Integer Optimization(借助ortools)
注:中文非直接翻译英文,而是理解加工后的笔记,记录英文仅为学其专业表述。
Mixed-Integer Programming
变量部分(非全部)为整数的问题,可以用混合整数规划来解决Mixed Integer Programming (MIP)。MIP也可称为混合整数线性规划问题,Mixed Integer Linear Programming (MILP)。
MIP solvers
OR-Tools 提供多种MIP求解器,默认是开源求解器 Coin-or branch and cut (CBC)。如果从源码安装,可以使用其他第三方求解器如:
- SCIP
- GLPK
- Gurobi
步骤:
- 导入求解器
- 声明求解器
- 调用求解器
eg:
- 目标: maximize(x + 10y)
- 约束:
- x + 7 y ≤ 17.5
- x ≤ 3.5
- x ≥ 0
- y ≥ 0
- x, y 都是整数
from ortools.linear_solver import pywraplp
def main():
# Create the mip solver with the CBC backend.
solver = pywraplp.Solver('simple_mip_program',
pywraplp.Solver.CBC_MIXED_INTEGER_PROGRAMMING)
infinity = solver.infinity()
# x and y are integer non-negative variables.
x = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, 'x')
y = solver.IntVar(0.0, infinity, 'y')
print('Number of variables =', solver.NumVariables())
# x + 7 * y <= 17.5.
solver.Add(x + 7 * y <= 17.5)
# x <= 3.5.
solver.Add(x <= 3.5)
print('Number of constraints =', solver.NumConstraints())
# Maximize x + 10 * y.
solver.Maximize(x + 10 * y)
result_status = solver.Solve()
# The problem has an optimal solution.
assert result_status == pywraplp.Solver.OPTIMAL
# The solution looks legit (when using solvers others than
# GLOP_LINEAR_PROGRAMMING, verifying the solution is highly recommended!).
assert solver.VerifySolution(1e-7, True)
print('Solution:')
print('Objective value =', solver.Objective().Value())
print('x =', x.solution_value())
print('y =', y.solution_value())
print('\nAdvanced usage:')
print('Problem solved in %f milliseconds' % solver.wall_time())
print('Problem solved in %d iterations' % solver.iterations())
print('Problem solved in %d branch-and-bound nodes' % solver.nodes())
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
运行得
Number of variables = 2
Number of constraints = 2
Solution:
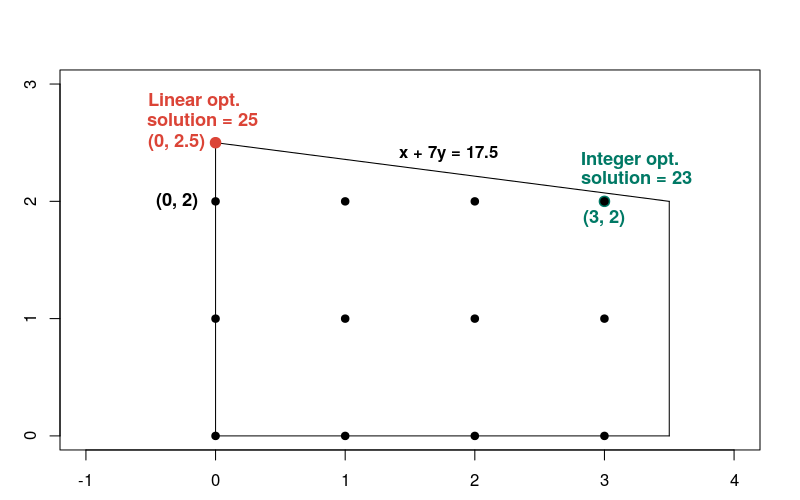
Objective value = 23.0
x = 3.0
y = 2.0
Advanced usage:
Problem solved in 28.000000 milliseconds
Problem solved in 1 iterations
Problem solved in 0 branch-and-bound nodes
solver.NumVar实数变量solver.IntVar整数变量
对比线性和整数规划
猜测整数规划的解也许接近线性规划,但情况并非如此。
You might guess that the solution to the integer problem would be the integer point in the feasible region closest to the linear solution — namely, the point x = 0, y = 2. But as you will see next, this is not the case.
替换约束条件为
infinity = solver.infinity()
x = solver.NumVar(0, infinity, 'x')
y = solver.NumVar(0, infinity, 'y')
print('Number of variables =', solver.NumVariables())
运行得
Number of variables = 2
Number of variables = 2
Number of constraints = 2
Solution:
Objective value = 25.0
x = 0.0
y = 2.5
Advanced usage:
Problem solved in 20.000000 milliseconds
Problem solved in 0 iterations
Problem solved in 0 branch-and-bound nodes
CP Approach to Integer Optimization
约束优化(CP)不同于传统优化理论,它更关注约束和变量,而不是目标函数。有些问题,CP可以比MIP求解器更快地找到最优解。
-
对于标准整数规划问题,可行点必须满足所有约束,MIP求解速度更快。在这种情况下,可行集是凸的:对于集合中的任意两点,连接它们的线段完全位于集合中。
-
对于具有高度非凸可行集的问题,CP-SAT解算器通常比MIP解算器更快。当可行集由多个“或”连接的约束定义时,意味着一个点只需要满足其中一个约束即可。
eg: 转换非整数约束
为了提高计算速度,CP-SAT解算器和原始CP解算器都对整数进行运算。
To solve a problem in which some of the constraints have non-integer terms, you must first transform those constraints by multiplying them by a sufficiently large integer.
eg:
- 目标: maximize(2x + 2y + 3z)
- 约束:
\begin{align} x+\frac{7}{2}y+\frac{3}{2}z\leq25 \\ 3x - 5y + 7z \leq 45 \\ 5x + 2y - 6z \leq 37 \\ x, y, z \geq 0 \\ x, y, z \quad integers \\ \end{align}
用CP-SAT求解器来解
from ortools.sat.python import cp_model
def main():
model = cp_model.CpModel()
var_upper_bound = max(50, 45, 37)
x = model.NewIntVar(0, var_upper_bound, 'x')
y = model.NewIntVar(0, var_upper_bound, 'y')
z = model.NewIntVar(0, var_upper_bound, 'z')
model.Add(2*x + 7*y + 3*z <= 50)
model.Add(3*x - 5*y + 7*z <= 45)
model.Add(5*x + 2*y - 6*z <= 37)
model.Maximize(2*x + 2*y + 3*z)
solver = cp_model.CpSolver()
status = solver.Solve(model)
if status == cp_model.OPTIMAL:
print('Maximum of objective function: %i' % solver.ObjectiveValue())
print()
print('x value: ', solver.Value(x))
print('y value: ', solver.Value(y))
print('z value: ', solver.Value(z))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
运行得
Maximum of objective function: 35
x value: 7
y value: 3
z value: 5
用原始CP求解器来解
from ortools.constraint_solver import pywrapcp
from ortools.constraint_solver import solver_parameters_pb2
def main():
# Instantiate a CP solver.
parameters = pywrapcp.Solver.DefaultSolverParameters()
solver = pywrapcp.Solver('simple_CP', parameters)
var_upper_bound = max(50, 45, 37)
x = solver.IntVar(0, var_upper_bound, 'x')
y = solver.IntVar(0, var_upper_bound, 'y')
z = solver.IntVar(0, var_upper_bound, 'z')
solver.Add(2*x + 7*y + 3*z <= 50)
solver.Add(3*x - 5*y + 7*z <= 45)
solver.Add(5*x + 2*y - 6*z <= 37)
objective = solver.Maximize(2*x + 2*y + 3*z, 1)
decision_builder = solver.Phase([x, y, z],
solver.CHOOSE_FIRST_UNBOUND,
solver.ASSIGN_MAX_VALUE)
# Create a solution collector.
collector = solver.LastSolutionCollector()
# Add the decision variables.
collector.Add(x)
collector.Add(y)
collector.Add(z)
# Add the objective.
collector.AddObjective(2*x + 2*y +3*z)
solver.Solve(decision_builder, [objective, collector])
if collector.SolutionCount() > 0:
best_solution = collector.SolutionCount() - 1
print("Maximum of objective function:", collector.ObjectiveValue(best_solution))
print()
print('x= ', collector.Value(best_solution, x))
print('y= ', collector.Value(best_solution, y))
print('z= ', collector.Value(best_solution, z))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
运行得
Maximum of objective function: 35
x= 7
y= 3
z= 5




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号