leetcode426 - Convert Binary Search Tree to Sorted Doubly Linked List - medium
Convert a Binary Search Tree to a sorted Circular Doubly-Linked List in place.
You can think of the left and right pointers as synonymous to the predecessor and successor pointers in a doubly-linked list. For a circular doubly linked list, the predecessor of the first element is the last element, and the successor of the last element is the first element.
We want to do the transformation in place. After the transformation, the left pointer of the tree node should point to its predecessor, and the right pointer should point to its successor. You should return the pointer to the smallest element of the linked list.
Example 1:
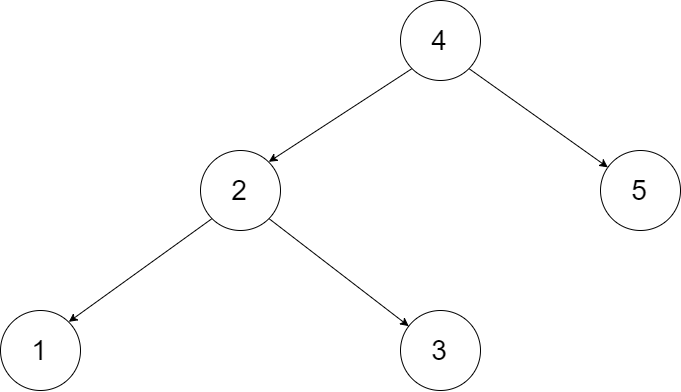
Input: root = [4,2,5,1,3]
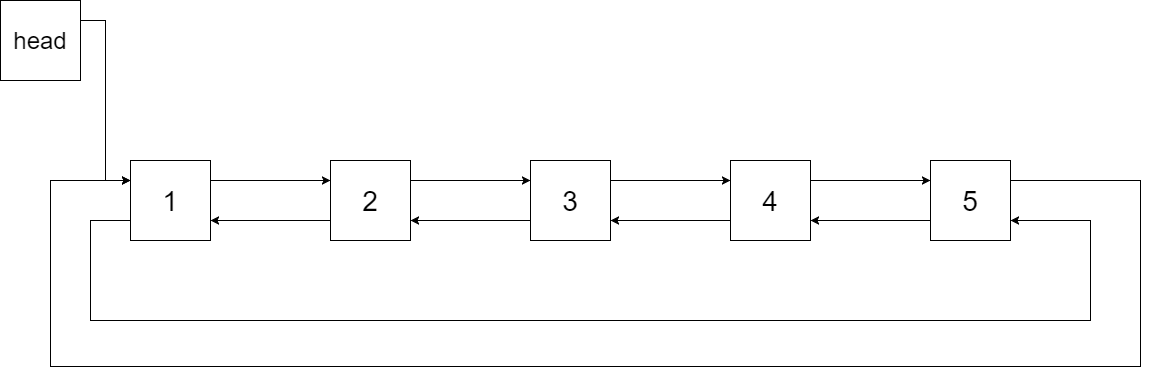
Output: [1,2,3,4,5] Explanation: The figure below shows the transformed BST. The solid line indicates the successor relationship, while the dashed line means the predecessor relationship.
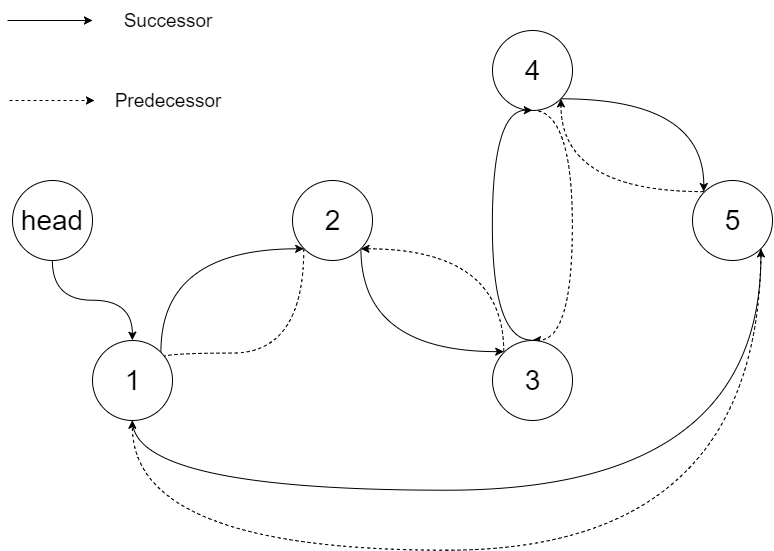
Example 2:
Input: root = [2,1,3] Output: [1,2,3]
Example 3:
Input: root = [] Output: [] Explanation: Input is an empty tree. Output is also an empty Linked List.
Example 4:
Input: root = [1] Output: [1]
Constraints:
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000Node.left.val < Node.val < Node.right.val- All values of
Node.valare unique. 0 <= Number of Nodes <= 2000
In case of BST, Inorder traversal gives nodes in non-decreasing order.
inorder traversal的路上动动pointers。需要两个helper指针一个指向头,一个指向尾,每次操作相当于把node append到队尾,然后把node作为队尾。注意无头的情况,也就是无头也无尾,先把node确定成头。出了recursion头尾互相指一指。
实现: Time&Space O(n)
We have to keep a recursion stack of the size of the tree height, which is O(logn) for the best case of a completely balanced tree and O(n) for the worst case of a completely unbalanced tree.
class Solution { public: Node *first = NULL; Node *last = NULL; void inorder (Node *node) { if (!node) return; inorder(node->left); if (!first) { first = node; } else { last->right = node; node->left = last; } last = node; inorder(node->right); } Node* treeToDoublyList(Node* root) { if (!root) return nullptr; inorder(root); first->left = last; last->right = first; return first; } };


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号