返回一个字典对象,用来渲染模板上下文
from django.views.generic import TemplateView class IndexView(TemplateView): template_name = 'firstapp/index.html'#指定模板的位置 def get_context_data(self, **kwargs): context=super(IndexView,self).get_context_data(**kwargs) context['hello']='你好啊!' return context
创建模板firstapp/templates/firstapp/index.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>index</title> </head> <body> <h1>{{ hello }}</h1><!--应用变量的形式--> </body> </html>
urls.py
urlpatterns = [ path('index/',index.IndexView.as_view()),
也可以用
class IndexView(TemplateView): def get_template_names(self): return 'firstapp/index.html'
或者
def inde_view(request): return render(request, 'firstapp/index.html', context={'hello':'你好啊!'} )
重定向的RedirectView
RedirectView(permanent,url,pattern_name,query_string) #permanent是否为永久重定向 #url重定向的url #pattern_name path中的name #query_string是否将查询字符拼接在新地址中
展示model的ListView
ListView(MultipleObjectTemplateResponseMixin,BaseListView) #MultipleObjectTemplateResponseMixin有一个get_template_names方法,返回模板路径;还有一个默认属性,template_name_suffix="_list",如果不适用这个属性,那么他会默认的给你的模板加_list后缀 #BaseListView只定义了get方法,这个方法有三个属性self.object_list=self.get_query()(获取视图展示的model列表) #allow_empty=self.get_allow_empty()(默认为Ture,允许表示空的Model列表) #context=self.get_context_data()(返回用于渲染模板的上下文数据)
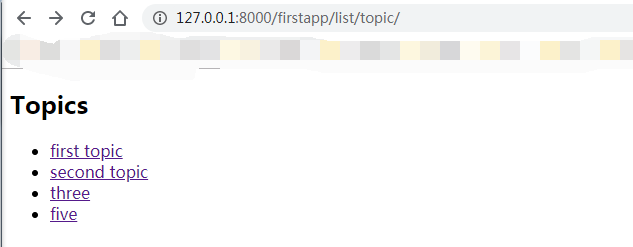
首先先新建在firstapp/templates/firstapp下一个topic_list.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Topic列表</title> </head> <body> {% block content %}{% comment %}暂时还不知道是干嘛的,后面会详细讲{% endcomment %} <h2>Topics</h2> <ul> {% for topic in object_list %} {% comment %}对传过来的modellist做each循环{% endcomment %} <li> <a href="{% url 'first:topic-detail' topic.id %}">{% comment %}将循环出来的id通过反向解析使用topic详情获取topic详情{% endcomment %} {{ topic.title }}</a>{% comment %}这里放每一个话题title{% endcomment %} </li> {% endfor %} </ul> {% endblock %} </body> </html>
views.py中写一个类视图继承ListView
#用来显示model列表的ListView from django.views.generic import ListView class TopicList(ListView): #model = Topic queryset = Topic.objects.all()#可以使用这个方法,也可以达到一样的效果 allow_empty = True
最后配置urls.py
path('list/topic/',views.TopicList.as_view())
用来展示model的DdetailView
DetailView(SingleObjectTemplateResponseMixin,BaseDetailView)#用法与BaseListView一样
#返回model详情的detailView from django.views.generic import DetailView from firstApp.models import Comment class TopicDetail(DetailView): model = Topic#会找对应model的_detail文件 def get_context_data(self, **kwargs):#返回模板渲染上下文的字典数据 context=super(TopicDetail,self).get_context_data(**kwargs) pk=self.kwargs.get(self.pk_url_kwarg)#根据pk_url_kwarg获取url的主键值,这里获取topic的id context.update({ 'comment_list':Comment.objects.filter(topics=pk)#这里用topic的id pk当做过滤条件 }) return context
path('detail/topic/<int:pk>/',views.TopicDetail.as_view())
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>topic_detail</title> </head> <body> {% block content %} <h1>Topic详情</h1> <ul> <li>id:{{ topic.id }}</li> <li>标题:{{ topic.title }}</li> <li>内容:{{ topic.content }}</li> <li>是否在线:{{ topic.is_online }}</li> <li>用户:{{ topic.user }}</li> <li>创建时间:{{ topic.create_time }}</li> <li>修改时间:{{ topic.update_time }}</li> <table border="1"> <tr> <th>id</th> <th>评论内容</th> <th>赞</th> <th>踩</th> <th>创建时间</th> <th>修改时间</th> <th>所属文章</th> </tr> {% for comment in comment_list %} <tr> <td>{{ comment.id }}</td> <td>{{ comment.content }}</td> <td>{{ comment.up }}</td> <td>{{ comment.down }}</td> <td>{{ comment.create_time }}</td> <td>{{ comment.update_time }}</td> <td>{{ comment.topics }}</td> </tr> {% endfor %} </table> </ul> {% endblock %} </body> </html>

解决一值多键的QueryDict
MultiValueDict方法
>>> from django.utils.datastructures import MultiValueDict >>> d = MultiValueDict({'name':['A','B'],'names':['product']}) >>> d['name'] 'B' >>> d.getlist('name') ['A', 'B'] >>> d.getlist('names') ['product'] >>> d.getlist('abc') [] >>> d.getlist('abc',['C','D']) ['C', 'D']
QueryDict方法(方法继承MultiValueDict)
>>> from django.http.request import QueryDict >>> QueryDict('a=1&b=2&c=3') <QueryDict: {'a': ['1'], 'b': ['2'], 'c': ['3']}> >>> QueryDict('a=1&a=2&c=3') <QueryDict: {'a': ['1', '2'], 'c': ['3']}>
重点掌握django/utils/http.py中的limited_parse_qsl
def limited_parse_qsl(qs, keep_blank_values=False, encoding='utf-8', errors='replace', fields_limit=None): """ 返回从查询字符串解析的键/值元组的列表。 从urlparse复制,带有额外的“fields_limit”参数。 版权所有(C)2013 Python软件基金会(见LICENSE.Python)。 论据: qs:要分析的百分比编码查询字符串 keep_blank_values:指示空白值是否在百分比编码查询应视为空字符串。一个真值表示空白应保留为空白串。默认的false值表示空值将被忽略,并将其视为未包括在内。 编码和错误:指定如何解码百分比编码序列 转换成Unicode字符,由bytes.decode()方法接受。 字段限制:解析的最大字段数或异常 是升起的。无表示无限制,是默认值。 """ if fields_limit: #fields_limit限制字段的最大个数,默认是1000 pairs = FIELDS_MATCH.split(qs, fields_limit) if len(pairs) > fields_limit: raise TooManyFieldsSent( 'The number of GET/POST parameters exceeded ' 'settings.DATA_UPLOAD_MAX_NUMBER_FIELDS.' ) else: pairs = FIELDS_MATCH.split(qs) r = [] for name_value in pairs: if not name_value: continue nv = name_value.split('=', 1) if len(nv) != 2: # 处理不带等号的控件名大小写 if keep_blank_values: nv.append('') else: continue #keep_blank_values标识是否保留空字符,默认为true if len(nv[1]) or keep_blank_values: name = nv[0].replace('+', ' ') name = unquote(name, encoding=encoding, errors=errors) value = nv[1].replace('+', ' ') value = unquote(value, encoding=encoding, errors=errors) r.append((name, value)) return r
>>> from django.utils.http import limited_parse_qsl >>> limited_parse_qsl('a=1&b=2&c=3') [('a', '1'), ('b', '2'), ('c', '3')]
View分析
view定义于django/views/generic/base.py中,其功能主要依赖于http_method_not_allowed、dispatch、as_view
http_method_not_allowed这个方法返回405,标识当前请求类型不支持
dispatch定义当前view支持的请求类型:get、post、put、patch、delete、head、options、trace
as_view:方法上有@classonlymethod,只允许调用这个方法




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号