第9次全天课笔记-20180909
练习题1:
"abcdefgh"里面挑出3个字母进行组合,一共有多少种组合,要求三个字母中不能有任何重复的字母,三个字母的同时出现次数,在所有组合中只能出现一次,例如出现abc了,不能出现cab和bca等。
result = [] for i in "abcdefgh": for j in "abcdefgh": for m in "abcdefgh": s = i+j+m if s.count(i) >1 or s.count(j)>1 or s.count(m)>1: continue if sorted(list(s)) not in list(map(lambda x:sorted(list(x)),result)): #或者使用 if "".join(sorted(list(s))) not in result: result.append(s) print (len(result))
练习题2:
复制一个列表,不能使用切片和复制的函数进行赋值,尽可能使用少的内置函数
a = [1,2,3,4,5] arr_length = 0 for i in a: arr_length+=1 def iter_arr(n): arr = [] i = 0 while i<=n-1: arr+=[i] i+=1 return arr result = [""]*arr_length for i in iter_arr(arr_length): result[i] = a[i] print(result)
迭代器
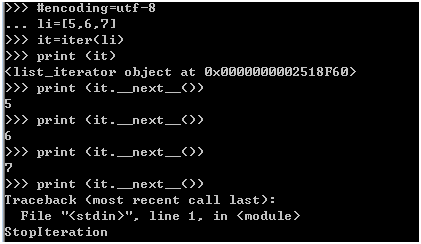
#encoding=utf-8
li=[5,6,7]
it=iter(li)
print (it)
print (it.__next__()) #或者 print(next(it))
print (it.__next__())
print (it.__next__())
print (it.__next__())
列表,元组,字典 都可以使用 iter()
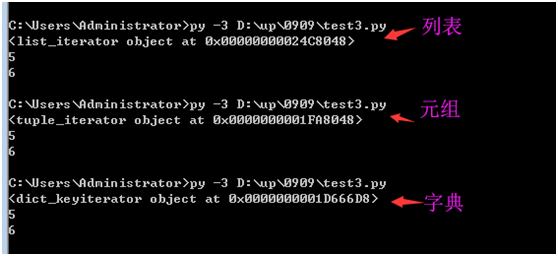
>>> a= iter({1:2,3:4})
>>> type(a)
<class 'dict_keyiterator'>
>>> a= iter({1:2,3:4}.values()) 对values做迭代
>>> type(a)
<class 'dict_valueiterator'>
迭代器有什么用,对于大数据,使用迭代器进行取值。分而治之。
生成器 (一般循环一半计算,节省空间)
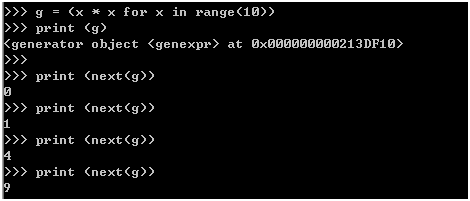
方法1: 推导列表,[] 变成()
g = (x * x for x in range(10))
print (g)
print (next(g))
print (next(g))
print (next(g))
print (next(g))
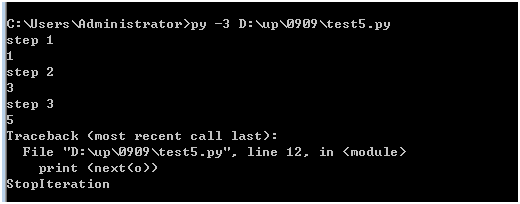
方法2:
def odd():
print ('step 1')
yield 1
print ('step 2')
yield 3
print ('step 3')
yield 5
o = odd()
print (next(o))
print (next(o))
print (next(o))
print (next(o))
#for i in o:
# print i
迭代器和生成器的区别

枚举
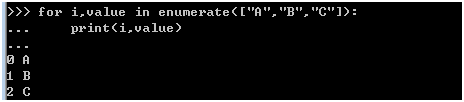
>>> for i,value in enumerate(["A","B","C"]):
... print(i,value)
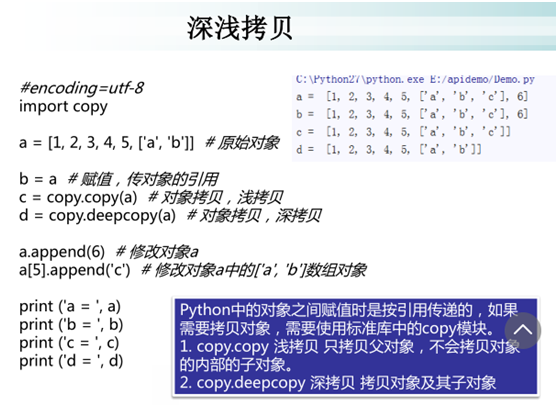
深浅拷贝
#encoding=utf-8
from collections import deque
queue = deque(["Eric", "John", "Michael"])
queue.append("Terry") # Terry arrives
queue.append("Graham") # Graham arrives
print (queue.popleft()) # The first to arrive now leaves
print (queue.popleft()) # The second to arrive now leaves
print (queue)
堆栈:
后进先出 list append() pop()
队列:
先进先出 list append() pop(0)/remove(x[0])
列表的操作:
增 list.append() list.extend(seq) list.insert(i,obj)
删 pop() remove(list[i]) del list[i]
改 list[i]=y
查 list[i] , list[i:j] , list.index(obj)
其他 len(list) list.count(i), list.reverse(),list.sort(key=?,reverse=True),sorted(list)
>>> a=[[1,2],[-1,-2]]
>>> a.sort(key=lambda x:x[0])
>>> a
[[-1, -2], [1, 2]]
代码大全2
自我介绍:
1 看你的口才
2 看看你的简历有没有造假
3 自我表述亮点的机会:
你要从他的角度说一些,他关注的东西。招聘的岗位需求。
质量结果
bug预防体系:
功能测试框架
探索式测试
编程:写过3万行。我有博客。。。。。100篇
每月读一本技术的书--》代码大全2
用作品说话
测试框架:
数据驱动
关键字驱动
混合驱动
行为驱动
分布式
多并发
UI
接口
网站
加一个github地址:
2万行。
字典:
d.clear() # 清空词典所有条目
del d # 删除词典
小练习:
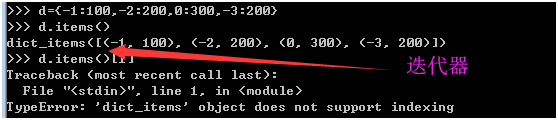
d={-1:100,-2:200,0:300,-3:200}
按照key的大小顺序升序进行输出,输出key=value
-3=200,-2=200,-1=100,0=300
d={-1:100,-2:200,0:300,-3:200}
for key in sorted(d.keys()):
print ("%s = %s ," %(key,d[key]),end=" ")
//自己写的方法
d={-1:100,-2:200,0:300,-3:200}
s = []
for i in sorted(d.keys()):
s.append(str(i)+"="+str(d[i]))
result = ",".join(s)
print(result)
>>> d.items()[1]
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
TypeError: 'dict_items' object does not support indexing
一个字符串排序,排序规则:小写<大写<奇数<偶数,
# 原理:先比较元组的第一个值,FALSE<TRUE,如果相等就比较元组的下一个值,以此类推。
s='9a13C85c7B24A6b' #确的顺序应该为:abcABC135792468
s="".join(sorted(list(s)))
lis=sorted(s,key=lambda x:(x.isdigit(),x.isdigit() and int(x)%2==0,x.isalpha() and x.isupper(),x.isalpha() and x.islower()))
print(''.join(lis))
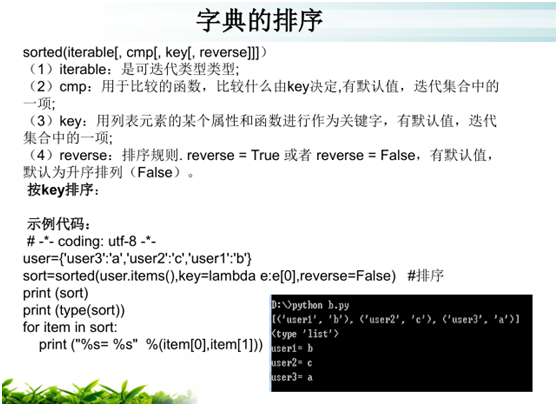
字典内置的常用函数
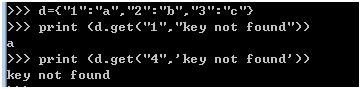
读取字典的key,又不想处理异常,可以按照如下方式处理:
d={"1":"a","2":"b","3":"c"}
print (d.get("1","key not found"))
print (d.get("4",'key not found'))
若字典中的key不存在,则生成key,并使用默认值赋值
d={"1":"a","2":"b","3":"c"}
d.setdefault("1","xx")
d.setdefault("4","d")
print (d)

创建字典
使用命名参数创建字典:
data=dict(red=1,blue=2,green=3)
print (data)
data=dict(zip(['one', 'two', 'three'], [1, 2, 3]))
print(data)
data=dict([('one', 1), ('two', 2), ('three', 3)])
print (data)

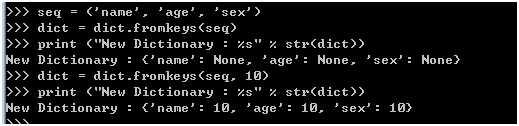
使用fromkeys来创建字典
seq = ('name', 'age', 'sex')
dict = dict.fromkeys(seq)
print ("New Dictionary : %s" % str(dict))
dict = dict.fromkeys(seq, 10)
print ("New Dictionary : %s" % str(dict))
生成小写字母的字典,值是ascii码
d={}
for i in range(97,123):
d[chr(i)]=i
print(d)
>>> import string
>>> {s:ord(s) for s in string.ascii_lowercase}
切片:
越界问题,切片可以越界
l[start:end:span]
遍历 [start,end),间隔为 span,当 span>0 时顺序遍历, 当 span<0 时,逆着遍历。
start 不输入则默认为 0,end 不输入默认为长度。
>>> a[11]
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
IndexError: list index out of range
>>> a[11:]
[]
>>> a = list(range(9))
>>> a
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]
>>> a[::-1]
[8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]
>>> a[-1::-1]
[8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0]
【字符串】
>>> s = "abc"
>>> type(s)
<class 'str'>
>>> s = "abc".encode("utf-8")
>>> type(s)
<class 'bytes'>
>>> s="中"
>>> s
'中'
>>> ord(s)
20013
>>> chr(20013)
'中'
>>> import sys
>>> sys.getdefaultencoding()
'utf-8'
字符串是不可变类型
>>> s1="a"
>>> id(s1)
34344888
>>> s1+="b"
>>> id(s1)
38588912
将”abc”变为 “a1c”
方法1:
>>> s
'abc'
>>> list(s)
['a', 'b', 'c']
>>> letter_list = list(s)
>>> letter_list[1]="1"
>>> "".join(letter_list)
'a1c'
方法2:
>>> s.replace("b","1")
'a1c'
方法3:
>>> s[0]+"1"+s[-1]
'a1c'
方法4:
>>> "1".join(s.split("b"))
'a1c'
方法5:
print(re.sub(r'b','1',s))
判断开头和结尾
>>> s
'abc'
>>> s.startswith("a")
True
>>> s.startswith("ab")
True
>>> s.endswith("bc")
True
.strip() 去空白
>>> " \t\nabc ".strip()
'abc'
>>> " \t\nabc ".lstrip()
'abc '
>>> " \t\nabc ".rstrip()
' \t\nabc'
>>> "a".upper()
'A'
>>> "aB".lower()
'ab'
>>> "aB".swapcase()
'Ab'
左对齐
>>> "abc".ljust(10)
'abc '
>>> "abc".rjust(10)
' abc'
>>> "abc".center(10)
' abc '
>>> "abc".ljust(10,"*")
'abc*******'
>>> "abc".rjust(10,"*")
'*******abc'
>>> "abc".center(10,"*")
'***abc****'
>>> "abacaaaddaa".find("a")
0
>>> "abacaaaddaa".find("axx")
-1
>>> "abacaaaddaa".rfind("daa")
8
>>> "abacaaaddaa".count("a")
7
>>> "abacaaaddaa".index("axx") #index如果没有找到,会报错
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module>
ValueError: substring not found
>>> "abc def".capitalize()
'Abc def'
>>> "abc def".title()
'Abc Def'
>>> import string
>>> string.capwords("abc def")
'Abc Def'
>>> string.punctuation
'!"#$%&\'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\\]^_`{|}~'
小练习:
删除一句英文中的所有英文标点。
>>> "abc".zfill(10)
'0000000abc'
>>> "dabd".rindex("d")
3




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号