反射
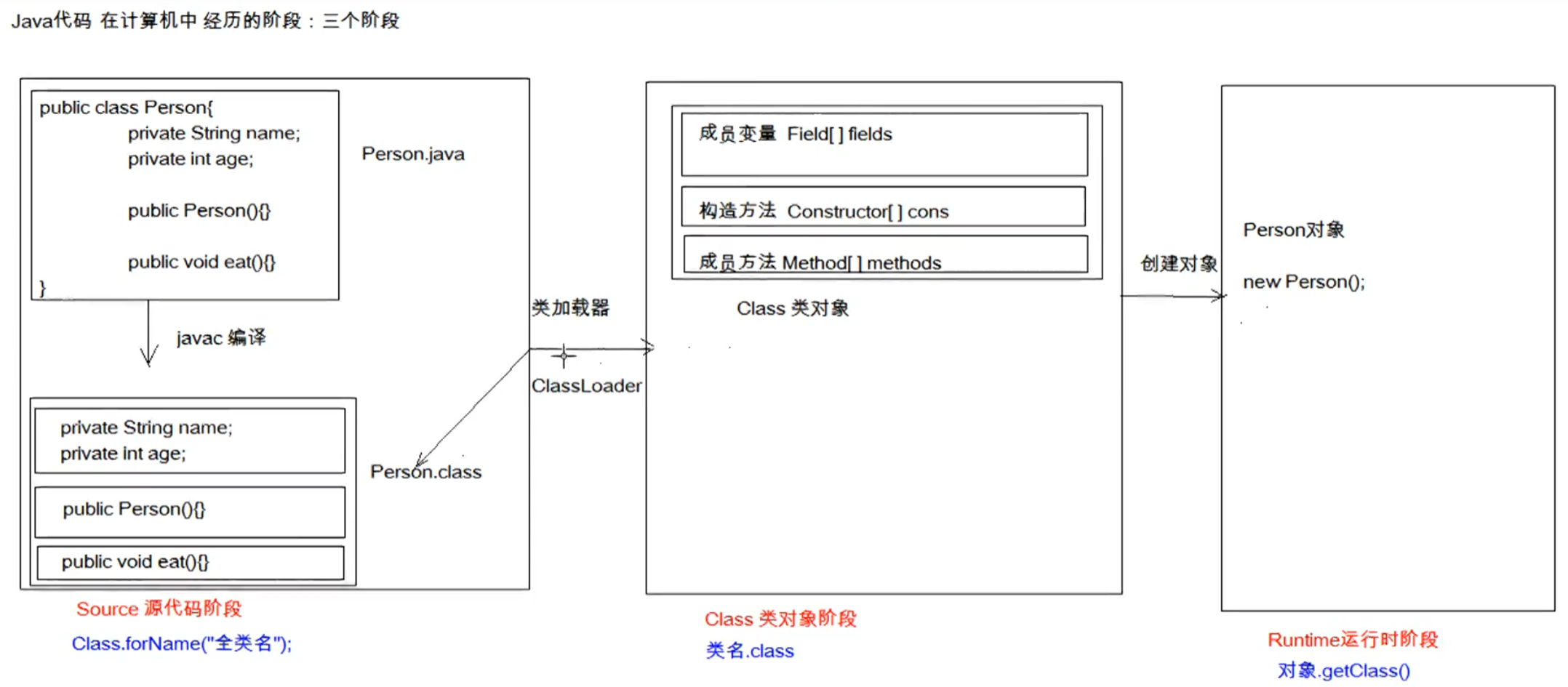
java代码编译的三个阶段:
1、概念
反射:将类的各个组成部分封装为其他对象,这就是反射机制。
好处:
- 可以在程序运行过程中,操作这些对象(Field、Constructor、Method)
- 可以解耦,提高程序的可扩展性
2、获取Class对象的方式
获取Class对象的三种方式分别对应java代码编译的三个阶段。
- Class.forName("全类名"):将字节码文件加载进内存,返回Class对象;
- 多用于配置文件,将类名定义在配置文件中。读取文件,加载类。
- 类名.class:通过类名的属性class获取;
- 多用于参数的传递。
- 对象.getClass():getClass()方法在Object类中定义。
- 多用于对象的获取字节码的方式。
public class ReflectDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.Class.forName("全类名")
Class cls1 = Class.forName("com.xuqp.study.reflect.Person");
//2.类名.class
Class cls2 = Person.class;
//3.对象.getClass()
Person person = new Person();
Class cls3 = person.getClass();
//比较三个对象
System.out.println(cls1 == cls2);//true
System.out.println(cls1 == cls3);//true
}
}
结论:同一个字节码文件(*.class)在一次程序运行过程中,只会被加载一次,无论通过哪一种方式获取的Class对象都是同一个。
3、Class对象功能
3.1 获取功能
3.1.1 获取成员变量
- Field[] getFields():获取所有public修饰的成员变量
- Field getField(String name):获取指定名称的public修饰的成员变量
- Field[] getDeclaredFields():获取所有的成员两边,不考虑修饰符
- Field getDeclaredField(String name)
3.1.2 获取构造方法
- Constructor<?>[] getConstructors()
- Constructor
getConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes) - Constructor<?>[] getDeclaredConstructors()
- Constructor
getDeclaredConstructor(Class<?>... parameterTypes)
3.1.3 获取成员方法
- Method[] getMethods()
- Method getMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)
- Method[] getDeclaredMethods()
- Method getDeclaredMethod(String name, Class<?>... parameterTypes)
3.1.4 获取类名
- String getName()
3.2 Field:成员变量
- 设置值:void set(Object obj, Object value)
- 获取值:Object get(Object obj)
- 忽略访问权限修饰符的安全检查:setAccessible(true)
Class<Person> personClass = Person.class;
Field name = personClass.getField("name");
//获取成员变量name的值
Person person = new Person();
Object value = name.get(person);
//设置name的值
name.set(person,"张三");
Field age = personClass.getDeclaredField("age");
//忽略访问权限修饰符的安全检查
age.setAccessible(true);//暴力反射
3.3 Constructor:构造方法
- 创建对象
- T newInstance(Object ... initargs)
- 如果使用空参数构造方法创建对象,操作可以简化:Class对象的newInstance方法
- 忽略访问权限修饰符的安全检查:setAccessible(true)
Constructor<Person> constructor = personClass.getConstructor(String.class, int.class);
//创建对象
Object person1 = constructor.newInstance("张三", 18);
Object person2 = constructor.newInstance();
Object person3 = personClass.newInstance();
3.4 Method:成员方法
- 执行方法:Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
- 获取方法名称:String getName()
- 忽略访问权限修饰符的安全检查:setAccessible(true)
//获取指定名称的方法
Method method1 = personClass.getMethod("sleep");
Person person4 = new Person();
//执行方法
method1.invoke(person4);
4、案例
写一个"框架",可以帮我们创建任意类的对象,并且执行其中任意方法。(前提:不能改变该类的任何代码,可以创建任意类的对象,可以执行任意方法)
public class ReflectTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//获取类加载器加载配置文件
Properties properties = new Properties();
ClassLoader classLoader = ReflectTest.class.getClassLoader();
InputStream inputStream = classLoader.getResourceAsStream("reflect.properties");
properties.load(inputStream);
//获取配置文件中定义的数据
String className = properties.getProperty("className");
String methodName = properties.getProperty("methodName");
//加载该类进内存
Class aClass = Class.forName(className);
//创建对象
Object instance = aClass.newInstance();
//获取方法对象
Method method = aClass.getMethod(methodName);
//执行方法
method.invoke(instance);
}
}
配置文件reflect.properties
className=com.xuqp.study.reflect.Person
methodName=sleep



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号