实验二
任务一
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#define N 5
#define N1 80
#define N2 35
int main() {
int cnt;
int random_major, random_no;
srand(time(NULL)); // 以当前系统时间作为随机种子
cnt = 0;
while(cnt < N) {
random_major = rand() % 2;
if(random_major) {
random_no = rand() % N1 + 1;
printf("20256343%04d\n", random_no);
}
else {
random_no = rand() % N2 + 1;
printf("20256136%04d\n", random_no);
}
cnt++;
}
return 0;
}
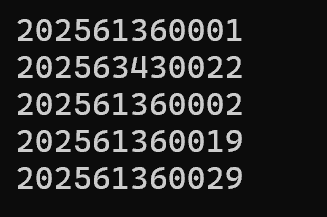
1.srand(time(NULL))的作用是以时间为随机参考,因为每次运行的时候时间必定不同,所以两次相邻的生成学号必定不同。去掉这一行生成的数始终相同 2.这个代码是生成学号的作用
任务二
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int choice, quantity;
float total_price = 0, amount_paid, change;
while (1) {
printf("\n自动饮料售卖机菜单:\n");
printf("1. 可乐 - 3 元/瓶\n");
printf("2. 雪碧 - 3 元/瓶\n");
printf("3. 橙汁 - 5 元/瓶\n");
printf("4. 矿泉水 - 2 元/瓶\n");
printf("0. 退出购买流程\n");
printf("请输入饮料编号: ");
scanf("%d", &choice);
if (choice == 0)
break;
if (choice < 1 || choice > 4) {
printf("无效的饮料编号,请重新输入。\n");
continue;
}
printf("请输入购买的数量: ");
scanf("%d", &quantity);
if (quantity < 0) {
printf("购买数量不能为负数,请重新输入。\n");
continue;
}
if(choice == 1 || choice == 2)
total_price += 3 * quantity;
else if(choice == 3)
total_price += 5 * quantity;
else
total_price += 2 * quantity;
printf("请投入金额: ");
scanf("%f", &amount_paid);
change = amount_paid - total_price;
printf("本次购买总价: %.2f 元\n", total_price);
printf("找零: %.2f 元\n", change);
total_price = 0;
}
printf("感谢您的购买,欢迎下次光临!\n");
return 0;
}
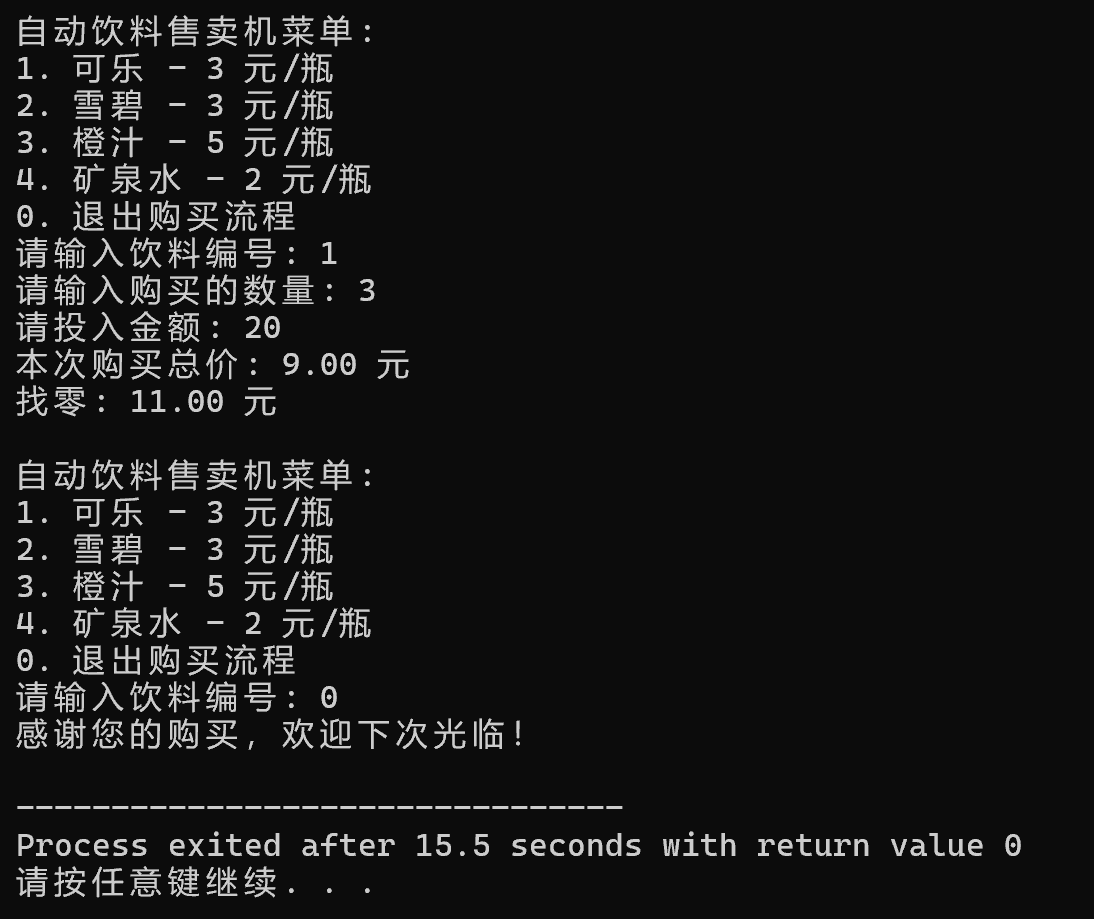
1.如果第47行删去,则未退出时第二次购买的总额是这次与第一次金钱总额的总和,即第一次的总额未清零。 2.语义是返回选择界面
任务三
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
char color;
while (scanf("%c", &color) != EOF){
if(color=='\n'){
continue;
}
else if(color=='r'){
printf("stop!\n");
}
else if(color=='g'){
printf("go go go\n");
}
else if(color=='y'){
printf("wait a minute\n");
}
else{
printf("something must be wrong...");
}
}
return 0;
}
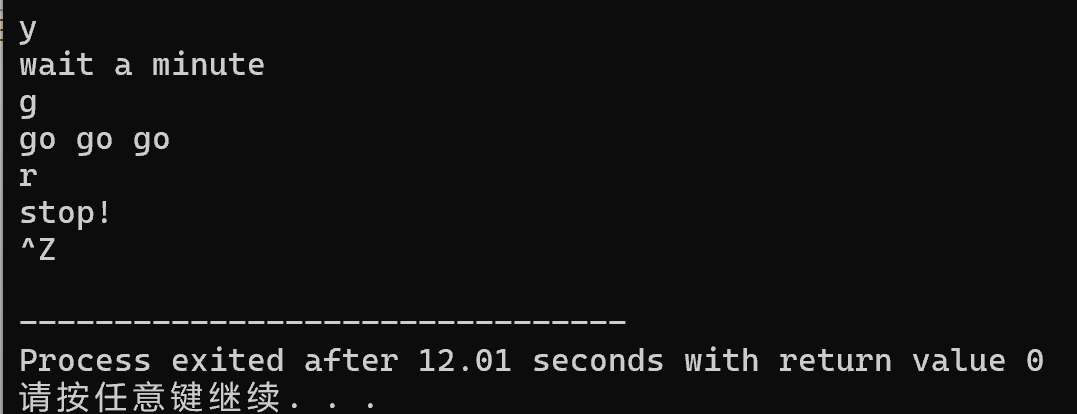
任务四
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
double expense;
double sum=0.0;
double max=0.0,min=20000.0;
int count=0;
printf("请输入今日开销,直到输入-1终止:\n");
while(1){
scanf("%lf",&expense);
if(expense==-1)
{
break;
}
if(expense>0&&expense<=20000){
count=1;
sum+=expense;
if(expense>max){
max=expense;
}
if(expense<min){
min=expense;
}
}
}
if(count){
printf("今日累计消费总额:%.1lf\n",sum);
printf("今日最高一笔开销:%.1lf\n",max);
printf("今日最低一笔开销:%.1lf\n",min);
}
return 0;
}
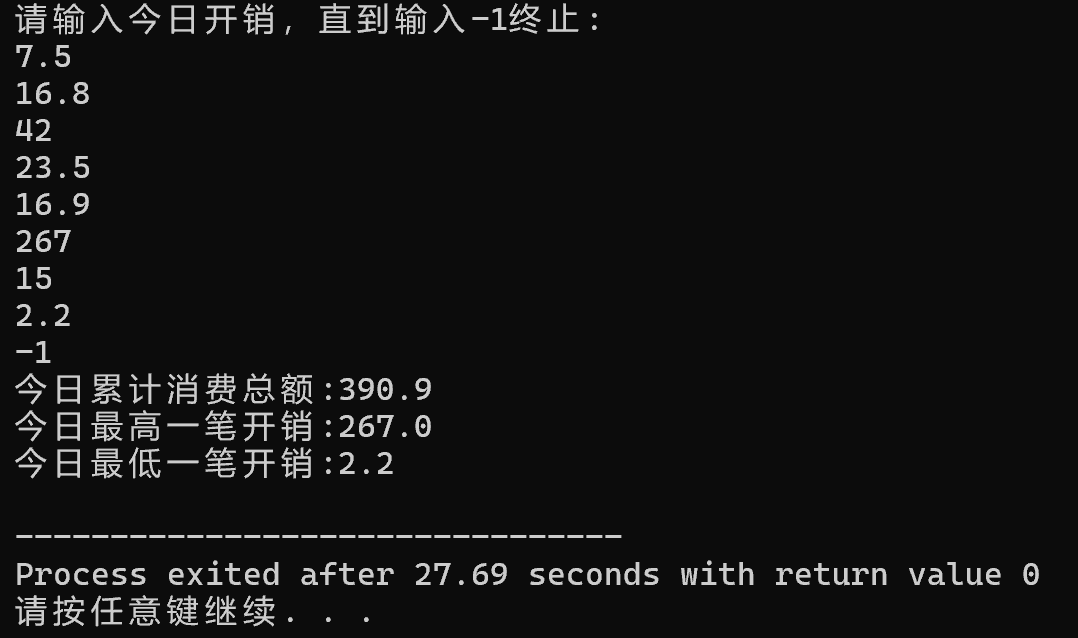
任务五
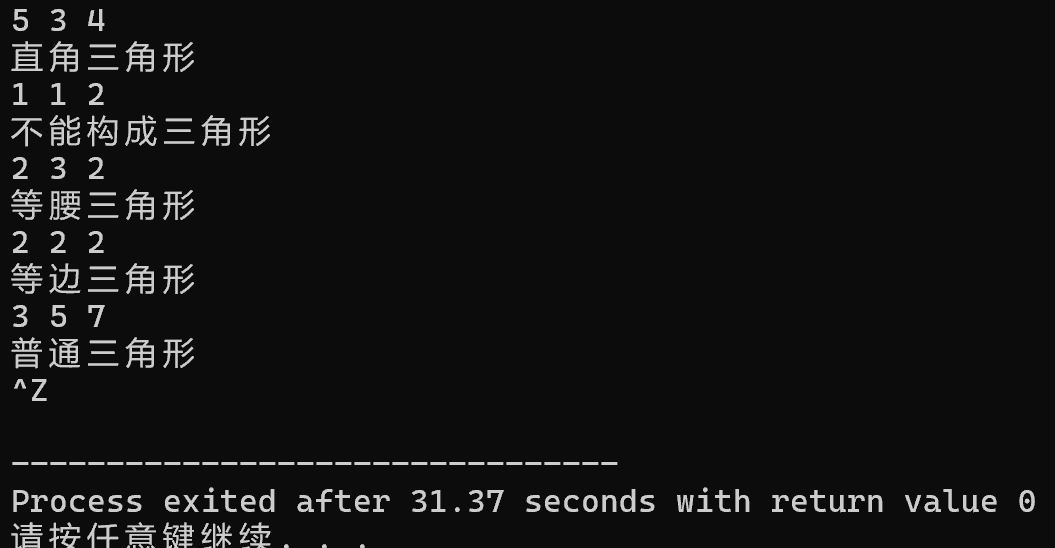
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
double a, b, c;
while(~scanf("%lf%lf%lf", &a, &b, &c)){
if(a+b>c&&a+c>b&&b+c>a){
if(a*a+b*b==c*c||b*b+c*c==a*a||a*a+c*c==b*b)
printf("直角三角形\n");
else if(a==b&&b==c){
printf("等边三角形\n");
}
else if(a==b||a==c||c==b) {
printf("等腰三角形\n");
}
else printf("普通三角形\n");
}
else
printf("不能构成三角形\n");
}
return 0;
}
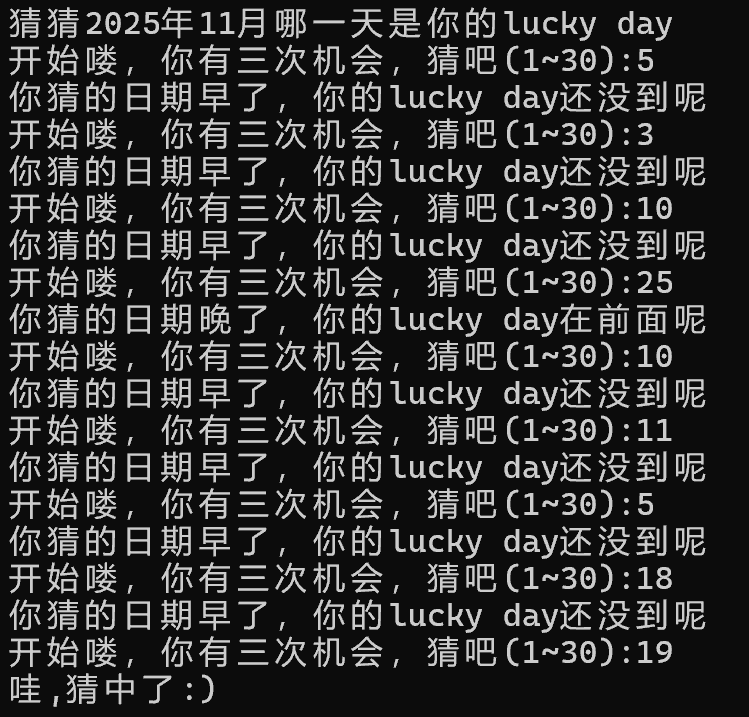
任务六
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
#define red(a,b) a+rand()%(b-a+1)
int main()
{
int cnt=1,right,num;
srand(time(NULL));
red(1,30);
right=1+rand()%30;
printf("猜猜2025年11月哪一天是你的lucky day\n");
while(cnt<=3){
if(cnt=1)
{
printf("开始喽,你有三次机会,猜吧(1~30):");
}
else{
printf("猜吧(1~30):");
}
scanf("%d",&num);
if(num<right)
printf("你猜的日期早了,你的lucky day还没到呢\n");
else if(num>right)
printf("你猜的日期晚了,你的lucky day在前面呢\n");
else if(num==right){
printf("哇,猜中了:)");
break;
}
if(cnt==3)
printf("次数用光啦。偷偷告诉你,你11月的lucky day是%d号",&right);
cnt++;
}
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号