4.0-day10-C语言基础-指针和数组
C语言基础-指针和数组
指针变量可以作为函数返回值使用,只能把全局变量的地址,静态局部变量的地址或者通过参数得到的地址当作返回值使用,普通局部变量的地址绝对不可以当返回值使用。
字符串是由内存中一组连续的字符变量构成的。C语言程序中使用第一个字符的地址表示整个字符串。'\0'是字符串的结尾字符,它的位置决定了一个字符串中有效字符变量的个数。这个字符在ASCII表中对应数字0。
字面值是程序中表示字符串的一种写法,用双引号表示。字面值表示的字符串不可以被修改。多个相同内容的字面值在程序运行时都是同一个。多个连续的字符串字面值在编译时会被合并成一个。
字符数组也可以表示字符串,它存储在栈中。它可以被修改,可以使用多种方式进行初始化。
fgets函数可以用来从键盘读取字符串,不会出现字符数组溢出问题。
strlen函数可以计算字符串中有效字符的个数
strcat函数可以把两个字符串合并,可能造成数组溢出。使用strncat函数可以避免溢出。
strcpy函数可以把一个字符串赋值成另一个字符串。使用strncpy函数可以避免溢出。
strcmp函数可以比较两个字符串的大小关系。strncmp的函数比较两个字符串中前面几个字符的大小。
预处理指令#define可以用于实现宏定义,宏可以用来当作数字的名称。
可以在gcc命令行中使用-D选项定义宏
宏可以带参数,宏的参数都既是输入参数也是输出参数
宏的所有参数在使用的时候要用小括号包括起来
宏的计算结果要用小括号包括起来
不要使用自增或自减的计算结果作为宏的参数使用
#操作符可以把宏的某个参数变成字符串字面值
##操作符可以把宏的某个参数代表的标示符和其他内容合并成为一个新的标示符
编译器内部提供了一些预定义的宏,在编译的时候编译器把他们替换成正确的内容
使用如下预处理指令可以实现条件编译
#ifdef 宏名称 (#ifndef 宏名称)
....
#else
....
#endif
其中#ifdef和#ifndef意思相反
使用#if和#elif可以根据任何逻辑表达式实现条件编译,并且可以从更多语句组中进行选择。
01ptr.c
/*指针练习*/#include<stdio.h>int*func(){staticint value;printf("value是%d\n", value);return&value;}int main(){int*p_value = NULL;p_value = func();*p_value =7;func();return0;}
02str.c
/*字符串练习*/#include<stdio.h>int main(){char*p_str ="abc";char ch ='x';printf("%p\n","abc");printf("%c\n",*p_str);printf("%s\n", p_str);p_str =&ch;printf("%s\n", p_str);//不可以当字符串使用return0;}
03str.c
/*字符串练习*/#include<stdio.h>int main(){char*p_str ="abcdef";char str[]="abc";char str1[3]="abc";//错误char str2[]={'a','b','c'};//错误char str3[]={'a','b','c',0};//*p_str = 'x'; 字符串字面值不可以修改printf("%p\n","abcdef");printf("p_str是%p\n", p_str);printf("%s\n","abc""xyz");printf("%s\n", str);printf("字符变量个数是%d\n",sizeof(str)/sizeof(str[0]));str[0]='y';str[1]=0;printf("%s\n", str);printf("%s\n", str2);return0;}
04str.c
/*字符串练习*/#include<stdio.h>int main(){char buf[10]={0};printf("请输入一个字符串:");//scanf("%s", buf);fgets(buf,10, stdin);printf("%s\n", buf);return0;}
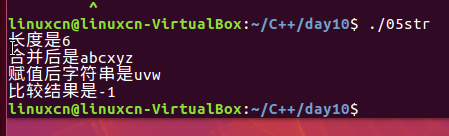
05str.c
/*字符串函数练习*/#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>int main(){char str[20]="abc";printf("长度是%d\n", strlen("abcdef"));printf("合并后是%s\n", strcat(str,"xyz"));printf("赋值后字符串是%s\n", strcpy(str,"uvw"));printf("比较结果是%d\n", strcmp("abc","abd"));return0;vi}
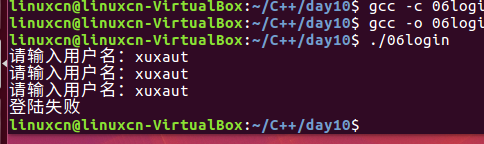
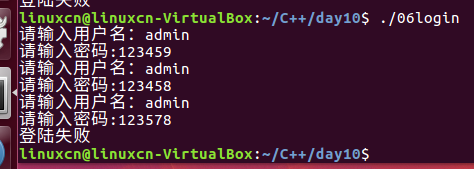
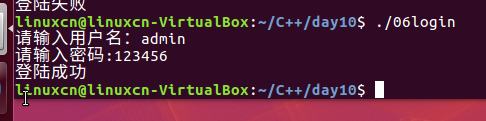
06login.c
/*模拟登陆练习*/#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>int main(){int loop =0;char buf[10];for(loop =0; loop <3; loop++){printf("请输入用户名:");fgets(buf,10, stdin);if(strcmp(buf,"admin\n")){continue;}printf("请输入密码:");fgets(buf,10, stdin);if(!strcmp(buf,"123456\n")){break;}}if(loop <3){printf("登陆成功\n");}else{printf("登陆失败\n");}return0;}
07main.c
/*main函数的参数*/#include<stdio.h>int main(int argc,char*argv[]){int loop =0;for(loop =0; loop <= argc -1; loop++){printf("%s\n", argv[loop]);}return0;}

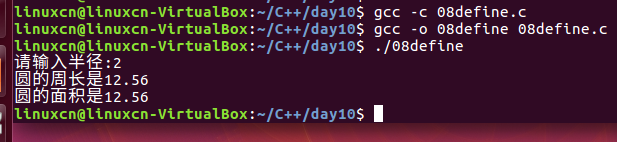
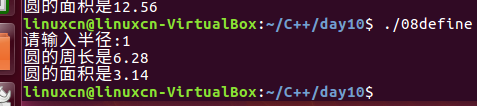
08define.c
/*宏练习*/#include<stdio.h>#define PI 3.14f#define CIRCLE(r)2* PI * r#define AREA(r) PI * r * rint main(){int radius =0;printf("请输入半径:");scanf("%d",&radius);printf("圆的周长是%g\n", CIRCLE(radius));printf("圆的面积是%g\n", AREA(radius));return0;}
09macro.c
/*宏练习*/#include<stdio.h>#define NEG(n) n =0- nvoid neg(int value){value =0- value;}int main(){int value =4;//neg(value);NEG(value);printf("value是%d\n", value);return0;}
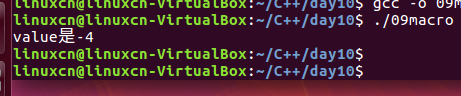
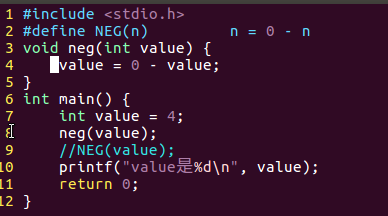
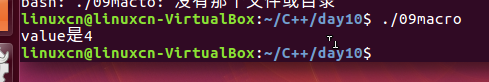
函数没有返回值,返回的是局部变量的值;因为是
void neg(int value)
10max.c
/*宏练习*/#include<stdio.h>#define MAX(n,m) n > m ? n : mint main(){printf("MAX(4, 8)是%d\n", MAX(4,8));return0;}
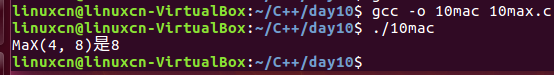
11macro.c
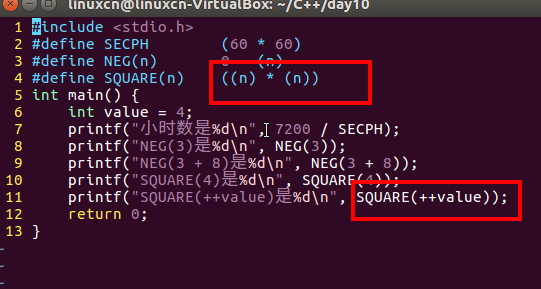
/*宏练习*/#include<stdio.h>#define SECPH (60*60)#define NEG(n)0-(n)#define SQUARE(n)((n)*(n))int main(){int value =4;printf("小时数是%d\n",7200/ SECPH);printf("NEG(3)是%d\n", NEG(3));printf("NEG(3 + 8)是%d\n", NEG(3+8));printf("SQUARE(4)是%d\n", SQUARE(4));printf("SQUARE(++value)是%d\n", SQUARE(++value));return0;}
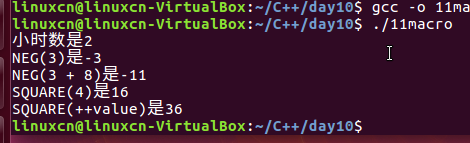
注意:SQUARE(++value)要执行两次的n*n,相当于4加了两次变为6,6*6=36;
12macro.c
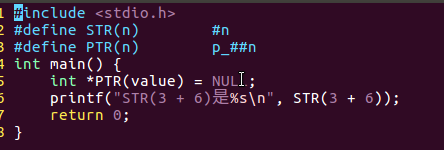
/*宏练习*/#include<stdio.h>#define STR(n)#n#define PTR(n) p_##nint main(){int*PTR(value)= NULL;printf("STR(3 + 6)是%s\n", STR(3+6));return0;}
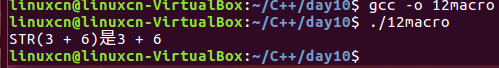
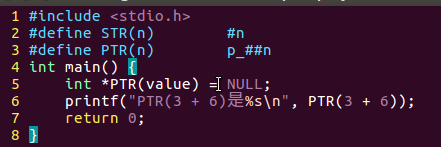
#n变成字符串的字面值,不会执行参数里面的内容。
13macro.c
/*预定义宏练习*/#include<stdio.h>int main(){printf("行号是%d\n", __LINE__);printf("文件名是%s\n", __FILE__);printf("日期是%s\n", __DATE__);printf("时间是%s\n", __TIME__);printf("%sC标准\n", __STDC__ ?"符合":"不符合");return0;}
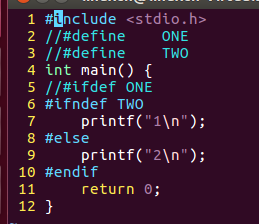
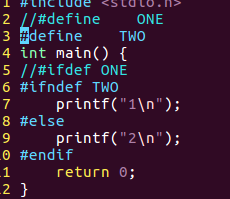
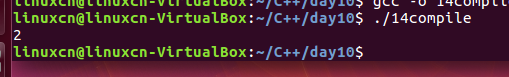
14compile.c
/*条件编译练习*/#include<stdio.h>//#define ONE//#define TWOint main(){//#ifdef ONE#ifndef TWOprintf("1\n");#elseprintf("2\n");#endifreturn0;}
希望明确规定转出的数字是几---宏;
不关心转出的数字是几---枚举;
一旦开始使用堆中的变量,必须保证适合的时候只消灭一次;
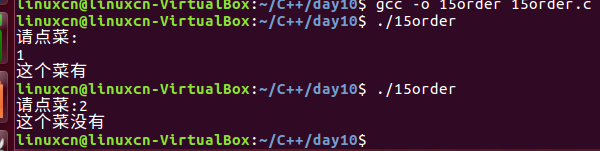
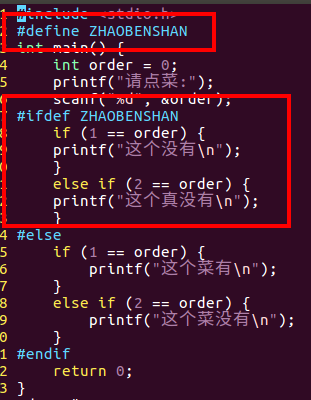
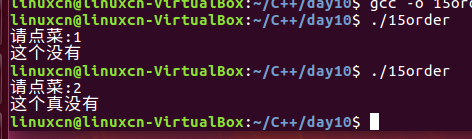
15order.c
/*点菜练习*/#include<stdio.h>int main(){int order =0;printf("请点菜:");scanf("%d",&order);//#ifdef ZHAOBENSHAN#if defined(ZHAOBENSHAN)if(1== order){printf("这个没有\n");}elseif(2== order){printf("这个真没有\n");}#elseif(1== order){printf("这个菜有\n");}elseif(2== order){printf("这个菜没有\n");}#endifreturn0;}
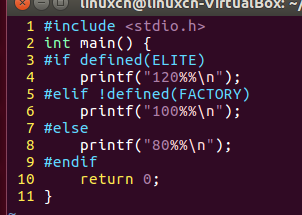
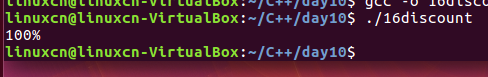
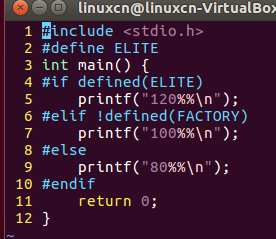
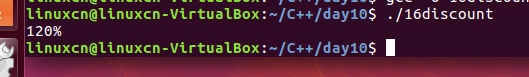
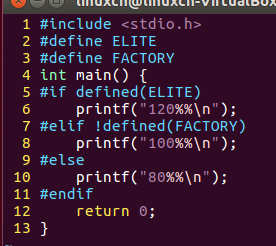
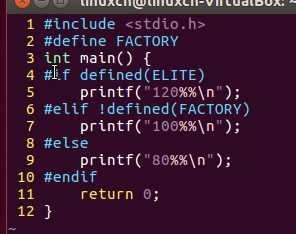
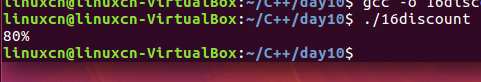
16discount.c
/*条件编译练习*/#include<stdio.h>int main(){#if defined(ELITE)printf("120%%\n");#elif!defined(FACTORY)printf("100%%\n");#elseprintf("80%%\n");#endifreturn0;}
#ifndef 在此之前没有定义过该宏(条件编译)
#elif !defined(FACTORY)在此之前没有定义过FACTORY这个宏。
<wiz_tmp_tag id="wiz-table-range-border" contenteditable="false" style="display: none;">


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号