如何优雅地使用vuex状态管理
状态替换为变量,状态管理就是统一管理多组件共同使用的公共变量,如用户信息。
状态管理是一个杯子,大家都用一个吸管。
1 使用Vuex进行状态管理
- 在State定义变量
- 在Mutation为State赋值
- 在Action拿数据并调用Mutation写State
- 在页面组件用Getter读取State
2 Vuex组成
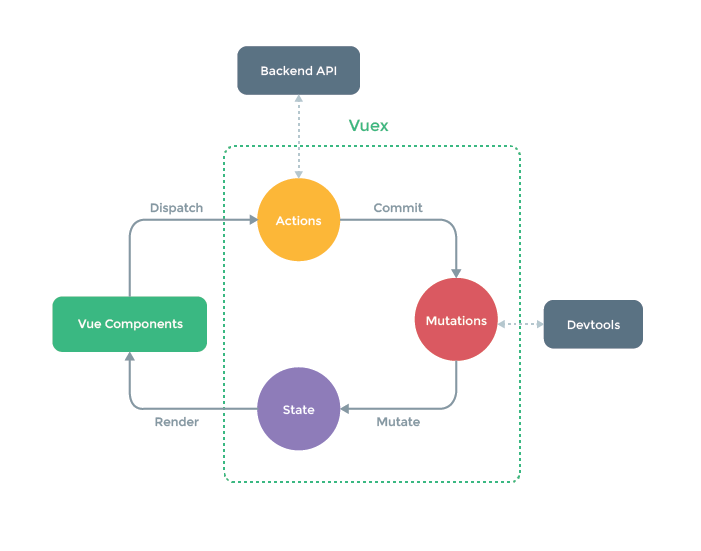
页面组件并不直接操作State
- State == 公共变量
- Mutation封装State读操作
- Getter让组件以计算属性形式读取State
- Action封装对State读写操作,再以Mutation提交,比如异步操作(网络 and etc)
State
存放公共变量
Getters
封装State的读操作,然后放在组件的计算属性,组件中就能以 this.count 获得
computed: {
count () {
return this.$store.state.todos
.filter(todo => todo.done).length
}
}
上面的操作并不优雅,最佳实践是:
使用mapGetters获得State
export default {
username: (state) =>
state.user.info.name,
dicts: (state) => state.dict.dicts,
count: (state) => state.calc.count
}
组件直接引入
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
computed: {
...mapGetters(['count', 'dicts'])
}
Mutations
更改Vuex的store中State的唯一方法是提交 mutation。
定义一个Mutation
mutations: {
DICT_ALL(state, dicts) {
state.dicts = dicts
}
}
使用Mutation初始化State
commit('DICT_ALL', dicts)
Actions
封装State写操作
actions: {
getAllDict: function({ commit }, account) {
return
new Promise(async(resolve, reject) => {
try {
let { data } = await getUserInfo(account)
commit('USER_INFO', data)
resolve()
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
})
}
}
3 最佳实践
以字典数据为例,试举一个完整例子
3.1 组件使用的字典数据
this.dicts[`${dict_name}`][`${dict_code}`]
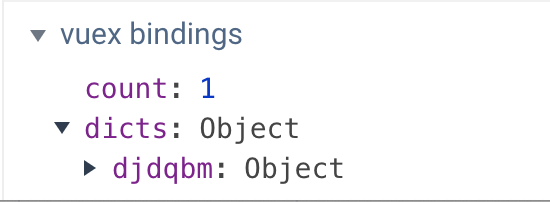
3.2 构建vuex store
3.2.1 分文件定义
新建 src/store
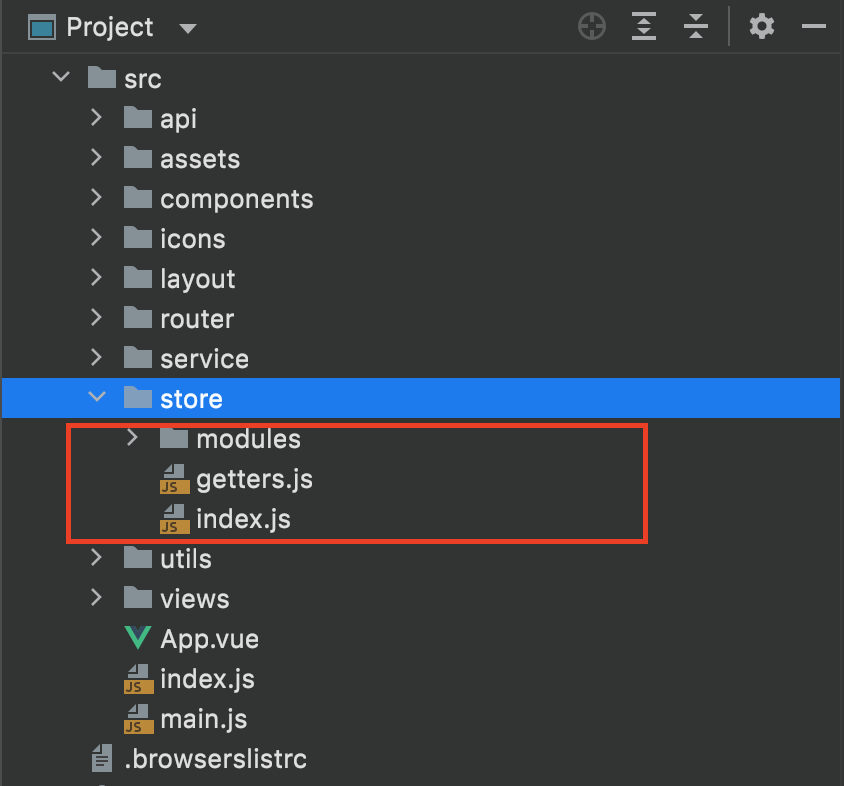
其中:
- index.js vuex的全局实例
- getters.js 在此定义 读state为计算属性
- mudules State小模块,各类信息分开存放,比如字典
3.2.1 index.js
做了以下:
- 自动挂载mudules下所有子模块
- 本地存储State, 让数据只需拉取一次
- 挂载Getters
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import getters from './getters'
import persistedstate from 'vuex-persistedstate'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const files = require.context('./modules', false, /\.js$/)
const modules = {}
files.keys().map((key) => {
modules[key.replace(/(\.\/|\.js)/g, '')] = files(key).default
})
export default new Vuex.Store({
plugins: [
persistedstate({
key: 'kOSS'
})
],
modules,
getters
})
3.2.2 getters.js
此处定义字典数据的读操作:
export default {
dicts: (state) => state.dict.dicts
}
组件中酱紫挂载:
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
computed: {
...mapGetters(['dicts'])
}
3.2.3 mudules
该目录下定义 dict.js
import { listDictionaryByDictCodes } from '@/service/dict.system.service'
import _ from 'lodash'
export default {
namespaced: true,
state: {
dicts: null
},
mutations: {
DICT_ALL(state, dicts) {
state.dicts = dicts
}
},
actions: {
getAllDict: function({ commit }) {
return new Promise(async(resolve, reject) => {
try {
const dictCodeList = ['companyCode']
const { result } = await listDictionaryByDictCodes(dictCodeList.map((o) => { return o }).join(','))
const dicts = {}
_.forEach(result, (item) => {
dicts[`${item.dictCode}`] = item.dictItem
})
console.log('Dict Result', dicts)
commit('DICT_ALL', dicts)
resolve()
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
})
}
}
}
3.2.4 main.js
在main.js挂载上文src/store/index.js中的store实例
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import store from '@/store'
import router from '@/router'
Vue.use(Vuex)
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,
render: (h) => h(App)
})
3.3 初始化State
找个场景搭便车即可。
敏感数据,就在用户登录成功的回调函数内;
否则插在App的生命周期函数中, created 或者 mounted都可。
created() {
// 只有缓存不存在时才请求数据
if (!this.dicts) {
this.$store.dispatch('dict/getAllDict')
}
},
4 总结
状态管理其目标,还是在分离视图、数据、操作。
本文中使用状态管理,无非网络延迟太高,vuex减少了网络请求的次数。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号